原始的AlexNet用来处理277*277*3的数据集, 并且采用5层卷积,3层全连接层来处理图像分类。
具体结构和参数信息见
http://blog.csdn.net/chenhaifeng2016/article/details/72758053
这里在前面MNIST CNN LeNet的基础上,借鉴AlexNet的思想做进一步优化。(非标准AlexNet模型)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#加载数据
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
#训练数据
inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 784])
#训练标签数据
labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
#dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
#把inputs更改为4维张量,第1维代表样本数量,第2维和第3维代表图像长宽, 第4维代表图像通道数, 1表示黑白
x = tf.reshape(inputs, [-1,28,28,1])
#第一层卷积
conv1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 64])) #卷积核大小为3*3, 当前层深度为1, 过滤器深度为64
#卷积
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(x, conv1_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #移动步长为1, 使用全0填充
conv1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64]))
#激活函数Relu去线性化
relu1 = tf.nn.relu( tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv1_biases) )
#最大池化
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') #池化层过滤器的大小为2*2, 移动步长为2,使用全0填充
#规范化
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75)
norm1 = tf.nn.dropout(norm1, keep_prob)
print(norm1.shape) #14*14*64
#第二层卷积
conv2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 128])) #卷积核大小为3*3, 当前层深度为64, 过滤器深度为128
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, conv2_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #移动步长为1, 使用全0填充
conv2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([128]))
relu2 = tf.nn.relu( tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_biases) )
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(pool2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75)
norm2 = tf.nn.dropout(norm2, keep_prob)
print(norm2.shape) #7*7*128
#第三层卷积
conv3_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 128, 256])) #卷积核大小为3*3, 当前层深度为128, 过滤器深度为256
conv3 = tf.nn.conv2d(norm2, conv3_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #移动步长为1, 使用全0填充
conv3_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256]))
relu3 = tf.nn.relu( tf.nn.bias_add(conv3, conv3_biases) )
pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
norm3 = tf.nn.lrn(pool3, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75)
norm3 = tf.nn.dropout(norm3, keep_prob)
print(norm3.shape) #4*4*256
#全连接层 1
fc1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*256, 1024]))
fc1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024]))
fc1 = tf.reshape(norm3, [ -1, fc1_weights.get_shape().as_list()[0] ] )
fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, fc1_weights), fc1_biases)
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
#全连接层 2
fc2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 1024]))
fc2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024]))
fc2 = tf.reshape(fc1, [ -1, fc2_weights.get_shape().as_list()[0] ] )
fc2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2, fc2_weights), fc2_biases)
fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2)
#输出层
out_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 10]))
out_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
pred = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2, out_weights), out_biases)
#定义交叉熵损失函数
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=labels))
#选择优化器
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(cost)
#评估函数
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(labels,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
#训练模型
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(10000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={inputs: batch[0], labels: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.75}) # 训练阶段使用75%的Dropout
if i % 100 == 0:
train_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={inputs:batch[0], labels: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0}) #评估阶段不使用Dropout
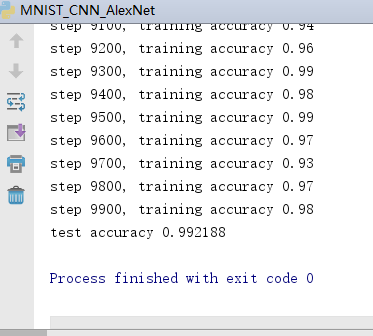
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
#评估模型
#只使用256个测试数据,机器太差, 跑10000内存溢出了
print("test accuracy %g" % sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={inputs: mnist.test.images[:256], labels: mnist.test.labels[:256], keep_prob: 1.0})) #评估阶段不使用Dropout























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








