菜鸟nginx源码剖析 框架篇(一) 从main函数看nginx启动流程
Author:Echo Chen(陈斌)
Email:chenb19870707@gmail.com
Blog:Blog.csdn.net/chen19870707
Date:Nov 9th, 2014
俗话说的好,牵牛要牵牛鼻子 驾车顶牛,处理复杂的东西,只要抓住重点,才能理清脉络,不至于深陷其中,不能自拔。对复杂的nginx而言,main函数就是“牛之鼻”,只要能理清main函数,就一定能理解其中的奥秘,下面我们就一起来研究一下nginx的main函数。
1.nginx的main函数解读
nginx启动显然是由main函数驱动的,main函数在在core/nginx.c文件中,其源代码解析如下,涉及到的数据结构在本节仅指出其作用,将在第二节中详细解释。
nginx main函数的流程图如下:
需要说明的:
1) 初始化错误提示列表,以errno为下标,元素就是对应的错误提示信息。
1: if (ngx_strerror_init() != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
2)获取命令行参数,保存在全局变量中,可以设置的命令行参数如下表所示:
1: if (ngx_get_options(argc, argv) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
命令行参数 作用 -h或-? 显示版本信息和help信息 -v 显示版本信息 -V 显示nginx版本信息、编译器版本和配置选项信息 -t 测试配置文件信息是否OK,即检测配置文件语法的正确性,并尝试打开配置文件中所引用到的文件 -q 在测试配置文件的时候,屏蔽无错误信息,即quiet模式 -s signal 发送信号到master进程(如stop、quit、reopen、reload) -p prefix 设置前缀路径(默认为当前目录) -c filename 设置配置文件(默认为conf/nginx.conf) -g directives 在配置文件外设置全局的指令
3)时间、正则表达式和log的初始化。
4) 初始化cycle结构,并创建内存块大小为1024的内存池,内存池创建已经在《 菜鸟nginx源码剖析数据结构篇(九) 内存池ngx_pool_t》讨论过了,nginx框架就是围绕着ngx_cycle_t结构体来控制运行的,其定义详情请参考下一节。1: ngx_time_init();2:3: (NGX_PCRE)4: ngx_regex_init();5: if6:7: ngx_pid = ngx_getpid();8:9: log = ngx_log_init(ngx_prefix);10: if (log == NULL) {11: return 1;12: }
1: ngx_memzero(&init_cycle, sizeof(ngx_cycle_t));2: init_cycle.log = log;3: ngx_cycle = &init_cycle;4:5: init_cycle.pool = ngx_create_pool(1024, log);6: if (init_cycle.pool == NULL) {7: return 1;8: }5) 将命令行参数保存到ngx_os_argv、ngx_argc以及ngx_argv这几个全局的变量中。这算是一个备份存储,方便以后master进程做热代码替换之用。
1: if (ngx_save_argv(&init_cycle, argc, argv) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
6)用命令行参数得来的全局变量初始化cycle的conf_prefix(配置文件所在路径的前缀)、prefix(nginx可执行文件所在路径)、conf_file(配置文件名)和conf_param(通过命令行-g选项指定的全局配置信息)。
1: if (ngx_process_options(&init_cycle) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
7) 根据操作系统确定一些参数,信息会被保存到一些全局变量中,如页大小ngx_pagesize, CPU cacheline1: if (ngx_os_init(log) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
8) 初始化一个做循环冗余校验的表,由此可以看出后续的循环冗余校验将采用高效的查表法1: if (ngx_crc32_table_init() != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
9)通过环境变量NGINX完成socket的继承,继承来的socket将会放到init_cycle的listening数组中。同时可以读取master进程传递的平滑升级信息等等1: if (ngx_add_inherited_sockets(&init_cycle) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
10)初始化所有模块的index信息,即对所有模块进行编号,ngx_modules数却是在自动编译的时候生成的,位于objs/ngx_modules.c文件中
1: ngx_max_module = 0;2: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {3: ngx_modules[i]->index = ngx_max_module++;4: }
11) 用上面收集的init_cycle信息初始化ngx_cycle,这行代码是nginx启动过程中最重要的一个步骤,在第3节将详细展开。
1: cycle = ngx_init_cycle(&init_cycle);2: if (cycle == NULL) {3: if (ngx_test_config) {4: ngx_log_stderr(0, "configuration file %s test failed",5: init_cycle.conf_file.data);6: }7:8: return 1;9: }
12)ccf 为ngx_core_conf_t 将在第2节给出详细定义,这个地方需要解释下,ccf->master是从配置文件中解析master_process配置项所得的值,初始化为NGX_CONF_UNSET(-1),在配置项中,如果flag类型的配置项master_process被设置为on,则其值为1,如果为off,则其值为0,ngx_process为全局变量,用于记录要采用的工作模式,未被初始化,因此初始值是0(uint型全局变量会被系统默认初始化为0),相关宏定义如下:
- #define NGX_PROCESS_SINGLE 0
- #define NGX_PROCESS_MASTER 1
- #define NGX_PROCESS_SIGNALLER 2
- #define NGX_PROCESS_WORKER 3
- #define NGX_PROCESS_HELPER 4
因此,下面的if判断语句的含义就是:用来处理一种特殊情况,即如果在配置项中未设置master_process配置项或者是设置为打开,ngx_process未被设置,采用默认值0,这个时候要采用master工作模式。因为master_process优先级高,且nginx默认采用master模式如果在配置项中设置master_process为off,那么if依据不会执行。最终nginx工作模式取决于ngx_proces的初值0,即采用单进程模式。
1: ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);2:3: if (ccf->master && ngx_process == NGX_PROCESS_SINGLE) {4: ngx_process = NGX_PROCESS_MASTER;5: }
