难易程度:★★★
阅读点:python; web安全;
文章作者:xiaoye
文章来源:i春秋
关键字:网络渗透技术
前言
python是门简单易学的语言,强大的第三方库让我们在编程中事半功倍,今天,我们来谈谈python多线程在渗透测试中的应用,本文,我们将编写一个简易c段存活主机扫描脚本,以及一个python版本的多线程御剑--目录扫描工具
一、python 多线程
python多线程有几种写法
1. thread模块
python的一个多线程模块,小脚本可以用,但是有瑕疵,比如不稳定,线程数不好控制
下方贴出一个c段存活主机扫描脚本,这个脚本i春秋ado老师也有教过哦
思想:输入一个ip,经过字符拆分,获取c段,多线程地ping -c 2 ip ,根据返回的信息来判断主机是否存活
demo ping_thread.py:
'''
Created on 2017-2-27
@author: xiaoye
'''
#coding: utf-8
import thread
import time
from subprocess import Popen,PIPE
def scan_ip(ip):
process = Popen('ping -c 2 ' + ip, stdin=PIPE, stdout=PIPE, shell=True)
data = process.stdout.read()
if 'ttl' in data:
print '%s is live ,now time is %s' % (ip, time.strftime('%H:%M:%S'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
#scan_ip('111.13.147.229')
ips = raw_input()
ip_header = '.'.join(ips.split('.')[:3])
for i in range(1,255):
ip = ip_header + '.' + str(i)
#print ip
thread.start_new_thread(scan_ip, (ip,))
time.sleep(0.1)
运行情况:
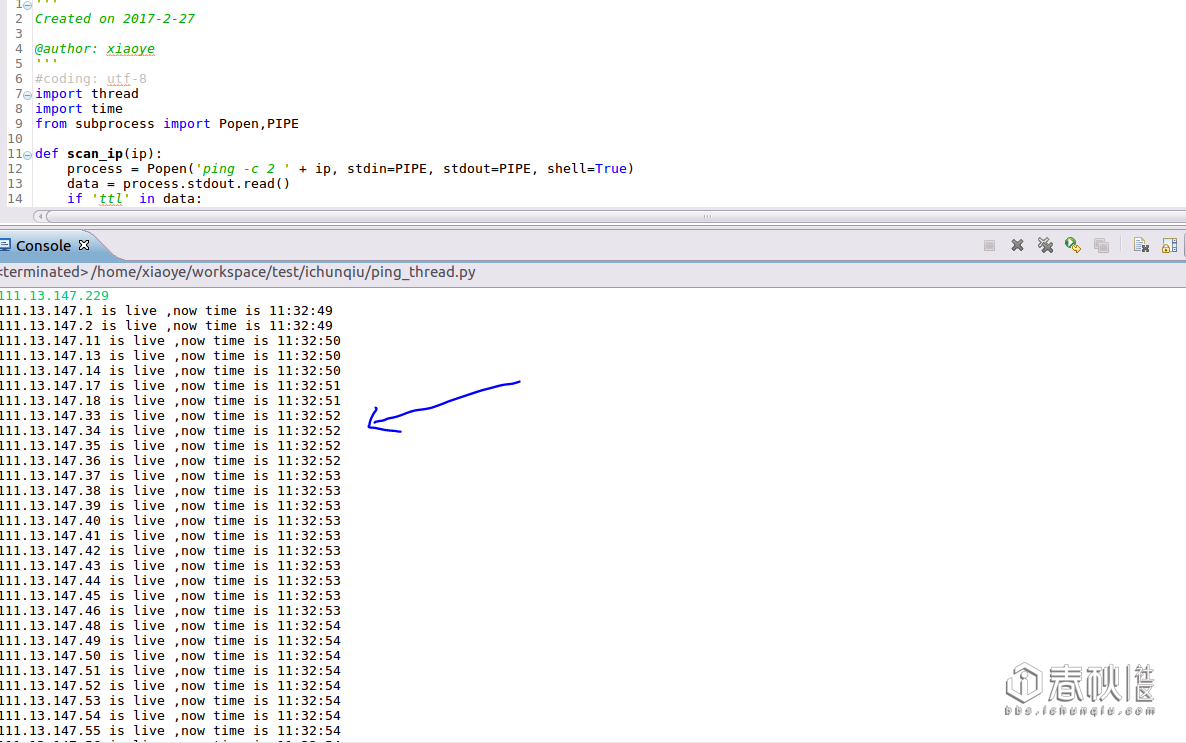
速度还行,稳定性一般
thread模块,核心在:
thread.start_new_thread(scan_ip, (ip,))
