web.xml配置
<filter>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>targetFilterLifecycle</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
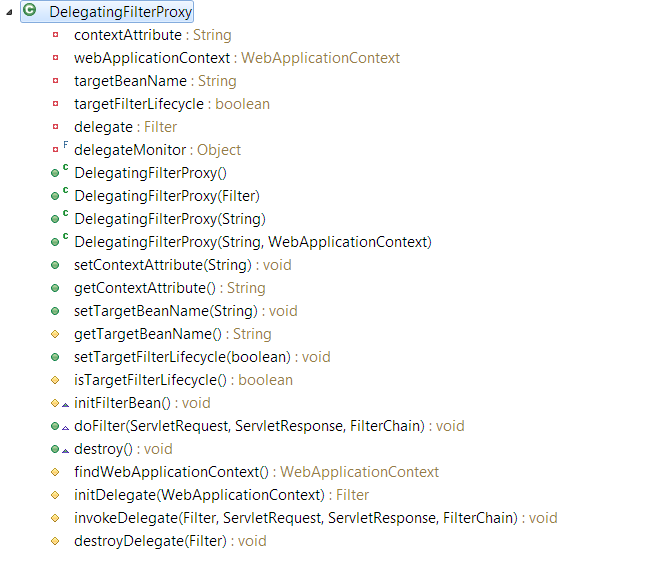
</filter>DelegatingFilterProxy中的方法
源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2011 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
/**
* Proxy for a standard Servlet 2.3 Filter, delegating to a Spring-managed
* bean that implements the Filter interface. Supports a "targetBeanName"
* filter init-param in {@code web.xml}, specifying the name of the
* target bean in the Spring application context.
*
* <p>{@code web.xml} will usually contain a {@code DelegatingFilterProxy} definition,
* with the specified {@code filter-name} corresponding to a bean name in
* Spring's root application context. All calls to the filter proxy will then
* be delegated to that bean in the Spring context, which is required to implement
* the standard Servlet 2.3 Filter interface.
*
* <p>This approach is particularly useful for Filter implementation with complex
* setup needs, allowing to apply the full Spring bean definition machinery to
* Filter instances. Alternatively, consider standard Filter setup in combination
* with looking up service beans from the Spring root application context.
*
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> The lifecycle methods defined by the Servlet Filter interface
* will by default <i>not</i> be delegated to the target bean, relying on the
* Spring application context to manage the lifecycle of that bean. Specifying
* the "targetFilterLifecycle" filter init-param as "true" will enforce invocation
* of the {@code Filter.init} and {@code Filter.destroy} lifecycle methods
* on the target bean, letting the servlet container manage the filter lifecycle.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code DelegatingFilterProxy} has been updated to optionally accept
* constructor parameters when using Servlet 3.0's instance-based filter registration
* methods, usually in conjunction with Spring 3.1's
* {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} SPI. These constructors allow
* for providing the delegate Filter bean directly, or providing the application context
* and bean name to fetch, avoiding the need to look up the application context from the
* ServletContext.
*
* <p>This class was originally inspired by Spring Security's {@code FilterToBeanProxy}
* class, written by Ben Alex.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 1.2
* @see #setTargetBeanName
* @see #setTargetFilterLifecycle
* @see javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter
* @see javax.servlet.Filter#init
* @see javax.servlet.Filter#destroy
* @see #DelegatingFilterProxy(Filter)
* @see #DelegatingFilterProxy(String)
* @see #DelegatingFilterProxy(String, WebApplicationContext)
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#addFilter(String, Filter)
* @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer
*/
public class DelegatingFilterProxy extends GenericFilterBean {
private String contextAttribute;
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
private String targetBeanName;
private boolean targetFilterLifecycle = false;
private Filter delegate;
private final Object delegateMonitor = new Object();
/**
* Create a new {@code DelegatingFilterProxy}. For traditional (pre-Servlet 3.0) use
* in {@code web.xml}.
* @see #setTargetBeanName(String)
*/
public DelegatingFilterProxy() {
}
/**
* Create a new {@code DelegatingFilterProxy} with the given {@link Filter} delegate.
* Bypasses entirely the need for interacting with a Spring application context,
* specifying the {@linkplain #setTargetBeanName target bean name}, etc.
* <p>For use in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based registration of
* filters is supported.
* @param delegate the {@code Filter} instance that this proxy will delegate to and
* manage the lifecycle for (must not be {@code null}).
