1 概念
为什么要用mybatis
JDBC:
SQL夹在Java代码块里,耦合度高导致硬编码内伤,维护不易且实际开发需求中sql是有变化,频繁修改的情况多见。
Hibernate和JPA:
长难复杂SQL,对于Hibernate而言处理也不容易
内部自动生产的SQL,不容易做特殊优化。
对开发人员而言,核心sql还是需要自己优化+掌握在自己手上,简单来说,就是一句话,
* sql和java编码分开,功能边界清晰,一个专注业务、一个专注数据,可以使用简单的XML或注解
用于配置和原始映射,将接口和Java的POJO映射成数据库中的记录,完成业务代码+底层数据库的媒介
2 mybatis--helloworld
1) 导包
mybatis的jar包 : mybatis-3.2.8.jar
数据库驱动 : mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar
mybatis在工作的时候,为了方便观察sql。导入日志包: log4j.jar
log4j必须有一个配置文件才能工作。
2) 编写mybatis的全局配置文件。指导mybatis如何工作的。引入约束文件(为了有提示)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!-- mybatis的全局配置文件。 -->
<configuration>
<!--配置所有的mybatis运行时信息 -->
<!--http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd 这是约束文件,作用就是约束标签该怎么写。
-->
<!--1、配置mybatis'的数据库环境,default="development"指定默认使用哪个环境 -->
<environments default="development">
<!--配置一个具体的环境 id="development"指定环境的唯一标识-->
<environment id="development">
<!--配置事务管理器 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--配置数据源。使用连接池技术.mybatis内置了数据库连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置连接池信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_0829"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!-- <environment id="test"></environment>
<environment id="product"></environment> -->
</environments>
<!--注册接口的映射文件。否则接口是找不到的。 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/atguigu/dao/PersonDao.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>3) log4j.xml的三种配置方式
① 第一种
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd">
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j="http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<param name="Encoding" value="UTF-8" />
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%-5p %d{MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} %m (%F:%L) \n" />
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="java.sql">
<level value="debug" />
</logger>
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis">
<level value="debug" />
</logger>
<root>
<level value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</root>
</log4j:configuration>
②第二种简洁版
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd">
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j="http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/">
<appender name="log.console" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} %5p (%C{1}:%M) - %m%n" />
</layout>
</appender>
<!-- -->
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis">
<level value="info" />
<appender-ref ref="log.console" />
</logger>
<logger name="com.atguigu">
<level value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="log.console" />
</logger>
</log4j:configuration>
③ 第三种 .properties文件
# For JBoss: Avoid to setup Log4J outside $JBOSS_HOME/server/default/deploy/log4j.xml!
# For all other servers: Comment out the Log4J listener in web.xml to activate Log4J.
#log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout, logfile
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m%n
#log4j.appender.logfile=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
#log4j.appender.logfile.File=system.log
#log4j.appender.logfile.MaxFileSize=512KB
# Keep three backup files.
#log4j.appender.logfile.MaxBackupIndex=3
# Pattern to output: date priority [category] - message
#log4j.appender.logfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
#log4j.appender.logfile.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m%n
4) 建对应的entity持久化实体
5)建Mapper接口并定义好方法
6) 编写这个接口对应的xml文件。这个xml文件就是指导这个接口的每一个方法是如何工作。不用编 写接口的实现类。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace:指定接口的全类名
mapper文件:作用:指导dao接口里面的每一个方法如何工作
-->
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.dao.PersonDao">
<!-- public void add(Person person); -->
<!-- 1、指定一个插入操作。id是方法名
parameterType:指定参数类型。
-->
<insert id="add" parameterType="com.atguigu.entities.Person">
<!--#{属性名}:取出参数里面这个属性的值 -->
INSERT INTO tbl_person(NAME,age,birth,registerTime,salary)
VALUES(#{name},#{age},#{birth},#{registerTime},#{salary});
</insert>
</mapper>7)在全局注册这个【配置文件】(添加到mybatis的全局配置文件里边)
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/atguigu/mybatis/mapper/PersonMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
8)编写Junit单元测试类,执行CRUD操作
package com.atguigu.test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.atguigu.dao.PersonDao;
import com.atguigu.entities.Person;
public class MyBatisTest {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//1、根据配置文件创建出sqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2、获取一个称为SqlSession的对象,用来执行数据的增删改查
SqlSession openSession = null;
try {
openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//4、获取到接口
PersonDao mapper = openSession.getMapper(PersonDao.class);
//5、调用方法
mapper.add(new Person(null, "张三", 18, new Date(), new Date(), 9998.98));
//6、提交数据
openSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//7、关闭资源
openSession.close();
}
}
}
第一个case总结:
XXXMapper.xml文件中,namespace必须是接口全路径
XXXMapper.xml中的id必须是接口里面的方法名 ,两者一致
XXXMapper.xml中的parameterType类型必须和对应方法的形参一致
XXXMapper.xml中的resultType类型必须和对应方法的返回值类型一致
每个线程都应该有它自己的SqlSession实例。SqlSession的实例不能共享使用,
它也是线程不安全的,定义为局部变量
mapper接口实现动态代理对象:
定义:只需要编写mapper接口的(等价于传统的dao接口),
Impl实现类,也即动态代理+面向接口
XXXdao接口-------->XXXMapper.java
XXXdao接口Impl实现类-------->XXXMapper.xml
3 Mapper+Annotation入门增强
3.1 传统的dao : Dao接口 DaoImpl
3. 2 Mybatis也是支持注解:
① 重写接口
② 在接口方法上新增加注解
public interface PersonMapperAnnotation
{
@Insert("insert into tbl_person(name,age,birth,registerTime,salary) "
+ "values(#{name},#{age},#{birth},#{registerTime},#{salary})")
public void add(Person person);
@Delete("delete from tbl_person where id=#{id}")
public void delete(Integer id);
@Update("update tbl_person set name=#{name},age=#{age},birth=#{birth},registerTime=#{registerTime},salary=#{salary} where id=#{id}")
public void update(Person person);
@Select("select * from tbl_person where id=#{id}")
public Person getPersonById(Integer id);
@Select("select * from tbl_person")
public List<Person> getAllPerson();
}
③到mybatis的配置文件里面注册该接口类(含注解)
<!-- 配置注解接口的类 -->
<mapper class="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapperAnnotation"/>
如果没有注册进配置文件,报如下异常信息:
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Type interface com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapperAnnotation is not known to the MapperRegistry.
