Spring框架
Spring是一个开放源代码的设计层面框架,他解决的是业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,因此它将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用。Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson创建。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
轻量级框架:在系统初始化的时候不用加载所有的服务这里写代码片,为系统节约了资源
- 作用:
提供一种方法管理对象:spring提供一个核心容器,其中存储着各层的对象,通过调用容器中的对象对各层进行操作
使JavaEE易用和促进良好的编译习惯
解决JavaEE应用的各层的问题,贯穿表现层、业务层、持久层(一站式),将它们无缝的整合在一起
- 体系结构:
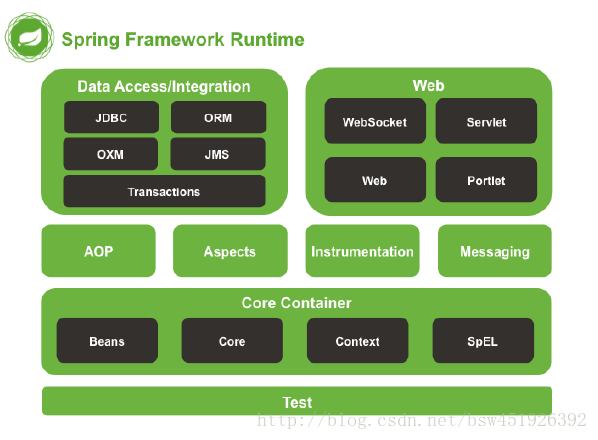
- 1.核心容器Core Container:
Beans和Core模块提供了Spring最基本的功能,包含控制反转(IOC)和依赖注入(DI)
context 上下文对象,基于beans与cores
spel它是spring提供的一个表达式语言
- 2.数据访问和集成Data access/integration
数据访问
集成
- 3.网页web
Spring提供Spring mvc
可以与其他的web框架进行集成
-4.面向切面编程AOP
大部分情况下使用动态代理实现
Aspects模块:使用AspectJ框架实现AOP
-5.测试Test
使用spring可以方便的进行测试
- 优点:
1.方便解耦,简化开发
Spring就是一个大工厂,可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理2.AOP编程的支持
Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能3.声明式事务的支持
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程4.方便程序的测试
Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring程序5.方便集成各种优秀框架
Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的直接支持6.降低JavaEE API的使用难度
Spring 对JavaEE开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低
- Spring的Jar包下载:
- Spring官方网站
步骤:
a)点击右上方的PROJECTS,进入界面b)点击第一排第三个图标c)点击右侧Spring Framework下任意一个即可下载d)注意:spring3.0.2版本后,不再依赖jar包docs 存在API和规范文档 libs 开发jar包 schema 开发过程中需要的xml的schema约束
- Spring开发环境搭建:
注意:
在不同的情况下需要导入不同的jar包,当前是实现IOC和DI对于当前情况,只需要使用spring的核心jar包即可
-以上jar包均在解压后的spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE\libs路径下可找到配置文件
我们需要在src下创建一个关于spring的配置文件,一般情况名称叫applicationContext.xml,可以更改这个配置文件的文件名a)约束如何获取?