* @see #doFilter(ServletRequest, ServletResponse, FilterChain)
* @see #invokeDelegate(Filter, ServletRequest, ServletResponse, FilterChain)
* @see #destroy()
* @see #setEnvironment(org.springframework.core.env.Environment)
*/
public DelegatingFilterProxy(Filter delegate) {
Assert.notNull(delegate, "delegate Filter object must not be null");
this.delegate = delegate;
}
/**
* Create a new {@code DelegatingFilterProxy} that will retrieve the named target
* bean from the Spring {@code WebApplicationContext} found in the {@code ServletContext}
* (either the 'root' application context or the context named by
* {@link #setContextAttribute}).
* <p>For use in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based registration of
* filters is supported.
* <p>The target bean must implement the standard Servlet Filter.
* @param targetBeanName name of the target filter bean to look up in the Spring
* application context (must not be {@code null}).
* @see #findWebApplicationContext()
* @see #setEnvironment(org.springframework.core.env.Environment)
*/
public DelegatingFilterProxy(String targetBeanName) {
this(targetBeanName, null);
}
/**
* Create a new {@code DelegatingFilterProxy} that will retrieve the named target
* bean from the given Spring {@code WebApplicationContext}.
* <p>For use in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based registration of
* filters is supported.
* <p>The target bean must implement the standard Servlet Filter interface.
* <p>The given {@code WebApplicationContext} may or may not be refreshed when passed
* in. If it has not, and if the context implements {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext},
* a {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() refresh()} will be attempted before
* retrieving the named target bean.
* <p>This proxy's {@code Environment} will be inherited from the given
* {@code WebApplicationContext}.
* @param targetBeanName name of the target filter bean in the Spring application
* context (must not be {@code null}).
* @param wac the application context from which the target filter will be retrieved;
* if {@code null}, an application context will be looked up from {@code ServletContext}
* as a fallback.
* @see #findWebApplicationContext()
* @see #setEnvironment(org.springframework.core.env.Environment)
*/
public DelegatingFilterProxy(String targetBeanName, WebApplicationContext wac) {
Assert.hasText(targetBeanName, "target Filter bean name must not be null or empty");
this.setTargetBeanName(targetBeanName);
this.webApplicationContext = wac;
if (wac != null) {
this.setEnvironment(wac.getEnvironment());
}
}
/**
* Set the name of the ServletContext attribute which should be used to retrieve the
* {@link WebApplicationContext} from which to load the delegate {@link Filter} bean.
*/
public void setContextAttribute(String contextAttribute) {
this.contextAttribute = contextAttribute;
}
/**
* Return the name of the ServletContext attribute which should be used to retrieve the
* {@link WebApplicationContext} from which to load the delegate {@link Filter} bean.
*/
public String getContextAttribute() {
return this.contextAttribute;
}
/**
* Set the name of the target bean in the Spring application context.
* The target bean must implement the standard Servlet 2.3 Filter interface.
* <p>By default, the {@code filter-name} as specified for the
* DelegatingFilterProxy in {@code web.xml} will be used.
*/
public void setTargetBeanName(String targetBeanName) {
this.targetBeanName = targetBeanName;
}
/**
* Return the name of the target bean in the Spring application context.
*/
protected String getTargetBeanName() {
return this.targetBeanName;
}
/**
* Set whether to invoke the {@code Filter.init} and
* {@code Filter.destroy} lifecycle methods on the target bean.
* <p>Default is "false"; target beans usually rely on the Spring application
* context for managing their lifecycle. Setting this flag to "true" means
* that the servlet container will control the lifecycle of the target
* Filter, with this proxy delegating the corresponding calls.
*/
public void setTargetFilterLifecycle(boolean targetFilterLifecycle) {
this.targetFilterLifecycle = targetFilterLifecycle;
}
/**
* Return whether to invoke the {@code Filter.init} and
* {@code Filter.destroy} lifecycle methods on the target bean.
*/
protected boolean isTargetFilterLifecycle() {
return this.targetFilterLifecycle;
}
@Override
protected void initFilterBean() throws ServletException {
synchronized (this.delegateMonitor) {
if (this.delegate == null) {
// If no target bean name specified, use filter name.
if (this.targetBeanName == null) {
this.targetBeanName = getFilterName();
}
// Fetch Spring root application context and initialize the delegate early,
// if possible. If the root application context will be started after this
// filter proxy, we'll have to resort to lazy initialization.
