目录
1. 概念2. 步骤3. 执行原理4. 生命周期5. Servlet3.0 注解配置
编辑6. Servlet的体系结构 Servlet -- 接口 | GenericServlet -- 抽象类 | HttpServlet -- 抽象类
* 概念:Hyper Text Transfer Protocol 超文本传输协议
(***) * forward 和 redirect 区别(面试题)
1. 概念:代表整个web应用,可以和程序的容器(服务器)来通信
Servlet
知识回顾
1. 概念
2. 步骤
3. 执行原理
4. 生命周期
5. Servlet3.0 注解配置
6. Servlet的体系结构
Servlet -- 接口
|
GenericServlet -- 抽象类
|
HttpServlet -- 抽象类
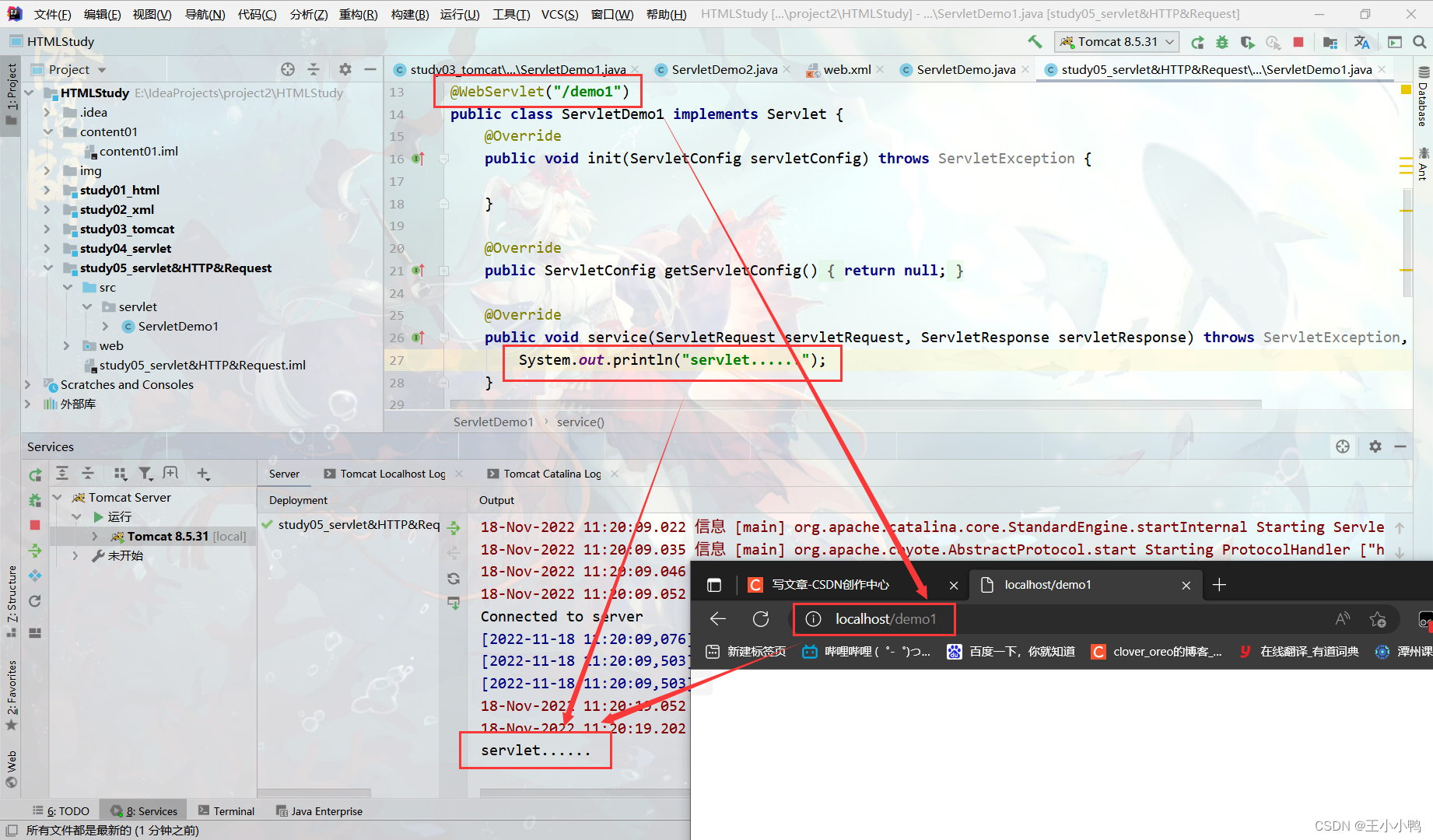
