遍历方式
增强型for循环
也称为for-each循环,是jdk 1.5中新增的循环模式,我们在程序中会越来越倾向于使用这种方式遍历集合,因为它使用起来更方便。
而在郭大侠的文章:Android最佳性能实践(三)中提到对于ArrayList这种集合,“自己的手写for循环比for-each快”,针对这一结论,我们做一个小实验来验证下结论的可靠性:
实验过程
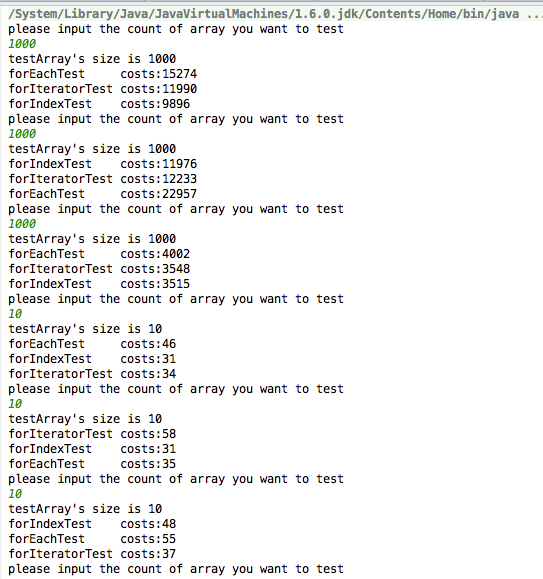
采用3种遍历ArrayList的方式,比较各种遍历模式的花费时间
实验结论
从图中实验结果我们可以知道,在ArrayList的遍历上的确手写for循环花费时间少,那么下次我们自己写的时候就可要注意咯。
实验代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Created by xixi on 15/10/8.
*/
public class ForTraverseMethodsTest {
private static ArrayList<String> testIndexArray;
private static ArrayList<String> testEachArray;
private static ArrayList<String> testIteratorArray;
private static int ArrayCount;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
while (true) {
System.out.println("please input the count of array you want to test");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String count = scanner.next();
ArrayCount = Integer.parseInt(count);
if (ArrayCount == 0) {
return;
}
System.out.println("testArray's size is " + ArrayCount);
int[] testType = {1, 2, 3};
boolean[] testState = {false, false, false};
int validCount = 0;
int index;
// 随机调用一种测试方法,并且保证每种循环方法都能调到
while(true) {
index = (int) (Math.random() * testType.length);
int randomNumber = testType[index];
if (!testState[randomNumber-1]) {
forIteratorTest(randomNumber);
testState[randomNumber-1] = true;
validCount ++;
}
if (validCount == 3) {
break;
}
}
}
}
private static void forIteratorTest(int index) {
ArrayList<String> testArray = new ArrayList<String>();
testArray.clear();
for (int i =0; i < ArrayCount; i++) {
if ( i%2 ==0) {
testArray.add("a");
} else {
testArray.add("b");
}
}
switch (index) {
case 1:
testIndexArray = testArray;
forIndexTest();
break;
case 2:
testIteratorArray = testArray;
forIteratorTest();
break;
case 3:
testEachArray = testArray;
forEachTest();
}
}
private static void forEachTest() {
long beginTime = System.nanoTime();
for (String item : testEachArray) {
if ("a".equals(item)) {
item.replace("a", "b");
} else {
item.replace("b", "a");
}
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long costTime = (endTime - beginTime) / 1000;
System.out.println("forEachTest costs:" + costTime);
}
private static void forIndexTest() {
long beginTime = System.nanoTime();
int count = testIndexArray.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
String item = testIndexArray.get(i);
if ("a".equals(item)) {
item.replace("a", "b");
} else {
item.replace("b", "a");
}
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long costTime = (endTime - beginTime) / 1000;
System.out.println("forIndexTest costs:" + costTime);
}
private static void forIteratorTest() {
long beginTime = System.nanoTime();
Iterator<String> iterator = testIteratorArray.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String item = iterator.next();
if ("a".equals(item)) {
item.replace("a", "b");
} else {
item.replace("b", "a");
}
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long costTime = (endTime - beginTime) / 1000;
System.out.println("forIteratorTest costs:" + costTime);
}
}





















 1156
1156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








