springboot 2.2.0开始引入Junit5作为单元测试的默认库
JUnit5和之前的版本有很大的不同,由单个子项目的几个不同模块组成
JUnit Platform ,是在JVM上启动测试框架的技术,不仅支持Junit自己的测试引擎,其他的测试引擎也可以
JUnit Jupiter,提供了Junit5的最新的编程模型,是Junit5 的核心,内部包含了一个测试引擎,用于在Junit Platform上运行
JUnit Vintager: 提供了兼容Junit4/3 的测试引擎
Junit5 = JUnit Platform+ JUnit Jupiter+JUnit Vintager

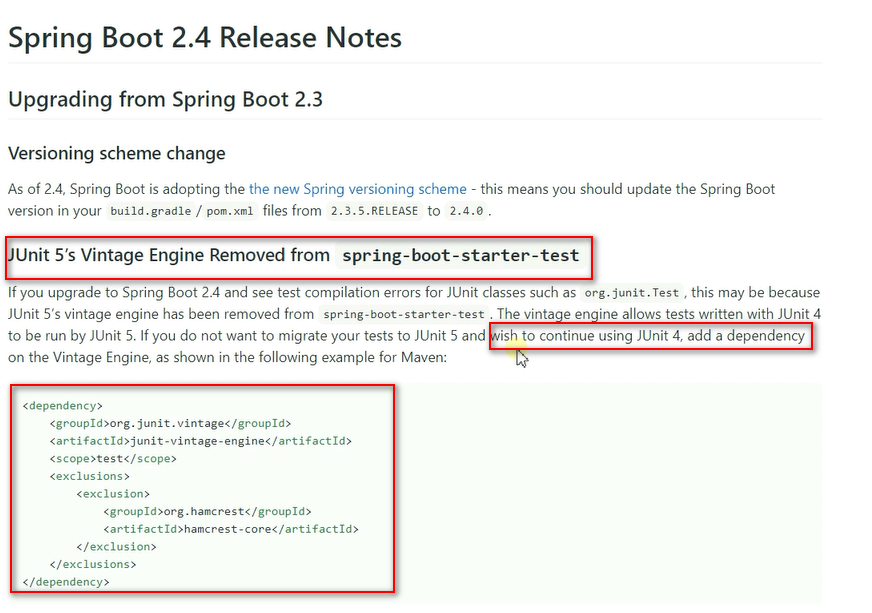
Junit支持Spring中的注解,测试起来比较方便, @Autowired @Transactional 等
package com.msb;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.pagination.Page;
import com.msb.mapper.DeptMapper;
import com.msb.pojo.Dept;
import com.msb.service.DeptService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.junit.platform.commons.annotation.Testable;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper;
import org.springframework.test.context.BootstrapWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootTest // 使用springboot的容器功能
/*@BootstrapWith(SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper.class)
@ExtendWith({SpringExtension.class})*/
@DisplayName("Junit5测试类")// 测试类描述
class SpringbootMybatisplusApplicationTests2 {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
@BeforeEach
public void testForeach(){
System.out.println("beforeach");
}
@AfterEach
public void testAftereach(){
System.out.println("aferEach");
}
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll(){
System.out.println("beforall");
}
@AfterAll
public static void aferAll(){
System.out.println("afterAll");
}
@RepeatedTest(3)// 重复测试3次
@Timeout(value = 10000,unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)// 超时时间设置
@DisplayName("Junit测试方法1")
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println("a");
System.out.println(deptMapper);
}
@Disabled// 设置不可用
@DisplayName("Junit测试方法2") // 方法描述
@Test
public void test2(){
System.out.println("b");
}
}
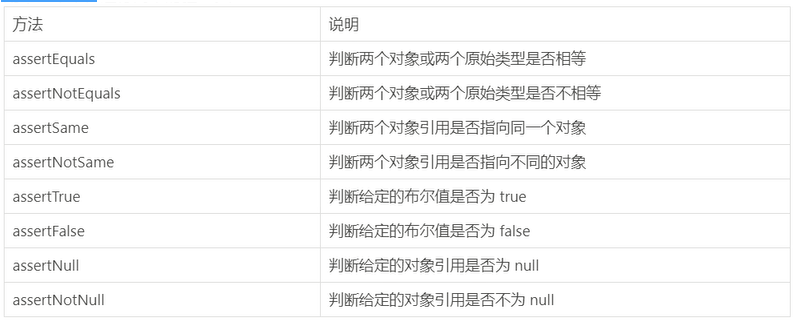
断言机制
断定某件事情,一定会发生,如果没有发生,那就是出现了问题,所欲的测试运行结束后,会有一个详细的断言报告
用来对测试需要满足的条件进行验证,这些断言方法都是org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions中的静态方法,
简单断言
package com.msb;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootTest
@DisplayName("Junit5断言测试类")
class SpringbootMybatisplusApplicationTests3 {
@DisplayName("简单断言1")
@Test
public void testAssertions1(){
int add = add(1, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals(6,add,"add结果计算错误");
}
public int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
@DisplayName("简单断言2")
@Test
public void testAssertions2(){
String s =new String("xxx");
String s2=new String("abc");
Assertions.assertEquals(s,s2,"String对象不一样");
}
// 组合断言
@DisplayName("组合断言")
@Test
public void testAssertAll(){
Assertions.assertAll("AssertAll",
()-> Assertions.assertTrue(true&& false),
()-> Assertions.assertEquals(1,2));
}
// 异常断言 认为应该会出现异常
@DisplayName("异常断言")
@Test
public void testAssertException(){
Assertions.assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class, ()->{ int i=1/0;}, "没有抛出异常");
}
// 超时断言 判断有没有超时
@DisplayName("超时断言")
@Test
public void testAssertTimeOut(){
Assertions.assertTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(1000),()-> Thread.sleep(5000));
}
// 快速失败
@DisplayName("快速失败")
@Test
public void testFail(){
if(true){
Assertions.fail("测试 失败");
}
}
}
前置条件(assumptions假设)
类似于断言,不同在于,不满足断言回事方法测试失败,而不满足的前置条件会使得的是方法的执行中止,前置条件可以看成是测试方法执行的前提,当条件不满足时,就没有继续执行的必要
package com.msb;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.time.Duration;
@SpringBootTest
@DisplayName("Junit5测试前置条件")
class SpringbootMybatisplusApplicationTests4 {
@DisplayName("测试前提条件")
@Test
public void testAssumptions(){
// 假设为true,才会执行
Assumptions.assumeTrue(false,"结果不是true");
System.out.println("后面的测试代码前提条件");
}
@DisplayName("简单断言1")
@Test
public void testAssertions1(){
int add =10;
Assertions.assertEquals(6,add,"add结果计算错误");
System.out.println("后面的测试代码简单断言");
}
}
嵌套测试
package com.msb;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
import java.util.Stack;
@DisplayName("嵌套测试")
class SpringbootMybatisplusApplicationTests5 {
Stack<Object> stack;
@Test
@DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()")
void isInstantiatedWithNew() {
new Stack<>();
// 外层的测试不能驱动内层的测试方法
assertNull(stack);
}
@Nested
@DisplayName("when new")
class WhenNew {
@BeforeEach
void createNewStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("is empty")
void isEmpty() {
assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped")
void throwsExceptionWhenPopped() {
assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::pop);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked")
void throwsExceptionWhenPeeked() {
assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::peek);
}
@Nested
@DisplayName("after pushing an element")
class AfterPushing {
String anElement = "an element";
@BeforeEach // 内层Test可以驱动外层的BeforeEach
void pushAnElement() {
stack.push(anElement);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("it is no longer empty")
void isNotEmpty() {
assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty")
void returnElementWhenPopped() {
assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop());
assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty")
void returnElementWhenPeeked() {
assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek());
assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());
}
}
}
}
参数化测试

