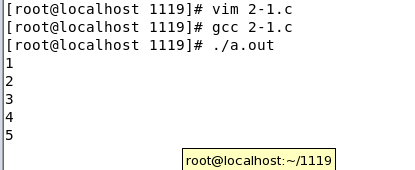
1. 内置宏
/*****************************************************
copyright (C), 2016, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:liuhao Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#define PP(s) do{ \
time_t t; \
struct tm* ti; \
time(&t); \
ti = localtime(&t); \
printf ("%s[%s,%d],%s\n", asctime(ti), __FILE__, __LINE__ , s); \
}while(0)
void f()
{
PP("Enter f1()...");
PP("EXIT f1()...");
}
int main()
{
PP("Enter main()...");
f();
PP("EXIT main()...");
printf("Date : %s\n", __DATE__);
printf("Time : %s\n", __TIME__);
printf("File : %s\n", __FILE__);
printf("Line : %d\n", __LINE__);
return 0;
}
ANSI标准说明了五个预定义的宏名。它们是:
__LINE__
__FILE__
__DATE__
__TIME__
__STDC__
如果编译不是标准的,则可能仅支持以上宏名中的几个,或根本不支持。记住编译程序 也许还提供其它预定义的宏名。
是行连接符,会将下一行和前一行连接成为一行,即将物理上的两行连接成逻辑上的一行
__FILE__ 是内置宏 代表源文件的文件名
__LINE__ 是内置宏,代表该行代码的所在行号
__DATE__宏指令含有形式为月/日/年的串,表示源文件被翻译到代码时的日期。
源代码翻译到目标代码的时间作为串包含在__TIME__ 中。串形式为时:分:秒。
如果实现是标准的,则宏__STDC__含有十进制常量1。如果它含有任何其它数,则实现是非标准的。
2.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MALLOC(type, x) (type*)malloc(sizeof(type)*x)
#define FOREVER() while(1)
#define BEGIN {
#define END }
#define FOREACH(i, m) for(i=0; i<m; i++)
int main()
{
int array[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int x = 0;
int*p = MALLOC(int, 5);
FOREACH(x, 5)
BEGIN
p[x] = array[x];
END
FOREACH(x, 5)
BEGIN
printf("%d\n", p[x]);
END
FOREVER();
free(p);
printf("Last printf...\n");
return 0;
}.i文件中
int main()
{
int array[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int x = 0;
int*p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*5);
for(x=0; x<5; x++)
{
p[x] = array[x];
}
for(x=0; x<5; x++)
{
printf("%d\n", p[x]);
}
while(1);
free(p);
printf("Last printf...\n");
return 0;
}
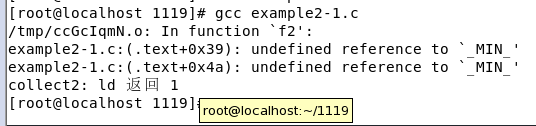
3.#undef
下面程序中
#include <stdio.h>
int f1(int a, int b)
{
#define _MIN_(a,b) ((a)<(b) ? a : b)
return _MIN_(a, b);
}
int f2(int a, int b, int c)
{
return _MIN_(_MIN_(a,b), c);
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", f1(2, 1));
printf("%d\n", f2(5, 3, 2));
return 0;
}
.i文件中
# 2 "example2-1.c" 2
int f1(int a, int b)
{
return ((a)<(b) ? a : b);
}
int f2(int a, int b, int c)
{
return ((((a)<(b) ? a : b))<(c) ? ((a)<(b) ? a : b) : c);
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", f1(2, 1));
printf("%d\n", f2(5, 3, 2));
return 0;
}

NOW:添加#undef
#include <stdio.h>
int f1(int a, int b)
{
#define _MIN_(a,b) ((a)<(b) ? a : b)
return _MIN_(a, b);
#undef _MIN_
}
int f2(int a, int b, int c)
{
return _MIN_(_MIN_(a,b), c);
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", f1(2, 1));
printf("%d\n", f2(5, 3, 2));
return 0;
}
4.总结
》宏表达式在预编译期被处理,编译器不知道宏表达式的存在;
》宏表达式用“实参”完全替代形参,不进行任何运算;
》宏表达式没有任何的“调用开销”,编译器只作文本替换;
》宏表达式不能出现递归定义;






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