④测试,通过getMapper重新获得注解接口版的XXXMapper.class
@Test
public void test_Add()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
PersonMapperAnnotation personMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(PersonMapperAnnotation.class);
Person person = new Person();
person.setAge(42);
person.setBirth(new Date());
person.setName("左冷禅");
person.setRegisterTime(new Date());
person.setSalary(4500.05);
personMapper.add(person);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(sqlSession != null) sqlSession.close();
}
}
3 Mybatis的全局配置文件 mybatis-config.xml 细节
MyBatis的XML配置文件包含了影响MyBatis行为甚深的设置和属性信息
3.1 configuration
3.1.1 properties 属性
JDBC--->C3P0,添加外部数据库链接演示
<!--1、引入外部配置文件作为属性
1)properties标签体中的key=value优先解析
2)外部配置文件的值,如果有同名,会覆盖properties标签体中
resource;引用类路径下的资源
url:引用网络下的资源 http://www.atguigu.com/dbconfig.properties
-->
<properties resource="dbconfig.properties" >
<property name="username" value="admin"/>
</properties>①src文件夹下面新建db.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=123456
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis0607?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8
②修改mybatis-config.xml
<!-- 引入外部资源文件,将数据库配置设为外部链接 -->
<properties resource="db.properties"></properties>
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据库连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
3.1.2 settings 全局参数定义
<!--2、配置某些全局属性,比如是否开启缓存等 -->
<!-- <settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings> -->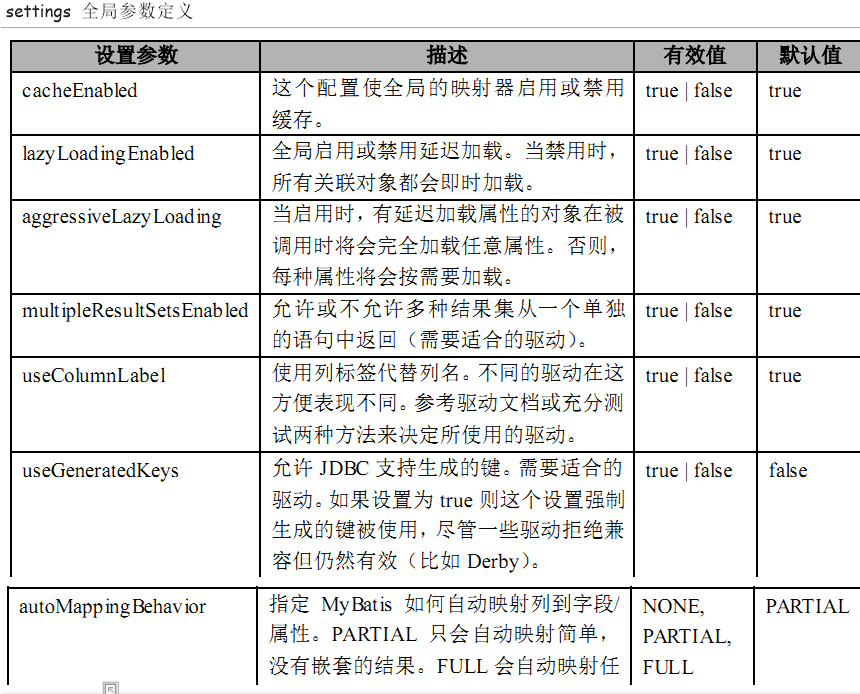



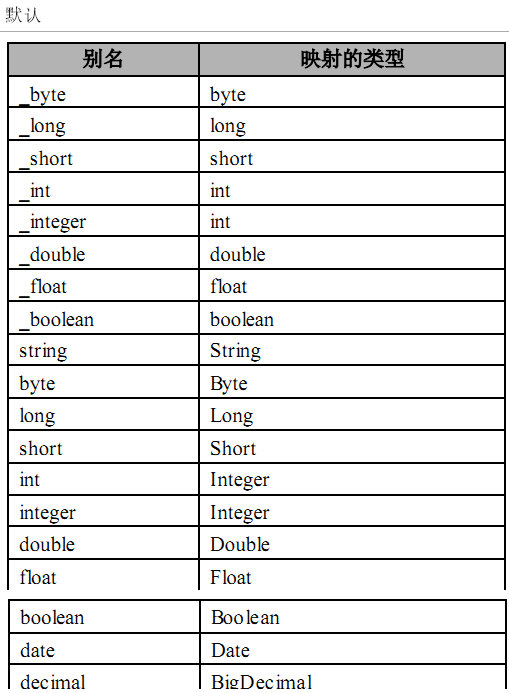
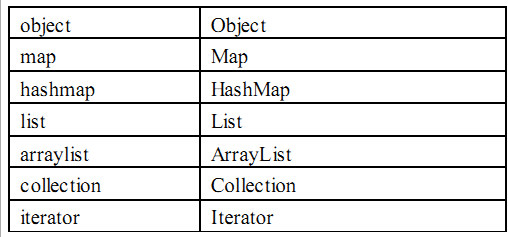
3.1.3 typeAliases 别名处理器
别名是为 Java类型命名一个短的名字。它只和 XML 配置有关,只用来减少类名重复的部分。
配置了mybatis-config.xml会影响XXXMapper.xml的使用
<!--3、别名处理器 -->
<typeAliases>
<!--为某个全类名起别名
type:全类名
alias:别名
-->
<!-- <typeAlias type="com.atguigu.entities.Person" alias="Person"/> -->
<!--批量别名,name:指定的是包名。这个包下的所有类,都会有别名,别名默认就是类名 -->
<package name="com.atguigu.entities"/>
<!--mybatis为java常用类型已经起好别名了。直接用,不区分大小写。 -->
</typeAliases>默认:
自定义
①单个
<typeAliases>
<!-- 单独为Perosn进行别名设置 -->
<typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Person" alias="Person"/>
</typeAliases>
<insert id="add" parameterType="Person"> 红色部分,前面的包名已经没有了。
insert into tbl_person(name,salary,birth,registerTime)
values(#{name},#{salary},#{birth},#{registerTime});
</insert>
②多个
<typeAliases>
<!-- 单独为Perosn进行别名设置
<typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Person" alias="Person"/>-->
<!--批处理别名,扫描整个包下的类 -->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.entities"/>
</typeAliases>
<insert id="add" parameterType="Person"> 红色部分,前面的包名已经没有了。
insert into tbl_person(name,salary,birth,registerTime)
values(#{name},#{salary},#{birth},#{registerTime});
</insert>
3.1.4 typeHandlers 类型处理器
<!--
4、mybatis将数据库字段映射成javaBean中某个属性的时候,默认使用对应的类型处理器在工作。
1)、我们也可以自定义类型处理器
2)、定义好以后注册这个类型处理
3)、我们一般都不需要再去写这些类型处理器了
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler=""/>
</typeHandlers> -->
①用于java类型和jdbc类型映射
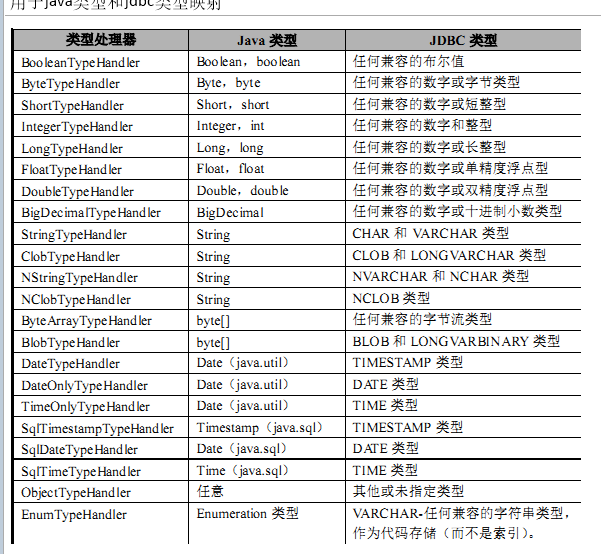
②Mybatis的映射基本已经满足,不太需要重新定义
3.1.5 environments 环境
①environment 环境变量
②transactionManager 事务管理器
③dataSource 数据源
<!--5)、mybatis运行的数据库等环境的配置。 -->
<!-- default="default":指定使用哪个环境作为默认环境 -->
<environments default="default">
<!--每个 environment表示一个具体的环境 -->
<environment id="default">
<!-- 事务管理器:
type="JDBC":这个配置就是直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务范围。
type="MANAGED ":这个配置几乎没做什么。它从来不提交或回滚一个连接,
而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接,然而一些容器并不希望这样,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止它默认的关闭行为。
type="自己的事务管理的全类名",如果自己写必须实现TransactionFactory接口
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- 数据源的配置
type="UNPOOLED":不使用连接池技术。
type="POOLED":使用连接池技术。mybatis自带的连接池
type="JNDI":Java Named Directory Interface(java命名目录接口,ejb)
type="指定自己的连接池的全类名":必须实现DataSourceFactory接口,返回第三方数据源即可
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- ${driver}取出properties配置的值 -->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>3.1.6 mappers 映射器
1) resource:XXXMapper.xml文件
<mapper resource="com/atguigu/mybatis/mapper/PersonMapper.xml"/>
2) class:接口注解实现
<mapper class="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapper"/>
3)url:外部路径
①<mapper url="file:///D:\43\mybatis_01\config\sqlmap\Person.xml" />
②不建议使用
4) package
<mappers>
<!-- XML配置文件 -->
<mapper resource="com/atguigu/mybatis/mapper/PersonMapper.xml"/>
<!-- Annotation -->
<mapper class="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapper"/>
<!-- 注册mapper包下的所有mapper接口,此种方法要求mapper接口名称和mapper映射文件名称遵守mabatis规范,且放在同一个目录中 -->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
<!-- 6)、注册mapper配置文件 -->
<mappers>
<!--resource:指定xml文件位置 -->
<mapper resource="mybatis/mapper/PersonMapper.xml"/>
<!--class:指定注解版的java文件位置 -->
<mapper class="com.atguigu.dao.PersonMapperAnnotation"/>
<mapper resource="mybatis/mapper/CatMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="mybatis/mapper/DogMapper.xml"/>
<!-- 批量注册。特别注意;必须满足一下条件
1)、mapper文件和mapper接口在同包下
2)、两个同名
-->
<!-- <package name="com.atguigu.dao"/> -->
</mappers>
<!--注意点:标签是有顺序的;顺序必须正确:
properties?,settings?,typeAliases?,typeHandlers?,objectFactory?,
objectWrapperFactory?,plugins?,environments?,databaseIdProvider?,mappers?
