axios笔记(一) 简单入门
个人博客:axios笔记(一) 简单入门
HTTP
之前的笔记:HTTP笔记 | 赤蓝紫 (clz.vercel.app)
1. 介绍
HTTP是一种能够获取如 HTML 这样的网络资源的protocol(通讯协议)。它是在 Web 上进行数据交换的基础,是一种 client-server 协议,也就是说,请求通常是由像浏览器这样的接受方发起的。一个完整的Web文档通常是由不同的子文档拼接而成的,像是文本、布局描述、图片、视频、脚本等等。
文档:HTTP
2. HTTP请求交互的基本过程
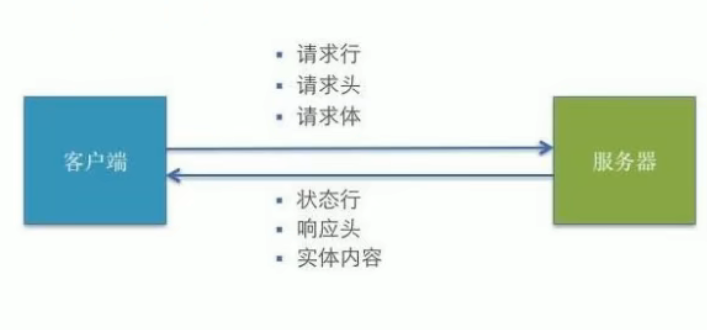
- 浏览器向服务器发送请求报文
- 后台服务器接收到请求后,调度服务器应用处理请求,向浏览器返回HTTP响应(响应报文)
- 浏览器接收到响应,解析显示响应体 / 调用监视回调
查看HTTP请求响应信息:DevTools Network面板