time.sleep(0.1)
scan_ip是要执行的函数,(ip,)是传入的参数,记得sleep一下
2.threading模块用法:
demo:
'''
Created on 2017-2-28
@author: xiaoye
'''
#coding: utf-8
import threading
import time
def test(th):
print 'i am doing %s %s' % (th, time.strftime('%H:%M:%S'))
def main():
thread = []
keys = ['movie_th','swim_th','listen_th','learn_th','movie_th','swim_th','listen_th','learn_th','movie_th','swim_th','listen_th','learn_th','movie_th','swim_th','listen_th','learn_th']
thread_count = len(keys)
#print thread_count
for i in range(thread_count):
t = threading.Thread(target=test, args=(keys[i],))
thread.append(t)
for i in range(thread_count):
thread[i].start()
for i in range(thread_count):
thread[i].join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行情况: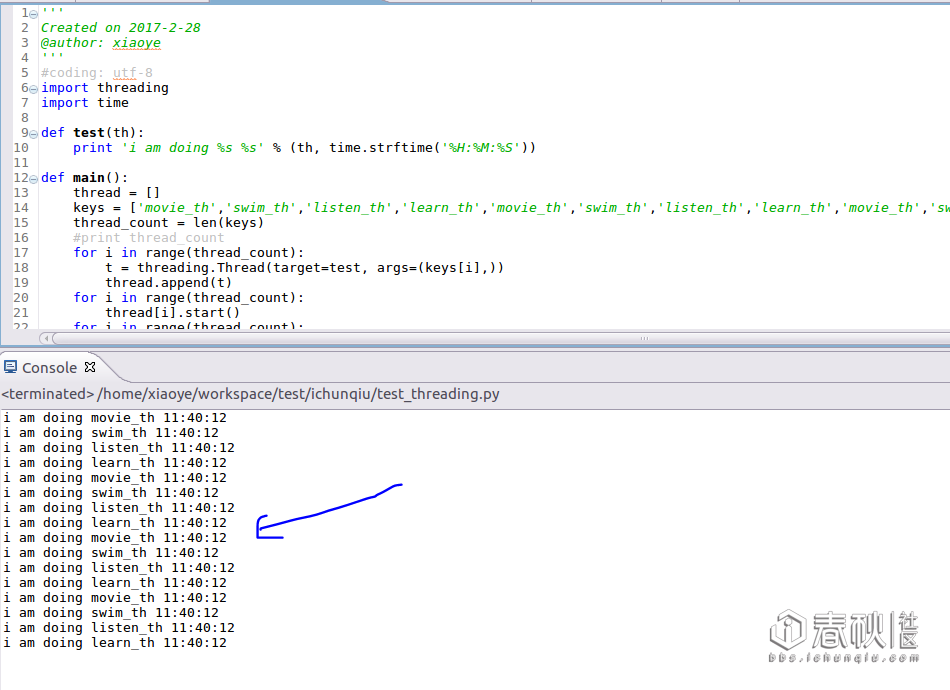
可以看到,基本是同时运行的,threading.Thread模块的一种用法就是这样:
for i in range(thread_count):
t = threading.Thread(target=test, args=(keys[i],))
thread.append(t)
for i in range(thread_count):
thread[i].start()
for i in range(thread_count):
thread[i].join()
模式1.:一个列表存放所有线程,start()执行列表中线程,join()等待运行完毕
模式1?,还有模式2吗?