它的路径: spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE-dist\spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html中的xsd-configuration.html文件b)找到
复制以下代码至applicationContext.xml中
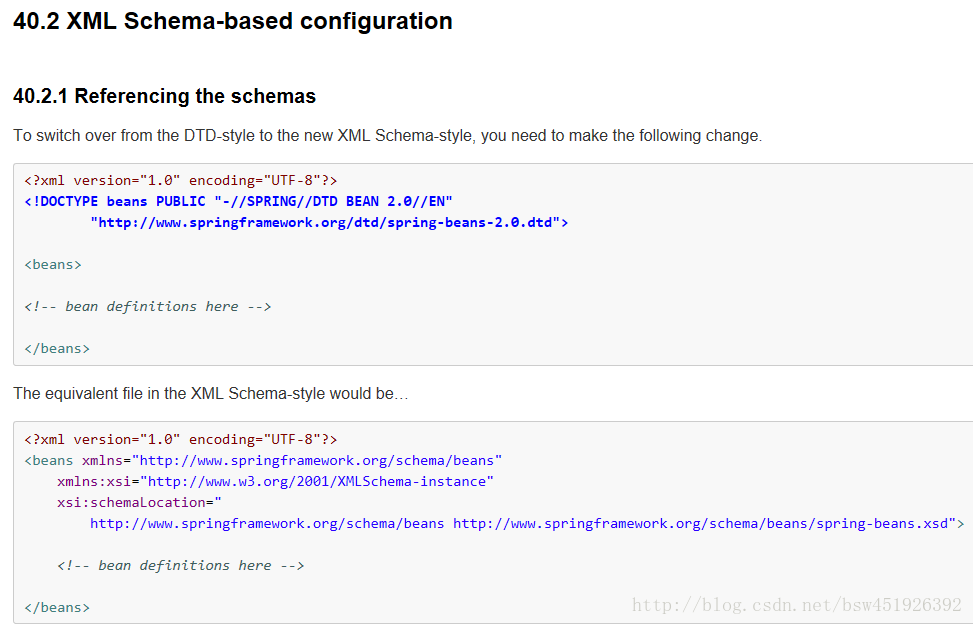
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN"
"http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd">
<beans>
<!-- bean definitions here -->
</beans>- IOC的快速入门:
IOC是什么 :
inversion of Controller 控制反转:将实例化对象的权利交给Spring容器来初始化,也就是说这样讲初始化对象的权利进行了反转原理是如何实现的:
通过xml配置文件+工厂模式+反射- 代码编写:
1.创建一个接口:
public interface IUserService {
public void sayHello();
}
2.创建接口实现类:
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello ioc");
}
}
3.在applicationContext.xml文件中配置属性:
<beans>
<!--
配置一下最终需要使用的类的映射因为用到了反射
name可以替换成id,
两者的区别是:
name可以有一些特殊字符,
id是唯一的不能有特殊字符
class是最终需要使用的类的全路径
-->
<bean name="iuserService" class="com.baidu.ioc.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
</beans>
4.创建测试类:
import org.junit.Test;
public class IOCTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// 在spring中,内置一个BeanFactory工厂,我们一般使用其子类接口ApplicationContext
/*
* 创建一个AppliCationContext对象ApplicationContext它是BeanFactory的一个子接口,
* 我们在使用时使用的是AppliCationContext的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext可以帮助我们在src下查找“”中名字的配置文件
*/
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 通过获取到的对象,调用getBean方法,获取到最终需要使用的对象IUserService,getBean中的参数,需要与配置文件中的Bean的name或id名相同
IUserService userService = (IUserService) context.getBean("iuserService");
// 使用其中的方法
userService.sayHello();
}
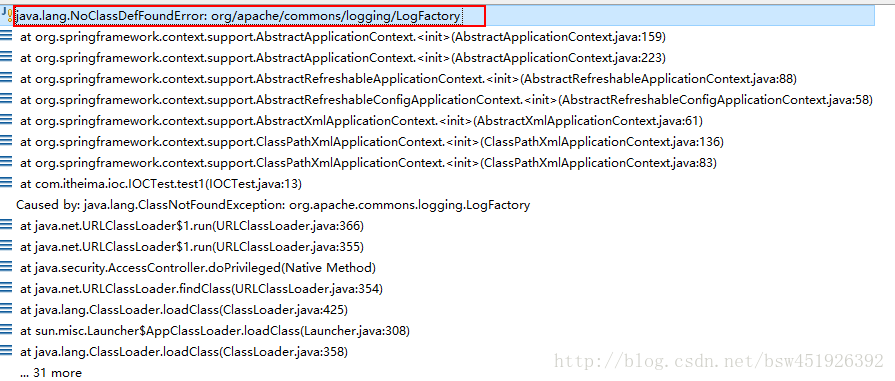
}!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!这时运行会报错,错误信息:
这个错误信息是说缺少一个jar包:commons-logging的jar包,可以同时将log4j(用于写日志的,同时需要导入一个名为log4j.properties的配置文件放到src下)的jar包也导入
- 总结:
步骤:
1.导入jar相关jar包