WebApplicationContext wac = findWebApplicationContext();
if (wac != null) {
this.delegate = initDelegate(wac);
}
}
}
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Lazily initialize the delegate if necessary.
Filter delegateToUse = null;
synchronized (this.delegateMonitor) {
if (this.delegate == null) {
WebApplicationContext wac = findWebApplicationContext();
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: no ContextLoaderListener registered?");
}
this.delegate = initDelegate(wac);
}
delegateToUse = this.delegate;
}
// Let the delegate perform the actual doFilter operation.
invokeDelegate(delegateToUse, request, response, filterChain);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
Filter delegateToUse = null;
synchronized (this.delegateMonitor) {
delegateToUse = this.delegate;
}
if (delegateToUse != null) {
destroyDelegate(delegateToUse);
}
}
/**
* Return the {@code WebApplicationContext} passed in at construction time, if available.
* Otherwise, attempt to retrieve a {@code WebApplicationContext} from the
* {@code ServletContext} attribute with the {@linkplain #setContextAttribute
* configured name} if set. Otherwise look up a {@code WebApplicationContext} under
* the well-known "root" application context attribute. The
* {@code WebApplicationContext} must have already been loaded and stored in the
* {@code ServletContext} before this filter gets initialized (or invoked).
* <p>Subclasses may override this method to provide a different
* {@code WebApplicationContext} retrieval strategy.
* @return the {@code WebApplicationContext} for this proxy, or {@code null} if not
* found
* @see #DelegatingFilterProxy(String, WebApplicationContext)
* @see #getContextAttribute()
* @see WebApplicationContextUtils#getWebApplicationContext(javax.servlet.ServletContext)
* @see WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE
*/
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// the user has injected a context at construction time -> use it
if (this.webApplicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
if (!((ConfigurableApplicationContext)this.webApplicationContext).isActive()) {
// the context has not yet been refreshed -> do so before returning it
((ConfigurableApplicationContext)this.webApplicationContext).refresh();
}
}
return this.webApplicationContext;
}
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName != null) {
return WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
}
else {
return WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
}
}
/**
* Initialize the Filter delegate, defined as bean the given Spring
* application context.
* <p>The default implementation fetches the bean from the application context
* and calls the standard {@code Filter.init} method on it, passing
* in the FilterConfig of this Filter proxy.
* @param wac the root application context
* @return the initialized delegate Filter
* @throws ServletException if thrown by the Filter
* @see #getTargetBeanName()
* @see #isTargetFilterLifecycle()
* @see #getFilterConfig()
* @see javax.servlet.Filter#init(javax.servlet.FilterConfig)
*/
protected Filter initDelegate(WebApplicationContext wac) throws ServletException {
Filter delegate = wac.getBean(getTargetBeanName(), Filter.class);
if (isTargetFilterLifecycle()) {
delegate.init(getFilterConfig());
}
return delegate;
}
/**
* Actually invoke the delegate Filter with the given request and response.
* @param delegate the delegate Filter
* @param request the current HTTP request
* @param response the current HTTP response
* @param filterChain the current FilterChain
* @throws ServletException if thrown by the Filter
* @throws IOException if thrown by the Filter
*/
protected void invokeDelegate(
Filter delegate, ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
delegate.doFilter(request, response, filterChain);
}
/**
* Destroy the Filter delegate.
* Default implementation simply calls {@code Filter.destroy} on it.
* @param delegate the Filter delegate (never {@code null})
* @see #isTargetFilterLifecycle()
* @see javax.servlet.Filter#destroy()
*/
protected void destroyDelegate(Filter delegate) {
if (isTargetFilterLifecycle()) {
delegate.destroy();
}
}
}
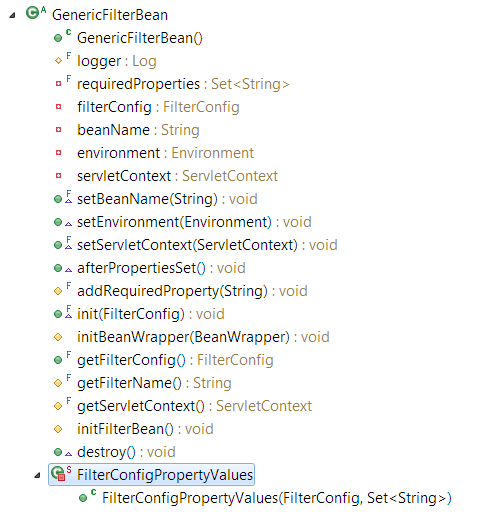
GenericFilterBean上文已经介绍过
其中的方法
其源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2011 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.filter;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessorFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceEditor;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.StandardServletEnvironment;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletContextResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException;
/**
* Simple base implementation of {@link javax.servlet.Filter} which treats
* its config parameters (<code>init-param</code> entries within the
* <code>filter</code> tag in <code>web.xml</code>) as bean properties.
