Prototype design pattern is used when very similar objects frequently are required. Prototype pattern clones objects and set the changed feature. This way less resources are consumed. Think about why less resources are consumed?
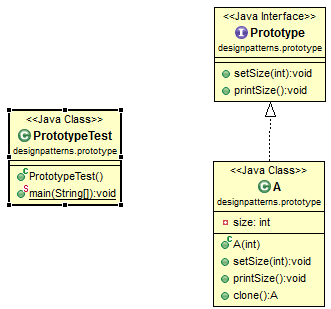
1. Prototype Pattern Class Diagram
2. Prototype Pattern Java Example
package designpatterns.prototype;
//prototype
interface Prototype {
void setSize(int x);
void printSize();
}
// a concrete class
class A implements Prototype, Cloneable {
private int size;
public A(int x) {
this.size = x;
}
@Override
public void setSize(int x) {
this.size = x;
}
@Override
public void printSize() {
System.out.println("Size: " + size);
}
@Override
public A clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (A) super.clone();
}
}
//when we need a large number of similar objects
public class PrototypeTest {
public static void main(String args[]) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
A a = new A(1);
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
Prototype temp = a.clone();
temp.setSize(i);
temp.printSize();
}
}
}3. Prototype Design Pattern Used in Java Standard Library
java.lang.Object – clone()





















 107
107

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