* GenericServlet:将Servlet接口中其他的方法做了默认空实现,只将service()方法作为抽象
* 将来定义Servlet类时,可以继承GenericServlet,实现service()方法即可
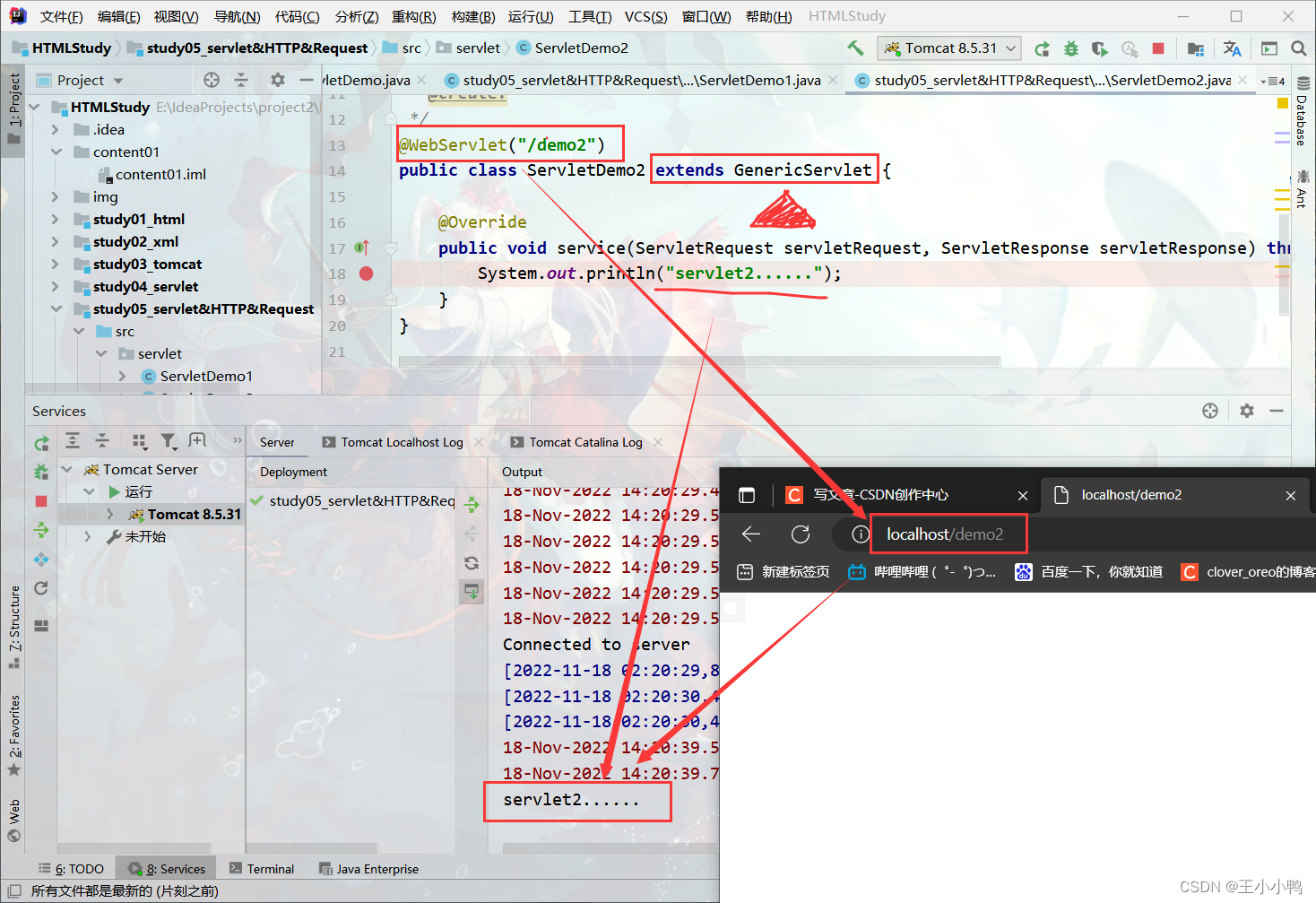
@WebServlet("/demo2")
public class ServletDemo2 extends GenericServlet {
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("servlet2......");
}
}
* HttpServlet:对http协议的一种封装,简化操作
1. 定义类继承HttpServlet
2. 复写doGet/doPost方法