13)初始化信号;主要完成信号处理程序的注册
1: if (ngx_init_signals(cycle->log) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
14)若无继承sockets,且设置了守护进程表示,则创建守护进程
1: if (!ngx_inherited && ccf->daemon) {2: if (ngx_daemon(cycle->log) != NGX_OK) {3: return 1;4: }5:6: ngx_daemonized = 1;7: }8:9: if (ngx_inherited) {10: ngx_daemonized = 1;11: }
15) 创建进程记录文件;(非NGX_PROCESS_MASTER=1进程,不创建该文件)
1: if (ngx_create_pidfile(&ccf->pid, cycle->log) != NGX_OK) {2: return 1;3: }
16) 进入进程主循环,根据ngx_process确定启动单进程模式还是多进程模式。
1: if (ngx_process == NGX_PROCESS_SINGLE) {2: ngx_single_process_cycle(cycle);3:4: } else {5: ngx_master_process_cycle(cycle);6: }
2.相关结构体
2.1. ngx_module_t
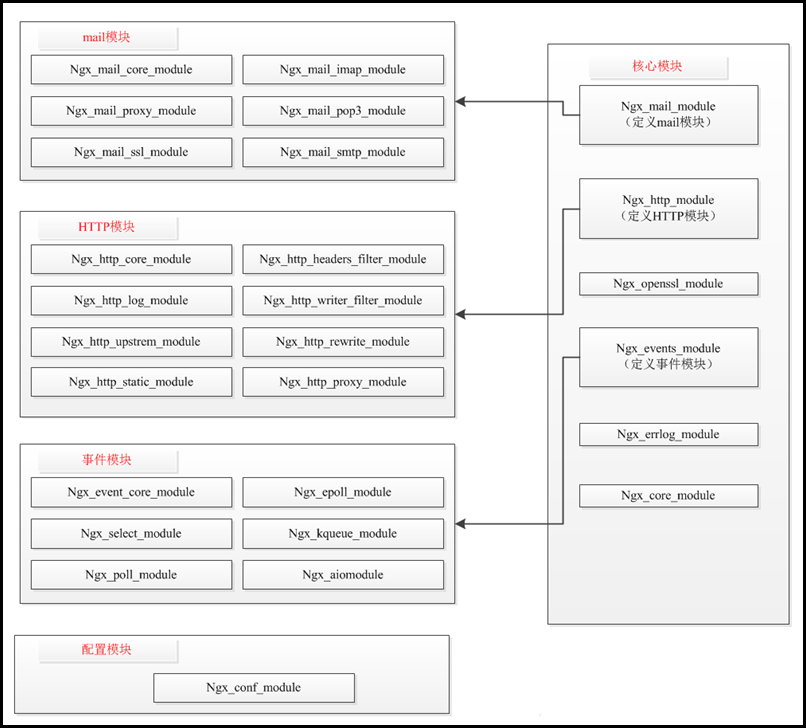
nginx中所有模块的类型都是ngx_module_t类型的,定义了模块的一些属性。nginx是完全模块化的,所有的组件都是模块,从而实现了nginx的高度松耦合。同时,我们在进行nginx模块开发时,也离不开这个数据结构。在上面初始化过程中的第10步就是初始化这个结构。
1: struct ngx_module_s {2: /**3: * 在具体类型模块(http、event等)的全局配置结构数组的下标。以http module模块为例,4: * nginx把所有的http module的config信息存放在ngx_http_conf_ctx_t类型的变量中,5: * 这个变量只有3个属性,分别是所有http module的main、srv、loc的config信息的数组。6: * 如果该模块是http module,则ctx_index是该模块的config信息(main、srv、loc)7: * 在ngx_http_conf_ctx_t中的下标。8: */9: ngx_uint_t ctx_index;10:11: /**12: * nginx把所有模块(ngx_module_t)存放到ngx_modules数组中,这个数组在nginx源码路13: * 径的objs/ngx_modules.c中,是在运行configure脚本后生成的。index属性就是该模块14: * 在ngx_modules数组中的下标。同时nginx把所有的core module的配置结构存放到ngx_cycle的15: * conf_ctx数组中,index也是该模块的配置结构在ngx_cycle->conf_ctx数组中的下标。16: */17: ngx_uint_t index;18:19: ……20:21: /**22: * 模块的上下文属性,同一类型的模块的属性是相同的,比如core module的ctx是ngx_core_module_t类型。23: * 而http module的ctx是ngx_http_moduel_t类型,event module的ctx是ngx_event_module_t类型等等。24: * 相应类型的模块由分开处理的,比如所有的http module由ngx_http_module解析处理,而所有的event module25: * 由ngx_events_module解析处理。26: */27: void *ctx;28:29: /**30: * 该模块支持的指令的数组,最后以一个空指令结尾。ngx_commond_t的分析见下文。31: */32: ngx_command_t *commands;33:34: /**35: * 模块的类型,nginx所有的模块类型:36: * NGX_CORE_MODULE37: * NGX_CONF_MODULE38: * NGX_HTTP_MODULE39: * NGX_EVENT_MODULE40: * NGX_MAIL_MODULE41: * 这些不同的类型也指定了不同的ctx。42: */43: ngx_uint_t type;44:45: /* 接下来都是一些回调函数,在nginx初始化过程的特定时间点调用 */46: ngx_int_t (*init_master)(ngx_log_t *log);47:48: /* 初始化完所有模块后调用,在ngx_int_cycle函数(ngx_cycle.c)中 */49: ngx_int_t (*init_module)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);50:51: /* 初始化完worker进程后调用,在ngx_worker_process_init函数(ngx_process_cycle.c)中 */52: ngx_int_t (*init_process)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);53: ngx_int_t (*init_thread)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);54: void (*exit_thread)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);55: void (*exit_process)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);56:57: void (*exit_master)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);58: ……59: };
模块类型(type) 上下文属性类型(ctx) NULL ngx_mail_module_t(mail/ngx_mail.h)
2.2 ngx_commond_t
ngx_commond_t描述的是模块的配置指令,也就是出现在配置文件的指令。nginx模块支持多个配置指令,所以是以ngx_commond_t数组形式存储的。这个结构在配置文件解析和模块的配置结构信息初始化时会用到。