2.创建applicationContext.xml配置文件
3.创建接口以及接口实现类
4.在配置文件中配置bean
5.创建测试类,通过new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("配置文件路径");获取BeanFactory工厂下ApplicationContext接口的对象
6.使用对象中的getBean("配置文件中bean的name/id");获取具体的类
7.使用通过BeanFactory工厂获得的类对象,调用自定义的sayHello方法
- DI:
Di是什么:
DI:dependency injection 依赖注入;即在spring框架创建Bean时,动态的依赖注入到Bean组件中
简单案例:
// 这是一个UserService的实现类,需要在里面定义一个成员变量name
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
private String name;
// 依赖注入可以没有get方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// 依赖注入,必须有的方法,set
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello ioc" + " " + name);
}
}
// 在配置文件中配置
<bean name="iuserService" class="com.baidu.ioc.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<!-- 这里name中的值,需要与Bean中的成员变量名称一致才能被注入,这里value中设置的值,就是到时候注入的值,UserServiceImpl对象被创建后,对象中name的值就是张三-->
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
// 在测试方法中调用方法打印属性,即可获得张三
// 通过ClassPathXml获取ApplicationContext对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 通过getBean获取实际对象
IUserService userServiceImpl = (IUserService) context.getBean("iuserService");
// 调用方法a
userServiceImpl.sayHello();面试题:
IOC和DI的区别:
IOC:是控制反转,将创建对象的权利交给了Spring容器
DI:依赖注入,在创建对象时,将对象依赖的属性,通过配置,注入到对象中
- Bean获取与实例化:
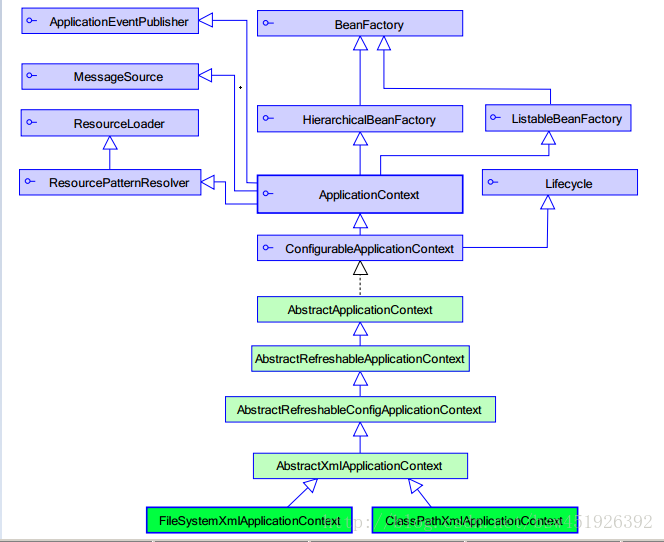
ApplicationContext与BeanFactory的关系:
ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的一个子接口,我们在使用时,一般使用ApplicationContext接口下的实现类-- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 根据类路径获取 FileSystemXmlAppliCationContext 根据文件路径获取 BeanFactory采用一种延时加载方法,只有在调用getBean时,才会实例化对象 ApplicationContext采用的是立即加载,会在加载配置文件时,就会初始化Bean,并且,ApplicationContext提供不同应用层Context实现,比如web层使用WebApplicationContext优点:在配置文件加载时就初始化Bean可以避免程序在执行时出现的一些问题,在加载时就提前判断
// 通过断点就能证明上述加载方式的结论
public class BeanTest {