当然,模式2就是从threading.Thread继承一个子类class,重写父类run方法,实现多线程运行run函数,而这种也是非常良好的写法
demo:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import threading
class T(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
def run(self): #继承,threading.Thread子类, 重写run方法, run方法在start()后自动执行
print 'i love you'
def main():
thread = []
for i in range(10):
thread.append(T())
for i in thread:
i.start()
for i in thread:
i.join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行情况: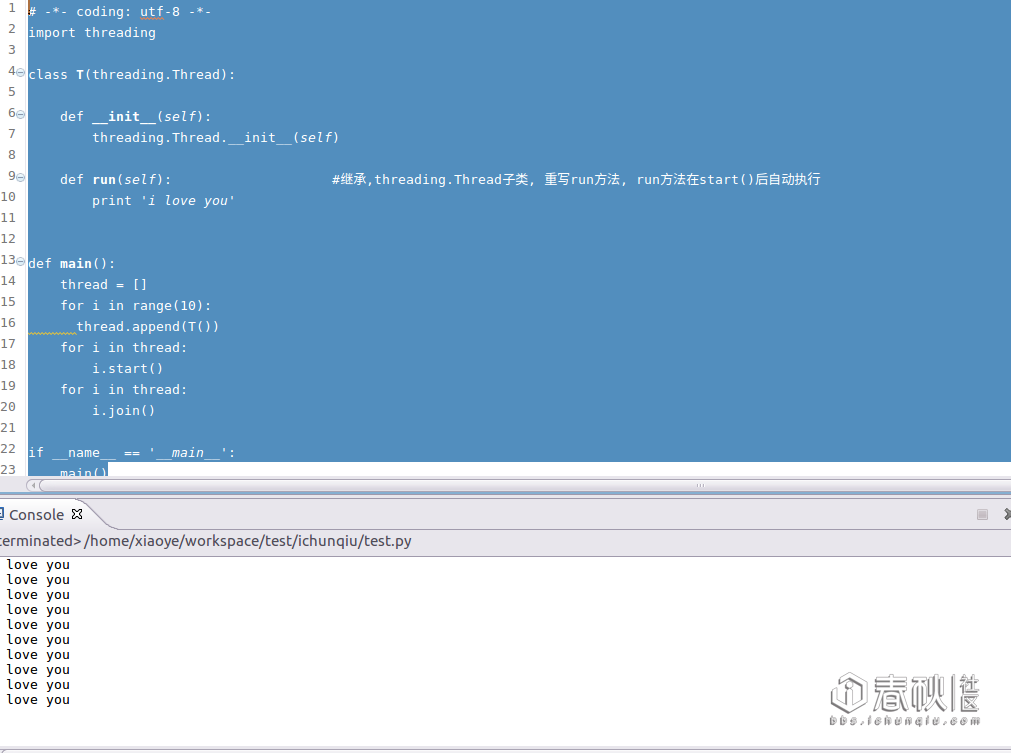
二、线程间的数据守护
Queue绝对是保护线程间数据安全的好选择,有关于Queue,大家可以自行百度其用法,我发出一点经常用的:
Queue.qsize() 返回队列的大小
Queue.empty() 如果队列为空,返回True,反之False
Queue.full() 如果队列满了,返回True,反之False
Queue.full 与 maxsize 大小对应
Queue.get([block[, timeout]]) 获取队列,timeout等待时间
Queue.get_nowait() 相当Queue.get(False)
非阻塞 Queue.put(item) 写入队列,timeout等待时间
Queue.put_nowait(item) 相当Queue.put(item, False)
Queue.task_done() 在完成一项工作之后,Queue.task_done() 函数向任务已经完成的队列发送一个信号
Queue.join() 实际上意味着等到队列为空,再执行别的操作
三、多线程threading.Thread+Queue实现渗透测试工具编写
脚本放出来:
1.多线程c段存活主机扫描:
'''
Created on 2017-2-28
@author: xiaoye
'''
#coding: utf-8
import time
import sys
import threading
