目录
链表
一、理论基础
-
单链表
- 链表是一种通过 指针串联在一起的线性结构,每一个结点由两部分组成, 一个是数据域,一个是指针域(存放指向下一个结点的 指针),最后一个结点的指针域指向null。
单链表示意图:
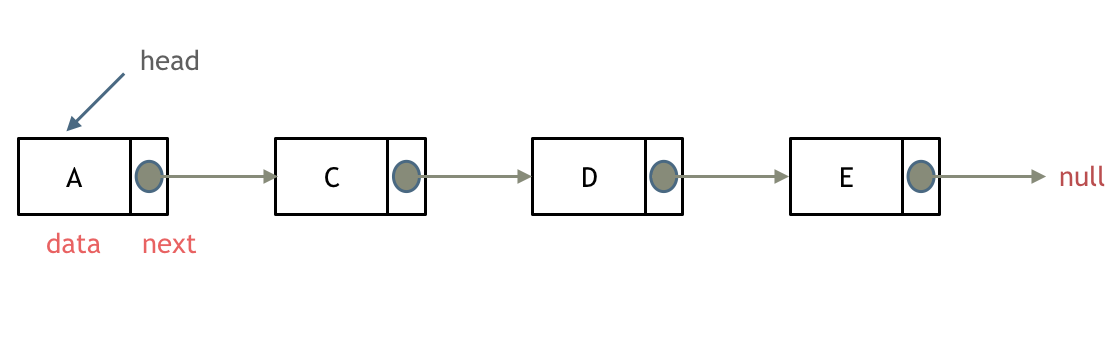
链表的入口节点称为链表的头结点也就是head。
-
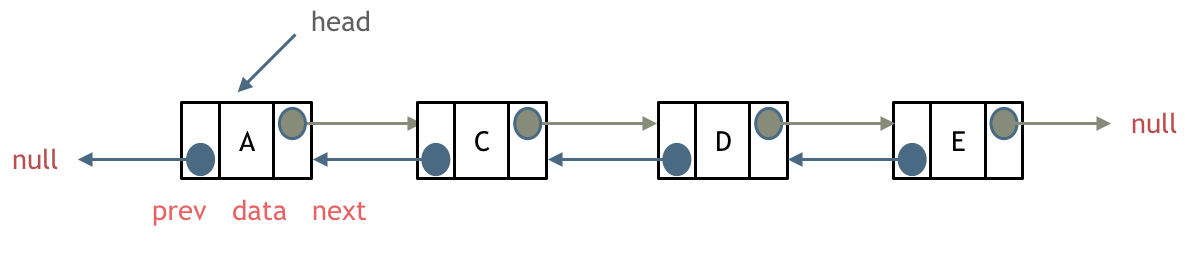
双链表
- 每一个结点有2个指针域,分别 指向上一个结点和下一个结点。因此,它既可以向前查询也可以向后查询。
双链表示意图
-
循环链表
- 顾名思义,就是 链表首尾相连。
循环链表示意图
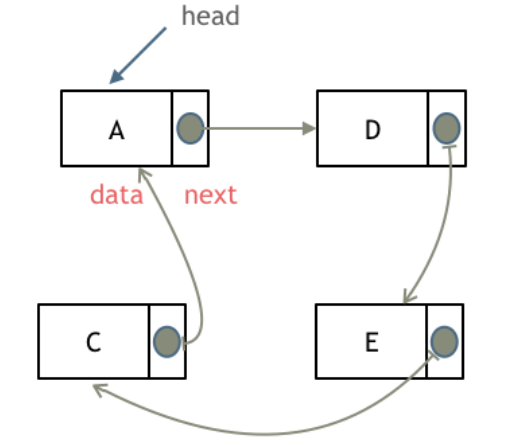
循环链表可以用来解决约瑟夫问题。
约瑟夫问题 < = = > <==> <==> 丢手绢 < = = > <==> <==> 约瑟夫环
有n个人围成一圈,从第一个人开始报数,报到m的人出圈,剩下的人继续从1开始报数,直到剩下最后一个人。求出最后一个出圈的人的编号。
链表的存储方式
链表中的节点在内存中不是连续分布的,而是散乱分布在内存中的某地址上。分配机制取决于操作系统的内存管理。
链表的删除
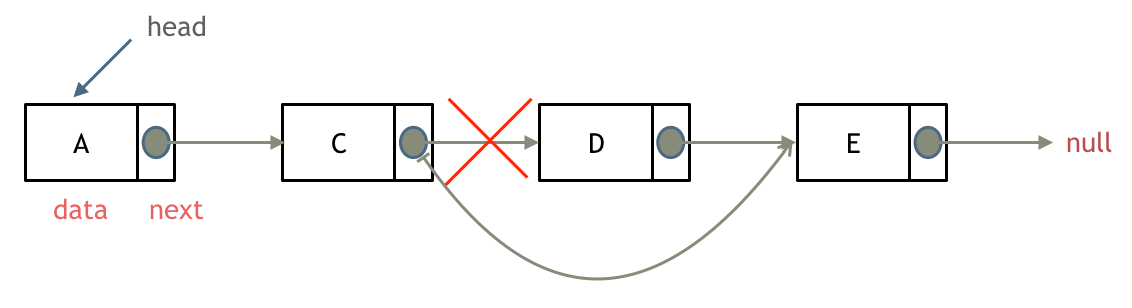
链表的添加
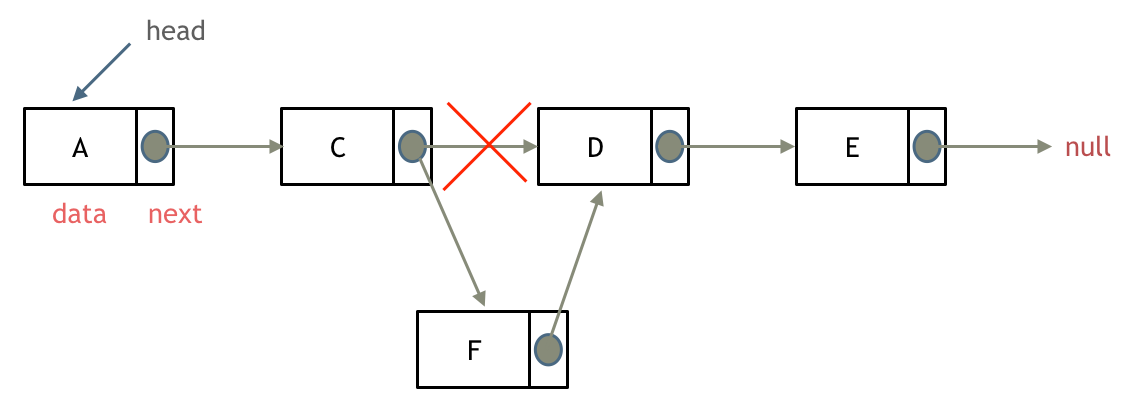
链表的定义
Java:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode() {
}
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
JavaScript
class ListNode {
val;
next = null;
constructor(value) {
this.val = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
Python
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
二、实践
203.移除链表元素
力扣链接