// 使用BeanFactory获取Bean1
@Test
public void test() {
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
Bean1 bean = (Bean1) factory.getBean("bean1");
bean.show();
}
// 使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext获取Bean
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
bean.show();
}
// 使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext获取Bean
@Test
public void test3() {
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
bean.show();
}
}- Bean的实例化方法:
-无参数构造方法-在Bean中必须提供无参构造方法:
只需要在配置文件中配置
<bean name="bean1" class="com.baidu.bean.Bean1"></bean>- 静态工厂方法
需要创建一个工厂类,在工厂类中提供一个static返回bean对象的方法即可
public class Bean2Factory {
public static Bean2 createBean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
在配置文件中
<!-- 静态工厂模式 -->
<bean name="bean2Factory" class="com.baidu.bean.Bean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2"></bean>
测试类中
public void test4() {
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/applicationContext.xml");
Bean2 bean = (Bean2) context.getBean("bean2Factory");
bean.show();
}实例工厂方法
需要创建一个工厂类,在工厂类中提供一个非static的创建bean对象的方法,在配置文件中需要将工厂配置,还需要配置bean
创建一个Bean
public class Bean3 {
public void show() {
System.out.println("Bean3 show...");
}
}
创建一个工厂类
public class BeanFactory{
public Bean3 createBean3() {
return new Bean3();
}
}
配置文件
<!-- 实例工厂模式 -->
<bean name="bean3Factory" class="com.baidu.bean.Bean3Factory" ></bean>
<bean name="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="createBean3"></bean>
<!--
factory-bean:指定当前使用的BeanFactory是哪一个
factory-method:指当前这个BeanFactory中创建Bean的方法是哪个,需要与BeanFactory中的方法名相同
-->
在测试类中调用一下Bean3的show方法- Bean的作用域:
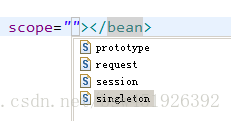
singleton:单例模式,代表在spring ioc容器中只有一个Bean实例 (默认的scope),会产生线程安全问题
prototype:多例模式,每一次从spring容器中获取时,都会返回一个新的实例,解决了线程安全问题