-->4 SQL映射的XML文件XXXMapper.xml
4.1 insert、delete、update、select
1)主键的生成方式 (Person插入数据后想获得主键)
①有自增Mysql
<insert id="add" parameterType="Person" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tbl_person(name,salary,birth,registerTime)
values(#{name},#{salary},#{birth},#{registerTime});
</insert>
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"
② 无自增Oracle
<insert id="add" parameterType="Person">
<selectKey order="BEFORE" keyProperty="id" resultType="_int">
select crm_seq.nextval from dual
</selectKey>
insert into tbl_person(name,salary,birth,registerTime)
values(#{name},#{salary},#{birth},#{registerTime});
</insert>
2)如果需要额外功能请自行文档
4.2 parameterType(输入参数类型)
1) 传入简单类型,比如按照id查Person(前面已讲过)
2) 传入POJO类型,前台选了多个条件
package com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Customer;
public interface CustomerMapper {
void saveCustomer(Customer customer);
Customer getCustomerById(Integer custId);
/**
* 将custName和custAge对应的查询条件封装到Customer对象中
* @param customer
* @return
*/
List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition01(Customer customer);
/**
* 查询条件已经无法使用一个实体类对象来封装,所以使用Map来保存
* @param map
* @return
*/
List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition02(Map<String, Object> map);
/**
* 传入多个参数
* @param minAge
* @param maxAge
* @return
*/
List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition03(
@Param("minAgeParam") int minAge,
@Param("maxAgeParam") int maxAge);
/**
* 使用Map类型封装查询结果
* @param orderId
* @return
*/
Map<String, Object> getDataMap(Integer orderId);
/**
* 将每一条查询结果的Map封装到List中返回
* @param orderAmount
* @return
*/
List<Map<String,Object>> getDataListMap(Integer orderAmount);
/**
* 通过resultMap的方式建立字段名和属性名之间的映射关系
* @param custId
* @return
*/
Customer getCustomerByResultMap(Integer custId);
void createTable(@Param("tableName") String tableName);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE
mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace属性:接口全类名 -->
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper">
<!-- 配置保存Customer对象的insert语句 -->
<!-- id属性:void saveCustomer(Customer customer)方法的方法名 -->
<!-- #{参数名}格式:如果传入参数是一个实体类对象时,参数名可以使用对象的属性名 -->
<!-- #{}最终会被替换为?占位符,所以#{}和${}有本质区别,${}只是拼字符串不会转换成?占位符,所以有SQL注入的风险 -->
<insert id="saveCustomer" parameterType="Customer">
insert into tbl_cust(cust_name,cust_age) values(#{custName},#{custAge})
</insert>
<!-- 以字段别名的方式解决字段名和对象属性名不一致问题 -->
<select id="getCustomerById" resultType="Customer">
SELECT cust_id custId,cust_name custName,cust_age custAge
FROM tbl_cust
WHERE cust_id=#{custId}
</select>
<select id="getCustomerByCondition01" resultType="Customer">
SELECT cust_id custId,cust_name custName,cust_age custAge
FROM tbl_cust
WHERE cust_name like #{custName} and cust_age>#{custAge}
</select>
<!-- #{key},根据key从map中获取对应的值作为SQL语句的参数 -->
<select id="getCustomerByCondition02" resultType="Customer" parameterType="map">
SELECT DISTINCT c.cust_id custId,cust_name custName,cust_age custAge
FROM tbl_cust c LEFT JOIN tbl_order o ON c.`cust_id`=o.`cust_id`
WHERE cust_name LIKE #{custNameKey} AND order_amount>#{orderAmountKey}
</select>
<select id="getCustomerByCondition03" resultType="Customer">
SELECT cust_id custId,cust_name custName,cust_age custAge
FROM tbl_cust
<![CDATA[WHERE cust_age > #{minAgeParam} and cust_age < #{maxAgeParam}]]>
</select>
<select id="getDataMap" resultType="map">
SELECT DISTINCT cust_name custName,order_name orderName
FROM tbl_cust c LEFT JOIN tbl_order o ON c.`cust_id`=o.`cust_id`
WHERE order_id=#{orderId}
</select>
<select id="getDataListMap" resultType="map">
SELECT DISTINCT cust_name custName,order_name orderName
FROM tbl_cust c LEFT JOIN tbl_order o ON c.`cust_id`=o.`cust_id`
WHERE order_amount>#{orderAmount}
</select>
<!-- type属性:指定实体类类型 -->
<resultMap type="Customer" id="customerResultMap">
<!-- column属性:指定字段名 -->
<!-- property属性:指定属性名 -->
<id column="cust_id" property="custId"/>
<result column="cust_name" property="custName"/>
<result column="cust_age" property="custAge"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getCustomerByResultMap" resultMap="customerResultMap">
SELECT cust_id,cust_name,cust_age
FROM tbl_cust
WHERE cust_id=#{custId}
</select>
<update id="createTable">
CREATE TABLE ${tableName}(
app_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
app_name CHAR(100)
)
</update>
</mapper>①新建表tbl_cat
CREATE TABLE `tbl_cat` (
`id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`catName` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`birth` date DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
INSERT INTO tbl_cat(catName,age,birth) VALUES('whiteCat',7,CURRENT_DATE());
INSERT INTO tbl_cat(catName,age,birth) VALUES('blackCat',5,CURRENT_DATE());
INSERT INTO tbl_cat(catName,age,birth) VALUES('yellowCat',3,CURRENT_DATE());
② 新建Cat.java
package com.atguigu.mybatis.entities;
import java.util.Date;
public class Cat
{
private Integer id;
private String catName;
private int age;
private Date birth;
public Cat() {}
public Integer getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getCatName()
{
return catName;
}
public void setCatName(String catName)
{
this.catName = catName;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirth()
{
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth)
{
this.birth = birth;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Cat [id=" + id + ", catName=" + catName + ", age=" + age
+ ", birth=" + birth + "]";
}
}
③新建CatMapper接口+方法public Cat getCatByConditions(Cat cat)
package com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper;
import java.util.Date;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Cat;
public interface CatMapper
{
public Cat getCatByConditions(Cat cat);
}
④新建CatMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.CatMapper">
<select id="getCatByConditions" parameterType="Cat" resultType="Cat">
select * from tbl_cat where id=#{id} and age=#{age} and birth=#{birth}
</select>
</mapper>
<!-- 配置保存Customer对象的insert语句 -->
<!-- id属性:void saveCustomer(Customer customer)方法的方法名 -->
<!-- #{参数名}格式:如果传入参数是一个实体类对象时,参数名可以使用对象的属性名 -->
<!-- #{}最终会被替换为?占位符,所以#{}和${}有本质区别,${}只是拼字符串不会转换成?占位符,所以有SQL注入的风险 -->
⑤通配注册或单独注册进mybatis配置文件,否则报:is not known to the MapperRegistry
⑥新建单元测试类
⑦ 演示下like并讲解
- 接口新建方法getCatByCatName
- #{ }
接口定义
public List<Cat> getCatByCatName(String catName);
Mapper.xml定义
<select id="getCatByCatName" parameterType="Cat" resultType="Cat">
SELECT * FROM tbl_cat WHERE catName LIKE #{catName}
</select>
如果使用#{},方法里加入%
List<Cat> result = catMapper.getCatByCatName("%cat%");
推荐用它,比较安全
- ${ }
- 建议+结论
Mybatis3 防止SQL注入
#{xxx},使用的是PreparedStatement,会有类型转换,所以比较安全;推荐使用#
${xxx},使用字符串拼接,可以SQL注入;
like查询不小心会有漏动,正确写法如下:
Mysql: select * from t_user where name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
Oracle: select * from t_user where name like '%' || #{name} || '%'
SQLServer: select * from t_user where name like '%' + #{name} + '%'
3) 传入HashMap
①接口新增方法
public List<Cat> getCatByMap(Map<String,Object> map);
②映射文件
<select id="getCatByMap" parameterType="hashmap" resultType="Cat">
SELECT * FROM tbl_cat WHERE catName LIKE #{catName} and id=#{id}
</select>
③ 测试类
@Test
public void test_GetCatByMap()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CatMapper catMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CatMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("catName","%cat%");
map.put("id","3");
List<Cat> list = catMapper.getCatByMap(map);
System.out.println(list.size());