1: struct ngx_command_s { 2: /** 3: * 指令名,与配置文件中一致 4: */ 5: ngx_str_t name; 6: 7: /** 8: * 指令的类型,以及参数的个数。这个属性有两个作用: 9: * 1. 实现只解析某个类型的指令,比如当前这个指令是event module类型的,而正在解析的是 10: * http module,所以会跳过所有不是http module类型的指令。 11: * 2. 实现指令参数个数的校验。 12: */ 13: ngx_uint_t type; 14: 15: /* 16: * 回调函数,在解析配置文件时,遇到这个指令时调用。 17: * cf: 包括配置参数信息cf->args(ngx_array_t类型),以及指令对应的模块上下文cf->ctx 18: * 在解析不同模块的指令时,这个上下文信息不同。比如在解析core module时,cf->ctx 19: * 是ngx_cycle->conf_ctx也就是所有core module的配置结构数组,而在解析http module 20: * 时cf->ctx是ngx_http_conf_ctx_t类型的,其中包含所有http module的main、srv、loc 21: * 的配置结构数组。 22: * cmd: 指令对应的ngx_command_t结构。 23: * conf:指令对应的模块的配置信息。 24: */ 25: char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf); 26: 27: /** 28: * 对http module有效,http module的配置结构信息(main、srv、loc)都存放在ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 29: * 中对应的数组,conf属性指示这个指令的配置结构是main、srv还是loc。 30: */ 31: ngx_uint_t conf; 32: 33: /** 34: * 指令对应属性在模块配置结构中的偏移量。 35: */ 36: ngx_uint_t offset; 37: 38: /** 39: * 一般是函数指针,在set回调函数中调用。 40: */ 41: void *post; 42: };
2.3 ngx_cycle_t
ngx_cycle_t是nginx中最重要的数据结构,包含了全局的配置信息、所有监听的套接字、连接池、读写事件等。ngx_cycle_t相当于nginx的一个生命周期,从nginx启动后直到向nginx发送stop或者reload信号。nginx中有一个全局变量ngx_cycle指向当前的cycle。
1: struct ngx_cycle_s { 2: /*保存着所有模块存储配置项的结构体的指针,它首先是一个数组,每个数组成员又是一个指针,这个指针指向另一个存储着指针的数组*/ 3: void ****conf_ctx; 4: //内存池 5: ngx_pool_t *pool; 6: 7: /*日志模块中提供了生成基本ngx_log_t日志对象的功能,这里的log实际上在还没有执行ngx_init_cycle方法前,也就是还没有解析配置前,如果有信息输出日志 8: 就会暂时使用log对象,它会输出到屏幕。在调用ngx_int_cycle后,将会根据nginx.comfg配置文件中的配置项构造出正确的日志,此时会对log进行重新赋值*/ 9: ngx_log_t *log; 10: /*由nginx.conf配置文件读取到日志文件路径后,将开始初始化error_log日志文件,由于log对象还在用于输出日志屏幕,这时会用new_log暂时性地替代log日志 11: 待初始化成功后,会用new_log的地址覆盖上面的log指针*/ 12: ngx_log_t new_log; 13: 14: ngx_uint_t log_use_stderr; /* unsigned log_use_stderr:1; */ 15: //files文件数组的个数 16: ngx_uint_t files_n; 17: /*对于poll、rtsig这样的事件模块,会以有效文件句柄来预先建立这些ngx_connection_t结构体,以加速时间的收集分发,这时files就会保存所有ngx_connection_t 18: 的指针成员数组,files_n就是指针的总数,而文件句柄的值用于访问files数组成员*/ 19: ngx_connection_t **files; 20: //可用连接池 21: ngx_connection_t *free_connections; 22: //可用连接池中连接总数 23: ngx_uint_t free_connection_n; 24: 25: /*双向链表容器,元素是ngx_connection_t结构体,表示可重复使用的连接队列*/ 26: ngx_queue_t reusable_connections_queue; 27: //动态数组,每个数组元素存储着ngx_listening_t成员,表示监听端口及相关参数 28: ngx_array_t listening; 29: //动态数组,存储着nginx所有要操作的目录,如果目录不存在,则试图创建,创建失败会导致nginx启动失败 30: ngx_array_t paths; 31: /*单链表容器,元素类型是nginx_open_file_t,表示已打开的所有文件。*/ 32: ngx_list_t open_files; 33: /*单链表容器,元素是ngx_shm_zone_t,每个元素表示一块共享内存*/ 34: ngx_list_t shared_memory; 35: //当前连接对象的总数 36: ngx_uint_t connection_n; 37: 38: //指向当前进程中所有连接对象 39: ngx_connection_t *connections; 40: //指向当前进程中的所有读事件对象,connection_n同时表示所有读事件总数 41: ngx_event_t *read_events; 42: //指向当前进程中的所有写事件对象,connection_n同时表示所有写事件总数 43: ngx_event_t *write_events; 44: //旧的ngx_cycle_t对象用于引用上一个ngx_cycle_t对象中的成员 45: ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle; 46: 47: ngx_str_t conf_file; // 配置文件名 48: ngx_str_t conf_param; // 由命令行-g提供配置参数 49: ngx_str_t conf_prefix; // 配置前缀 50: ngx_str_t prefix; // nginx所在路径 51: ngx_str_t lock_file; 52: ngx_str_t hostname; // 主机名 53: };3.ngx_init_cycle函数
ngx_init_cycle 初始化步骤 有以下操作,这里涉及到ngx_list_t和ngx_array_t,如果有不懂的同学请参考我之前对于这两个结构分析的文章,同时这个函数比较复杂,希望大家耐心点。
1) 更新时区和时间。
1: ngx_timezone_update();2:3: /* force localtime update with a new timezone */4:5: tp = ngx_timeofday();6: tp->sec = 0;7:8: ngx_time_update();
2) 创建内存池,并从内存池中创建ngx_cycle_t结构,然后给cycle日志和old_cycle赋值
1: log = old_cycle->log;2:3: pool = ngx_create_pool(NGX_CYCLE_POOL_SIZE, log);4: if (pool == NULL) {5: return NULL;6: }7: pool->log = log;8:9: cycle = ngx_pcalloc(pool, sizeof(ngx_cycle_t));10: if (cycle == NULL) {11: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);12: return NULL;13: }14:15: cycle->pool = pool;16: cycle->log = log;17: cycle->old_cycle = old_cycle;
3)根据old_cycle初始化cycle中的conf_file、conf_prefix、prefix和conf_param。
