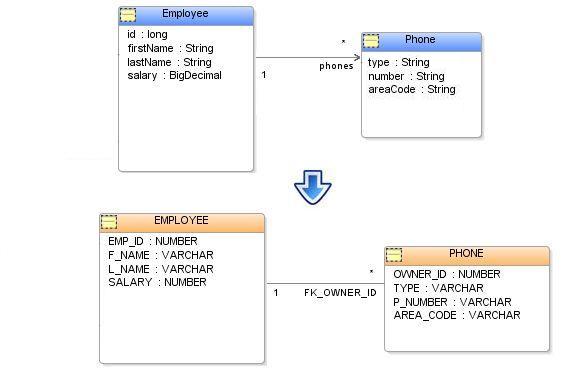
JPA 2.0 defines an ElementCollection mapping. It is meant to handle several non-standard relationship mappings. An ElementCollection can be used to define a one-to-many relationship to an Embeddable object, or a Basic value (such as a collection of Strings). An ElementCollection can also be used in combination with a Map to define relationships where the key can be any type of object, and the value is an Embeddable object or a Basic value.
In JPA an ElementCollection relationship is defined through the @ElementCollection annotation or the <element-collection> element.
The ElementCollection values are always stored in a separate table. The table is defined through the @CollectionTable annotation or the <collection-table>element. The CollectionTable defines the table's name and @JoinColumn or @JoinColumns if a composite primary key.
Embedded Collections[edit]
An ElementCollection mapping can be used to define a collection of Embeddable objects. This is not a typical usage of Embeddable objects as the objects are not embedded in the source object's table, but stored in a separate collection table. This is similar to a OneToMany, except the target object is anEmbeddable instead of an Entity. This allows collections of simple objects to be easily defined, without requiring the simple objects to define an Id orManyToOne inverse mapping. ElementCollection can also override the mappings, or table for their collection, so you can have multiple entities reference the same Embeddable class, but have each store their dependent objects in a separate table.
The limitations of using an ElementCollection instead of a OneToMany is that the target objects cannot be queried, persisted, merged independently of their parent object. They are strictly privately-owned (dependent) objects, the same as an Embedded mapping. There is no cascade option on an ElementCollection, the target objects are always persisted, merged, removed with their parent. ElementCollection still can use a fetch type and defaults to LAZY the same as other collection mappings.
Example of an ElementCollection relationship database[edit]
Example of an ElementCollection relationship annotations[edit]
@Entitypublic class Employee {
@Id
@Column(name="EMP_ID")
private long id;
...
@ElementCollection
@CollectionTable(
name="PHONE",
joinColumns=@JoinColumn(name="OWNER_ID")
)
private List<Phone> phones;
...}@Embeddablepublic class Phone {
private String type;
private String areaCode;
@Column(name="P_NUMBER")
private String number;
...}Example of an ElementCollection relationship XML[edit]
<entity name="Employee" class="org.acme.Employee" access="FIELD">
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<column name="EMP_ID"/>
</id>
<element-collection name="phones">
<collection-table name="PHONE">
<join-column name="OWNER_ID"/>
</collection-table>
</element-collection>
</attributes></entity><embeddable name="Phone" class="org.acme.Phone" access="FIELD">
<attributes>
<basic name="number">
<column name="P_NUMBER"/>
</basic>
</attributes></embeddable>Basic Collections[edit]
An ElementCollection mapping can be used to define a collection of Basic objects. The Basic values are stored in a separate collection table. This is similar to a OneToMany, except the target is a Basic value instead of an Entity. This allows collections of simple values to be easily defined, without requiring defining a class for the value.
There is no cascade option on an ElementCollection, the target objects are always persisted, merged, removed with their parent. ElementCollection still can use a fetch type and defaults to LAZY the same as other collection mappings.
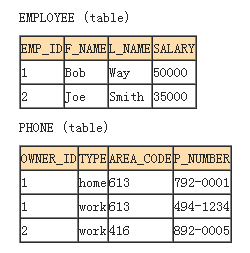
Example of an ElementCollection relationship to a basic value database[edit]

Example of a ElementCollection relationship to a basic value annotations[edit]
@Entitypublic class Employee {
@Id
@Column(name="EMP_ID")
private long id;
...
@ElementCollection
@CollectionTable(
name="PHONE",
joinColumns=@JoinColumn(name="OWNER_ID")
)
@Column(name="PHONE_NUMBER")
private List<String> phones;
...}Example of a ElementCollection relationship to a basic value XML[edit]
<entity name="Employee" class="org.acme.Employee" access="FIELD">
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<column name="EMP_ID"/>
</id>
<element-collection nam
<column name="PHONE_NUMBER"/>
<collection-table name="PHONE">
<join-column name="OWNER_ID"/>
</collection-table>
</element-collection>
</attributes></entity>See Also[edit]
Common Problems[edit]
Primary keys in CollectionTable[edit]
The JPA 2.0 specification does not provide a way to define the
Idin theEmbeddable. However, to delete or update a element of theElementCollectionmapping, some unique key is normally required. Otherwise, on every update the JPA provider would need to delete everything from theCollectionTablefor theEntity, and then insert the values back. So, the JPA provider will most likely assume that the combination of all of the fields in theEmbeddableare unique, in combination with the foreign key (JoinColumn(s)). This however could be inefficient, or just not feasible if theEmbeddableis big, or complex.
Some JPA providers may allow the
Idto be specified in theEmbeddable, to resolve this issue. Note in this case theIdonly needs to be unique for the collection, not the table, as the foreign key is included. Some may also allow theuniqueoption on theCollectionTableto be used for this. Otherwise, if yourEmbeddableis complex, you may consider making it anEntityand use aOneToManyinstead.





















 679
679

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