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
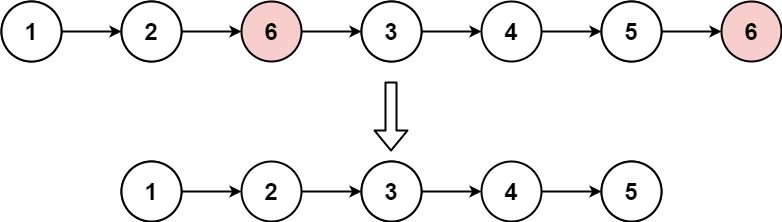
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
提示:
- 列表中的节点数目在范围[0, 1 0 4 10^4 104]内
- 1 <= Node.val <= 50
- 0 <= val <= 50
Java代码如下:
class Solution{
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
/**设置一个虚拟头结点(指向头结点head):不用单独把头结点摘出来考虑*/
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
/**
* 不设置虚拟头结点,将头结点和其他节点分别考虑
*/
public ListNode removeElementsSimple(ListNode head, int val) {
/**注意这里不是if啊! 将符合和即将符合条件的头结点全部去除*/
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
/**处理其他结点*/
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
/**
* 通过递归去实现
*/
public ListNode removeElementsRecursive(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
head.next = removeElementsRecursive(head.next, val);
return head.val == val ? head.next : head;
}
}
JavaScript代码如下:
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} val
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeElements = function(head, val) {
// 1.