1: cycle->conf_prefix.len = old_cycle->conf_prefix.len;2: cycle->conf_prefix.data = ngx_pstrdup(pool, &old_cycle->conf_prefix);3: if (cycle->conf_prefix.data == NULL) {4: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);5: return NULL;6: }7:8: cycle->prefix.len = old_cycle->prefix.len;9: cycle->prefix.data = ngx_pstrdup(pool, &old_cycle->prefix);10: if (cycle->prefix.data == NULL) {11: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);12: return NULL;13: }14:15: cycle->conf_file.len = old_cycle->conf_file.len;16: cycle->conf_file.data = ngx_pnalloc(pool, old_cycle->conf_file.len + 1);17: if (cycle->conf_file.data == NULL) {18: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);19: return NULL;20: }21: ngx_cpystrn(cycle->conf_file.data, old_cycle->conf_file.data,22: old_cycle->conf_file.len + 1);23:24: cycle->conf_param.len = old_cycle->conf_param.len;25: cycle->conf_param.data = ngx_pstrdup(pool, &old_cycle->conf_param);26: if (cycle->conf_param.data == NULL) {27: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);28: return NULL;29: }
4)初始化pathes,pathes是一个ngx_array_t结构
1: n = old_cycle->paths.nelts ? old_cycle->paths.nelts : 10;2:3: cycle->paths.elts = ngx_pcalloc(pool, n * sizeof(ngx_path_t *));4: if (cycle->paths.elts == NULL) {5: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);6: return NULL;7: }8:9: cycle->paths.nelts = 0;10: cycle->paths.size = sizeof(ngx_path_t *);11: cycle->paths.nalloc = n;12: cycle->paths.pool = pool;
5) 根据old_cycle的open_files的大小,初始化openfiles , openfiles为ngx_list_t
1: if (old_cycle->open_files.part.nelts) {2: n = old_cycle->open_files.part.nelts;3: for (part = old_cycle->open_files.part.next; part; part = part->next) {4: n += part->nelts;5: }6:7: } else {8: n = 20;9: }10:11: if (ngx_list_init(&cycle->open_files, pool, n, sizeof(ngx_open_file_t))12: != NGX_OK)13: {14: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);15: return NULL;16: }
6) 根据old_cycle的shared_memory的大小初始化shared_memory(ngx_list_t)。1: if (old_cycle->shared_memory.part.nelts) {2: n = old_cycle->shared_memory.part.nelts;3: for (part = old_cycle->shared_memory.part.next; part; part = part->next)4: {5: n += part->nelts;6: }7:8: } else {9: n = 1;10: }11:12: if (ngx_list_init(&cycle->shared_memory, pool, n, sizeof(ngx_shm_zone_t))13: != NGX_OK)14: {15: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);16: return NULL;17: }
7) 根据old_cycle的listenning大小初始化listening(ngx_array_t)。1: n = old_cycle->listening.nelts ? old_cycle->listening.nelts : 10;2:3: cycle->listening.elts = ngx_pcalloc(pool, n * sizeof(ngx_listening_t));4: if (cycle->listening.elts == NULL) {5: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);6: return NULL;7: }8:9: cycle->listening.nelts = 0;10: cycle->listening.size = sizeof(ngx_listening_t);11: cycle->listening.nalloc = n;12: cycle->listening.pool = pool;
8) 初始化conf_ctx(void ****)数组,大小是ngx_max_module,用于存储所有core module的配置结构信息。1: cycle->conf_ctx = ngx_pcalloc(pool, ngx_max_module * sizeof(void *));2: if (cycle->conf_ctx == NULL) {3: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);4: return NULL;5: }
9) 调用系统调用gethostname获取主机名,初始化hostname。
1: if (gethostname(hostname, NGX_MAXHOSTNAMELEN) == -1) {2: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno, "gethostname() failed");3: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);4: return NULL;5: }6:7: /* on Linux gethostname() silently truncates name that does not fit */8:9: hostname[NGX_MAXHOSTNAMELEN - 1] = '\0';10: cycle->hostname.len = ngx_strlen(hostname);11:12: cycle->hostname.data = ngx_pnalloc(pool, cycle->hostname.len);13: if (cycle->hostname.data == NULL) {14: ngx_destroy_pool(pool);15: return NULL;16: }17:18: ngx_strlow(cycle->hostname.data, (u_char *) hostname, cycle->hostname.len);
