一、convmv命令简介
单个文件编码转换我们可以使用系统自带的命令iconv,命令使用可以参考Linux命令之iconv命令。如果是整个中文文件夹及你们的文件全是乱码怎么办呢?这个时候我们可以使用convmv命令,通过-r参数完成整个目录里文件编码的转换。convmv能帮助我们很容易地对一个文件,一个目录下所有文件进行编码转换,比如gbk转为utf8等。convmv命令除了转换编码还可以转换文件名为大写或者小写,在需要批量更名大小写的时候非常有用。
二、使用示例
1、安装命令
[root@s145 tmp]# yum install convmv
2、获取命令帮助
[root@s145 tmp]# convmv --help
Your Perl version has fleas #22111 #37757 #49830
convmv 1.15 - converts filenames from one encoding to another
Copyright © 2003-2011 Bjoern JACKE bjoern@j3e.de
…
3、目录编码转换模拟

[root@s145 abc]# ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 120 Mar 30 15:55 ϲ???ĸ?
[root@s145 abc]# convmv -f GBK -t UTF8 -r ./
4、目录编码转换真实执行

[root@s145 abc]# convmv -f GBK -t UTF8 -r --notest ./
mv “./ϲ.mp3” “./ϲ - 佛系少女.mp3”
mv “./ϲ - .mp3” “./ϲ风吹麦浪.mp3”
mv “./ϲ- ŭ.mp3” “./ϲ怒放的生命.mp3”
mv “./ϲ.mp3” “./ϲ - 因为有你.mp3”
mv “./ϲ”./喜欢的歌"
Ready!
5、列出所执行的编码
#所支持的编码比iconv命令少,但是也有100+种编码,完全覆盖了常见编码类型。
[root@s145 abc]# convmv --list
7bit-jis
AdobeStandardEncoding
AdobeSymbol
AdobeZdingbat
ascii
ascii-ctrl
big5-eten
big5-hkscs
…
utf-8-strict
utf8
viscii
[root@s145 abc]# convmv --list |wc -l
124
6、将文件名转换为大写

#注意此修改是将文件后缀大小写一并修改
[root@s145 tmp]# convmv --upper abc2
Starting a dry run without changes…
mv “./abc2” “./ABC2”
No changes to your files done. Use --notest to finally rename the files.
7、将文件名转换为小写
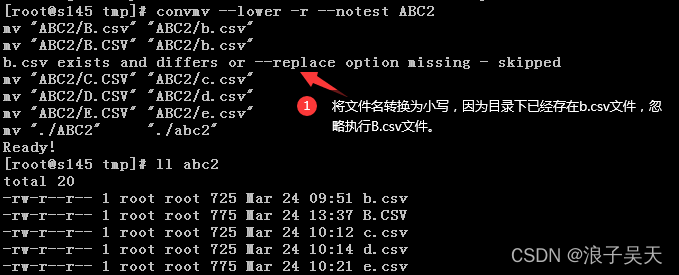
#注意此修改是将文件后缀大小写一并修改
[root@s145 tmp]# convmv --lower -r --notest ABC2
mv “ABC2/B.csv” “ABC2/b.csv”
mv “ABC2/B.CSV” “ABC2/b.csv”
b.csv exists and differs or --replace option missing - skipped
mv “ABC2/C.CSV” “ABC2/c.csv”
mv “ABC2/D.CSV” “ABC2/d.csv”
mv “ABC2/E.CSV” “ABC2/e.csv”
mv “./ABC2” “./abc2”
Ready!
[root@s145 tmp]# ll abc2
total 20
-rw-r–r-- 1 root root 725 Mar 24 09:51 b.csv
-rw-r–r-- 1 root root 775 Mar 24 13:37 B.CSV
-rw-r–r-- 1 root root 725 Mar 24 10:12 c.csv
-rw-r–r-- 1 root root 725 Mar 24 10:14 d.csv
-rw-r–r-- 1 root root 775 Mar 24 10:21 e.csv
8、转换前交互式确认是否执行
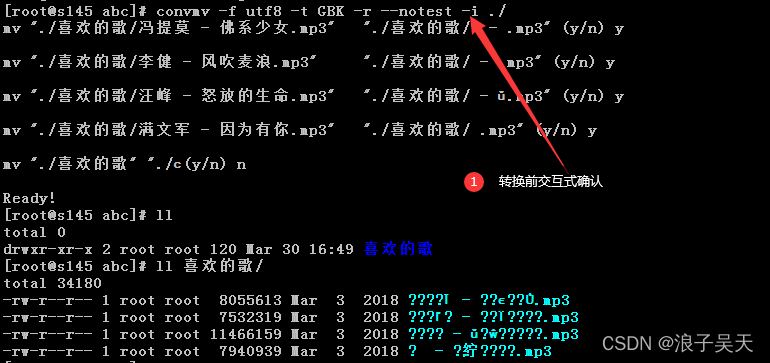
#使用-i参数执行交互式确认,选择y执行,选择n表示不执行转换。
[root@s145 abc]# convmv -f utf8 -t GBK -r --notest -i ./
mv “./喜欢的歌/冯提莫 - 佛系少女.mp3” “./喜欢的歌/Ī - .mp3” (y/n) y
…
三、使用语法及参数说明
1、使用语法
用法:#convmv [options] 文件/目录
2、常用参数说明
| 参数 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
| -f enc | 源编码 |
| -t enc | 新编码 |
| -r | 递归处理子文件夹 |
| -i | 交互文向转换,每次转换前询问 |
| –list | 显示所有可用编码 |
| –nosmart | 如果是utf8文件,忽略 |
| –notest | 直接转换不测试 |
| –replace | 文件相同直接替换 |
| –unescape | 可以做一下转义,比如把%20变成空格 |
| –upper | 全部转换成大写 |
| –lower | 全部转换成小定 |








 这篇博客介绍了Linux系统中用于批量转换文件编码和文件名的convmv命令。从安装到使用,包括目录编码转换、文件名大小写转换、交互式确认等功能,详尽展示了convmv的用法。此外,还列举了可用的编码列表,并提供了参数说明,对于需要进行文件管理的用户非常实用。
这篇博客介绍了Linux系统中用于批量转换文件编码和文件名的convmv命令。从安装到使用,包括目录编码转换、文件名大小写转换、交互式确认等功能,详尽展示了convmv的用法。此外,还列举了可用的编码列表,并提供了参数说明,对于需要进行文件管理的用户非常实用。

















 2598
2598

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










