一、API
API(Application Programming Interface,应用程序编程接口)
- java写好的技术(功能代码),咱们可以直接调用。
- Oracle也为Java提供的这些功能代码提供了相应的API文档(技术使用说明书)。
二、String
1、String类的简单介绍
String类定义的变量可用于存储字符串,同时String类提供了很多操作字符串的功能,我们可以直接使用。

2、String类概述
1)概述
- java.lang.String类代表字符串,String类定义的变量可以用于指向字符串对象,然后操作该字符串。
- java程序中的所有字符串文字(例如“abc”)都为此类的对象。
2)特点
- String其实常被称为不可变字符串类型,它的对象在创建后不能被更改。
-

3、String类创建对象的2种方式



4、String类常见面试题


5、字符串内容比较
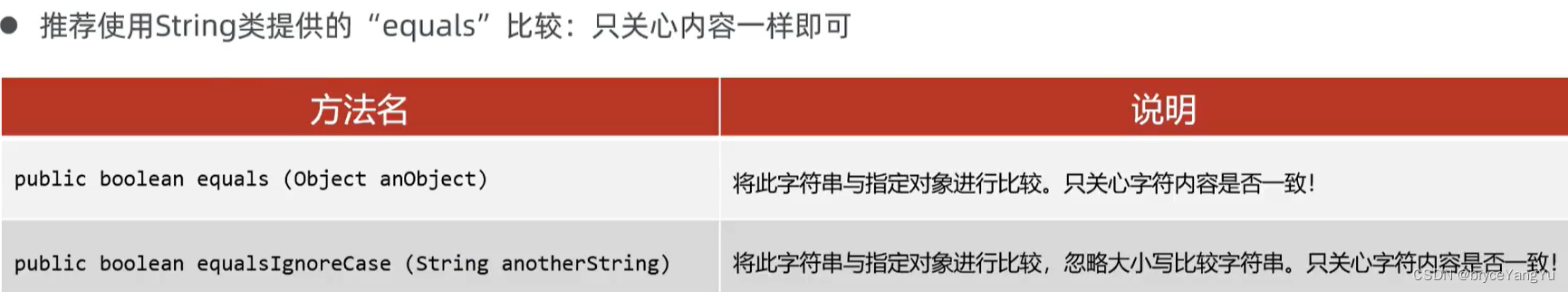

6、遍历、替换、截取、分割操作

7、String类案例实战

public class ProgramDemo03_1 {
final static String keyWord = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" +
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要产生的验证码个数:");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
getCode(n);
}
public static void getCode(int n) {
Random random = new Random();
String code = "";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(62);
code += keyWord.charAt(index);
}
System.out.println(code);
}
} 
public class ProgramDemo13 {
private final static String Name = "admin";
