客户端连接服务端具体过程

package com.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTCP01Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.在本机的9999端口监听,要求:在本机的其他服务没有监听9999端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务器端,在9999端口监听,等待连接。。。");
//2.当没有客户端连接9999端口,程序会阻塞,等待连接
//如果有客户端连接,会返回一个socket对象
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("socket="+socket.getClass());
}
}服务端执行,控制台显示
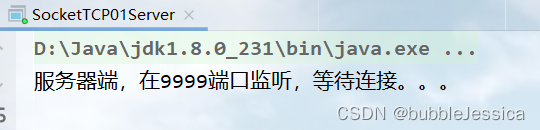
客户端一旦执行,结果如下:
package com.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTCP01Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.连接服务器端
//连接本机的9999端口,如果连接成功,返回Socket对象
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
System.out.println("客户端返回socket="+socket.getClass());
//2.连接上后,生成socket
//3.输出流 将数据写入数据通道
}
}
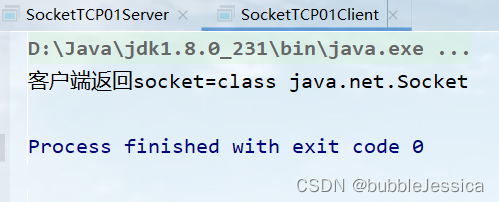
接下来看具体实现
package com.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTCP01Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.在本机的9999端口监听,要求:在本机的其他服务没有监听9999端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
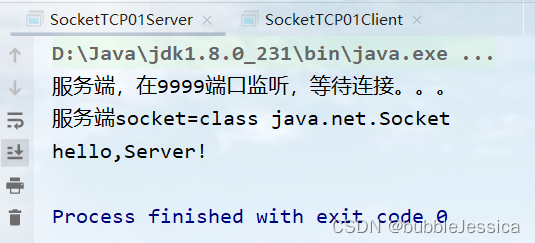
System.out.println("服务端,在9999端口监听,等待连接。。。");
//2.当没有客户端连接9999端口,程序会阻塞,等待连接
//如果有客户端连接,会返回一个socket对象
//ServerSocket 可以通过accept() 返回多个socket[多个客户端连接服务端的并发]
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("服务端socket=" + socket.getClass());
//3.通过输入流 读取客户端写入到数据通道的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//4.IO读取
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int readLength = 0;
while ((readLength = inputStream.read(b)) != -1) {
//根据读取到的实际长度,显示内容
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, readLength));
}
//5.关闭流和socket
inputStream.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}package com.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTCP01Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.连接服务器端
//连接本机的9999端口,如果连接成功,返回Socket对象
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
System.out.println("客户端返回socket="+socket.getClass());
//2.连接上后,生成socket
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.输出流 将数据写入数据通道
outputStream.write("hello,Server!".getBytes());
//4.关闭流对象和socket
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
System.out.println("客户端退出");
}
} 
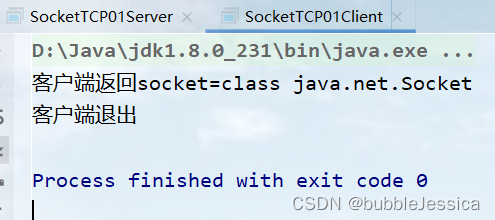
对客户端连接服务端优化

package com.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTCP02Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.在本机的9999端口监听,要求:在本机的其他服务没有监听9999端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务端,在9999端口监听,等待连接。。。");
//2.当没有客户端连接9999端口,程序会阻塞,等待连接
//如果有客户端连接,会返回一个socket对象
//ServerSocket 可以通过accept() 返回多个socket[多个客户端连接服务端的并发]
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("服务端socket=" + socket.getClass());
//3.获取socket关联的输入流 读取客户端写入到数据通道的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//4.IO读取
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int readLength = 0;
while ((readLength = inputStream.read(b)) != -1) {
//根据读取到的实际长度,显示内容
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, readLength));
}
//5.获取socket关联的输出流 将数据写入数据通道
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello,Client".getBytes());
//设置结束标记
socket.shutdownOutput();
//6.关闭流和socket
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}package com.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTCP02Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.连接服务器端
//连接本机的9999端口,如果连接成功,返回Socket对象
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
System.out.println("客户端返回socket="+socket.getClass());
//2.连接上后,生成socket
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.获取socket关联的输出流 将数据写入数据通道
outputStream.write("hello,Server!".getBytes());
//设置结束标记
socket.shutdownOutput();
//4.获取socket关联的输入流 读取服务端写入到数据通道的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] buf=new byte[1024];
int readLength=0;
while ((readLength=inputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,readLength));
}
//5.关闭流对象和socket
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
System.out.println("客户端退出");
}
}


跟开头代码相比,增加了上面内容,必须牢记添加输出流写完数据后,需要添加socket.shutdownOutput();






















 331
331











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








