我们在学习二叉树的基本操作之前,需要先创建一颗二叉树,现在我们先手动创建出一颗二叉树并进行学习,等到二叉树的结构了解差不多时,我们在来研究二叉树真正的创建方式
1.手动创建二叉树
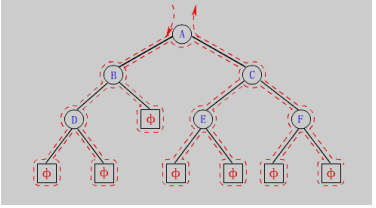
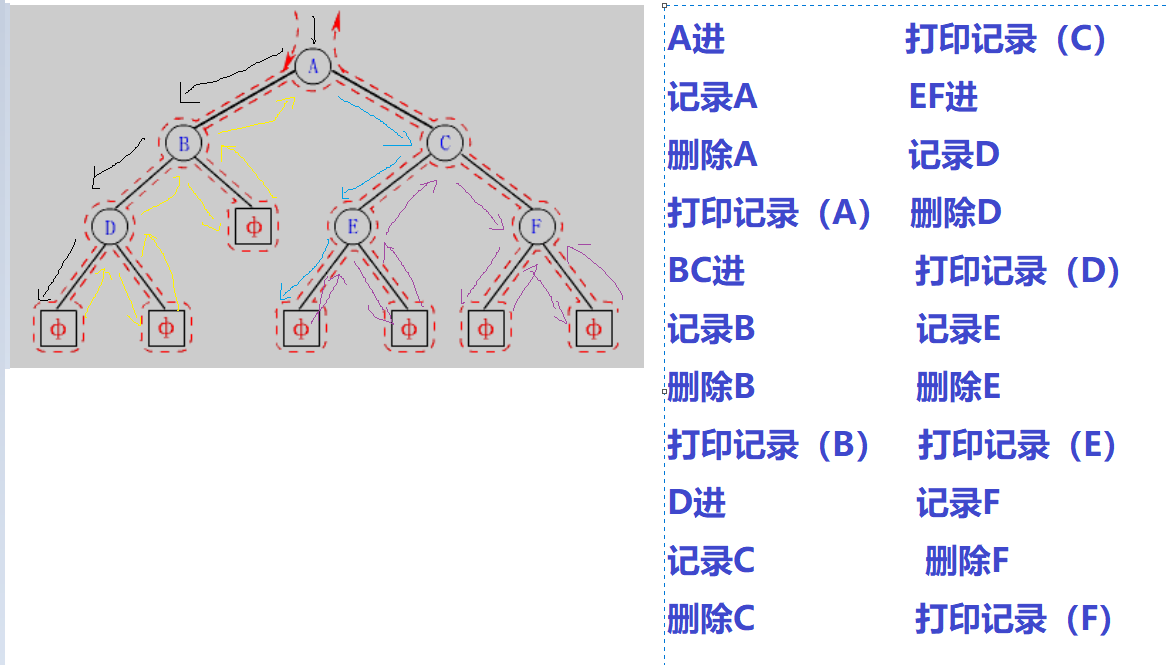
如何手动创建一颗二叉树呢,我们以上面这颗二叉树为例,通过观察我们发现这颗二叉树是由一个个节点连接起来的,每个节点包含值(val), 左指针,右指针,由此我们可以定义一个结构体变量
typedef char BTDataType; //存储数据的类型
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
接下来我们只需要创建结构体,并通过左右指针将他们手动连接起来即可。咱们直接上代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BTNodeCreat(char ch)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
node->data = ch;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* A = BTNodeCreat('A');
BTNode* B = BTNodeCreat('B');
BTNode* C = BTNodeCreat('C');
BTNode* D = BTNodeCreat('D');
BTNode* E = BTNodeCreat('E');
BTNode* F = BTNodeCreat('F');
A->left = B;
A->right = C;
B->left = D;
C->left = E;
C->right = F;
return 0;
}
到这里,我们就轻松的将一颗二叉树手动创建出来了。
2.二叉树的遍历
二叉树有前序遍历,中序遍历,后续遍历,层序遍历四种遍历方式。
2.1前序便利
所谓前序遍历,就是先访问二叉树的根,再访问左子树,再访问右子树。即(根——左子树——右子树)
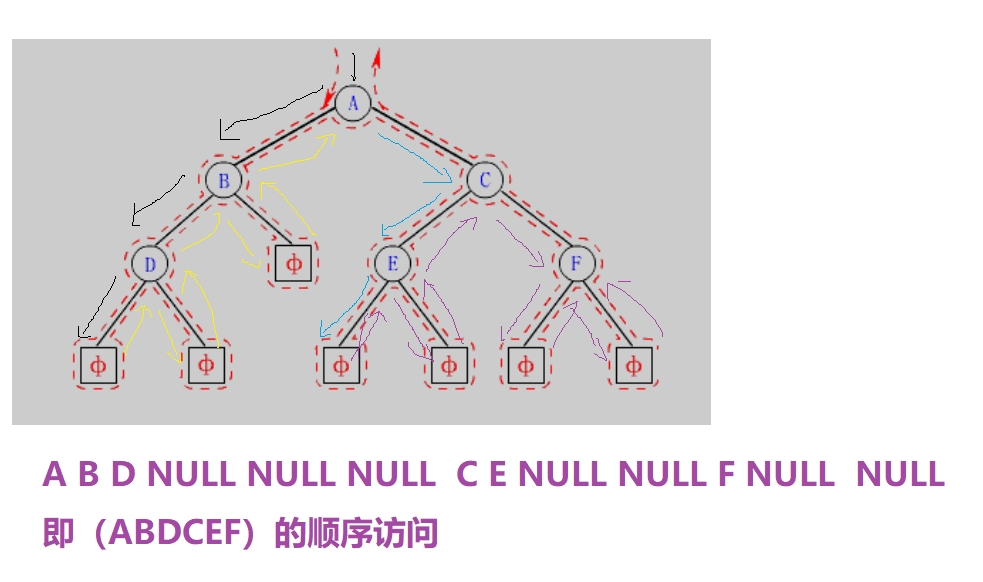
对于该图的前序访问如图所示。现在我们用代码将其实现
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BTNodeCreat(char ch)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
node->data = ch;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root) //前序遍历
{
if (root == NULL)//如果节点为空,就return
{
return;
}
else
{
printf("%c ", root->data);//不为空,将本节点的值打印,然后继续访问左子树右子树
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
}
int main()
{
BTNode* A = BTNodeCreat('A');
BTNode* B = BTNodeCreat('B');
BTNode* C = BTNodeCreat('C');
BTNode* D = BTNodeCreat('D');
BTNode* E = BTNodeCreat('E');
BTNode* F = BTNodeCreat('F');
A->left = B;
A->right = C;
B->left = D;
C->left = E;
C->right = F;
PrevOrder(A);
return 0;
}
2.2中序遍历,后续遍历
中序遍历和后续遍历都与前序遍历类似。
中序:左子树——根——右子树
后续:左子树——右子树——根
咱们直接上代码