sqlSession.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(sqlSession != null) sqlSession.close();
}
}
4)口袋POJO,混合型传入参数,进公司看团队技术流风格
4.3 resultType(输出参数类型)
1) 输出单个POJO对象,(前面已讲过)
2)输出多个List<POJO>,(前面已讲过)
3)输出hashmap
①说明:select的各个字段名称作为map的key,值写入value
② 接口 :
public Map<String,Object> getCatByMap2(int id);
③映射文件
<select id="getCatByMap2" parameterType="int" resultType="hashmap">
SELECT id,catName,age,birth FROM tbl_cat WHERE id=#{id}
</select>
④测试类
@Test
public void test_GetCatByMap2()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CatMapper catMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CatMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> map = catMapper.getCatByMap2(1);
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Object>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
Map.Entry<String,Object> entry = it.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"\t"+entry.getValue());
}
sqlSession.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(sqlSession != null) sqlSession.close();
}
}
4.4 resultMap(结果集映射)
POJO里面的field和数据库表里面column一一对应的话,resultType可以指定pojo将查询结 果映射为pojo
1)假如不一致那?新建Dog演示
①新建tbl_dog
CREATE TABLE `tbl_dog` (
`id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`dog_Name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`dog_Weight` int(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
INSERT INTO tbl_dog(dog_Name,dog_Weight) VALUES('ww1',10);
INSERT INTO tbl_dog(dog_Name,dog_Weight) VALUES('ww2',15);
SELECT * FROM tbl_dog;
②新建Dog.java
package com.atguigu.mybatis.entities;
public class Dog
{
private Integer id;
private String dogName;
private int dogWeight;
public Dog() {}
public Integer getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getDogName()
{
return dogName;
}
public void setDogName(String dogName)
{
this.dogName = dogName;
}
public int getDogWeight()
{
return dogWeight;
}
public void setDogWeight(int dogWeight)
{
this.dogWeight = dogWeight;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Dog [id=" + id + ", dogName=" + dogName + ", dogWeight="
+ dogWeight + "]";
}
}
③新建DogMapper接口,getDogByName
public interface DogMapper
{
public List<Dog> getDogByDogName(String dogName);
}
④新建DogMapper.xml
<select id="getDogByDogName" parameterType="String" resultType="Dog">
SELECT id,dog_Name,dog_Weight FROM tbl_dog WHERE dog_Name LIKE #{dogName}
</select>
⑤通配注册或者新注册到Mybatis配置文件
⑥test
DogMapper.xml
<select id="getDogByDogName" parameterType="String" resultType="Dog">
SELECT *
FROM tbl_dog WHERE dog_Name LIKE #{dogName}
</select>
test code
public class DogMapperTest
{
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
@Before
public void createSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException
{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void test()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
DogMapper dogMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DogMapper.class);
List<Dog> list = dogMapper.getDogByDogName("%dog%");
for (Dog dog : list)
{
System.out.println(dog.toString());
}
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2) 别名查询
<select id="getDogByDogName" parameterType="String" resultType="Dog">
SELECT id as id, dog_Name as dogName, dog_Weight as dogWeight
FROM tbl_dog WHERE dog_Name LIKE #{dogName}
</select>
3)结果映射
<!-- 靠resultMap来解决,类名和字段名不一致的情况 -->
<!-- id:查询结果集的唯一标识
column:数据库字段
property:POJO类的属性字段
result:映射结果,表示将数据库的值对应映射给POJO的类属性上
-->
<resultMap id="dogResultMap" type="Dog" >
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="dog_Name" property="dogName"/>
<result column="dog_Weight" property="dogWeight"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getDogByDogName2" parameterType="String" resultMap="dogResultMap">
SELECT id,dog_Name,dog_Weight FROM tbl_dog WHERE dog_Name LIKE #{dogName}
</select>
4.5 sql(定义重用的sql)
sql
这个元素可以被用来定义可重用的 SQL 代码段,可以包含在其他语句中。它可以被静态地(在加载参数) 参数化. 不同的属性值通过包含的实例变化. 比如:
<sql id="userColumns"> ${alias}.id,${alias}.username,${alias}.password </sql>
这个 SQL 片段可以被包含在其他语句中,例如:
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="map">
select
<include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t1"/></include>,
<include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t2"/></include>
from some_table t1
cross join some_table t2
</select>
属性值可以用于包含的refid属性或者包含的字句里面的属性值,例如:
<sql id="sometable">
${prefix}Table
</sql>
<sql id="someinclude">
from
<include refid="${include_target}"/>
</sql>
<select id="select" resultType="map">
select
field1, field2, field3
<include refid="someinclude">
<property name="prefix" value="Some"/>
<property name="include_target" value="sometable"/>
</include>
</select>
5 动态sql
5.1 概述
5.2 新建Student演示
5.3 if
1) 接口方法
public List<Student> getStudent_If(int age);
2)传入单参数age返回List<Student>,有就拼接没有就不参与,按照年龄查学生
3)重点难点:单参数时,mybatis找不到参数错误现象和处理
单独传入一个值,在开发中经常看到如下错误:
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException:
### Error querying database. Cause: org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectionException: There is no getter for property named 'age' in 'class java.lang.Integer'
### Cause: org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectionException: There is no getter for property named 'age' in 'class java.lang.Integer'
三种方法处理:
1 接口方法中添加注解@Param
之前:public List<Student> getStudentByIf(int age);
之后:public List<Student> getStudentByIf(@Param("age") int age);
2 XXXMapper.xml配置文件里面写_parameter
<select id="getStudentByIf" parameterType="int" resultType="Student">
select * from tbl_student where 1 = 1
<if test="_parameter > 0">
and age = #{age}
</if>
</select>
3 直接传递对象
5.4 where
1) 接口方法
public interface StudentMapper
{
public List<Student> getStudent_If(int age);
public List<Student> getStudent_Where(Student student);
}
2)Mapper文件
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="getStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="Student">
select * from tbl_student where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- where/if -->
<select id="getStudentByCondition" parameterType="Student" resultType="Student">
select * from tbl_student
<where>
<if test=" score !=null && score != '' ">
score > #{score}
</if>
<!--使用name !=null and name != ''也可以-->
<if test=" name !=null && name != '' ">
and name like #{name}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
3)where子句以and 或者or开头,它会自动删除第一个and或者or
4)一般建议Where和if结合起来用
5.5 choose/when/otherwise
1)接口方法
public List<Student> getStudent_choosewhenotherwise(Map<String,Object> map);
2)Mapper文件
<select id="getStudentByOption" parameterType="hashmap" resultType="Student">
select * from tbl_student
<choose>
<when test=" id != null && id !='' ">
where id >= #{id}
</when>
<when test=" birth != null && birth !='' ">
where birth > #{birth}
</when>
<otherwise>
where 1 = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
5.6 foreach
1) SQL里面的IN查询
2) if+where+foreach
①接口
public List<Student> getStudent_foreach(Map<String,Object> map);
② 映射文件
<select id="getStudentByForEach" parameterType="Map" resultType="Student">
select * from tbl_student
<if test="ages != null && ages !='' ">
<where>
age in
<foreach item="ages" collection="ages" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{ages}
</foreach>
</where>
</if>
</select>
③test
@Test
public void test_ForEach()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Integer> ages = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ages.add(33);
ages.add(64);
ages.add(0);
map.put("ages",ages);
List<Student> list = studentMapper.getStudentByForEach(map);