*
* <p>A handy superclass for any type of filter. Type conversion of config
* parameters is automatic, with the corresponding setter method getting
* invoked with the converted value. It is also possible for subclasses to
* specify required properties. Parameters without matching bean property
* setter will simply be ignored.
*
* <p>This filter leaves actual filtering to subclasses, which have to
* implement the {@link javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter} method.
*
* <p>This generic filter base class has no dependency on the Spring
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} concept.
* Filters usually don't load their own context but rather access service
* beans from the Spring root application context, accessible via the
* filter's {@link #getServletContext() ServletContext} (see
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils}).
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 06.12.2003
* @see #addRequiredProperty
* @see #initFilterBean
* @see #doFilter
*/
public abstract class GenericFilterBean implements
Filter, BeanNameAware, EnvironmentAware, ServletContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
/** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/**
* Set of required properties (Strings) that must be supplied as
* config parameters to this filter.
*/
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new HashSet<String>();
private FilterConfig filterConfig;
private String beanName;
private Environment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment();
private ServletContext servletContext;
/**
* Stores the bean name as defined in the Spring bean factory.
* <p>Only relevant in case of initialization as bean, to have a name as
* fallback to the filter name usually provided by a FilterConfig instance.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware
* @see #getFilterName()
*/
public final void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>Any environment set here overrides the {@link StandardServletEnvironment}
* provided by default.
* <p>This {@code Environment} object is used only for resolving placeholders in
* resource paths passed into init-parameters for this filter. If no init-params are
* used, this {@code Environment} can be essentially ignored.
* @see #init(FilterConfig)
*/
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
/**
* Stores the ServletContext that the bean factory runs in.
* <p>Only relevant in case of initialization as bean, to have a ServletContext
* as fallback to the context usually provided by a FilterConfig instance.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware
* @see #getServletContext()
*/
public final void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Calls the <code>initFilterBean()</code> method that might
* contain custom initialization of a subclass.
* <p>Only relevant in case of initialization as bean, where the
* standard <code>init(FilterConfig)</code> method won't be called.
* @see #initFilterBean()
* @see #init(javax.servlet.FilterConfig)
*/
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws ServletException {
initFilterBean();
}
/**
* Subclasses can invoke this method to specify that this property
* (which must match a JavaBean property they expose) is mandatory,
* and must be supplied as a config parameter. This should be called
* from the constructor of a subclass.
* <p>This method is only relevant in case of traditional initialization
* driven by a FilterConfig instance.
* @param property name of the required property
*/
protected final void addRequiredProperty(String property) {
this.requiredProperties.add(property);
}
/**
* Standard way of initializing this filter.
* Map config parameters onto bean properties of this filter, and
* invoke subclass initialization.
* @param filterConfig the configuration for this filter
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
* @see #initFilterBean
*/
public final void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
Assert.notNull(filterConfig, "FilterConfig must not be null");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing filter '" + filterConfig.getFilterName() + "'");
}
this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new FilterConfigPropertyValues(filterConfig, this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(filterConfig.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.environment));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
String msg = "Failed to set bean properties on filter '" +
filterConfig.getFilterName() + "': " + ex.getMessage();
logger.error(msg, ex);
throw new NestedServletException(msg, ex);
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initFilterBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Filter '" + filterConfig.getFilterName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
/**
* Initialize the BeanWrapper for this GenericFilterBean,
* possibly with custom editors.
* <p>This default implementation is empty.
* @param bw the BeanWrapper to initialize
* @throws BeansException if thrown by BeanWrapper methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper#registerCustomEditor
*/
protected void initBeanWrapper(BeanWrapper bw) throws BeansException {
}
/**
* Make the FilterConfig of this filter available, if any.
* Analogous to GenericServlet's <code>getServletConfig()</code>.
* <p>Public to resemble the <code>getFilterConfig()</code> method
* of the Servlet Filter version that shipped with WebLogic 6.1.
