一、原理分析
1、HashMap分析
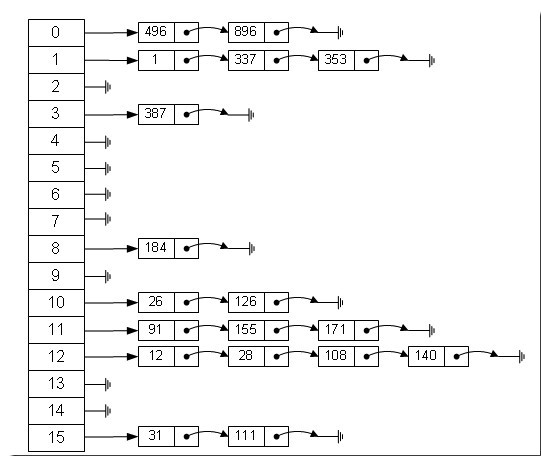
HashMap是基于hash表非同步map实现,key和value都可以为null。其hash表实现方式是”拉链法”,可理解为链表的数组,如下图所示:
HashMap部分源码如下:
/**
* The hash table. If this hash map contains a mapping for null, it is
* not represented this hash table.
*/
transient HashMapEntry<K, V>[] table;/**
* Maps the specified key to the specified value.
*
* @param key
* the key.
* @param value
* the value.
* @return the value of any previous mapping with the specified key or
* {@code null} if there was no such mapping.
*/
@Override public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return putValueForNullKey(value);
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
modCount++;
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the value of the mapping with the specified key.
*
* @param key
* the key.
* @return the value of the mapping with the specified key, or {@code null}
* if no mapping for the specified key is found.
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null) {
HashMapEntry<K, V> e = entryForNullKey;
return e == null ? null : e.value;
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
K eKey = e.key;
if (eKey == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(eKey))) {
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Creates a new entry for the given key, value, hash, and index and
* inserts it into the hash table. This method is called by put
* (and indirectly, putAll), and overridden by LinkedHashMap. The hash
* must incorporate the secondary hash function.
*/
void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
table[index] = new HashMapEntry<K, V>(key, value, hash, table[index]);
}static class HashMapEntry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
final int hash;
HashMapEntry<K, V> next;
HashMapEntry(K key, V value, int hash, HashMapEntry<K, V> next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.hash = hash;
this.next = next;
}HashMap的HashMapEntry
/**
* Doubles the capacity of the hash table. Existing entries are placed in
* the correct bucket on the enlarged table. If the current capacity is,
* MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method is a no-op. Returns th







 本文对比分析了HashMap、ArrayMap和SparseArray三种数据结构。HashMap使用拉链法实现,支持key和value为null,扩容时新建两倍大小的table。ArrayMap采用int[]保存hashCode,Object[]保存键值对,通过二分法查找,删除或添加数据时会进行空间调整,适用于小数据量场景。SparseArray则主要针对整数key,适合Android环境。在选择时需考虑数据量、性能和空间效率等因素。
本文对比分析了HashMap、ArrayMap和SparseArray三种数据结构。HashMap使用拉链法实现,支持key和value为null,扩容时新建两倍大小的table。ArrayMap采用int[]保存hashCode,Object[]保存键值对,通过二分法查找,删除或添加数据时会进行空间调整,适用于小数据量场景。SparseArray则主要针对整数key,适合Android环境。在选择时需考虑数据量、性能和空间效率等因素。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 161
161

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