// while (head !== null && head.val === val) {
// head = head.next;
// }
// let cur = head;
// while (cur !== null && cur.next !== null) {
// if (cur.next.val === val) {
// cur.next = cur.next.next;
// } else {
// cur = cur.next;
// }
// }
// return head;
// 2.
// let dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
// let cur = dummyHead;
// while (cur !== null && cur.next !== null) {
// if (cur.next.val === val) {
// cur.next = cur.next.next;
// } else {
// cur = cur.next;
// }
// }
// return dummyHead.next;
// 3.
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
return head.val == val ? head.next : head;
};
Python代码如下:
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: Optional[ListNode], val: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 1.
# while head and head.val == val:
# head = head.next
# cur = head
# while cur and cur.next:
# if cur.next.val == val:
# cur.next = cur.next.next
# else:
# cur = cur.next
# return head
# 2.
# dummyHead = ListNode(-1, head)
# cur = dummyHead
# while cur and cur.next:
# if cur.next.val == val:
# cur.next = cur.next.next
# else:
# cur = cur.next
# return dummyHead.next
# 3.
if not head:
return
head.next = self.removeElements(head.next, val)
return head.next if head.val == val else head
206. 反转链表
力扣链接
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例1:
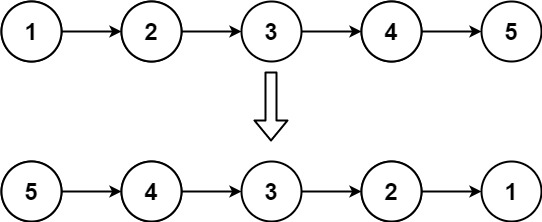
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例2:
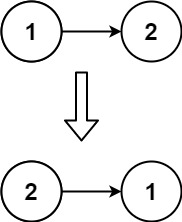
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 5000]
- -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Java代码如下(3种方法):
class Solution{
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
/*// 2.递归法
return reverse(null, head);*/
// 3.头插法
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
// 定义temp:保存当前结点的next指针指向
ListNode temp = null;
// 遍历所有结点
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
// 定义temp结点: 保存cur指针更新前的指向结点
ListNode temp = cur.next;
// 翻转指针
cur.next = prev;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
public ListNode reverseListByDoublePoint(ListNode head) {
// 1.双指针法
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 保存next指针改变前要指向的结点
temp = cur.next;
// 翻转指向
cur.next = prev;
// 更新
prev = cur;
// 更新
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
JavaScript代码如下:
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
let reverseList = function (head) {
/*// 2.递归法
return reverse(null, head);*/
// 3.头插法
let dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = null;
let temp = null, cur = head;
while (cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
