Can't write to the hard disk on a Linux or Unix-like systems? Want to diagnose corrupt disk issues on a server? Want to find out why you are getting "disk full" messages on screen? Want to learn how to solve full/corrupt and failed disk issues. Try these eight tips to diagnose a Linux and Unix server hard disk drive problems.

#1 - Error: No space left on device
When the Disk is full on Unix-like system you get an error message on screen. In this example, I'm running fallocate command and my system run out of disk space:
$ fallocate -l 1G test4.img fallocate: test4.img: fallocate failed: No space left on device
The first step is to run the df command to find out information about total space and available space on a file system including partitions:
$ df
OR try human readable output format:
$ df -h
Sample outputs:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda6 117G 54G 57G 49% / udev 993M 4.0K 993M 1% /dev tmpfs 201M 264K 200M 1% /run none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock none 1002M 0 1002M 0% /run/shm /dev/sda1 1.8G 115M 1.6G 7% /boot /dev/sda7 4.7G 145M 4.4G 4% /tmp /dev/sda9 9.4G 628M 8.3G 7% /var /dev/sda8 94G 579M 89G 1% /ftpusers /dev/sda10 4.0G 4.0G 0 100% /ftpusers/tmp
From the df command output it is clear that /dev/sda10 has 4.0Gb of total space of which 4.0Gb is used.
Fixing problem when the disk is full
- Compress uncompressed log and other files using gzip or bzip2 or tar command:
gzip /ftpusers/tmp/*.log bzip2 /ftpusers/tmp/large.file.name
- Delete unwanted files using rm command on a Unix-like system:
m -rf /ftpusers/tmp/*.bmp
- Move files to other system or external hard disk using rsync command:
rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov /mnt/usbdisk/ rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov server2:/path/to/dest/dir/ - Find out the largest directories or files eating disk space on a Unix-like systesm:
du -a /ftpusers/tmp | sort -n -r | head -n 10 du -cks * | sort -rn | head
- Truncate a particular file. This is useful for log file:
truncate -s 0 /ftpusers/ftp.upload.log ### bash/sh etc ## >/ftpusers/ftp.upload.log ## perl ## perl -e'truncate "filename", LENGTH'
- Find and remove large files that are open but have been deleted on Linux or Unix:
## Works on Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD etc ## lsof -nP | grep '(deleted)' ## Only works on Linux ## find /proc/*/fd -ls | grep '(deleted)'
To truncate it:
## works on Linux/Unix/BSD/OSX etc all ## > "/path/to/the/deleted/file.name" ## works on Linux only ## > "/proc/PID-HERE/fd/FD-HERE"
#2 - Is the file system is in read-only mode?
You may end up getting an error such as follows when you try to create a file or save a file:
$ cat > file
-bash: file: Read-only file system
Run mount command to find out if the file system is mounted in read-only mode:
$ mount
$ mount | grep '/ftpusers'
To fix this problem, simply remount the file system in read-write mode on a Linux based system:
# mount -o remount,rw /ftpusers/tmp
Another example, from my FreeBSD 9.x server to remount / in rw mode:
# mount -o rw /dev/ad0s1a /
#3 - Am I running out of inodes?
Sometimes, df command reports that there is enough free space but system claims file-system is full. You need to check for the inode which identifies the file and its attributes on a file systems using the following command:
$ df -i
$ df -i /ftpusers/
Sample outputs:
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on /dev/sda8 6250496 11568 6238928 1% /ftpusers
So /ftpusers has 62,50,496 total inodes but only 11,568 are used. You are free to create another 62,38,928 files on /ftpusers partition. If 100% of your inodes are used, try the following options:
- Find unwanted files and delete or move to another server.
- Find unwanted large files and delete or move to another server.
#4 - Is my hard drive is dying?
I/O errors in log file (such as /var/log/messages) indicates that something is wrong with the hard disk and it may be failing. You can check hard disk for errors using smartctl command, which is control and monitor utility for SMART disks under Linux and UNIX like operating systems. The syntax is:
smartctl -a /dev/DEVICE
# check for /dev/sda on a Linux server
smartctl -a /dev/sda
You can also use "Disk Utility" to get the same information
Note: Don't expect too much from SMART tool. It may not work in some cases. Make backup on a regular basis.
#5 - Is my hard drive and server is too hot?
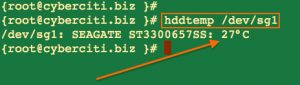