for (Student element : list)
{
System.out.println(element.toString());
}
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(sqlSession != null)sqlSession.close();
}
}
5.7 trim
1) 接口
public List<Student> getStudentByTrim(Student student);
或者
public List<Student> getStudentByTrim(Map<String,Object> map);
2)映射文件
<select id="getStudentByTrim" parameterType="Student" resultType="Student">
select * from tbl_student
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and|or">
<if test="age > 0">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="name !=null and name !='' ">
and name like #{name}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
3)trim+if,能替代where
4)前后缀动态覆盖拼装insert
public void insertByTrim(Map<String,Object> map);
<insert id="insertByTrim" parameterType="map">
insert into tbl_student
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">
name,
</if>
<if test="score != null">
score,
</if>
<if test="birth != null">
birth,
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix=" values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">
#{name},
</if>
<if test="score != null">
#{score},
</if>
<if test="birth != null">
#{birth},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
#{age},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
5.8 set
1)动态包含需要更新的列set+if
①会动态前置set关键字
②自动删除最后一个英文逗号
2)自动删除最后一个英文逗号
①接口
public void updateStudent(Student student);
②映射文件
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="Student">
<!--
update tbl_student
set name=#{name},score=#{score},birth=#{birth},age=#{age}
where id=#{id}
-->
update tbl_student
<set>
<if test="name !=null and name !=''">name=#{name},</if>
<if test="score >0 ">score=#{score},</if>
<if test="birth !=null and birth !=''">birth=#{birth},</if>
<if test="age !=null and age !=''">age=#{age},</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
6 关联查询
6.1 通用步骤
1)新建数据表+新增内容数据
2)建entity
3)Mapper接口
4)对应接口的Mapper.xml
5)通配注册或在mybatis-config.xml里面新增映射配置
6)测试类
6.2 一对一
1) 配置版
①新建数据表+新增数据表内容
CREATE TABLE `tbl_key` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`keyName` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE `tbl_lock` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`lockName` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`key_id` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fk_tblKey_id` (`key_id`),
CONSTRAINT `fk_tblKey_id` FOREIGN KEY (`key_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_key` (`id`)
)
SELECT * FROM tbl_key,tbl_lock WHERE tbl_key.id = tbl_lock.key_id AND tbl_lock.id=1
SELECT * FROM tbl_key LEFT OUTER JOIN tbl_lock ON tbl_key.id = tbl_lock.key_id WHERE tbl_lock.id=1
②建entity
public class Key
{
private Integer id;
private String keyName;
}
public class Lock
{
private Integer id;
private String lockName;
private Key key;
}
③ Mapper定义接口
KeyMapper.java
public interface KeyMapper
{
public Key getKeyById(Integer id);
}
LockMapper.java
public interface LockMapper
{
public Lock getLockById(Integer id);
}
④KeyMapper.xml定义
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.KeyMapper">
<select id="getKeyById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="Key">
select * from tbl_key where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
⑤LockMapper.xml实现,第一种(ResultMap+连接查询)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
association:用于1:1关联查询
javaType:对象属性的完整类型,建议包名+类名
property:entity对象的属性名称
column:对应数据库表的字段
-->
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.LockMapper">
<resultMap id="LockResultMap" type="Lock">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="lockName" column="lockName"/>
<association property="key" javaType="com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Key">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="keyName" column="keyName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getLockById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="LockResultMap" >
SELECT * FROM tbl_lock ,tbl_key
WHERE tbl_lock.key_id = tbl_key.id
AND tbl_lock.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
⑥LockMapper.xml实现,第二种(ResultMap+select分段查询)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.LockMapper">
<resultMap type="Lock" id="LockResultMap">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="lockName" column="lockName"/>
<association property="key" column="key_id" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.KeyMapper.getKeyById"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getLockById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="LockResultMap" >
SELECT * FROM tbl_lock where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
lock外键是key表的主键
<association property="key" column="key_id" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.KeyMapper.getKeyById"/>
⑦延时加载介绍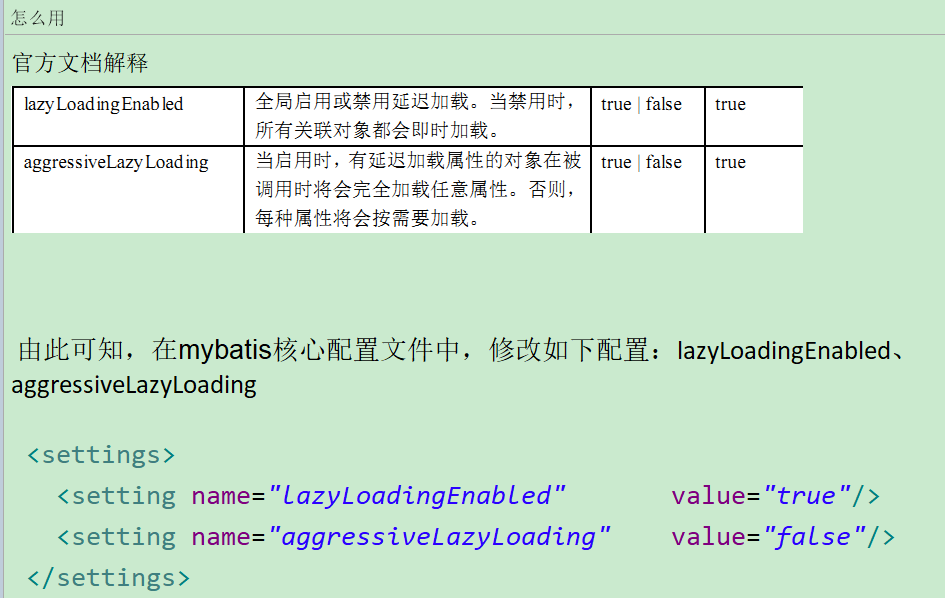
2)注解版
①KeyMapperAnnotation
public interface KeyMapperAnnotation
{
@Select("select * from tbl_key where id=#{id}")
public Key getKeyById(Integer id);
}
②LockMapperAnnotaion
public interface LockMapperAnnotaion
{
@Select("select * from tbl_lock where id=#{id}")
@Results({
@Result(id=true,property="id",column="id"),
@Result(property="lockName",column="lockName"),
@Result(property="key",column="key_id",
one=@One(select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.KeyMapperAnnotation.getKeyById"))
})
public Lock getLockById(Integer id);
}
6.3 一对多
配置版
1)先是单向1:N,一个部门下有多个员工
①建entity
Dept.java
import java.util.List;
public class Dept
{
private Integer id;
private String deptName;
private String locAdd;
private List<Emp> emps;
public Dept() {}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDeptName() {
return deptName;
}
public void setDeptName(String deptName) {
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public String getLocAdd() {
return locAdd;
}
public void setLocAdd(String locAdd) {
this.locAdd = locAdd;
}
public List<Emp> getEmps() {
return emps;
}
public void setEmps(List<Emp> emps) {
this.emps = emps;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Dept [id=" + id + ", deptName=" + deptName + ", locAdd="
+ locAdd + ", emps=" + emps + "]";
}
}
Emp.java
public class Emp
{
private Integer id;
private String name;
//private Dept dept;//后续双向关系的时候记得添加
public Emp() {}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", dept=" + dept + "]";
}
}
②新建DeptMapper接口和方法,按照id查询部门
import com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Dept;
public interface DeptMapper
{
public Dept getDeptById(Integer id);
}
③新建DeptMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapper">
<resultMap id="DeptResultMap" type="Dept">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="deptName" column="deptName"/>
<result property="locAdd" column="locAdd"/>
<!-- private List<Emp> emps; column="id"写被集合对象主键,select按照外键键查询,通过deptid查出emp给dept-->
<collection property="emps" column="id" ofType="Emp" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper.getEmpByDeptId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="DeptResultMap">
select * from tbl_dept where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
=====================================================================================
解释如下:
collection :一对多关联查询
ofType:集合中元素对象的类型
④新建EmpMapper接口和方法
public interface EmpMapper
{
public List<Emp> getEmpByDeptId(Integer deptId);
}
⑤新建EmpMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper">
<resultMap id="EmpResultMap" type="Emp">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getEmpByDeptId" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="EmpResultMap">
