当我们的项目代码过大时,编译运行时会报Unable to execute dex: method ID not in[0, 0xffff]: 65536)错误。当出现这个错误时说明你本身自己的工程代码中含有的太多的方法,或者你的工程lib文件夹下引用的第三方插件jar包有太多的方法,这两者的方法加起来已经超过了65536这个数目。而谷歌规定单个dex文件中的方法不能超过65536的限制。
那么这个时候,我们就需要分包处理解决。一般情况下的解决方案就是把整个项目工程包括jar,区分开来分解成两个dex文件。
网上很多这些解决方案,有的把项目代码中比较独立的模块打包成jar文件,然后利用dx工具将打包的jar文件转成dex文件的jar,然后将其放到SD卡中去动态加载。这种方案是不符合我们的需求的。
那么问题来了,该如何更好的去拆分Dex文件,绕过谷歌规定的65536呢?其实,网上已经有些牛人帮我们提出了很多方案了,尤其是在github上。特别是mmin18提出的方案,githut地址如下:
https://github.com/mmin18/Dex65536
该解决方案的原理差不多是这样:
1.在工程目录下创建custom_rules.xml文件,修改编译策略。将工程lib的文件中含有的第三方插件jar包全部打包成libs.apk,然后将其作为编译运行时的第二个dex文件。
2.最后通过ant命令执行操作,运行整个工程或签名加密打包整个工程。
怎么样,通过上面的介绍是不是觉得很简单,其实不然,如果要真正的去了解整个原理,还是很有难度,首先你得对custom_rules.xml文件的相关配置和android工程的编译策略非常熟悉。不过,这里我们不用管它,既然牛人已经帮我们写好了,那我们只要知道怎么去用到我们的项目中就行了。
接下来就是怎么去用到我们的项目代码中了(当然,感兴趣的同志可以去研究研究它的实现原理)。
custom_rules.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project name="custom_rules">
<dirname property="custom_rules.basedir" file="${ant.file.custom_rules}"/>
<path id="pathtool.antlibs">
<pathelement path="${custom_rules.basedir}/pathtool.jar" />
</path>
<taskdef resource="anttasks.properties" classpathref="pathtool.antlibs"/>
<target name="-post-compile">
<!--
libs="libs/" means pack all .jar library into the secondary dex.
if you to pack specific .jar into the secondary dex, change it to
libs="/android-support-v4.jar,/10k-methods.jar"
-->
<pathtool
libs="libs/"
refid="project.all.jars.path"
excludeRefid="out.dex.jar.input.ref"
includeRefid="out.dex.jar.assets" />
<mkdir dir="${out.absolute.dir}/libs.apk"/>
<dex executable="${dx}"
output="${out.absolute.dir}/libs.apk/classes.dex"
dexedlibs="${out.absolute.dir}/libs.apk"
nolocals="true"
forceJumbo="false"
disableDexMerger="false">
<path refid="out.dex.jar.assets" />
</dex>
<zip destfile="${out.absolute.dir}/libs-unaligned.apk"
basedir="${out.absolute.dir}/libs.apk"
includes="classes.dex"
update="true"/>
<zipalign
executable="${zipalign}"
input="${out.absolute.dir}/libs-unaligned.apk"
output="${asset.absolute.dir}/libs.apk"
verbose="${verbose}" />
</target>
<target name="-post-package">
<delete file="${asset.absolute.dir}/libs.apk"/>
</target>
<target name="run">
<xpath input="${manifest.abs.file}" expression="/manifest/@package" output="manifest.package" />
<xpath input="${manifest.abs.file}" expression="/manifest/application/activity[intent-filter/action/@android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" and intent-filter/category/@android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"]/@android:name"
output="manifest.activity"/>
<echo>component: ${manifest.package}/${manifest.activity}</echo>
<exec executable="${adb}" failοnerrοr="false">
<arg line="${adb.device.arg}" />
<arg value="shell" />
<arg value="am" />
<arg value="force-stop" />
<arg value="${manifest.package}" />
</exec>
<exec executable="${adb}" failοnerrοr="true">
<arg line="${adb.device.arg}" />
<arg value="shell" />
<arg value="am" />
<arg value="start" />
<arg value="-n" />
<arg value="${manifest.package}/${manifest.activity}" />
<arg value="-W" />
</exec>
</target>
<target name="rund">
<xpath input="${manifest.abs.file}" expression="/manifest/@package" output="manifest.package" />