10)调用所有core module的create_conf回调函数创建该core module的配置信息结构,并且更新cycle->conf_ctx数组,
nginx的core module主要有:
ngx_core_module(core/nginx.c)
ngx_http_module(http/ngx_http.c)
ngx_events_module(event/ngx_event.c)
ngx_errlog_module(core/ngx_log.c)
ngx_mail_module(mail/ngx_mail.c)
ngx_openssl_module(event/ngx_event_openssl.c)
ngx_google_perftools_module(misc/ngx_google_perftools_module.c)
只有ngx_core_module和ngx_google_perftools_module两个模块有定义create_conf,而ngx_google_perftools_module仅用于性能测试,所以真正使用时只有ngx_core_module有create_conf回调函数。这个会调用函数会创建ngx_core_conf_t结构,用于存储整个配置文件main scope范围内的信息,比如worker_processes,worker_cpu_affinity等。
1: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) { 2: if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) { 3: continue; 4: } 5: 6: module = ngx_modules[i]->ctx; 7: 8: if (module->create_conf) { 9: rv = module->create_conf(cycle); 10: if (rv == NULL) { 11: ngx_destroy_pool(pool); 12: return NULL; 13: } 14: cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index] = rv; 15: } 16: }11)初始化ngx_conf_t,用于解析配置文件并保存解析出来的信息。args是配置文件中指令的信息的数组,args[0]是指令名,args[1] - args[n]是指令的参数,参数个数需要根据ngx_commond_t的type属性做校验。ngx_conf_t中的module_type和cmd_type用于控制解析什么类型的指令,module_type表示只解析该类型模块包含的指令,cmd_type表示将要解析的指令的类型,也就是说只有符合module_type和cmd_type的指令才会被解析。比如module_type取NGX_HTTP_MODULE,而cmd_type取NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF,那么在一次配置文件解析中,只会对http module的server块的指令进行解析。
1: ngx_memzero(&conf, sizeof(ngx_conf_t)); 2: /* STUB: init array ? */ 3: conf.args = ngx_array_create(pool, 10, sizeof(ngx_str_t)); 4: if (conf.args == NULL) { 5: ngx_destroy_pool(pool); 6: return NULL; 7: } 8: 9: conf.temp_pool = ngx_create_pool(NGX_CYCLE_POOL_SIZE, log); 10: if (conf.temp_pool == NULL) { 11: ngx_destroy_pool(pool); 12: return NULL; 13: } 14: 15: 16: conf.ctx = cycle->conf_ctx; 17: conf.cycle = cycle; 18: conf.pool = pool; 19: conf.log = log; 20: conf.module_type = NGX_CORE_MODULE; 21: conf.cmd_type = NGX_MAIN_CONF;
12) 对通过nginx -g xxx 设置的全局配置指令初始化、解析。
1: if (ngx_conf_param(&conf) != NGX_CONF_OK) { 2: environ = senv; 3: ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf); 4: return NULL; 5: }
13)解析配置文件。配置文件的解析类似一棵树的遍历,nginx中的指令分为块指令和普通指令,每个块指令对应一棵子树,比如http块和event块。由这些块指令负责调用ngx_conf_parse函数解析块内部的指令。配置文件的具体分析会另开一片文章,这里忽略这些细节。在ngx_conf_parse函数返回后,整个配置文件解析完毕,所有模块的指令已经初始化,也就意味着所有模块基本上都初始化完,实际上ngx_conf_parse函数后面隐藏了大量的信息,包括http模块的初始化和事件模块的初始化。关于http的初始化我们后面再详细描述,这里接着讲述ngx_init_cycle。
1: if (ngx_conf_parse(&conf, &cycle->conf_file) != NGX_CONF_OK) { 2: environ = senv; 3: ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf); 4: return NULL; 5: }
14)初始化所有core module模块的config结构调用ngx_core_module_t的init_conf 。在所有core module中,只有ngx_core_module有init_conf回调,用于对ngx_core_conf_t中没有配置的字段设置默认值。
1: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) { 2: if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) { 3: continue; 4: } 5: 6: module = ngx_modules[i]->ctx; 7: 8: if (module->init_conf) { 9: if (module->init_conf(cycle, cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index]) 10: == NGX_CONF_ERROR) 11: { 12: environ = senv; 13: ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf); 14: return NULL; 15: } 16: } 17: }
15) 创建nginx的pid文件。创建所有的文件路径、打开文件描述符以及创建共享内存。