private final static String Password = "kb0824";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Login...");
int i = 0;
do {
System.out.println("please input the name:");
String checkName = scanner.next();
if (checkName.equals(Name)) {
System.out.println("please input the Password:");
String checkPassword = scanner.next();
if (checkPassword.equals(Password)){
System.out.println("Login successful!");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("password error!");
i++;
}
}else {
System.out.println("userName error!");
i++;
}
} while (i < 3);
}
} 
public class ProgramDemo14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("please input the phone number:");
String phoneNum = scanner.next();
if (phoneNum.length() == 11){
String beginPNum = phoneNum.substring(0,3);
String endPNum = phoneNum.substring(7);
String newPNum = beginPNum + "****" + endPNum;
System.out.println(newPNum);
break;
}else {
System.out.println("error phone number!please input again:");
}
}
}
}三、ArrayList
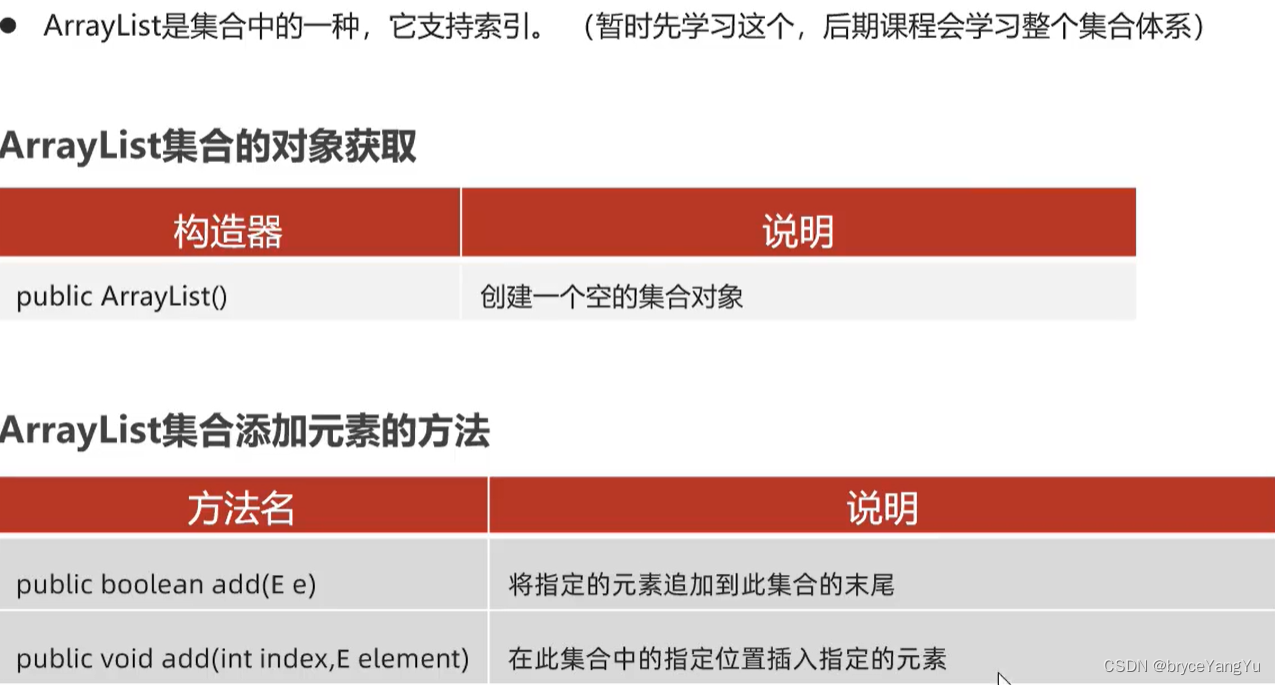
1、ArrayList简介