3. API分类
3.1 REST API(restful)
- 发送请求进行CRUD哪个操作由请求方式来决定
- 同一个请求路径可以进行多个操作
- 请求方式会用到GET / POST / PUT / DELETE等
3.2 非REST API(restless)
- 请求方式不决定请求的CRUD操作(甚至可以用GET请求进行删除操作)
- 一个请求路径只对应一个操作
- 请求方式一般只有GET / POST
4. json-server搭建REST接口
-
全局安装
npm install -g json-server -
新建
db.json文件{ "posts": [ { "id": 1, "title": "json-server", "author": "typicode" } ], "comments": [ { "id": 1, "body": "some comment", "postId": 1 } ], "profile": { "name": "typicode" } } -
开启服务器(支持热更新)
json-server --watch db.json -
打开
http://localhost:3000/,可以在Resources中看到所有的接口
-
点击对应接口,可以获取对应数据
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-h2AxCkyD-1646125753799)(C:\Users\CZH0318\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220228105310624.png)]
-
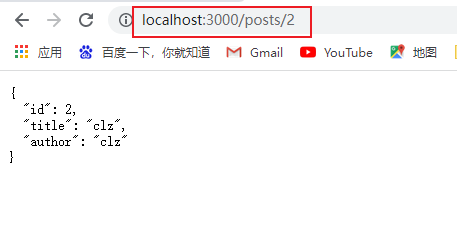
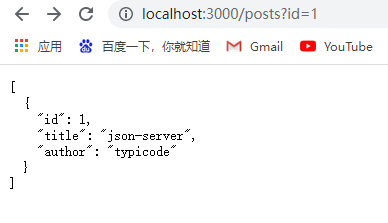
支持携带参数
-
params参数
-
query参数
-
两种参数区别:query参数是从所有的数据中筛选,所以最后是数组的形式;params参数则是特定查找的形式,所以最后是对象的形式
-
使用axios请求REST接口
上面开启的服务器不要关
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="testGet()">GET请求</button>
<button onclick="testPost()">POST请求</button>
<button onclick="testPut()">PUT请求</button>
<button onclick="testDelete()">DELETE请求</button>
<script src="./node_modules/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const testGet = () => {
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/posts', {
// params: {
// id: 2
// }
})
.then(response => {
console.log('/posts get', response.data)
})
}
const testPost = () => {
axios.post('http://localhost:3000/posts', {
title: 'czh',
author: 'czh'
})
.then((response) => {
console.log('/posts post', response.data)
})
}
const testPut = () => {
axios.put('http://localhost:3000/posts/3', {
title: 'czh...',
author: 'czh...'
})
.then((response) => {
console.log('/posts put', response.data)
})
}
const testDelete = () => {
axios.delete('http://localhost:3000/posts/3')
.then((response) => {
console.log('/posts delete', response.data)
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
XHR
1. 介绍
XMLHttpRequest(XHR)对象用于与服务器交互。通过 XMLHttpRequest 可以在不刷新页面的情况下请求特定 URL,获取数据。这允许网页在不影响用户操作的情况下,更新页面的局部内容。XMLHttpRequest在 AJAX 编程中被大量使用。
2. ajax请求与一般的http请求
-
ajax请求是一种特殊的http请求
-
对服务器端来说,没有任何请求,区别在于浏览器端(ajax请求有专门的ajax引擎帮忙发送)
-
浏览器端发送请求,只有XHR或fetch发出的才是ajax请求,其他的都不是ajax请求
-
浏览器端接收到响应(一般请求浏览器会自动更新页面,而ajax请求需要手动更新)
-
一般请求:浏览器会直接显示响应体数据,即刷新/跳转页面
-
ajax请求:浏览器不会对页面进行任何更新操作,而只是调用监视的回调函数并传入响应相关数据
-
3. 常用API
-
XMLHttpRequest():创建XHR对象的构造函数
-
status:响应状态码,如200、404等
-
statusText:响应状态文本
-
readyState:标识请求状态的只读属性
0: 初始
1: open()之后
2: send()之后
3: 请求中
4: 请求完成
-
onreadystatechange:绑定readyState改变的监听
-
responseType:指定响应数据类型
-
timeout:指定请求超时时间,默认为0,表示没有限制
-
open():初始化一个请求。参数为
(method, url [, async]) -
send(data):发送请求
-
setRequestHeader(name, value):设置请求头
-
getResponseHeader(name):获取指定名称的响应头值
封装axios
axios
function axios({
url,
method = 'GET',
params = {},
data = {}
}) {
// 返回Promise对象
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 处理method大小写
method = method.toUpperCase()
// 把请求参数拼接到url中
let queryString = ''
Object.keys(params).forEach(key => {
queryString += `${key}=${params[key]}&`
})
if (queryString) { // 有查询参数,需要把最后的&去掉
queryString = queryString.substring(0, queryString.length - 1)
url += `?${queryString}`
}
// 1. 执行异步ajax请求
// 1.1 创建xhr对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 1.2 打开连接,初始化请求
xhr.open(method, url, true) // 第三个参数表示是否异步执行操作,默认为true。如果值为false,send()方法直到收到答复前不会返回。
// 1.3 发送请求
if (method === 'GET' || method === 'DELETE') {
xhr.send()
} else if (method === 'POST' || method === 'PUT') {
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json;charset=utf-8') // 设置请求头,通知服务器请求体的格式是json
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(data)) // 发送json格式请求体参数
}
// 1.4 绑定状态的监听,监听的定义能放在后面是因为这里是异步发送请求
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState !== 4) {
return
}
const {
status, // 响应状态在[200, 300)之间代表成功,否则失败
statusText
} = xhr
// 2.1 如果请求成功,调用resolve()
if (status >= 200 && status < 300) {
const response = {
data: JSON.parse(xhr.response), // 把响应转化成JSON对象
status,
statusText
}
resolve(response)
} else {
// 2.2 如果请求失败,调用reject()
reject(new Error('request error status is ' + status))
}
}
})
}
使用:
// GET请求: 服务端获取数据
const testGet = () => {
axios({
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts',
method: 'GET',
params: {
id: 1
}
})
.then(response => {
console.log(response)
},
error => {
alert(error.message)
})
}
// POST请求: 服务端增加数据
const testPost = () => {
axios({
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts',
method: 'POST',
data: {
title: 'axios',
author: 'clz'
}
})
.then(response => {
console.log(response)
},
error => {
alert(error.message)
})
}
// PUT请求: 服务端更新数据
const testPut = () => {
axios({
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts/1',
method: 'put',
data: {
title: 'axios!!!!!',
author: 'clz!!!!!!'
}
}).then(response => {
console.log(response)
}, (error) => {
alert(error.message)
})
}
// DELETE请求: 服务端删除数据
const testDelete = () => {
axios({
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts/2',
method: 'delete'
}).then(response => {
console.log(response)
}, (error) => {
alert(error.message)
})
}
发送POST、PUT等需要修改服务器端的资源的请求时会发送OPTIONS请求,查看是否能够修改,即预请求。而GET请求不需要,因为GET请求不需要修改服务器上的资源

学习链接:尚硅谷_axios核心技术






















 1787
1787











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