* @return the FilterConfig instance, or <code>null</code> if none available
* @see javax.servlet.GenericServlet#getServletConfig()
*/
public final FilterConfig getFilterConfig() {
return this.filterConfig;
}
/**
* Make the name of this filter available to subclasses.
* Analogous to GenericServlet's <code>getServletName()</code>.
* <p>Takes the FilterConfig's filter name by default.
* If initialized as bean in a Spring application context,
* it falls back to the bean name as defined in the bean factory.
* @return the filter name, or <code>null</code> if none available
* @see javax.servlet.GenericServlet#getServletName()
* @see javax.servlet.FilterConfig#getFilterName()
* @see #setBeanName
*/
protected final String getFilterName() {
return (this.filterConfig != null ? this.filterConfig.getFilterName() : this.beanName);
}
/**
* Make the ServletContext of this filter available to subclasses.
* Analogous to GenericServlet's <code>getServletContext()</code>.
* <p>Takes the FilterConfig's ServletContext by default.
* If initialized as bean in a Spring application context,
* it falls back to the ServletContext that the bean factory runs in.
* @return the ServletContext instance, or <code>null</code> if none available
* @see javax.servlet.GenericServlet#getServletContext()
* @see javax.servlet.FilterConfig#getServletContext()
* @see #setServletContext
*/
protected final ServletContext getServletContext() {
return (this.filterConfig != null ? this.filterConfig.getServletContext() : this.servletContext);
}
/**
* Subclasses may override this to perform custom initialization.
* All bean properties of this filter will have been set before this
* method is invoked.
* <p>Note: This method will be called from standard filter initialization
* as well as filter bean initialization in a Spring application context.
* Filter name and ServletContext will be available in both cases.
* <p>This default implementation is empty.
* @throws ServletException if subclass initialization fails
* @see #getFilterName()
* @see #getServletContext()
*/
protected void initFilterBean() throws ServletException {
}
/**
* Subclasses may override this to perform custom filter shutdown.
* <p>Note: This method will be called from standard filter destruction
* as well as filter bean destruction in a Spring application context.
* <p>This default implementation is empty.
*/
public void destroy() {
}
/**
* PropertyValues implementation created from FilterConfig init parameters.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class FilterConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
/**
* Create new FilterConfigPropertyValues.
* @param config FilterConfig we'll use to take PropertyValues from
* @param requiredProperties set of property names we need, where
* we can't accept default values
* @throws ServletException if any required properties are missing
*/
public FilterConfigPropertyValues(FilterConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set<String> missingProps = (requiredProperties != null && !requiredProperties.isEmpty()) ?
new HashSet<String>(requiredProperties) : null;
Enumeration<?> en = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = (String) en.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (missingProps != null && missingProps.size() > 0) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from FilterConfig for filter '" + config.getFilterName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
}
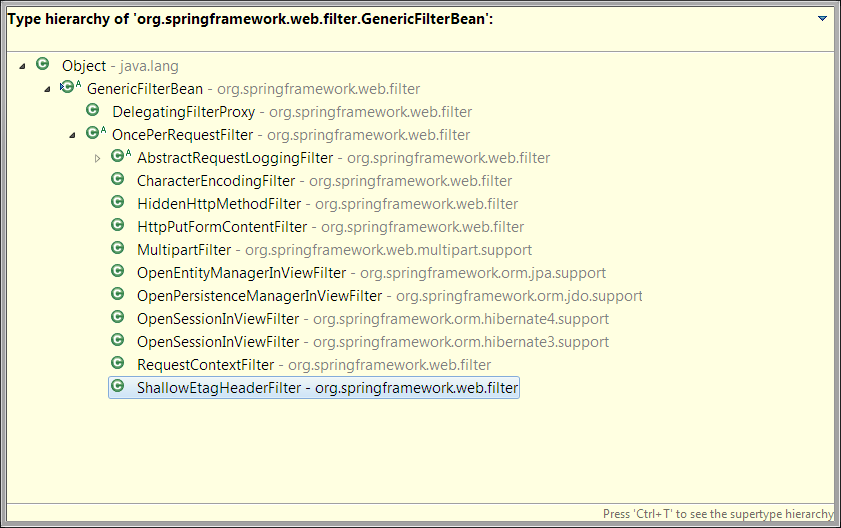
,其继承关系如图






















 359
359

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