let reverse = function (prev, cur) {
if (!cur) {
return prev;
}
let temp = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
let reverseListDoublePoint = function (head) {
// 1.双指针法
let cur = head,
prev = null,
temp = null;
while (cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
};
Python代码如下:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
'''# 2.递归法
return self.reverse(None, head)'''
# 3.头插法
dummyHead = ListNode()
cur, temp = head, None
while cur:
temp = cur.next
cur.next = dummyHead.next
dummyHead.next = cur
cur = temp
return dummyHead.next
def reverse(self, prev, cur):
if not cur:
return prev
temp = cur.next
cur.next = prev
return self.reverse(cur, temp)
def reverseListDoublePoint(self, head):
# 1.双指针
cur, prev, temp = head, None, None
while cur:
temp = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = temp
return prev
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
力扣链接
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例1:
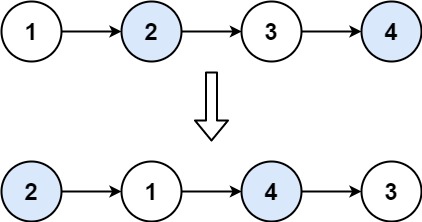
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
Java代码如下:
class Solution {
/**
* @param head
* @return ListNode
* @Description: 方法二:递归
* @Author ami168cc@163.com
* @CreateTime 2023/6/11 14:25
*/
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode secondNode = head.next;
ListNode ThirdNode = swapPairs(secondNode.next);
/**第1个结点指向第3个结点*/
head.next = ThirdNode;
/**第2个结点指向第1个结点*/
secondNode.next = head;
return secondNode;
}
/**
* @param head
* @return ListNode
* @Description: 方法一:使用虚拟头结点 + 循环
* @Author ami168cc@163.com
* @CreateTime 2023/6/11 14:01
*/
public ListNode swapPairsMethodOne(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
ListNode firstNode;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
/**通过第一个和第二个结点均为非null,可以排除奇数结点情况下的最后一个结点的处理
* 1.将第2个结点挂到虚拟头结点后面
* 2.将第2个结点的后继结点(第3个结点)挂到第1个结点后面
* 3.将第1个结点挂到第2个结点后面
* 备注: 也可以将第2步和第3步顺序颠倒
* */
firstNode = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
firstNode.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = firstNode;
/**步长为2*/
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return cur.next;
}
}
JavaScript代码如下:
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
let swapPairs = function (head) {
// 2.递归
if (!head || !head.next) {
return head;
}
let secondNode = head.next,
thirdNode = swapPairs(secondNode.next) || null;
head.next = thirdNode;
secondNode.next = head;
return secondNode;
}
let swapPairsMethodOne = function (head) {
// 1.虚拟头结点 + 循环
let dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
let cur = dummyHead,
firstNode = null;