request:用在web开发中,将bean对象request.setAttribute()存储到request域中
session:用在web开发中,将bean对象session.setAttribute()存储到session域中
开发中单例和多例用的比较多
singleton:
配置文件中
<bean name="bean1" class="com.baidu.bean.Bean1" scope="singleton" />
测试类中
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
Bean1 bean2 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
bean.show();
System.out.println(bean == bean2);// 返回值为true,说明获取到的是同一个bean
}
prototype:
配置文件中
<bean name="bean1" class="com.baidu.bean.Bean1" scope="prototype" />
测试类中
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
Bean1 bean2 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
bean.show();
System.out.println(bean == bean2);// 返回值为false,说明获取到的不是同一个bean
}总结:
无参构造创建bean对象
1.创建一个Bean类-给出无参构造方法(必须有无参构造)
2.配置文件中配置一个<bean />
3.测试类中通过三步(获取ApplicationContext对象,获取Bean对象,执行Bean方法),进行检验
静态工厂创建bean对象
1.创建一个Bean类
2.创建一个Bean工厂,提供static方法返回一个bean对象
3.配置文件中配置<bean />
4.测试类中通过三步(获取ApplicationContext对象,获取Bean对象,执行Bean方法),进行检验
实例工厂创建bean对象
1.创建一个Bean类
2.创建一个Bean工厂,提供非static方法返回一个bean对象
3.配置文件中配置<bean />
4.测试类中通过三步(获取ApplicationContext对象,获取Bean对象,执行Bean方法),进行检验
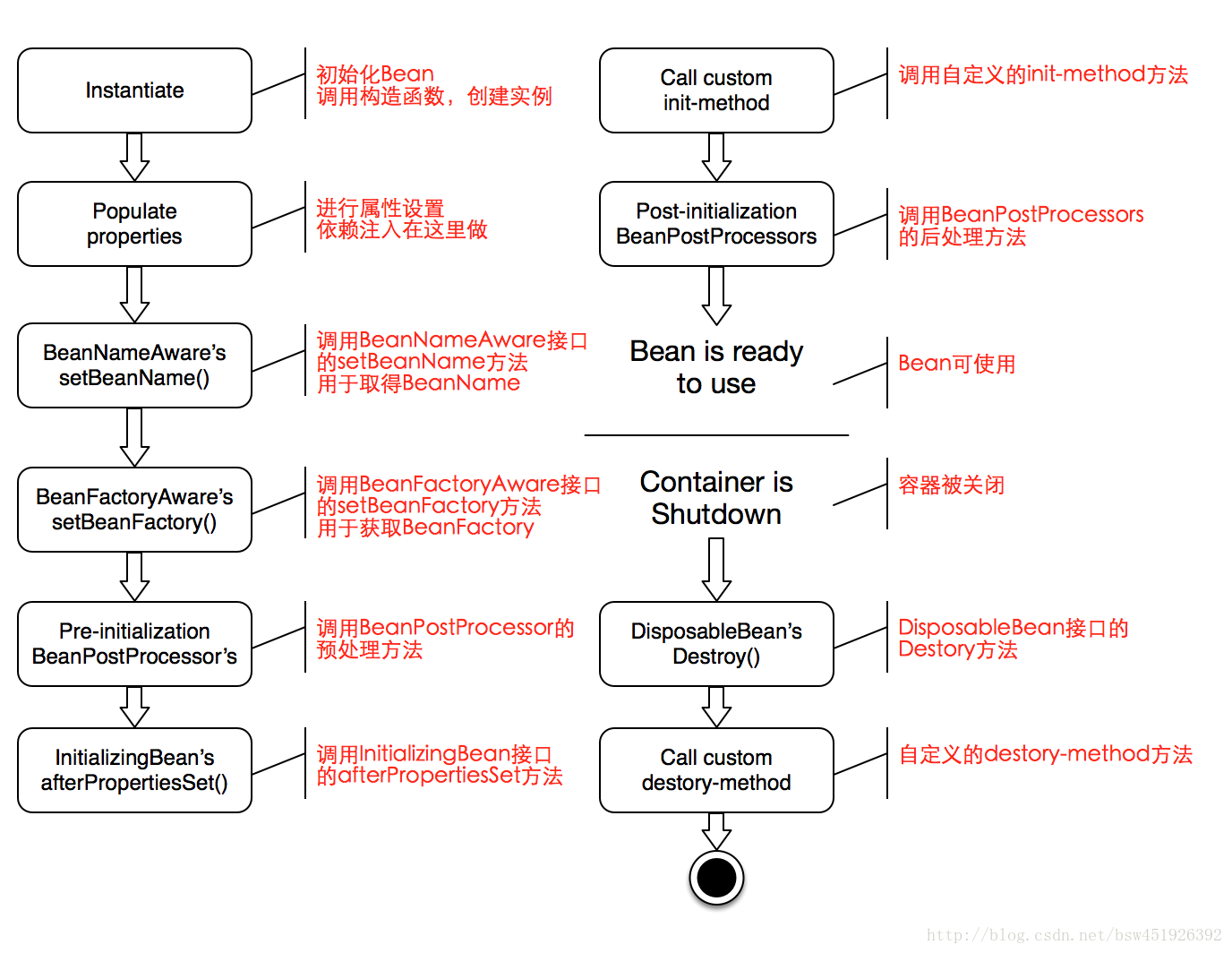
- Bean的生命周期
instantiate bean对象实例化
populate properties 封装属性
如果Bean实现BeanNameAware执行setBeanName
如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAwar或ApplicationContextAwar设置工厂setBeanFactory或上下文对象setApplicationContext
如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean),执行postProcessBeforeInitialization
如果Bean实现InitializingBean执行afterPropertiesSet
调用自定义的init-method方法
如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean),执行postProcessAfterInitialization
执行业务处理
如果Bean实现DisposableBean执行destroy
调用自定义的destroy-method
- 总结:
对于bean的生命周期方法:
第三步与第四步是让Bean了解spring容器。
第五步与第八步 可以针对指定的Bean进行功能增强,这时一般会使用动态代理.
