第三章讲的主要是数组和字符串的一些遍历和枚举技巧。
包括开灯问题,蛇形填数问题,竖式问题和最长回文子串,四个。
1. 开灯问题


package tessst;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LightOpen {
/*
* 3-2 开灯问题
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean a[] = new boolean[1000];
int n,k;
n=s.nextInt(); // 代表灯数
k=s.nextInt(); // 代表人数
for(int i=1; i<=k; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) {
if((j)%(i)==0) {
a[j]=!a[j];
}
}
}
boolean first=true;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(a[i]) {
// 第一个输出不用加空格,后面的都要加
if(first) first=false;else System.out.printf(" ");
System.out.print(i);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
这个主要考察的是两个循环的嵌套(外层是人,内层是灯,每个人都会使得所有的灯发生变化),第二个是输出的空格间隔的控制处理可以用一个first变量管理,非first都要加空格。
2. 蛇形填数

package tessst;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* 3-3 蛇形填数
*/
public class SpiralSquare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int MAXN = 10;
int a[][] = new int[MAXN][MAXN];
/*
* 并非必要的,因为新数组的默认值就是0
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<a[i].length; j++) {
a[i][j] = 0;
}
}
*/
int x, y, n, tot;
Scanner sin = new Scanner(System.in);
n=sin.nextInt();
x=0;
y=n-1; // 起始点是左上角,数组坐标为(0,n-1)
a[x][y]=1;
tot=1;
while(tot<n*n) { // 循环结束的条件就是能够达到方阵的最大值(由n决定)
while(x+1<n && a[x+1][y]==0) a[++x][y] = ++tot; // 从起点开始往南(下)走到尽头
while(y-1>=0 && a[x][y-1]==0) a[x][--y] = ++tot; // 同理,接着往西(左)走到尽头
while(x-1>=0 && a[x-1][y]==0) a[--x][y] = ++tot;
while(y+1<n && a[x][y+1]==0) a[x][++y] = ++tot;
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
System.out.printf("%3d", a[i][j]); // 输出格式,占三个位的整型,不足补空格
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
这个的主要难度在于对二维数组转化为数组坐标的理解,以及二层while嵌套。
注)我根据自己的理解,结合参考代码,得出来的一个对付二维数组的一种坐标系,x轴的正方向是竖直向下指,y轴正方向是水平向右指。
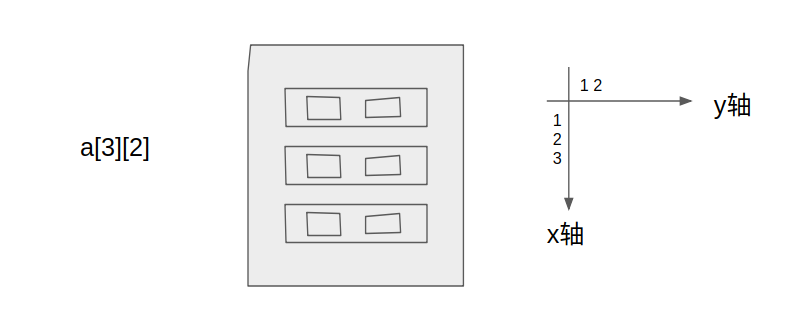
在这个坐标系中,我们可以根据a[x][y],中二维的x、y的值来在坐标系中定位它的位置,这样对于画一些矩形、理解他们的边界是很有帮助的。
3. 竖式问题

直观地看代码:
package tessst;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* 竖式问题
*/
public class ShuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char s[] = new char[20], buf[] = new char[99];
int abc, de, x, y, z, count=0;
boolean ok;
Scanner sin = new Scanner(System.in);
s=sin.nextLine().toCharArray();
for(abc=111; abc<=999; abc++) { // 枚举所有的三位数
for(de=11; de<=99; de++) { //枚举二位数
ok=true;
x=(de%10)*abc; // 二位数的个位乘以三位数
y=(de/10)*abc; // 二位数的十位乘以三位数
z=abc*de; // 相乘的最终结果
buf=(String.valueOf(x)+String.valueOf(y)+String.valueOf(z)+String.valueOf(abc)+String.valueOf(de)).toCharArray(); // 用来存储一个包含所有竖式中数字,用于indexOf遍历的判断
for(int i=0; i<buf.length; i++) {
if(String.valueOf(s).indexOf(buf[i])==-1) ok=false; // 一旦竖式中的一个数不存在于输入的s字符串中时,将会导致这次枚举的失败
}
if(ok) { // 枚举成功后,格式化地输出竖式
System.out.printf("%5d\nX%4d\n-----\n%5d\n%4d\n-----\n%5d\n\n", abc, de, x, y, z);
count++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("总共有"+count+"个竖式");
}
}
4. 最长回文子串

答案的重点在于,创建的一个大写字母数组以及一个标记该字母在原来字符数组中的位置的数组。
三个数组:buf存储输入的语句(包括标点),s存储所有的字母字符(不包括标点),p存储s中所有字符在buf中的位置(p数组的元素和s数组的元素一一对应)。
package tessst;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* 3-4 最长回文子串
*/
public class LongestHuiWen {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n, m=0, max=0, x=0, y = 0, MAXN=100;
String str = sc.nextLine();
n = str.length();
char s[] = new char[MAXN], buf[] = str.toCharArray(); // s stocks all the letters
int p[] = new int[MAXN]; // write down the position of alphabet char in buf
System.out.println(buf);
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length ; i++) {
if(Character.isAlphabetic(buf[i])) {
p[m] = i;
s[m++] = Character.toUpperCase(buf[i]);
}
}
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
// when the substring is odd
for(int j=0; i-j >= 0 && i+j < m; j++) {
if(s[i-j]!=s[i+j]) break;
if(2*j+1 > max) {
max = 2*j+1;
x = p[i-j]; // x代表当前取max时的原String的起点
y = p[i+j]; // y代表终点
}
}
// when the substring is even
for(int j=0; i-j >=0 && i+j+1<m; j++) {
if(s[i-j]!=s[i+j+1]) break;
if(j*2+2 > max) {
max = 2*j+2;
x = p[i-j];
y = p[i+j+1];
}
}
}
for(int i=x; i<=y; i++) {
System.out.printf("%c", buf[i]);
}
}
}
这里巧妙地运用了分奇偶的方式,只需遍历中间点i就可以通过j++找到最大的回文串。
最后输出原文。
\
勿忘初心。





















 412
412

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