select * from tbl_emp where deptId=#{deptId}
</select>
</mapper>
⑥测试junit,查出一个部门下所有员工
public class TestOne2Many
{
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TestOne2Many.class);
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException
{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void test_GetDeptById()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
DeptMapper deptMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DeptMapper.class);
Dept dept = deptMapper.getDeptById(1);
System.out.println("############"+dept.getDeptName());
List<Emp> list = dept.getEmps();
for (Emp emp : list)
{
System.out.println(emp.toString());
}
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != sqlSession) sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
2)再来双向1:N,每一个员工都属于一个部门
①Emp类里新增定义 private Dept dept;
②接口EmpMapper新增方法getEmpById
public interface EmpMapper
{
//为部门查询服务,从一的一端查询,协助按照deptId查询并获得所有员工
public List<Emp> getEmpByDeptId(Integer deptId);
//为员工查询服务,查出该员工信息+属于哪个部门
public Emp getEmpById(Integer id);
}
③修改EmpMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper">
<resultMap id="EmpResultMap" type="Emp">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<association property="dept" column="deptId" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapper.getDeptById"/> <!--双向映射,员工里面有部门 -->
</resultMap>
<!-- 为部门查询服务,从一的一端查询,协助按照部门id查询并获得所有员工 -->
<select id="getEmpByDeptId" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="EmpResultMap">
select * from tbl_emp where deptId=#{deptId}
</select>
<!-- 为员工查询服务,查出该员工自身信息+属于哪个部门 -->
<select id="getEmpById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="EmpResultMap">
select * from tbl_emp where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
④测试junit,查出某员工属于哪个部门
@Test
public void test_GetEmpById()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpMapper empMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Emp emp = empMapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(emp.toString());
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != sqlSession) sqlSession.close();
}
}
注解版
3)先是单向1:N,一个部门下有多个员工
①新建接口DeptMapperAnnotation+添加注解
public interface DeptMapperAnnotation
{
@Select("select * from tbl_dept where id=#{id}")
@Results({
@Result(id=true,property="id",column="id"),
@Result(property="deptName",column="deptName"),
@Result(property="locAdd",column="locAdd"),
@Result(property="emps",column="id",
many=@Many(select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapperAnnotation.getEmpByDeptId"))
})
public Dept getDeptById(Integer id);
}
②新建接口EmpMapperAnnotation+添加注解
public interface EmpMapperAnnotation
{
@Select("select * from tbl_emp where deptId=#{deptId}")
@Results({
@Result(id=true,property="id",column="id"),
@Result(property="name",column="name")
})
public List<Emp> getEmpByDeptId(Integer deptId);
}
③通配注册或新增注册进mybatis配置文件
④测试1:N
4)再来双向1:N,每一个员工都属于一个部门
①修改EmpMapperAnnotation接口
@Select("select * from tbl_emp where id=#{id}")
@Results({
@Result(id=true,property="id",column="id"),
@Result(property="name",column="name"),
@Result(property="dept",column="deptId",
one=@One(select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapperAnnotation.getDeptById"))
})
public Emp getEmpById(Integer id);
②测试
@Test
public void test_GetEmpByIdAnnotation()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpMapperAnnotation empMapperAnnotation = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapperAnnotation.class);
Emp emp = empMapperAnnotation.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(emp.toString());
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != sqlSession) sqlSession.close();
}
}
=============================================================
1.搭建环境
①导入jar包
[1]MyBatis本身的核心jar包:mybatis-3.2.8.jar
[2]MySQL数据库驱动:mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar
[3]数据库连接池(可选):c3p0-0.9.1.2.jar
[4]日志抓取:log4j-1.2.17.jar
②提供连接数据库的基本信息:jdbc.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis160829③创建MyBatis自身的配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
④创建log4j专用的配置文件:log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,myConsole
log4j.appender.myConsole=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.myConsole.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.myConsole.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.myConsole.layout.ConversionPattern=[%-5p] %d(%r) --> [%t] %l: %m %x %nTips:所有我们自定义的东西,如果想要让框架找到,只有两个办法
-
- 以某种方式明确告诉框架文件的路径和文件名:mybatis-config.xml
- 遵守框架默认的约定:log4j.properties
2.给SQL语句传入参数的方式
①单一值:Integer、String、……
| 传入方式:Customer getCustomerById(Integer custId); |
| 在XML中引用的方式:#{随意} |
②实体类对象:Customer等
| 传入方式:List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition01(Customer customer) |
| 在XML中引用的方式:#{实体类对象的属性名} |
③Map
| 传入方式:List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition02(Map<String, Object> map) |
| 在XML中引用的方式:#{map的key} |
④@Param注解
| 传入方式:List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition03( @Param("minAgeParam") int @Param("maxAgeParam") int maxAge); |
| 在XML中引用的方式:#{注解中指定的名称} |
3.获取SQL语句执行结果数据
①封装到实体类对象中
| 必要的配置:resultType="Customer" |
| SQL语句中可以使用别名的方式解决字段名和属性名不一致问题 SELECT cust_id custId,cust_name custName,cust_age custAge ... |
| 接口方法返回值类型:实体类类型 Customer getCustomerById(Integer custId); |
②封装到实体类对象的集合中
| 必要的配置:resultType="Customer" 对于集合类型的数据,不必考虑集合类型,只需要指定实体类类即可 |
| SQL语句中可以使用别名的方式解决字段名和属性名不一致问题 SELECT cust_id custId,cust_name custName,cust_age custAge ... |
| 接口方法返回值类型:实体类类型的集合 List<Customer> getCustomerByCondition01(Customer customer) |
③将每一条记录封装到Map中
| 必要的配置:resultType="map" |
| SQL语句中对是否指定别名没有要求 |
| 返回值类型:Map<String,Object> |
④如果查询结果有多条记录,则返回Map的List
| 必要的配置:resultType="map" |
| SQL语句中对是否指定别名没有要求 |
| 返回值类型:List<Map<String,Object>> |
⑤使用resultMap建立字段名和属性名之间的映射关系
| <!-- type属性:指定实体类类型 --> <resultMap type="Customer" id="customerResultMap"> <!-- column属性:指定字段名 --> <!-- property属性:指定属性名 --> <id column="cust_id" property="custId"/> <result column="cust_name" property="custName"/> <result column="cust_age" property="custAge"/> </resultMap> <select id="getCustomerByResultMap" resultMap="customerResultMap"> SELECT cust_id,cust_name,cust_age FROM tbl_cust WHERE cust_id=#{custId} </select> |
⑥单一值
| resultType="int/double/String/..." |
4.${}和#{}的区别
${}仅仅是拼字符串
使用的场合:一般是在无法使用#{}或者说不能用?占位符的地方使用,例如:创建数据库表时表名
#{}是读取数据后作为?占位符的参数数据
使用的场合:给SQL语句传入具体数值时
5.关联关系
①生活中,数据之间的关联关系
[1]多对一:Order和OrderItem;Customer和Order
[2]一对一:Husband和Wife;Key和Lock
[3]多对多:Teacher和Student
②MyBatis对关联关系的支持
[1]对多:获取多的一端
order.getOrderItemSet();
teacher.getStudentSet();
不必关心是从多还是一的一端出发,总之目标是获取一个集合对象
[2]对一:获取一的一端
orderItem.getOrder();
wife.getHusband();
不必关心是从多还是一的一端出发,总之目标是获取一个单个对象
③MyBatis中建立关联关系的配置方式
[1]对一
一次性全部加载:
简洁版:在resultMap标签内通过级联属性将数据注入
经典版:association标签配合javaType属性
分两条SQL语句加载:association标签配合select属性
[2]对多
一次性全部加载:collection标签配合ofType属性
分两条SQL语句加载:collection标签配合select属性
④测试关联关系的实验
[1]根据orderId查询Order对象,同时将关联的Customer对象也查询出来:使用resultMap
[2]根据orderId查询Order对象,同时将关联的Customer对象也查询出来:association配合javaType
[3]根据orderId查询Order对象,使用另外一条SQL语句查询Customer对象:association配合select
[4]根据custId查询Customer对象,同时将关联的Order对象的集合也查询出来
collection标签配合ofType属性
[5]根据custId查询Customer对象,使用另外一条SQL语句查询关联的Order对象的集合
collection标签配合select属性
⑤为什么要使用resultMap?
因为SQL语句不支持级联形式的别名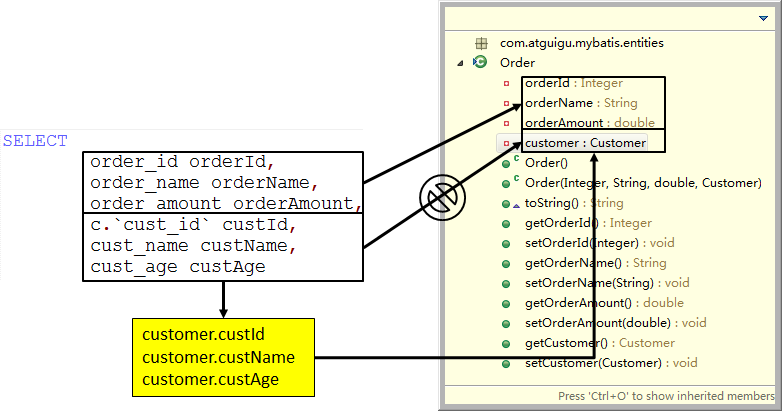
| c.`cust_id` customer.custId, cust_name customer.custName, cust_age customer.custAge |
| 这样写不符合SQL语法 |
⑥为什么分两条语句加载?