第六步与第十步:通过实现指定的接口来完成init与destroy操作
但是在开发中一般不使用第6步与第10步,原因是我们可以使用第7步与第11步来完成。
第7步与第11步的初始化与销毁操作它无耦合,推荐使用的。但是必须在配置文件中指定初始化与销毁的方法
我们需要关注的主要有两个方法:
1.增强bean的功能可以使用后处理Bean, BeanPostProcessor
2.如果需要初始化或销毁操作我们可以使用init-method destroy-method
注意:destroy-method只对scope=singleton有效果。
- Bean的属性注入
- 构造器注入
创建一个bean类-设置两个属性,提供有参,提供get/set方法,重写toString方法
public class Car {
private String name;
private Double price;
public Car() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Car(String name, Double price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
配置文件
<!-- 构造注入 -->
<bean name="car1" class="com.baidu.di.Car">
<constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="保时捷"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" type="Double" value="100000"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--
index属性说明当前这个值是有参构造中第几个参数的值,从0开始
当不写index时,会根据配置文件中<constructor-arg></constructor-arg>的设置先后来注入数据
type说明注入的数据是什么数据类型的,这里很容易出错,一定要细心,当不写时,或默认与bean中设置的那个数据的数据类型相同
-->
创建测试类
public class DITest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// 获取ApplicationContext对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 获取bean对象
Car car = (Car) context.getBean("car1");
System.out.println(car);
}
}- Setter方法注入
创建一个bean类-设置两个属性,提供有参和无参构造,提供get/set方法,重写toString方法,因为这里使用无参构造方法创建bean,所以必须要提供无参构造
public class Car {
private String name;
private Double price;
public Car() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Car(String name, Double price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
配置文件
<!-- 构造注入 -->
<bean name="car" class="com.baidu.di.Car">
<property name="name" value="保时捷"></property>
<property name="price" value="100000"></property>
</bean>
<!--
index属性说明当前这个值是有参构造中第几个参数的值,从0开始
当不写index时,会根据配置文件中<constructor-arg></constructor-arg>的设置先后来注入数据
type说明注入的数据是什么数据类型的,这里很容易出错,一定要细心,当不写时,或默认与bean中设置的那个数据的数据类型相同
-->
创建测试类
public class DITest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// 获取ApplicationContext对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 获取bean对象
Car car = (Car) context.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car);
}
}构造注入和Setter注入的区别:
构造注入可以不提供无参构造;Setter注入必须提供无参构造 构造注入的配置文件中使用的是<constructor-arg />标签,其中有index,value,type,ref属性;Setter注入的配置文件中使用的是<property />标签,其中有index,value,ref属性ref属性:
使用ref来引入另一个bean对象,完成bean之间注入
创建一个bean,其中有一个属性,是需要引入的Bean的类型,提供无参构造、set/get方法,重写toString方法
public class Person {
private String name;
private Car car;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
public Person() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
配置文件配置
<!-- src-前提,有car1这个Bean -->
<bean name="person" class="com.baidu.di.Person">
<property name="name" value="tom"></property>
<property name="car" ref="car1"></property>
</bean>
测试类
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) context.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}集合属性注入
在spring中对于集合属性,可以使用专门的标签来完成注入例如:list set map properties等集合元素来完成集合属性注入.