void InOrder(BTNode* root)//中序
{
if (root == NULL)//为空就return
{
return;
}
else
{ //不为空就左——根——右
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//为空就return
{
return;
}
else
{
PostOrder(root->left);//不为空就左——右——根
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
}
2.3层序遍历
所谓层序遍历,就是按照从左往右的顺序,依次访问第一层,第二层,第三层……

还是以该图为例,层序遍历的访问顺序就是 ABCDEF
想要实现层序遍历,我们需要借助队列。下面我先将之前写的队列添加到项目中
queue.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode BTNode;
typedef BTNode* QDateType;
typedef struct QListNode
{
QDateType data;
struct QListNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//队列初始化
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDateType x);//入队
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//出队
QDateType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//获取队列头元素
QDateType QueueBack(Queue* pq);//获取队列尾元素
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);//有效元素个数
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//检测队列是否为空
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//销毁队列
queue.c
#include "queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDateType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
QDateType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDateType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
size_t sz = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
sz++;
}
return sz;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
下面我们就利用队列来实现层序遍历
首先我先把代码放在下面,然后在附上思路
#include "queue.h"
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BTNodeCreat(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
printf("%c ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
}
void TreeLeveOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QDateType m = root;
if (m)
{
QueuePush(&q, m);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%c ", front->data);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* A = BTNodeCreat('A');
BTNode* B = BTNodeCreat('B');
BTNode* C = BTNodeCreat('C');
BTNode* D = BTNodeCreat('D');
BTNode* E = BTNodeCreat('E');
BTNode* F = BTNodeCreat('F');
A->left = B;
A->right = C;
B->left = D;
C->left = E;
C->right = F;
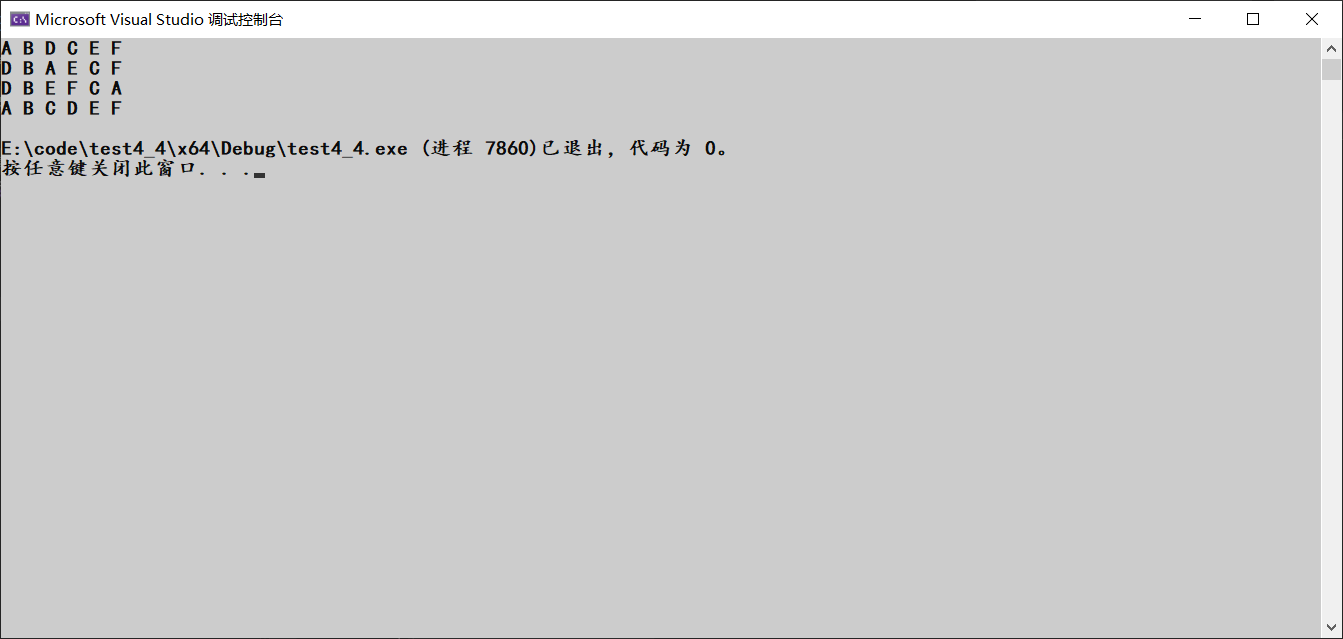
PrevOrder(A);
printf("\n");
InOrder(A);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(A);
printf("\n");
TreeLeveOrder(A);
return 0;
}
3.求二叉树的节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
4.二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
5.二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
6二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
BTNode* lret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (lret)
{
return lret;
}
BTNode* rret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (rret)
{
return rret;
}
}
7.判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
//思路就是我利用层序遍历,在第一次遇到空指针的地方停下来,如果是完全二叉树,那么后面应该全是空指针,
//否则不是完全二叉树。
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}//第一次遇到空指针的地方停下
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))//检查第一个空指针后面的元素是否均为空指针
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
8.二叉树的销毁
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode** pproot)
{
//为什么传参传二级指针?
//我们找一颗二叉树是通过他的根,而根(root)的类型是一级指针(BTNode*)
//我们想要销毁二叉树,是想销毁这个一级指针所指向的空间,并且把这个一级指针制空。
//如果传一级指针,形参只是实参的一份临时拷贝,虽然可以销毁这个根指向的空间,但是
//无法把这个根制空,这个根会变成野指针,所以需要传二级指针
if (*pproot == NULL)
{
return;
}
BinaryTreeDestroy(&(*pproot)->left);
BinaryTreeDestroy(&(*pproot)->right);
free(*pproot);
*pproot = NULL;
}























 624
624











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