<xpath input="${manifest.abs.file}" expression="/manifest/application/activity[intent-filter/action/@android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" and intent-filter/category/@android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"]/@android:name"
output="manifest.activity"/>
<echo>component: ${manifest.package}/${manifest.activity}</echo>
<echo>Debug package ${mainfest.package}. You should prepare your eclipse.</echo>
<echo>Keep your project open, and if you get a red bug icon in DDMS, you</echo>
<echo>should stop and manually debug it once.</echo>
<exec executable="${adb}" failοnerrοr="false">
<arg line="${adb.device.arg}" />
<arg value="shell" />
<arg value="am" />
<arg value="force-stop" />
<arg value="${manifest.package}" />
</exec>
<exec executable="${adb}" failοnerrοr="true">
<arg line="${adb.device.arg}" />
<arg value="shell" />
<arg value="am" />
<arg value="set-debug-app" />
<arg value="${manifest.package}" />
</exec>
<exec executable="${adb}" failοnerrοr="true">
<arg line="${adb.device.arg}" />
<arg value="shell" />
<arg value="am" />
<arg value="start" />
<arg value="-n" />
<arg value="${manifest.package}/${manifest.activity}" />
<arg value="-W" />
<arg value="-D" />
</exec>
</target>
<target name="help">
<!-- displays starts at col 13
|13 80| -->
<echo>Android Ant Build. Available targets:</echo>
<echo> help: Displays this help.</echo>
<echo> clean: Removes output files created by other targets.</echo>
<echo> This calls the same target on all dependent projects.</echo>
<echo> Use 'ant nodeps clean' to only clean the local project</echo>
<echo> debug: Builds the application and signs it with a debug key.</echo>
<echo> The 'nodeps' target can be used to only build the</echo>
<echo> current project and ignore the libraries using:</echo>
<echo> 'ant nodeps debug'</echo>
<echo> release: Builds the application. The generated apk file must be</echo>
<echo> signed before it is published.</echo>
<echo> The 'nodeps' target can be used to only build the</echo>
<echo> current project and ignore the libraries using:</echo>
<echo> 'ant nodeps release'</echo>
<echo> instrument:Builds an instrumented package and signs it with a</echo>
<echo> debug key.</echo>
<echo> test: Runs the tests. Project must be a test project and</echo>
<echo> must have been built. Typical usage would be:</echo>
<echo> ant [emma] debug install test</echo>
<echo> emma: Transiently enables code coverage for subsequent</echo>
<echo> targets.</echo>
<echo> install: Installs the newly build package. Must either be used</echo>
<echo> in conjunction with a build target (debug/release/</echo>
<echo> instrument) or with the proper suffix indicating</echo>
<echo> which package to install (see below).</echo>
<echo> If the application was previously installed, the</echo>
<echo> application is reinstalled if the signature matches.</echo>
<echo> installd: Installs (only) the debug package.</echo>
<echo> installr: Installs (only) the release package.</echo>
<echo> installi: Installs (only) the instrumented package.</echo>
<echo> installt: Installs (only) the test and tested packages (unless</echo>
<echo> nodeps is used as well.</echo>
<echo> uninstall: Uninstalls the application from a running emulator or</echo>