如果通过左外连接的方式用一条SQL语句进行查询,那么无法实现“延迟加载”效果。如果想要实现延迟加载效果,前提就是用一条SQL语句查询Order,另一条SQL语句查询Customer。
⑦小结
[1]对一
一次性加载:association+javaType
分两条SQL语句加载:association+select
[2]对多
一次性加载:collection+ofType
分两条SQL语句加载:collection+select
6.延迟加载/懒加载
①概念:对于一个实体类对象(Order)关联的其他对象(Customer),在查询Order时并没有马上把关联的Customer也查询出来,而是等到真正用到Customer属性时才发送SQL语句进行查询。
②影响系统性能的两个方面
[1]访问数据库的次数:越少越好
[2]内存空间:空余空间越大越好
③三种查询方式比较
[1]立即加载:一定会发送两条SQL语句
确定Customer需要用到,但是无法通过左外连接等技术手段一次性查询得到
[2]延迟加载:可能发送两条SQL语句,也可能只发送一条
查询Order之后,Customer可能不会被用到,甚至我们确定Customer根本就不会被用到
[3]左外连接:发送一条SQL语句
查询Order的同时,确定Customer一定会被使用,或有很大的可能性要使用
④MyBatis环境下使用延迟加载需要在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中加入如下配置
| <settings> <!-- 开启延迟加载功能 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 关闭立即加载功能 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings> |
注意:还需要额外导入两个jar包
asm-3.3.1.jar
cglib-2.2.2.jar
7._parameter
当动态SQL标签的属性中需要引用外部传入的单一值时,单一值没有通过@Param注解明确指定名称,则使用_parameter来引用
8.缓存
①存在的意义:提升项目运行的性能。
如果查询、获取某个数据的操作是比较消耗资源的,那么我们应该在获取之后将数据在缓存中保存起来,这样下一次再使用就不必重新执行“昂贵”操作了。
②MyBatis缓存体系
[1]一级缓存:线程级别,由SqlSession对象负责维护的
[2]二级缓存:进程级别,由SqlSessionFactory对象负责维护的
内置
第三方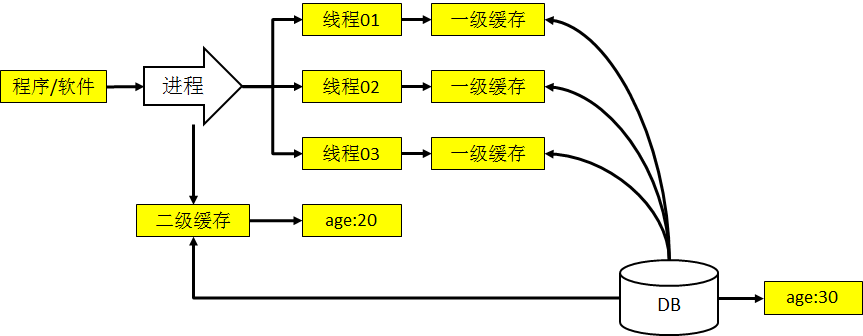
③进程和线程的关系
[1]空间的角度

[2]时间的角度
衡量进程(服务器进程)执行时间的单位:月/年
衡量线程(处理请求的线程)执行时间的单位:毫秒/秒
④★二级缓存中适合和不适合保存的数据
[1]适合
-
-
- 经常被查询,而且很少被修改的数据
- 不是特别重要,允许偶尔的并发问题
- 不会被其他应用程序修改
-
[2]不适合
-
-
- 经常被修改的数据
- 特别重要,不允许任何的并发问题,例如:财务数据
- 有可能被其他应用程序修改的数据
-
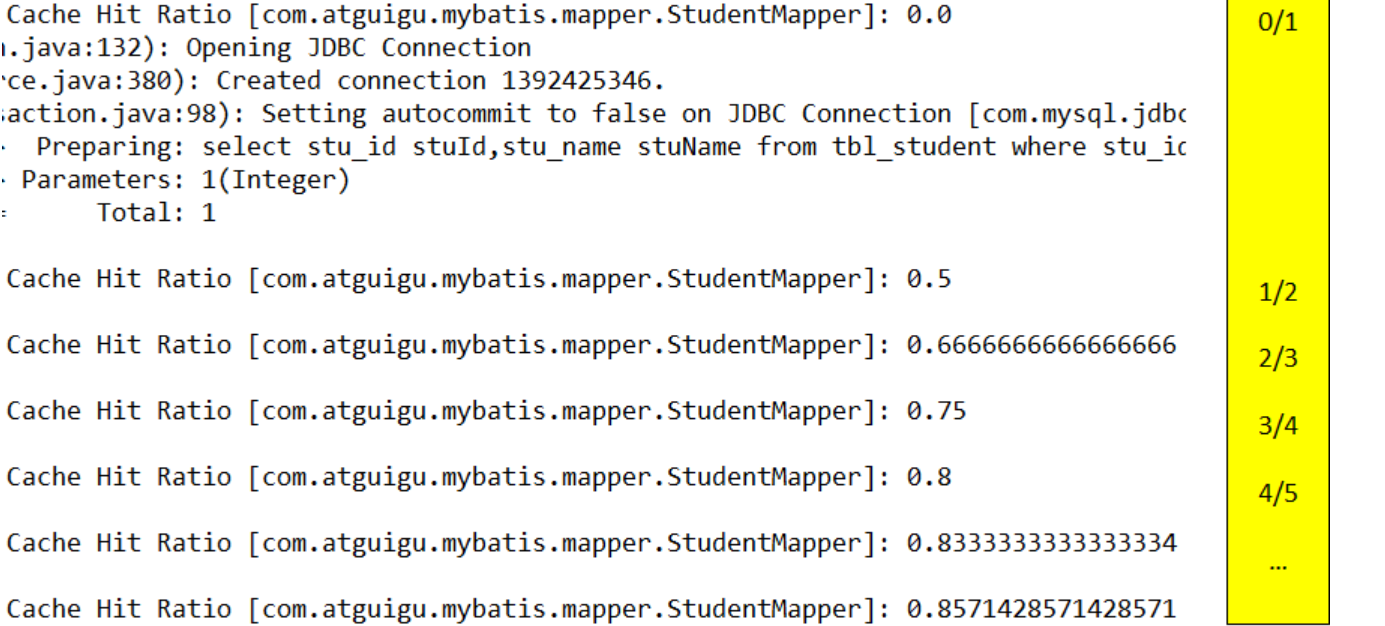
⑤二级缓存的缓存命中率:成功从缓存中获取到数据的次数/查询总次数
⑥EHCache配置文件说明
| <ehcache> <!-- 指定一个硬盘上的目录,用于在内存中的缓存区域溢出时保存对象 --> <diskStore path="D:\\MyCache"/> <!-- defaultCache:默认缓存区域的设置 --> <defaultCache <!-- 缓存区域中最多保存多少个元素 --> maxElementsInMemory="10000" <!-- 是否永不过期,如果设置为true,那么会忽略timeToIdleSeconds和timeToLiveSeconds 属性的设置--> eternal="false" <!-- 控制数据在缓存中,闲置的最长时间 --> timeToIdleSeconds="120" <!-- 控制数据在缓存中,存活的总时间 --> timeToLiveSeconds="120" <!-- 内存中的缓存空间满了以后是否要保存到硬盘上 --> overflowToDisk="true" /> </ehcache> |
⑦缓存的本质:Map
| //1.从Map形式的缓存区域中获取key对应的value Object value = map.get(key); //2.检查value是否为空 if(value == null){ //3.当前需要的数据并没有事先存入缓存,所以需要真正查询数据库得到 value = mapper.getById(5); /4.将value存入缓存区域 map.put(key,value); } //5.将value返回 return value; |
9.MyBatis和Spring整合开发
①整合的思路
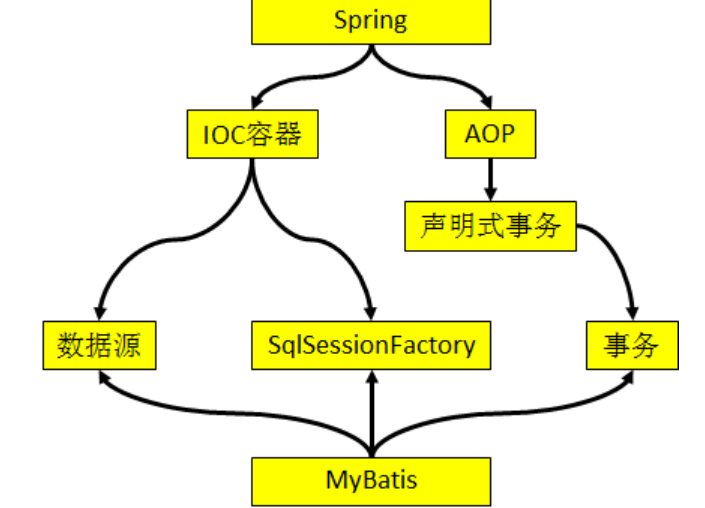
②整合的任务
[1]引入外部属性文件:jdbc.properties
[2]配置数据源的bean
[3]配置SqlSessionFactory的bean
-
-
- 装配数据源的bean
- 指定MyBatis自身配置文件的位置
- 配置typeAliasPackage
-
[4]配置事务管理器bean:装配数据源
[5]开启基于注解的声明式事务的功能:装配事务管理器
[6]配置XxxMapper的扫描器
③需要额外导入的jar包:mybatis-spring-1.2.2.jar
④Spring需要的jar包
[1]SpringIOC容器需要的jar包
[2]Spring声明式事务需要的jar包
=====================================================================
7 查询缓存
7.1 介绍
1 默认情况下,mybatis是启用一级缓存的,它是SqlSession级别的,也即同一个SqlSession接口对象调用了相同的select语句,
就会从缓存里面拿到,而不是再去查询一次数据库,给学生演示下看看。
默认情况下,select使用缓存,增删改不使用。当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该Session中的所有 Cache 就将清空。
2 二级缓存
3 外部缓存
4 作用域
正如大多数持久层框架一样,MyBatis 同样提供了一级缓存和二级缓存的支持;
一级缓存基于 PerpetualCache 的 HashMap 本地缓存,其存储作用域为 Session,当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该Session中的所有 Cache 就将清空。
二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap存储,不同在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache、Hazelcast等。
7.2 一级缓存
1) 案例步骤
①建表tbl_user
CREATE TABLE tbl_user(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20),
age INT
);
INSERT INTO tbl_user(NAME, age) VALUES('苏武', 22);
INSERT INTO tbl_user(NAME, age) VALUES('李青', 31);
②建entity
public class User
{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private int age;
public User(){}
public User(Integer id, String name, int age)
{
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
③UserMapper接口和方法
public interface UserMapper
{
public User getUserById(Integer id);
public void updateUser(User user);
}
④UserMapper.xml实现
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="User">
select * from tbl_user where id=#{id}
</select>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User">
update tbl_user set name=#{name},age=#{age} where id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
⑤通配注册或新增注册到配置文件
⑥演示缓存失效情况
@Test
public void test_OneLevelCache()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user.toString());
/**
* 一级缓存默认会被使用,执行下面的结果可以看到,User user2,但是sql还是一条*/
User user2 = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2.toString());
/**
* 1必须是同样的查询条件
User user2 = userMapper.getUserById(2);
System.out.println(user2.toString()); */
/**
* 2必须是同一个sqlSession,如果关闭过一次,那就另外算了。
sqlSession.close();
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user2 = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2.toString());*/
/**
* 3没有执行过sqlSession.clearCache();
sqlSession.clearCache();
User user2 = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2.toString());*/
/**
*
* 4没有执行过增删改
userMapper.updateUser(new User(1,"lisi",363));
sqlSession.commit();
user = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user.toString());*/
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != sqlSession) sqlSession.close();
}
}
2) 原理结论
Mybatis内部缓存是使用了一个HashMap,map数据结构需要key/value
key:hashCode+查询的SqlId+编写的sql查询语句
value:执行上面的查询所获得java对象
一级缓存作用域是SqlSession,每次查询先找缓存,找到使用,
找不到再从数据库查询。查询到数据将数据写入缓存。
缓存启效前提条件:
1查询条件一样
2必须是同一个sqlSession,如果关闭过一次,那就另外算了。
3没有执行过sqlSession.clearCache();
4没有执行过增删改,sqlSession执行insert、update、delete等操作, commit提交后会清空缓存区域。
7.3 二级缓存
1)案例步骤
①mybatis-config.xml配置中开启显示的定义二级缓存

②提醒,用二级缓存时entity类必须实现序列化接口
③添加一个<cache>在userMapper.xml
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
④测试+效果
package com.atguigu.mybatis.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.User;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
public class TestTwoLvLCache
{
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TestTwoLvLCache.class);
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException
{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void test_GetUserById()
{
//当前会话没关的时候,数据不会放在二级缓存中,会话关闭的时候会将之前所有查询过的数据放在二级缓存中,所以关闭要有顺序才能测验出缓存。会话没关,数据都是在一级缓存中放着,只有关闭了会话,才会将一级缓存中保存的数据清理到二级缓存中去
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user1 = userMapper1.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user1.toString());