import Queue
from subprocess import Popen,PIPE
class Quethread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, que):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self._que = que
def run(self):
while not self._que.empty():
ip = self._que.get()
process = Popen('ping -c 2 ' + ip, stdin=PIPE, stdout=PIPE, shell=True)
data = process.stdout.read()
if 'ttl' in data:
sys.stdout.write('%s is live %s\n' % (ip, time.strftime('%H:%M:%S')))
def main():
que = Queue.Queue()
ips = raw_input()
thread = []
thread_count = 200
ip_head = '.'.join(ips.split('.')[:3])
#print ip_head
for i in range(1, 255):
que.put(ip_head + '.' + str(i))
'''for i in range(1,255):
print que.get()'''
for i in range(thread_count):
thread.append(Quethread(que))
for i in thread:
i.start()
for i in thread:
i.join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
ubuntu下运行成功,win下需要修改Popen里的命令等,截图: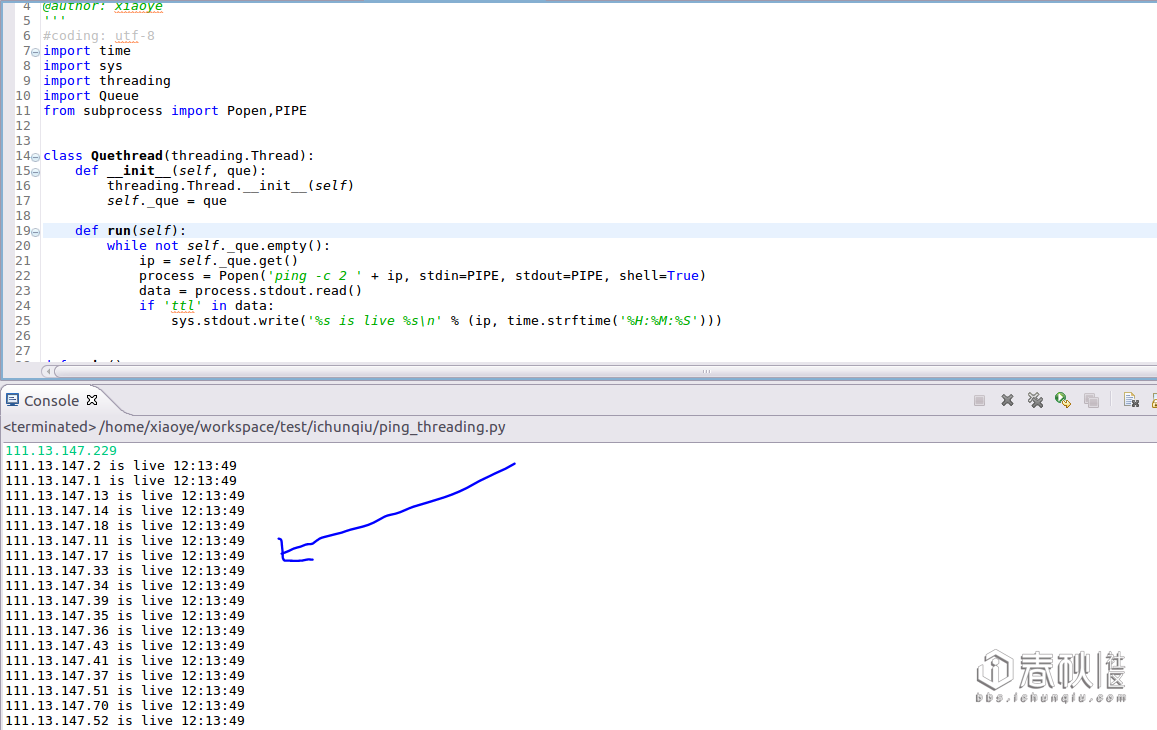
速度很快,稳定性较强
c段主机存活脚本:https://github.com/xiaoyecent/ping_threading_Queue
2.py版多线程御剑--目录扫描--支持自定义字典、输出文件位置以及自定义线程数:
'''
@author: xiaoye
'''
#coding: utf-8
import requests
import sys
import threading
#import time