1: if (ngx_test_config) { 2: 3: if (ngx_create_pidfile(&ccf->pid, log) != NGX_OK) { 4: goto failed; 5: } 6: 7: } else if (!ngx_is_init_cycle(old_cycle)) { 8: 9: /* 10: * we do not create the pid file in the first ngx_init_cycle() call 11: * because we need to write the demonized process pid 12: */ 13: 14: old_ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(old_cycle->conf_ctx, 15: ngx_core_module); 16: if (ccf->pid.len != old_ccf->pid.len 17: || ngx_strcmp(ccf->pid.data, old_ccf->pid.data) != 0) 18: { 19: /* new pid file name */ 20: 21: if (ngx_create_pidfile(&ccf->pid, log) != NGX_OK) { 22: goto failed; 23: } 24: 25: ngx_delete_pidfile(old_cycle); 26: } 27: } 28: 29: 30: if (ngx_test_lockfile(cycle->lock_file.data, log) != NGX_OK) { 31: goto failed; 32: } 33: 34: 35: if (ngx_create_paths(cycle, ccf->user) != NGX_OK) { 36: goto failed; 37: } 38: 39: 40: if (ngx_log_open_default(cycle) != NGX_OK) { 41: goto failed; 42: } 43: 44: /* open the new files */ 45: 46: part = &cycle->open_files.part; 47: file = part->elts; 48: 49: for (i = 0; /* void */ ; i++) { 50: 51: if (i >= part->nelts) { 52: if (part->next == NULL) { 53: break; 54: } 55: part = part->next; 56: file = part->elts; 57: i = 0; 58: } 59: 60: if (file[i].name.len == 0) { 61: continue; 62: } 63: 64: file[i].fd = ngx_open_file(file[i].name.data, 65: NGX_FILE_APPEND, 66: NGX_FILE_CREATE_OR_OPEN, 67: NGX_FILE_DEFAULT_ACCESS); 68: 69: ngx_log_debug3(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_CORE, log, 0, 70: "log: %p %d \"%s\"", 71: &file[i], file[i].fd, file[i].name.data); 72: 73: if (file[i].fd == NGX_INVALID_FILE) { 74: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno, 75: ngx_open_file_n " \"%s\" failed", 76: file[i].name.data); 77: goto failed; 78: } 79: 80: !(NGX_WIN32) 81: if (fcntl(file[i].fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC) == -1) { 82: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno, 83: "fcntl(FD_CLOEXEC) \"%s\" failed", 84: file[i].name.data); 85: goto failed; 86: } 87: dif 88: } 89: 90: cycle->log = &cycle->new_log; 91: pool->log = &cycle->new_log; 92: 93: 94: /* create shared memory */ 95: 96: part = &cycle->shared_memory.part; 97: shm_zone = part->elts; 98: 99: for (i = 0; /* void */ ; i++) { 100: 101: if (i >= part->nelts) { 102: if (part->next == NULL) { 103: break; 104: } 105: part = part->next; 106: shm_zone = part->elts; 107: i = 0; 108: } 109: 110: if (shm_zone[i].shm.size == 0) { 111: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, 0, 112: "zero size shared memory zone \"%V\"", 113: &shm_zone[i].shm.name); 114: goto failed; 115: } 116: 117: shm_zone[i].shm.log = cycle->log; 118: 119: opart = &old_cycle->shared_memory.part; 120: oshm_zone = opart->elts; 121: 122: for (n = 0; /* void */ ; n++) { 123: 124: if (n >= opart->nelts) { 125: if (opart->next == NULL) { 126: break; 127: } 128: opart = opart->next; 129: oshm_zone = opart->elts; 130: n = 0; 131: } 132: 133: if (shm_zone[i].shm.name.len != oshm_zone[n].shm.name.len) { 134: continue; 135: } 136: 137: if (ngx_strncmp(shm_zone[i].shm.name.data, 138: oshm_zone[n].shm.name.data, 139: shm_zone[i].shm.name.len) 140: != 0) 141: { 142: continue; 143: } 144: 145: if (shm_zone[i].tag == oshm_zone[n].tag 146: && shm_zone[i].shm.size == oshm_zone[n].shm.size) 147: { 148: shm_zone[i].shm.addr = oshm_zone[n].shm.addr; 149: 150: if (shm_zone[i].init(&shm_zone[i], oshm_zone[n].data) 151: != NGX_OK) 152: { 153: goto failed; 154: } 155: 156: goto shm_zone_found; 157: } 158: 159: ngx_shm_free(&oshm_zone[n].shm); 160: 161: break; 162: } 163: 164: if (ngx_shm_alloc(&shm_zone[i].shm) != NGX_OK) { 165: goto failed; 166: } 167: 168: if (ngx_init_zone_pool(cycle, &shm_zone[i]) != NGX_OK) { 169: goto failed; 170: } 171: 172: if (shm_zone[i].init(&shm_zone[i], NULL) != NGX_OK) { 173: goto failed; 174: } 175: 176: shm_zone_found: 177: 178: continue; 179: }16)处理监听socket的,如果监听地址相同的话,则把新、旧cycle的监听socket合并