sqlSession1.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user2 = userMapper2.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2.toString());
sqlSession2.close();
}
}
2) 原理结论
1 Mybatis二级缓存是多个SqlSession共享的,其作用域是mapper的同一个namespace,
不同的sqlSession两次执行相同namespace下的sql语句且向sql中传递参数也相同即最终执行相同的sql语句。
2 Mybatis显示定义开启二级缓存,需要在setting全局参数中配置
①Cache参数解释
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
上面的配置意思如下:
创建了FIFO的策略,每个1分钟刷新一次,存512个对象而且返回的对象被认为是只读的。
eviction:缓存的回收策略
flushInterval:时间间隔,单位是毫秒,
size:引用数目,内存大就多配置点,要记住你缓存的对象数目和你运行环境的可用内存资源数目。默认值是1024
readOnly:true,只读
四大策略:
1.LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象,它是默认
2.FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
3.SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
4.WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
②禁用二级缓存
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="User" useCache="true">
select * from tbl_user where id=#{id}
</select>
设置useCache=false可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次查询都会发出sql去查询,
默认情况是true,即该sql使用二级缓存。
③刷新(清空)二级缓存
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User" flushCache="true">
UPDATE tbl_user SET NAME=#{name},age=#{age} WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
insert、update、delete操作数据后需要刷新缓存,如果不执行刷新缓存会出现脏读,所以默认为true,
默认情况下为true即刷新缓存,一般不用修改,知道即可。
④ 一级缓存和二级缓存的使用顺序
如果你的 MyBatis 使用了二级缓存,并且你的 Mapper 和 select 语句也配置使用了二级缓存,那么在执行 select 查询的时候, MyBatis 会先从二级缓存中取输入,其次才是一级缓存,即 MyBatis 查询数据的顺序是:
二级缓存 -----> 一级缓存 -----> 数据库
⑤要想使某条 Select查询支持二级缓存的前提条件
1. MyBatis支持二级缓存的总开关:全局配置变量参数 cacheEnabled=true
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
2. 该select语句所在的Mapper,配置了<cache> 节点且有效
3. 该select语句的参数 useCache=true
7.4mybatis整合Ehcache
1)EhCache 是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,
是Hibernate中默认的CacheProvider。
2)怎么用
①添jar包
②ehcache.xml配置,用自定义的
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="D:\44\ehcache" />
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
<!--
属性说明:
l diskStore:指定数据在磁盘中的存储位置。
l defaultCache:当借助CacheManager.add("demoCache")创建Cache时,EhCache便会采用<defalutCache/>指定的的管理策略
以下属性是必须的:
l maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目
l maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大
l eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断
l overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上
以下属性是可选的:
l timeToIdleSeconds - 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大
l timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区.
l diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。
l diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作
l memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)
-->
③开启ehcache缓存
修改mapper.xml文件,在cache中指定EhcacheCache
<!-- mybatis和ehcache结合-->
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache>
④测试
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.User;
import com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
public class TestTwoLvLCache
{
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TestTwoLvLCache.class);
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException
{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void test_GetUserById()
{
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user1 = userMapper1.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user1.toString());
sqlSession1.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user2 = userMapper2.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2.toString());
sqlSession2.close();
SqlSession sqlSession3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user3 = userMapper3.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user3.toString());
sqlSession3.close();
SqlSession sqlSession4 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper4 = sqlSession4.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user4 = userMapper4.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user4.toString());
sqlSession4.close();
SqlSession sqlSession5 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper5 = sqlSession5.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user5 = userMapper5.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user5.toString());
sqlSession5.close();
}
}
8 Spring+Mybatis整合
1)spring3.0以下不支持mybatis
2)添jar包
3)db.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=123456
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis0607?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8
4)applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.mybatis"></context:component-scan>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" />
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置mybatis的sqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.atguigu.mybatis"></property>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
5)新建mybatis配置文件mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
</configuration>
6)新建entity+Mapper接口/XML配置+Service
7) 测试调用
public interface UserMapper
{
public void add(User user);
public User getUserById(Integer id);
}
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<insert id="add" parameterType="User">
insert into tbl_user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})
</insert>
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="User">
select * from tbl_user where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
9 Mybatis逆向工程
9.1 是什么
Mybatis官方提供的逆向工程,可以将单表生生成
常用的Mapper、entity等配置
9.2 能干嘛
从数据库表反向生成mapper.java/mapper.xml/entity/辅助查询类
9.3 怎么用
1)有数据库表提供给MyBatisGenerator反向生产素材
2)打开mybatis-generator-core-1.3.2-bundle\mybatis-generator-core-1.3.2\docs里面的文档照着官网配置
3)官方文档generatorConfig.xml
4)拷贝出entity/mapper/mapper.xml
5)测试
@Test
public void testselectByExample()
{
DogExample example = new DogExample();
DogExample.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
criteria.andDogNameEqualTo("哈士奇");
List<Dog> list = dogService.selectByExample(example);
System.out.println(list.get(0).toString());
}
9.4 注意事项
1 覆盖和追加问题
1.1 工具自动化会生产3个东东,entity+Mapper接口+Mapper接口对应的xml
1.2 假如xxxMapper.xml文件已经存在了,再次生成则mapper.xml文件内容不被覆盖而是进行内容追加,有时候会导致mybatis解析失败。所以,建议为了确保它的正确性和完整性,建议删除重建。
1.3 entity和接口是因为是直接覆盖,没有上述问题。





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