import Queue
from optparse import OptionParser
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
class Doscan(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, que):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self._que = que
def run(self):
while not self._que.empty():
d = self._que.get()
try:
r = requests.get(url + d, headers=headers, timeout=3)
sys.stdout.write(d + ' is scan status:' + str(r.status_code) + '\n')
if r.status_code == 200:
with open(option.outfile, 'a') as f:
f.write(url + d + '\n')
except:
pass
def main():
thread = []
thread_count = option.threadcount
que = Queue.Queue()
with open(option.dictname, 'r') as f:
for d in f.readlines():
d = d.strip('\n')
que.put(d)
for i in range(thread_count):
thread.append(Doscan(que))
for i in thread:
i.start()
for i in thread:
i.join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
parse = OptionParser()
parse.add_option('-u', '--url', dest='input_url', type='string', help='the url you wan to scan dir')
parse.add_option('-o', '--out', dest='outfile', type='string', help='output filename', default='result.txt')
parse.add_option('-s', '--speed', dest='threadcount', type='int', default=60, help='the thread_count')
parse.add_option('-d', '--dict', dest='dictname', type='string', help='dict filename')
(option, args) = parse.parse_args()
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:50.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/50.0'}
url = option.input_url
main()
Usage: scan_dir.py [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-u INPUT_URL, --url=INPUT_URL
the url you wan to scan dir
-o OUTFILE, --out=OUTFILE
output filename
-s THREADCOUNT, --speed=THREADCOUNT
the thread_count
-d DICTNAME, --dict=DICTNAME
dict filename
参数用法贴出来
运行情况
举个例子:
-u http://localhost -s 30 -d d://PHP.txt -o d://ichunqiu.txt: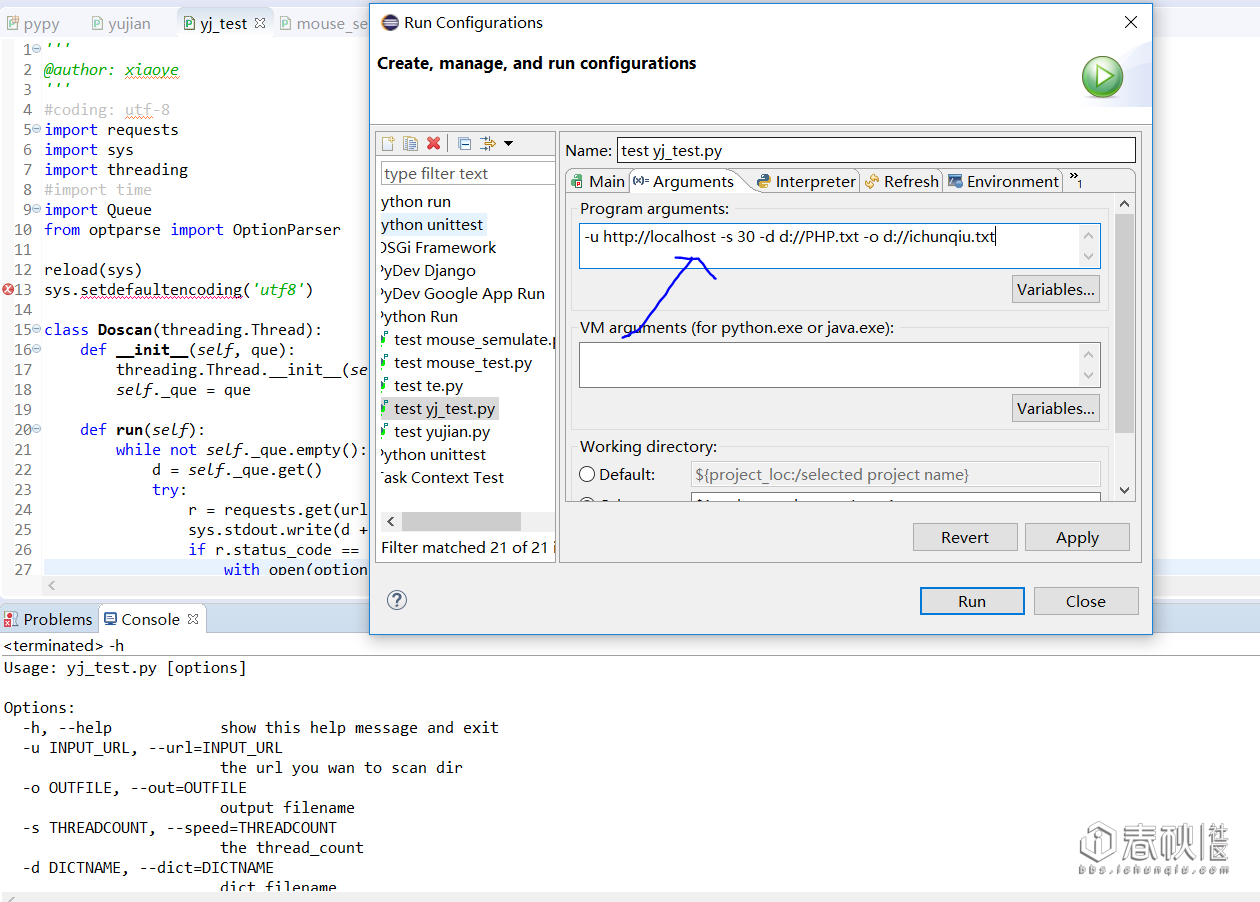
结果: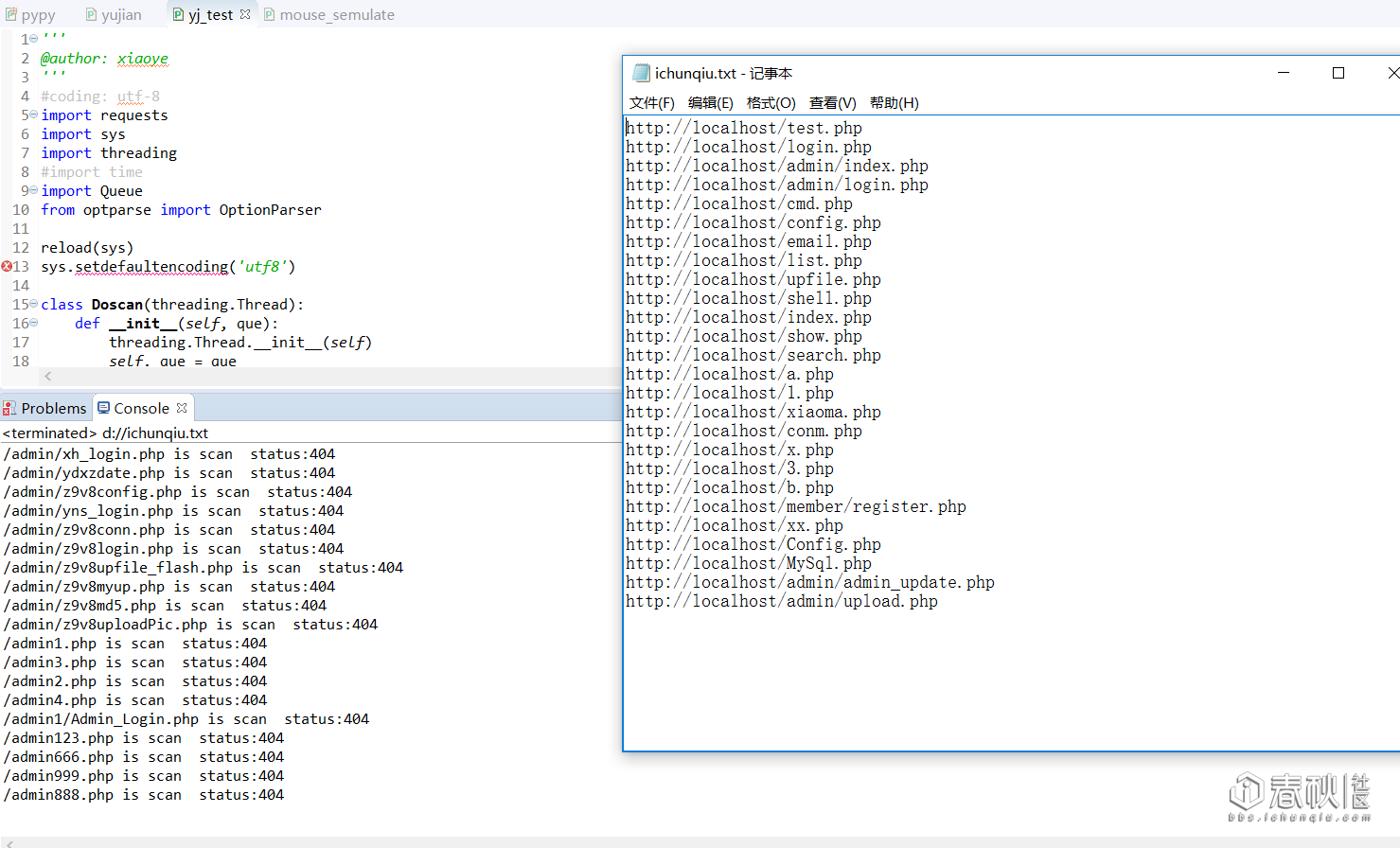
运行速度取决于线程数(默认60)和实际环境
源码:https://github.com/xiaoyecent/scan_dir
四、总结
多线程加队列实现线程间的数据保护是很好的搭配,threading.Thread+Queue的用法希望大家能够掌握,另外,继承threading.Thread写出子类,重写父类run方法来实现多线程的写法也值得借鉴
更多安全资讯请关注i春秋公众号(微信搜索:icqedu)~
欢迎来i春秋学院学习网络安全知识,一起培育信息时代的安全感!





















 2907
2907

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