while (cur.next && cur.next.next) {
firstNode = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
firstNode.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = firstNode;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
};
**Python代码如下: **
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 2. 递归
if not head or not head.next:
return head
secondNode = head.next
thirdNode = self.swapPairs(secondNode.next)
head.next = thirdNode
secondNode.next = head
return secondNode
def swapPairsMethodOne(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 1. 虚拟头结点 + 循环
dummyHead = ListNode(-1, head)
cur, firstNode = dummyHead, None
while cur.next and cur.next.next:
firstNode = cur.next
cur.next = cur.next.next
firstNode.next = cur.next.next
cur.next.next = firstNode
# 步长为2
cur = cur.next.next
return dummyHead.next
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
力扣链接
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例1:
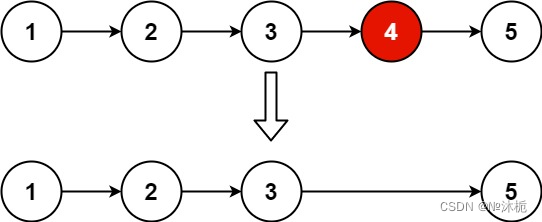
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
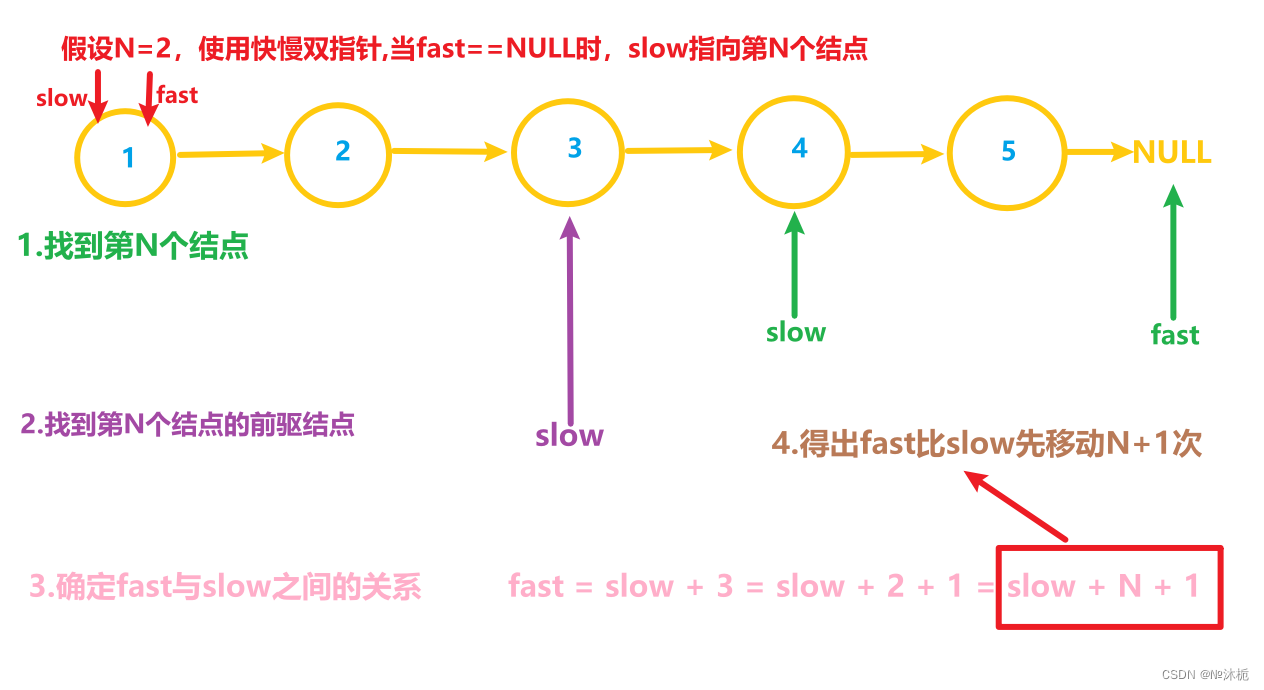
思路如图:
Java代码如下:
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
/**
* 关键:怎么去找到倒数第N个结点呢(很难受,并不是找指定的值),
* 思路:使用快慢双指针: 首先,快指针单独移动N次;其次,双指针一起移动,直到快指针==NULL,那么慢指针就指向倒数第N个结点了
* 但是,题目是要删除它,而不是找到它,因此呢,我们要去找到它的前驱结点
* 那么,就可以将快指针先移动N+1次,这样当快指针==NULL时,慢指针就指向它的前驱结点了。
* */
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode fastNode = dummyHead;
ListNode slowNode = dummyHead;
/**快指针先移动N+1次*/
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
fastNode = fastNode.next;
}
while (fastNode != null) {
fastNode = fastNode.next;
slowNode = slowNode.next;
}
slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
JavaScript代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
let fastNode = slowNode = dummyHead;
for (let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
fastNode = fastNode.next;
}
while (fastNode != null) {
fastNode = fastNode.next;
slowNode = slowNode.next;
}
slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
};
Python代码如下:
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummyHead = ListNode(-1, head)
fastNode = slowNode = dummyHead
for i in range(n + 1):
fastNode = fastNode.next
while fastNode != None:
fastNode = fastNode.next
slowNode = slowNode.next
slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next
return dummyHead.next
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
力扣链接
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
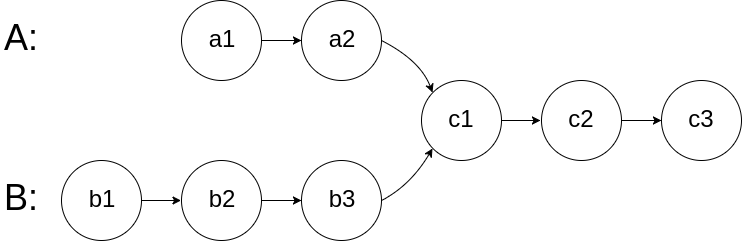
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例1:
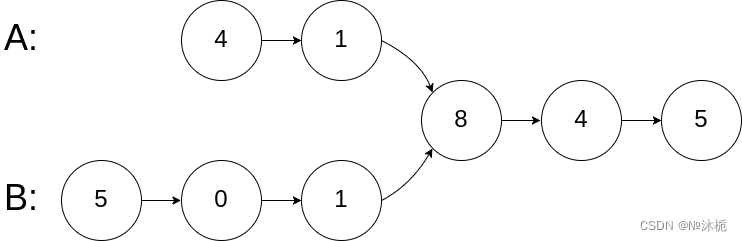
