主要参考来自这里,http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-graphvis/
主要操作
- 安装graphviz,在fedora下yum install graphviz-devel。
- 从IBM的deveopworks的网页下载pvtrace, 并编译安装之,详见其说明。
- gcc -g -finstrument-functions test.c instrument.c -o test
- ./test
- pvtrace test
- dot -Tjpg graph.dot -o graph.jpg
例中test.c的代码为
#include <stdio.h>
int c(void){
int p;
p = 0;
return 0;
}
int b(void){
c();
c();
c();
printf("fd");
return 0;
}
int a(void){
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i < 200; i++){
b();
}
for(i=0; i < 1200; i++){
c();
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
a();
b();
c();
a();
c();
return 0;
}
大功告成!
思考1
多个文件可以工作么?
于是增加tr.h 和tr.c 修改test.c
tr.h
int d(void);tr.c
int d(void){
int t;
return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "tr.h"
int c(void){
int p;
p = 0;
return 0;
}
int b(void){
c();
c();
c();
printf("fd");
return 0;
}
int a(void){
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i < 200; i++){
b();
d();
}
for(i=0; i < 1200; i++){
c();
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
a();
b();
c();
a();
c();
return 0;
}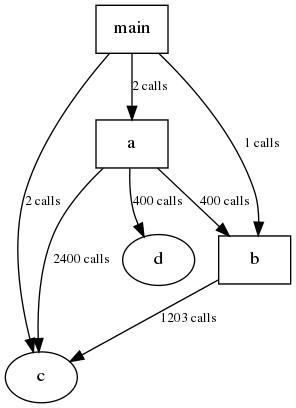
思考2
有心的读者,也许已经看出来了,在第一个例子中没有输出对库函数printf的调用。是不是就是这样的呢。特将tr.c 编译为动态库。
- gcc -shared tr.c -o libdzc.so
- gcc -g -ldzc -L. -finstrument-functions test.c instrument.c -o test
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=.:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- 之后就是重复上述过程。得到与第一个例子相同的图。








 本文详细介绍了如何在Fedora环境下安装graphviz,并通过pvtrace进行调用分析,包括安装步骤、示例代码及结果展示。此外,还探讨了多个文件工作的可能性以及如何将tr.c编译为动态库进行分析。
本文详细介绍了如何在Fedora环境下安装graphviz,并通过pvtrace进行调用分析,包括安装步骤、示例代码及结果展示。此外,还探讨了多个文件工作的可能性以及如何将tr.c编译为动态库进行分析。














 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