<echo> device. Also uninstall tested package if applicable</echo>
<echo> unless 'nodeps' is used as well.</echo>
<echo></echo>
<echo>Custom targets:</echo>
<echo> run: Run your application.</echo>
<echo> rund: Run and attach to debugger.</echo>
<echo></echo>
<echo>--> Example:</echo>
<echo>--> ant debug install run</echo>
<echo>--> ant rund</echo>
</target>
</project>
一.配置和运行工程步骤如下:
1. 竟然要用到ant,首先就要先下载ant和配置ant环境,下载链接地址为:http://ant.apache.org/bindownload.cgi。下载好apache-ant-1.9.4-bin.zip包后,解压到指定目录。然后配置环境变量,创建变量名为ANT_HOME,值为ant文件对应的路径,比如我的是ANT_HOME = E:\apache-ant-1.9.4-bin\apache-ant-1.9.4。然后在Path变量的值中追加%ANT_HOME%/bin;%ANT_HOME%/lib。这样ant环境变量就配置好了。
2. 接下来就是拷贝文件custom_rules.xml和pathtool.jar到我们项目的根目录下。
3. 然后就在我们的项目运行之前添加代码执行去加载第二个dex文件,下面的dexTool方法就是执行加载第二个dex文件的功能代码,直接copy到我们的自定义application类中就行了,代码如下:
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
privatevoid dexTool() {
FiledexDir = new File(getFilesDir(), "dlibs");
dexDir.mkdir();
FiledexFile = new File(dexDir, "libs.apk");
FiledexOpt = getCacheDir();
try{
InputStreamins = getAssets().open("libs.apk");
if(dexFile.length() != ins.available()) {
FileOutputStreamfos = new FileOutputStream(dexFile);
byte[]buf = new byte[4096];
intl;
while((l = ins.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf,0, l);
}
fos.close();
}
ins.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
thrownew RuntimeException(e);
}
ClassLoadercl = getClassLoader();
ApplicationInfoai = getApplicationInfo();
StringnativeLibraryDir = null;
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT > 8) {
nativeLibraryDir= ai.nativeLibraryDir;
}else {
nativeLibraryDir= "/data/data/" + ai.packageName + "/lib/";
}
DexClassLoaderdcl = new DexClassLoader(dexFile.getAbsolutePath(),
dexOpt.getAbsolutePath(),nativeLibraryDir, cl.getParent());
try{
Fieldf = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredField("parent");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(cl,dcl);
}catch (Exception e) {
thrownew RuntimeException(e);
}
}接着在自定义application类的onCreate方法中调用dexTool。
4. 自动生成build.xml文件。打开命令窗口,进入到工程的根目录下,输入如下命令android update project -p . 在输入该命令之前,要确保你配置的sdk/tools目录和sdk/tools/lib文件夹中有android.bat和find_java.bat文件。
5. 然后就是运行该工程了。输入命令ant clean debug install run,在输入该命令之前要确保你的ant环境配置没有问题。
二.签名混淆代码:
上面的运行apk并没有通过代码混淆和签名,一般情况下我们需要生成一个经过代码混淆和签名的apk,那么ant环境下怎么去配置才能生成代码混淆和签名的apk呢。接下来将进行说明。
1. 在刚刚已经配置好的工程根目录下创建ant.properties文件,该文件在创建工程时是不会自动生成的,需要我们自己去创建。这个文件会在build.xml文件中声明。
2. 然后在创建好的ant.properties中添加相关信息,比如我添加的信息如下
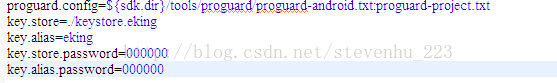
第一行内容为配置关联相关的加密信息文件(也可能为proguard.config = proguard.cfg)
第二行内容为指定签名文件所在路径,./keystore.eking,说明该签名文件在工程根目录下(拷贝签名文件到工程根目录)
第三行内容为签名文件的alias值为eking
第四、第五行分别为签名文件对应的store、alias密码。
3.接着在工程目录下执行如下命令antrelease, 执行完后会自动在工程的bin目录下生成appname-release.apk文件,这个就是签名后生成的apk。
Demo下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/stevenhu_223/8184135
注:该Demo已经通过验证。其中lib/60k-methods.jar有60k个方法,Demo工程中也有60k个方法,但是该Demo可以顺利执行,说明该方案是可行的。
关于拆分dex文件解决dex 65536有效解决方案的介绍就到此结束。有兴趣的同志还可以去深入研究它的实现原理。
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/stevenhu_223/article/details/41277827






















 432
432











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








