来源:https://www.iteblog.com/archives/1907.html
在使用 Apache Spark 的时候,作业会以分布式的方式在不同的节点上运行;特别是当集群的规模很大时,集群的节点出现各种问题是很常见的,比如某个磁盘出现问题等。我们都知道 Apache Spark 是一个高性能、容错的分布式计算框架,一旦它知道某个计算所在的机器出现问题(比如磁盘故障),它会依据之前生成的 lineage 重新调度这个 Task。
我们现在来考虑下下面的场景:
- 有个节点上的磁盘由于某些原因出现间歇性故障,导致某些扇区不能被读取。假设我们的 Spark 作业需要的数据正好就在这些扇区上,这将会导致这个 Task 失败。
- 这个作业的 Driver 获取到这个信息,知道 Task 失败了,所以它会重新提交这个 Task。
- Scheduler 获取这个请求之后,它会考虑到数据的本地性问题,所以很可能还是把这个 Task 分发到上述的机器,因为它并不知道上述机器的磁盘出现了问题。
- 因为这个机器的磁盘出现问题,所以这个 Task 可能一样失败。然后 Driver 重新这些操作,最终导致了 Spark 作业出现失败!
上面提到的场景其实对我们人来说可以通过某些措施来避免。但是对于 Apache Spark 2.2.0 版本之前是无法避免的,不过高兴的是,来自 Cloudera 的工程师解决了这个问题:引入了黑名单机制 Blacklist(详情可以参见SPARK-8425,具体的设计文档参见Design Doc for Blacklist Mechanism),并且随着 Apache Spark 2.2.0 版本发布,不过目前还处于实验性阶段。
黑名单机制其实是通过维护之前出现问题的执行器(Executors)和节点(Hosts)的记录。当某个任务(Task)出现失败,那么黑名单机制将会追踪这个任务关联的执行器以及主机,并记下这些信息;当在这个节点调度任务出现失败的次数超过一定的数目(默认为2),那么调度器将不会再将任务分发到那台节点。调度器甚至可以杀死那台机器对应的执行器,这些都可以通过相应的配置实现。
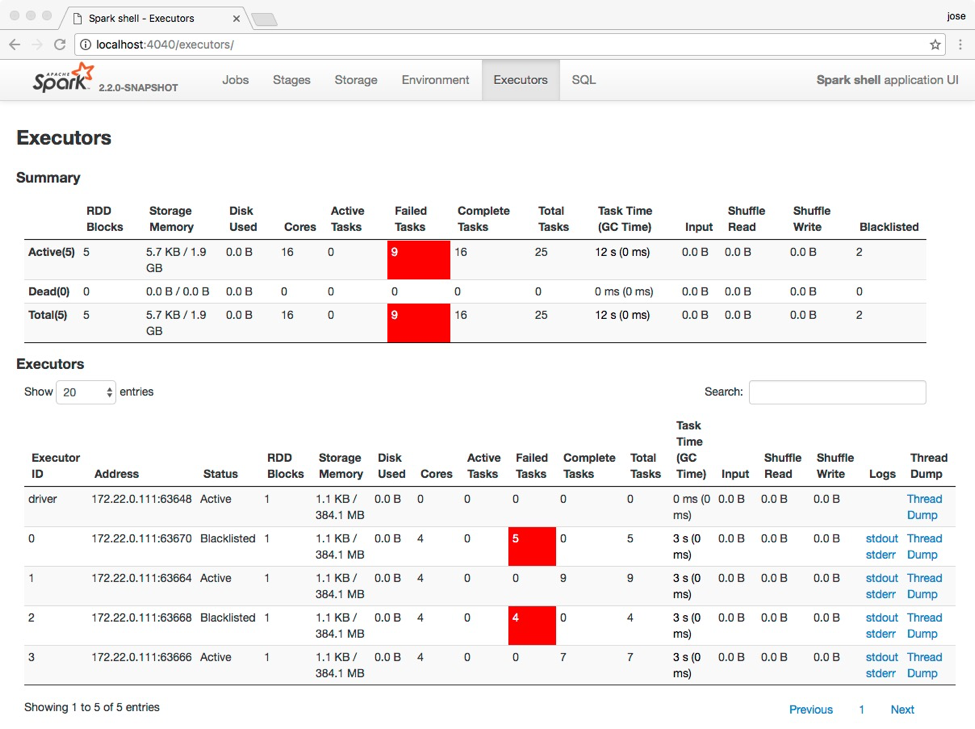
我们可以通过 Apache Spark WEB UI 界面看到执行器的状态(Status):如果执行器处于黑名单状态,你可以在页面上看到其状态为 Blacklisted ,否则为 Active。如下图所示:
目前黑名单机制可以通过一系列的参数来控制,主要如下:
| 参数 | 默认值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| spark.blacklist.enabled | false | 如果这个参数这为 true,那么 Spark 将不再会往黑名单里面的执行器调度任务。黑名单算法可以由其他“spark.blacklist”配置选项进一步控制,详情参见下面的介绍。 |
| spark.blacklist.timeout | 1h | (实验性) How long a node or executor is blacklisted for the entire application, before it is unconditionally removed from the blacklist to attempt running new tasks. |
| spark.blacklist.task.maxTaskAttemptsPerExecutor | 1 | (实验性) For a given task, how many times it can be retried on one executor before the executor is blacklisted for that task. |
| spark.blacklist.task.maxTaskAttemptsPerNode | 2 | (实验性) For a given task, how many times it can be retried on one node, before the entire node is blacklisted for that task. |
| spark.blacklist.stage.maxFailedTasksPerExecutor | 2 | (实验性) How many different tasks must fail on one executor, within one stage, before the executor is blacklisted for that stage. |
| spark.blacklist.stage.maxFailedExecutorsPerNode | 2 | (实验性) How many different executors are marked as blacklisted for a given stae, before the entire node is marked as failed for the stage. |
| spark.blacklist.application.maxFailedTasksPerExecutor | 2 | (实验性) How many different tasks must fail on one executor, in successful task sets, before the executor is blacklisted for the entire application. Blacklisted executors will be automatically added back to the pool of available resources after the timeout specified by spark.blacklist.timeout. Note that with dynamic allocation, though, the executors may get marked as idle and be reclaimed by the cluster manager. |
| spark.blacklist.application.maxFailedExecutorsPerNode | 2 | (实验性) How many different executors must be blacklisted for the entire application, before the node is blacklisted for the entire application. Blacklisted nodes will be automatically added back to the pool of available resources after the timeout specified by spark.blacklist.timeout. Note that with dynamic allocation, though, the executors on the node may get marked as idle and be reclaimed by the cluster manager. |
| spark.blacklist.killBlacklistedExecutors | false | (实验性) If set to "true", allow Spark to automatically kill, and attempt to re-create, executors when they are blacklisted. Note that, when an entire node is added to the blacklist, all of the executors on that node will be killed. |
因为黑名单机制目前还处于实验性状态,所以上面的一些参数可能会在后面的 Spark 中有所修改。





















 362
362

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