创建一个Bean类
public class CollectionDemo {
private List list;
private Map map;
private Properties pro;
private Set set;
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Map getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getPro() {
return pro;
}
public void setPro(Properties pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
public Set getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set set) {
this.set = set;
}
}
配置文件中
<!-- 集合注入 -->
<bean name="coolection" class="com.baidu.di.list.CollectionDemo">
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>15</value>
<ref bean="car"/>
</list>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>赵六</value>
<value>15</value>
<ref bean="person"/>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry value="王五" key="username"></entry>
<entry value="123" key="password"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="pro">
<props>
<prop key="name">李四</prop>
<prop key="age">15</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
测试类中
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CollectionDemo demo = (CollectionDemo) context.getBean("coolection");
// 注入List集合
System.out.println(demo.getList());
// 注入Set集合
System.out.println(demo.getSet());
// 注入Map集合
System.out.println(demo.getMap());
// 注入Properties集合
System.out.println(demo.getPro());
}- 名称空间p和c的使用
Spring2.0以后提供了xml命名空间。下面两种名称空间不是真正的名称空间,是虚拟的。它是嵌入到spring内核中的。
将xml文件中的约束从dtd改xsd,选用下面那种
- P名称空间
使用p名称空间可以解决我们setter注入时<property>简化
创建一个bean类
public class Dog {
private String name;
private String color;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [name=" + name + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
public Dog() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="dog" class="com.baidu.p.Dog" p:name="雪橇" p:color="白色"></bean>
</beans>
测试类
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Dog dog = (Dog) context.getBean("dog");
System.out.println(dog);
}配置文件中的这一行很重要:
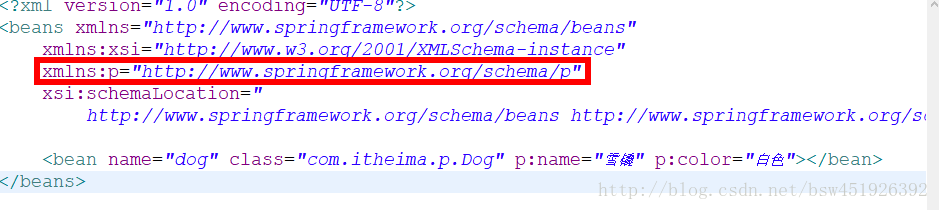
只有配置了这个,才能使用p名称空间
C名称空间
使用c名称空间可以解决我们构造器注入时<constructor-arg>简化
bean类与上面的p名称空间用的是一个
配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- c名称空间 -->
<bean name="dog1" class="com.baidu.p.Dog" c:name="" c:color=""></bean>
测试类
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Dog dog = (Dog) context.getBean("dog1");
System.out.println(dog);
}与p名称空间相似,需要配置一个
xmlns:c=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/c”才能使用c名称空间
- SpEL表达式
spring expression language 是在spring3.0以后的版本提供
它类似于ognl或el表达式,它可以提供在程序运行时构造复杂表达式来完成对象属性存储及方法调用等。
Spel表达式的格式 #{表达式}
- 示例1:完成bean之间的注入
<bean id="person1" class="cn.baidu.namesapce.Person">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
<!-- <property name="dog" ref="dog1"></property> -->
<property name="dog" value="#{dog1}"></property>
</bean>- 示例2 支持属性调用及方法调用
<bean id="person1" class="cn.baidu.namesapce.Person">
<property name="name" value="#{person.name}"></property>
<!-- <property name="dog" ref="dog1"></property> -->
<property name="dog" value="#{dog1}"></property>
<property name="age" value="#{person.getAge()+10}"></property>
</bean>- Spring注解开发