1: if (old_cycle->listening.nelts) {2: ls = old_cycle->listening.elts;3: for (i = 0; i < old_cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {4: ls[i].remain = 0;5: }6:7: nls = cycle->listening.elts;8: for (n = 0; n < cycle->listening.nelts; n++) {9:10: for (i = 0; i < old_cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {11: if (ls[i].ignore) {12: continue;13: }14:15: if (ngx_cmp_sockaddr(nls[n].sockaddr, nls[n].socklen,16: ls[i].sockaddr, ls[i].socklen, 1)17: == NGX_OK)18: {19: nls[n].fd = ls[i].fd;20: nls[n].previous = &ls[i];21: ls[i].remain = 1;22:23: if (ls[i].backlog != nls[n].backlog) {24: nls[n].listen = 1;25: }26: break;27: }28: }29:30: if (nls[n].fd == (ngx_socket_t) -1) {31: nls[n].open = 1;32:33: }34: }35:36: } else {37: ls = cycle->listening.elts;38: for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {39: ls[i].open = 1;40:41: }42: }
17)打开所有的监听socket,具体过程和用socket编程时是一样的,调用socket创建套接字 -> 调用setsockopt设置成可重用socket -> 设置成非阻塞socket -> 调用bind绑定要监听的socket地址 -> 调用listen转化成监听socket。
1: if (ngx_open_listening_sockets(cycle) != NGX_OK) {2: goto failed;3: }
18) 根据cycle配置所有的监听socket,包括设置监听socket的接收缓冲区大小、发送缓冲区大小以及accept filter等
1: if (!ngx_test_config) {2: ngx_configure_listening_sockets(cycle);3: }
-19) 调用所有模块的init_module回调函数,进行模块的初始化动作。
1: for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {2: if (ngx_modules[i]->init_module) {3: if (ngx_modules[i]->init_module(cycle) != NGX_OK) {4: /* fatal */5: exit(1);6: }7: }8: }20) ngx_init_cycle最后部分代码主要就是释放多余的资源,包括关闭共享内存、监听socket已经打开的文件等,然后ngx_init_cycle正常返回
1: /* close and delete stuff that lefts from an old cycle */2:3: /* free the unnecessary shared memory */4:5: opart = &old_cycle->shared_memory.part;6: oshm_zone = opart->elts;7:8: for (i = 0; /* void */ ; i++) {9:10: if (i >= opart->nelts) {11: if (opart->next == NULL) {12: goto old_shm_zone_done;13: }14: opart = opart->next;15: oshm_zone = opart->elts;16: i = 0;17: }18:19: part = &cycle->shared_memory.part;20: shm_zone = part->elts;21:22: for (n = 0; /* void */ ; n++) {23:24: if (n >= part->nelts) {25: if (part->next == NULL) {26: break;27: }28: part = part->next;29: shm_zone = part->elts;30: n = 0;31: }32:33: if (oshm_zone[i].shm.name.len == shm_zone[n].shm.name.len34: && ngx_strncmp(oshm_zone[i].shm.name.data,35: shm_zone[n].shm.name.data,36: oshm_zone[i].shm.name.len)37: == 0)38: {39: goto live_shm_zone;40: }41: }42:43: ngx_shm_free(&oshm_zone[i].shm);44:45: live_shm_zone:46:47: continue;48: }49:50: ld_shm_zone_done:51:52:53: /* close the unnecessary listening sockets */54:55: ls = old_cycle->listening.elts;56: for (i = 0; i < old_cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {57:58: if (ls[i].remain || ls[i].fd == (ngx_socket_t) -1) {59: continue;60: }61:62: if (ngx_close_socket(ls[i].fd) == -1) {63: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_socket_errno,64: ngx_close_socket_n " listening socket on %V failed",65: &ls[i].addr_text);66: }67: }68:69:70: /* close the unnecessary open files */71:72: part = &old_cycle->open_files.part;73: file = part->elts;74:75: for (i = 0; /* void */ ; i++) {76:77: if (i >= part->nelts) {78: if (part->next == NULL) {79: break;80: }81: part = part->next;82: file = part->elts;83: i = 0;84: }85:86: if (file[i].fd == NGX_INVALID_FILE || file[i].fd == ngx_stderr) {87: continue;88: }89:90: if (ngx_close_file(file[i].fd) == NGX_FILE_ERROR) {91: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno,92: ngx_close_file_n " \"%s\" failed",93: file[i].name.data);94: }95: }96:97: ngx_destroy_pool(conf.temp_pool);98:99: if (ngx_process == NGX_PROCESS_MASTER || ngx_is_init_cycle(old_cycle)) {100:101: /*102: * perl_destruct() frees environ, if it is not the same as it was at103: * perl_construct() time, therefore we save the previous cycle104: * environment before ngx_conf_parse() where it will be changed.105: */106:107: env = environ;108: environ = senv;109:110: ngx_destroy_pool(old_cycle->pool);111: cycle->old_cycle = NULL;112:113: environ = env;114:115: return cycle;116: }117:118:119: if (ngx_temp_pool == NULL) {120: ngx_temp_pool = ngx_create_pool(128, cycle->log);121: if (ngx_temp_pool == NULL) {122: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cycle->log, 0,123: "could not create ngx_temp_pool");124: exit(1);125: }126:127: n = 10;128: ngx_old_cycles.elts = ngx_pcalloc(ngx_temp_pool,129: n * sizeof(ngx_cycle_t *));130: if (ngx_old_cycles.elts == NULL) {131: exit(1);132: }133: ngx_old_cycles.nelts = 0;134: ngx_old_cycles.size = sizeof(ngx_cycle_t *);135: ngx_old_cycles.nalloc = n;136: ngx_old_cycles.pool = ngx_temp_pool;137:138: ngx_cleaner_event.handler = ngx_clean_old_cycles;139: ngx_cleaner_event.log = cycle->log;140: ngx_cleaner_event.data = &dumb;141: dumb.fd = (ngx_socket_t) -1;142: }143:144: ngx_temp_pool->log = cycle->log;145:146: old = ngx_array_push(&ngx_old_cycles);147: if (old == NULL) {148: exit(1);149: }150: *old = old_cycle;151:152: if (!ngx_cleaner_event.timer_set) {153: ngx_add_timer(&ngx_cleaner_event, 30000);154: ngx_cleaner_event.timer_set = 1;155: }156:157: return cycle;158:159:160: ailed:161:162: if (!ngx_is_init_cycle(old_cycle)) {163: old_ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(old_cycle->conf_ctx,164: ngx_core_module);165: if (old_ccf->environment) {166: environ = old_ccf->environment;167: }168: }169:170: /* rollback the new cycle configuration */171:172: part = &cycle->open_files.part;173: file = part->elts;174:175: for (i = 0; /* void */ ; i++) {176:177: if (i >= part->nelts) {178: if (part->next == NULL) {179: break;180: }181: part = part->next;182: file = part->elts;183: i = 0;184: }185:186: if (file[i].fd == NGX_INVALID_FILE || file[i].fd == ngx_stderr) {187: continue;188: }189:190: if (ngx_close_file(file[i].fd) == NGX_FILE_ERROR) {191: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_errno,192: ngx_close_file_n " \"%s\" failed",193: file[i].name.data);194: }195: }196:197: if (ngx_test_config) {198: ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);199: return NULL;200: }201:202: ls = cycle->listening.elts;203: for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {204: if (ls[i].fd == (ngx_socket_t) -1 || !ls[i].open) {205: continue;206: }207:208: if (ngx_close_socket(ls[i].fd) == -1) {209: ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, log, ngx_socket_errno,210: ngx_close_socket_n " %V failed",211: &ls[i].addr_text);212: }213: }214:215: ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
Echo Chen:Blog.csdn.net/chen19870707
-






















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