package com.msb;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Nested;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.MethodSource;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ValueSource;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@DisplayName("参数化测试")
class SpringbootMybatisplusApplicationTests6 {
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(ints = { 1, 2, 3 })
void testWithValueSource(int argument) {
System.out.println(argument);
assertTrue(argument > 0 && argument < 4);
}
@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource("stringProvider")
void testWithExplicitLocalMethodSource(String argument) {
assertNotNull(argument);
}
static Stream<String> stringProvider() {
return Stream.of("apple", "banana");
}
}





 本文介绍了SpringBoot2.2.0开始使用JUnit5作为默认单元测试库的情况,详细讲解了JUnit5的构成,包括JUnitPlatform、JUnitJupiter和JUnitVintager。同时展示了如何利用JUnit5的注解如@Autowired和@Transactional进行Spring环境下的测试。文章通过具体的代码示例,演示了@BeforeEach、@AfterEach、@BeforeAll、@AfterAll、@RepeatedTest、@Timeout等生命周期方法,以及断言机制、前置条件(Assumptions)、嵌套测试和参数化测试的用法。
本文介绍了SpringBoot2.2.0开始使用JUnit5作为默认单元测试库的情况,详细讲解了JUnit5的构成,包括JUnitPlatform、JUnitJupiter和JUnitVintager。同时展示了如何利用JUnit5的注解如@Autowired和@Transactional进行Spring环境下的测试。文章通过具体的代码示例,演示了@BeforeEach、@AfterEach、@BeforeAll、@AfterAll、@RepeatedTest、@Timeout等生命周期方法,以及断言机制、前置条件(Assumptions)、嵌套测试和参数化测试的用法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