使用注解开发必须在applicationContext.xml文件中添加一个标签:<context:annotation-config />,这个标签的作用是让spring中常用的注解生效,添加这个标签的同时,需要配置约束,约束存在的文件在之前的《Spring开发环境搭建》中有介绍,一个是:xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
另一个是 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
也可直接复制下面代码只xml文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
</beans>完成bean注册
需要使用这个注解:@Component
创建bean接口
public interface IUserService {
public void add();
}
创建接口实现类
// 下面这个操作等同于之前的<bean name="user" class="类名"/>
@Component("user")
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("userService add....");
}
}
配置文件
<!-- 添加识别注解的标签 -->
<context:annotation-config />
创建测试类
public class AnnoatationDemo {
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
IUserService user = (IUserService) context.getBean("user");
user.add();
}
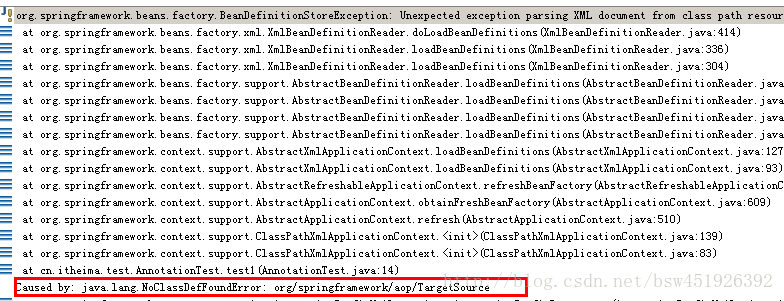
}如果按照上述操作,会报错
原因:如果你使用的是spring3.x那么不会出现这个错误,如果使用的是spring4.x会报错,原因是缺少jar包(spring-aop-4.2.4.RELEASE)。
导入jar包后运行,还是会报错
原因:我们在applicationContext.xml文件中使用了一个标签 <context:annotation-config />,它代表的是可以使用spring的注解,但是我们在类上添加的注解,spring不知道位置。
要解决这个问题,我们可以使用 < context:component-sacn base-package=”“>这个标签base-package=”“中写路径,spring会在这个路径下去寻找注解
<!-- 添加识别注解的标签,包含了context:annotation-config的功能,所以开发中常用下面这种-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.baidu.annotation.impl" />在spring2.5后为@Component添加了三个衍生的注解
@Repository 用于DAO层
@Service 用于service层
@Controller 用于表现层
对于我们的bean所处在的位置可以选择上述三个注解来应用,如果你的bean不明确位置,就可以使用@Component.
- 属性注入
- 简单属性注入
@Value(value="张三")
private String name;- 复杂属性注入
这样可以完成复杂属性的注入
@Autowired
private User user;注意:如果要扫描多个包下的注解可以写成以下:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.baidu.annotation.impl,com.baidu.annotation.dao" />
或
<context:component-scan base-package="com.baidu.annotation" />
扫描com.baidu.annotation包下所有子包
注意:@Value @Autowired它们可以修饰属性,也可以修饰setter方法,如果写在属性上,就不需要提供setter方法。
- @Autowired
默认根据类型注入
如果想要使用名称进行注入需要在这个注解下加一个@Qualifier(“bean的注解名称”),两个注解需一起使用
或者使用@Resource(name=“bean的注解名称”),这个注解,可以达到上面两个注解达到的效果
- 其他注解
@Scope描述bean的作用域
四种作用域:singleton单例,prototype多例,request,session这是一个多例的注解
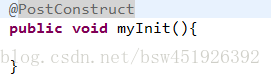
- @PostConstruct描述生命周期中的init-method
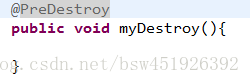
它相当于init-method=”myInit - @PreDestroy描述生命周期中的destroy-method
它相当于是destroy-method=”myDestroy”
注意:对于销毁的方法它只对bean的scope=singleton有效。
- Spring在web开发中的应用
在web项目中要使用spring需要导入一个jar包
在web.xml文件中配置Listener。
这个ContextLoaderListener它实现了ServletContextListener
在这个listener中,当服务器启动时,将ApplicationContext对象,其实是它的一个实现类
WebApplicationContext,对象存入到了ServletContext中。
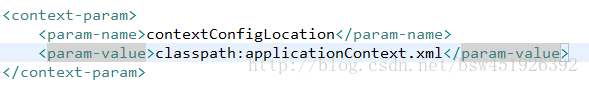
我们还需要在web.xml文件中配置applicationContext.xml文件的位置
默认情况下会在WEB-INF目录 下查找applicationContext.xml
如果applicationContext.xml文件不是在默认位置,我们可以在web.xml文件中配置
Classpath:applicationContext.xml 它代表的是在当前工程的类路径下(可以理解成是在src)下来查找applicationContext.xml文件。
contextConfigLocation它是在listener中声明的一个常量,描述的就是spring配置文件的位置。
- Spring整合junit4测试
Spring整合junit4可以方便我们的测试。
步骤:
导入一个spring-test.jar包:spring-test-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
2.可以在测试类上如下操作
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) // 整合JUnit4
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml") // 指定Spring的配置文件的位置































 2514
2514











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