High temperatures can cause server to function poorly. So you need to maintain the proper temperature of the server and disk. High temperatures can result into server shutdown or damage to file system and disk. Use hddtemp or smartctl utility to find out the temperature of your hard on a Linux or Unix based system by reading data from S.M.A.R.T. on drives that support this feature. Only modern hard drives have a temperature sensor. hddtemp supports reading S.M.A.R.T. information from SCSI drives too. hddtemp can work as simple command line tool or as a daemon to get information from all servers:
hddtemp /dev/DISK hddtemp /dev/sg0
Sample outputs:
You can use the smartctl command as follows too:
smartctl -d ata -A /dev/sda | grep -i temperature
How do I get the CPU temperature?
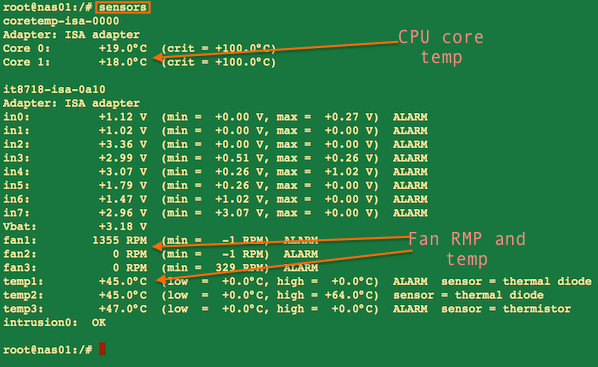
You can use Linux hardware monitoring tool such as lm_sensor to get the cpu temperature on a Linux based system:
sensors
Sample outputs from Debian Linux server:
#6 - Dealing with corrupted file systems
File system on server may be get corrupted due to a hard reboot or some other error such as bad blocks. You can repair corrupted file systems with the following fsck command:
umount /ftpusers
fsck -y /dev/sda8
See how to surviving a Linux filesystem failures for more info.
#7 - Dealing with software RAID on a Linux
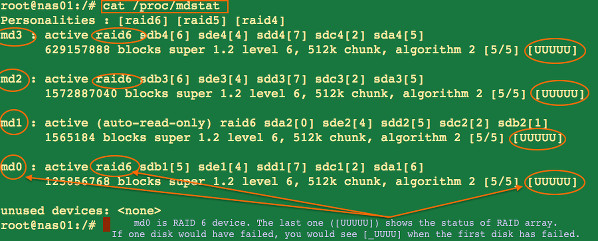
To find the current status of a Linux software raid type the following command:
## get detail on /dev/md0 raid ## mdadm --detail /dev/md0 ## Find status ## cat /proc/mdstat watch cat /proc/mdstat
Sample outputs:
You need to replace a failed hard drive. You must u remove the correct failed drive. In this example, I'm going to replace /dev/sdb (2nd hard drive of RAID 6). It is not necessary to take the storage offline to repair the RAID on Linux. This only works if your server support hot-swappable hard disk:
## remove disk from an array md0 ## mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1 mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --remove /dev/sdb1 # Do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ## # Power down if not hot-swappable hard disk: ## shutdown -h now ## copy partition table from /dev/sda to newly replaced /dev/sdb ## sfdisk -d /dev/sda | sfdisk /dev/sdb fdisk -l ## Add it ## mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1 # do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ## # Now md0 will sync again. See it on screen ## watch cat /proc/mdstat
See our tips on increasing RAID sync speed on Linux for more information.
#8 - Dealing with hardware RAID
You can use the samrtctl command or vendor specific command to find out the status of RAID and disks in your controller:
## SCSI disk smartctl -d scsi --all /dev/sgX ## Adaptec RAID array /usr/StorMan/arcconf getconfig 1 ## 3ware RAID Array tw_cli /c0 show
See your vendor specific documentation to replace a failed disk.
Monitoring disk health
See our previous tutorials:
- Monitoring hard disk health with smartd under Linux or UNIX operating systems
- Shell script to watch the disk space
- UNIX get an alert when disk is full
- Monitor UNIX / Linux server disk space with a shell scrip
- Perl script to monitor disk space and send an email
- NAS backup server disk monitoring shell script
Conclusion
I hope these tips will help you troubleshoot system disk issue on a Linux/Unix based server. I also recommend implementing a good backup plan in order to have the ability to recover from disk failure, accidental file deletion, file corruption, or complete server destruction:
- Debian / Ubuntu: Install Duplicity for encrypted backup in cloud
- HowTo: Backup MySQL databases, web server files to a FTP server automatically
- How To Set Red hat & CentOS Linux remote backup / snapshot server
- Debian / Ubuntu Linux install and configure remote filesystem snapshot with rsnapshot incremental backup utility
- Linux Tape backup with mt And tar command tutorial
- 30 Cool Open Source Software I Discovered in 2013

- 30 Handy Bash Shell Aliases For Linux / Unix / Mac OS X
- Top 30 Nmap Command Examples For Sys/Network Admins
- 25 PHP Security Best Practices For Sys Admins
- 20 Linux System Monitoring Tools Every SysAdmin Should Know
- 20 Linux Server Hardening Security Tips
- Linux: 20 Iptables Examples For New SysAdmins
- Top 20 OpenSSH Server Best Security Practices
- Top 20 Nginx WebServer Best Security Practices
- 20 Examples: Make Sure Unix / Linux Configuration Files Are Free From Syntax Errors
- 15 Greatest Open Source Terminal Applications Of 2012
- My 10 UNIX Command Line Mistakes
- Top 10 Open Source Web-Based Project Management Software
- Top 5 Email Client For Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows Users
- The Novice Guide To Buying A Linux Laptop























 3076
3076

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








