Description
A number of rectangular posters, photographs and other pictures of the same shape are pasted on a wall. Their sides are all vertical or horizontal. Each rectangle can be partially or totally covered by the others. The length of the boundary of the union of all rectangles is called the perimeter.
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
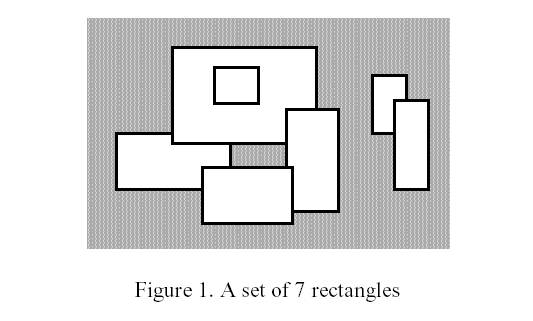
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.
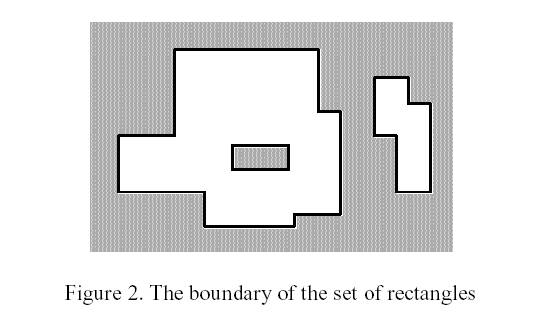
The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains the number of rectangles pasted on the wall. In each of the subsequent lines, one can find the integer coordinates of the lower left vertex and the upper right vertex of each rectangle. The values of those coordinates are given as ordered pairs consisting of an x-coordinate followed by a y-coordinate.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. The output must contain a single line with a non-negative integer which corresponds to the perimeter for the input rectangles.
Sample Input
7
-15 0 5 10
-5 8 20 25
15 -4 24 14
0 -6 16 4
2 15 10 22
30 10 36 20
34 0 40 16Sample Output
228思路:
方法一:
对每个矩形横轴的线段按照从下到上的顺序排序,按照顺序依次扫描每个线段,在扫描到某个矩形的底边时flag加一,顶边时减一。
同样方式对纵轴再扫描一遍,当然这时排序是按照从左到右的顺序,扫描也是从左到右。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int M = 1e5 + 10;
struct ss {
int l , r , h , flag;
}s1[M << 1] , s2[M << 1];
struct Node
{
int l , r , add , len;
}T[M << 4];
bool cmp(ss a, ss b)
{
if (a.h == b.h)
{
return a.flag > b.flag;
}
return a.h < b.h;
}
void build(int l, int r, int p)
{
T[p].l = l;
T[p].r = r;
T[p].add = 0;
T[p].len = 0;
if (l == r)
{
return;
}
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
build(l, mid, p << 1);
build(mid + 1, r, (p << 1) | 1);
}
void pushup(int p)
{
if (T[p].add)
{
T[p].len = T[p].r - T[p].l + 1;
}
else if (T[p].l == T[p].r)
{
T[p].len = 0;
}
else
{
T[p].len = T[p << 1].len + T[(p << 1) | 1].len;
}
}
void update(int l, int r, int p, int ad)
{
if (T[p].l == l && T[p].r == r)
{
T[p].add += ad;
pushup(p);
return;
}
int mid = T[p].l + (T[p].r - T[p].l) / 2;
if (mid >= r)
{
update(l, r, p << 1, ad);
}
else if (mid < l)
{
update(l, r, (p << 1) | 1, ad);
}
else
{
update(l, mid, p << 1, ad);
update(mid + 1, r, (p << 1) | 1, ad);
}
pushup(p);
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
x1 += M;
x2 += M;
y1 += M;
y2 += M;
s1[i].flag = 1;
s1[i].l = x1;
s1[i].r = x2;
s1[i].h = y1;
s1[i + n].flag = -1;
s1[i + n].l = x1;
s1[i + n].r = x2;
s1[i + n].h = y2;
s2[i].flag = 1;
s2[i].l = y1;
s2[i].r = y2;
s2[i].h = x1;
s2[i + n].flag = -1;
s2[i + n].l = y1;
s2[i + n].r = y2;
s2[i + n].h = x2;
}
sort(s1 + 1, s1 + 1 + 2 * n, cmp);
sort(s2 + 1, s2 + 1 + 2 * n, cmp);
int l, r;
build(1, 2 * M, 1);
ll result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
int last = T[1].len;
l = s1[i].l;
r = s1[i].r - 1;
update(l, r, 1, s1[i].flag);
result += abs(last - T[1].len);
}
build(1 , 2 * M , 1);
for (int i = 1 ; i <= 2 * n ; i++)
{
int last = T[1].len;
l = s2[i].l;
r = s2[i].r - 1;
update(l , r , 1 , s2[i].flag);
result += abs(last - T[1].len);
}
printf("%lld\n" , result);
return 0;
}
方法二:
对每个矩形的纵轴做延长线,这样分隔出的横轴线段来进行离散化。从下向上用每个矩形的横轴区域做扫描,扫描过程更新每个分割出的横轴线段。
同样,对横轴做同样的操作。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 1e5 +10;
ll result = 0;
int x[MAXN];
int y[MAXN];
struct Line
{
int s, e;
int h;
int flag;
}line1[MAXN << 1], line2[MAXN << 1];
struct Node
{
int s, e;
int flag;
bool end;
}node[MAXN << 4];
bool cmp(const Line &a, const Line &b)
{
return a.h < b.h;
}
void build(int rt, int s, int e, int *pLine)
{
node[rt].s = pLine[s];
node[rt].e = pLine[e];
node[rt].flag = 0;
if (s + 1 == e)
{
node[rt].end = true;
return;
}
node[rt].end = false;
int mid = s + (e - s) / 2;
build(rt << 1, s, mid, pLine);
build(rt << 1 | 1, mid, e, pLine);
}
void update(int rt, int s, int e, int flag)
{
if (s >= node[rt].e || e <= node[rt].s)
{
return;
}
if (node[rt].end)
{
if ((node[rt].flag == 0) && (flag == 1))
{
result += (node[rt].e - node[rt].s);
}
else if ((node[rt].flag == 1) && (flag == -1))
{
result += (node[rt].e - node[rt].s);
}
node[rt].flag += flag;
}
else
{
update(rt << 1, s, e, flag);
update(rt << 1 | 1, s, e, flag);
}
}
int main()
{
int m, n;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d", &n);
int count = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
count++;
x[count] = x1;
line1[count].s = x1;
line1[count].e = x2;
line1[count].h = y1;
line1[count].flag = 1;
y[count] = y1;
line2[count].s = y1;
line2[count].e = y2;
line2[count].h = x1;
line2[count].flag = 1;
count++;
x[count] = x2;
line1[count].s = x1;
line1[count].e = x2;
line1[count].h = y2;
line1[count].flag = -1;
y[count] = y2;
line2[count].s = y1;
line2[count].e = y2;
line2[count].h = x2;
line2[count].flag = -1;
}
sort(x, x + count + 1);
sort(line1, line1 + count + 1, cmp);
sort(y, y + count + 1);
sort(line2, line2 + count + 1, cmp);
build(1, 0, count, x);
for (int i = 0; i <= count; i++)
{
update(1, line1[i].s, line1[i].e, line1[i].flag);
}
build(1, 0, count, y);
for (int i = 0; i <= count; i++)
{
update(1, line2[i].s, line2[i].e, line2[i].flag);
}
printf("%lld\n", result);
return 0;
}
























 1263
1263

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