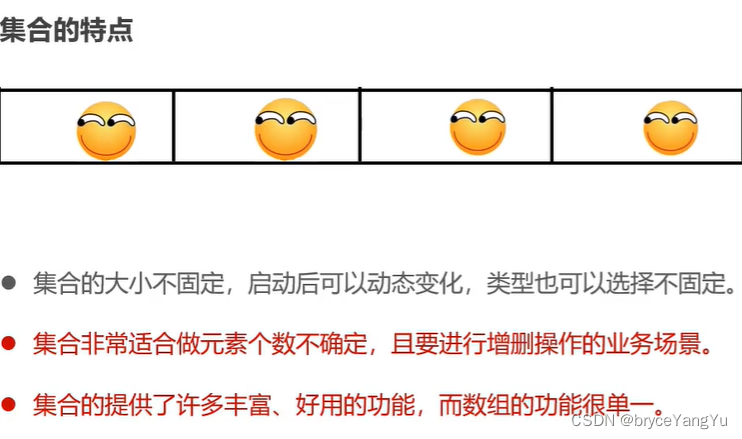
2、集合的概述

3、ArrayList的快速入门
4、ArrayList对泛型的支持

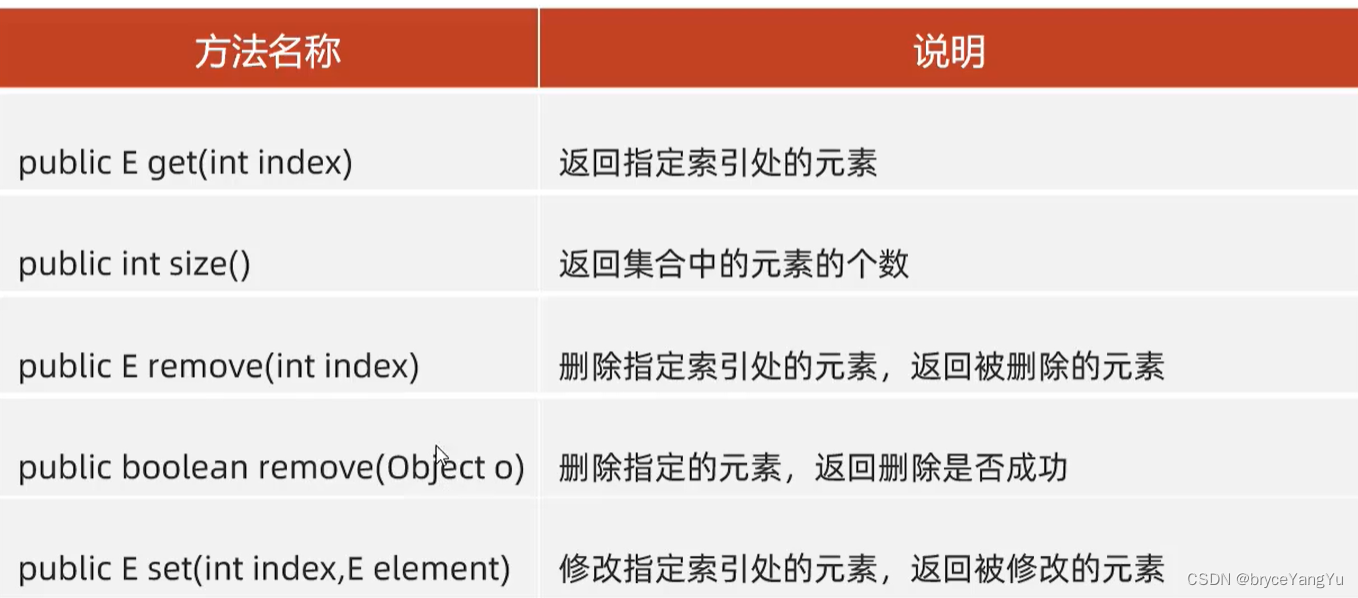
5、ArrayList常用API和遍历
6、ArrayList案例:遍历并删除对象

public class ProgramDemo15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> studentScore = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(studentScore,98,77,66,89,79,50,100);
for (int i = 0; i < studentScore.size(); i++) {
if (studentScore.get(i) < 80){
studentScore.remove(studentScore.get(i));
i--;
}
}
System.out.println(studentScore);
}
}7、ArrayList案例:存储自定义类型对象

public class Movie {
private String name;
private String director;
private String[] actors;
public Movie() {
}
public Movie(String name, String director, String[] actors) {
this.name = name;
this.director = director;
this.actors = actors;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Movie{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", director='" + director + '\'' +
", actors=" + Arrays.toString(actors) +
'}' + "\n";
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Movie> movies = new ArrayList<>();
Movie movie1 = new Movie("《飞驰人生2》", "韩寒"
, new String[]{"范丞丞", "沈腾"});
Movie movie2 = new Movie("《周处除三害》", "黄精甫"
, new String[]{"阮经天", "王净"});
Movie movie3 = new Movie("《你想过怎样的人生》"
, "宫崎骏", new String[]{"刘昊然"});
Movie movie4 = new Movie("《彷徨之刃》", "陈卓"
, new String[]{"王千源", "黄景春"});
Collections.addAll(movies, movie1, movie2, movie3, movie4);
System.out.println(movies);
}
}8、ArrayList案例:元素搜索

public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private double height;
private double weight;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, String sex, double height, double weight) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
'}' + "\n";
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student(20240808,"刘亦菲","女",176.6,49);
Student s2 = new Student(20240701,"张雪迎","女",174.3,43);
Student s3 = new Student(20240908,"陈钰琪","女",172.8,47);
Student s4 = new Student(20240806,"胡歌","男",181.3,78);
Student s5 = new Student(20241004,"李现","男",183.7,82);
Collections.addAll(students,s1,s2,s3,s4,s5);
System.out.println(students);
while (true) {
System.out.println("查找功能--->");
System.out.print("请输入您要查找的id:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
Student rs = searchById(students,id);
if (rs != null){
System.out.println(rs);
break;
}else {
System.out.println("未找到!");
}
}
}
public static Student searchById(ArrayList<Student> students,int id){
for (Student student : students) {
if (student.getId() == id){
return student;
}
}
return null;
}
}






















 15万+
15万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