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例2:
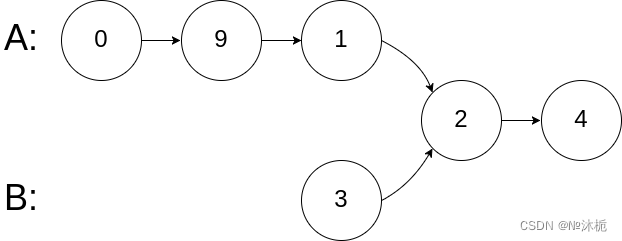
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例3:
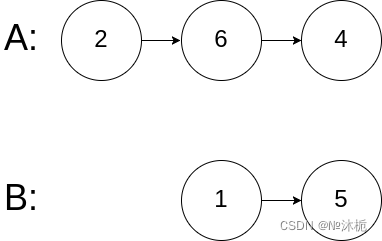
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
- listA 中节点数目为 m
- listB 中节点数目为 n
- 0 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105
- 0 <= skipA <= m
- 0 <= skipB <= n
- 如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
- 如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,
intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
思路:双指针
方法一:
- 如果2个链表相交,即有公共长度。那么假设链表A的长度为m,链表B的长度为n;A中不相交部分的长度为a,B中不相交部分的长度为b,二者相交部分的长度均为c。则有a + c = m, b + c = n。
- 如果 a==b, 那么双指针会同时到达相交部分。
- 如果 a!=b,那么双指针都会遍历完对应的链表,当它们各自遍历完成后,便将hA指向链表B的头结点,hB指向链表A的头结点,则当hA再遍历b次,hB再遍历a次,二者一定会同时到达相交部分,即
a + c + b = b + c + a。
- 如果2个链表未相交,
- 二者中至少有1个是为空链表,则返回
null - 当二者均非空链表,则当hA遍历完链表B,hB遍历完链表A,即 m + n == n + m后,二者均指向
null,则返回null
- 二者中至少有1个是为空链表,则返回

方法二:
通过移动较长链表的指针,使二者可以同时到达彼此链表的末尾。如果在同时移动过程中,二者指针相同,则返回指针;否则,返回null。

Java代码如下:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 方法1:
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode hA = headA, hB = headB;
// 比较的是指针,并不是节点内容。
while (hA != hB) {
hA = hA == null ? headB : hA.next;
hB = hB == null ? headA : hB.next;
}
return hA;
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNodeMethodTwo(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 方法2: 既然相交部分结点相同,
// 那么使hA指向结点和hB指向结点距离相交结点的距离相同
// 则当二者指针相同,便是相交结点
ListNode hA = headA, hB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (hA != null) {
lenA++;
hA = hA.next;
}
while (hB != null) {
lenB++;
hB = hB.next;
}
// 这里一定要注意: 因为hA和hB已经指向null
hA = headA;
hB = headB;
// 确保hA指向最长链表
if (lenA < lenB) {
int temp = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = temp;
ListNode tempL = hA;
hA = hB;
hB = tempL;
}
// 将hA移动到可以使其与hB共同到达的位置
int gap = lenA - lenB;
while (gap-- > 0) {
hA = hA.next;
}
// 寻找指针相同,不是内容相同
while (hA != hB) {
hA = hA.next;
hB = hB.next;
}
// 找到,hA即指向相交结点;未找到,hA指向null
return hA;
}
}
**JavaScript代码如下: **
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
// // 1
// if (!headA || !headB) return null;
// let hA =headA, hB = headB;
// while (hA != hB) {
// hA = hA == null ? headB : hA.next;
// hB = hB == null ? headA : hB.next;
// }
// return hA;
// 2
let hA =headA, hB = headB,
lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (hA) {
lenA++;
hA = hA.next;
}
while (hB) {
lenB++;
hB = hB.next;
}
// 复原
hA = lenA < lenB ? headB : headA;
hB = lenA < lenB ? headA : headB;
// 保证hA指向最长的链表
if (lenA < lenB) {
let temp = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = temp;
}
console.log(hA, hB);
// 使hA指向长度等于hB的结点,保证二者同时到达相交结点。
let gap = lenA - lenB;
while (gap-- > 0) {
hA = hA.next;
}
// 寻找相交结点
while (hA != hB) {
hA = hA.next;
hB = hB.next;
}
return hA;
};
Python代码如下:
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 2
hA, hB = headA, headB
lenA = lenB = 0
while hA:
lenA += 1
hA = hA.next
while hB:
lenB += 1
hB = hB.next
hA = headB if lenA < lenB else headA
hB = headA if lenA < lenB else headB
if lenA < lenB:
lenA, lenB = lenB, lenA
gap = lenA - lenB
while gap > 0:
hA = hA.next
gap -= 1
while hA != hB:
hA = hA.next
hB = hB.next
return hA
# # 1
# if not headA or not headB:
# return None
# hA, hB = headA, headB
# while hA != hB:
# hA = headB if not hA else hA.next
# hB = headA if not hB else hB.next
# return hA
142. 环形链表 II
力扣链接
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例1:
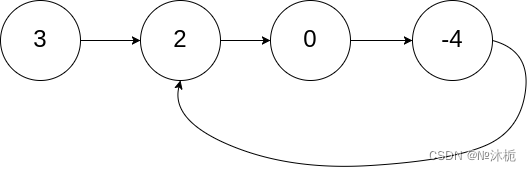
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例2:

输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围 [0, 104] 内
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
- pos 的值为 -1 或者链表中的一个有效索引

**Java代码如下: **
/**
* 方法1: 快慢指针
* @param head
* @return
*/
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
/**快慢指针相遇*/
if (fast == slow) {
/*将慢指针移到头结点,二者同时前进,再次相遇,便为所求*/
slow = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 方法2: 哈希表
* @param head
* @return
*/
public ListNode detectCycleM2(ListNode head) {
HashSet<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (visited.contains(cur)) {
return cur;
}
visited.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
JavaScript代码如下:
/**
* 方法1: 哈希表
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
let detectCycle = function(head) {
let visited = new Set(),
cur = head;
while (cur) {
if (visited.has(cur)) {
return cur;
}
visited.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
};
/**
* 方法2: 快慢指针
* @param head
* @returns {null|*}
*/
let detectCycleM2 = function(head) {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return null;
}
let slow = head,
fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
};
Python代码如下:
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 1. 哈希表
visited = set()
cur = head
while cur:
if cur in visited:
return cur
visited.add(cur)
cur = cur.next
return None
def detectCycleM2(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if slow == fast:
slow = head
while fast != slow:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return fast
return





















 52
52











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