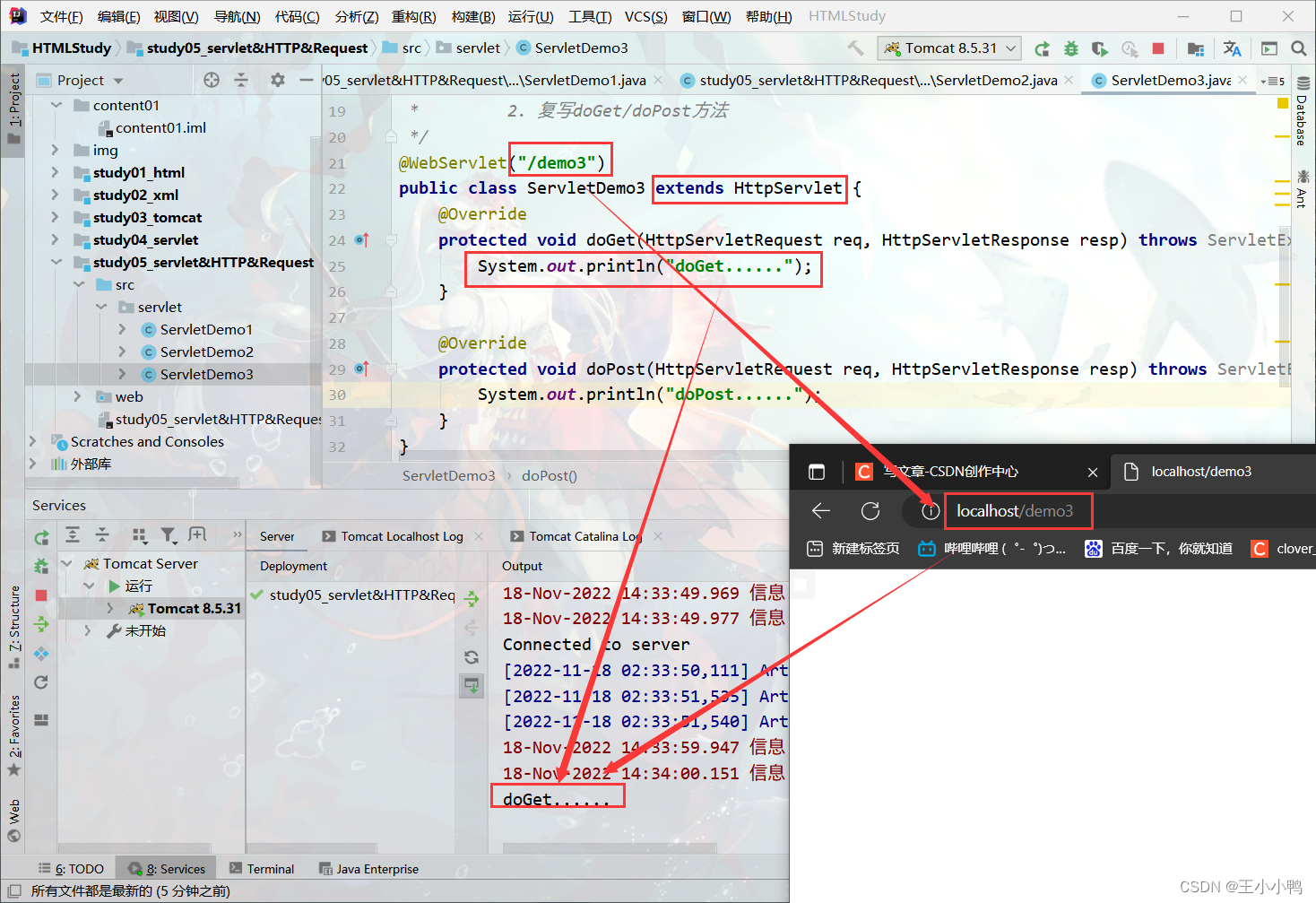
@WebServlet("/demo3")
public class ServletDemo3 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doGet......");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doPost......");
}
}
7. Servlet相关配置
1. urlpartten:Servlet访问路径
1. 一个Servlet可以定义多个访问路径 : @WebServlet({"/d4","/dd4","/ddd4"})
2. 路径定义规则:
1. /xxx:路径匹配
2. /xxx/xxx:多层路径,目录结构
3. *.do:扩展名匹配(不加/)
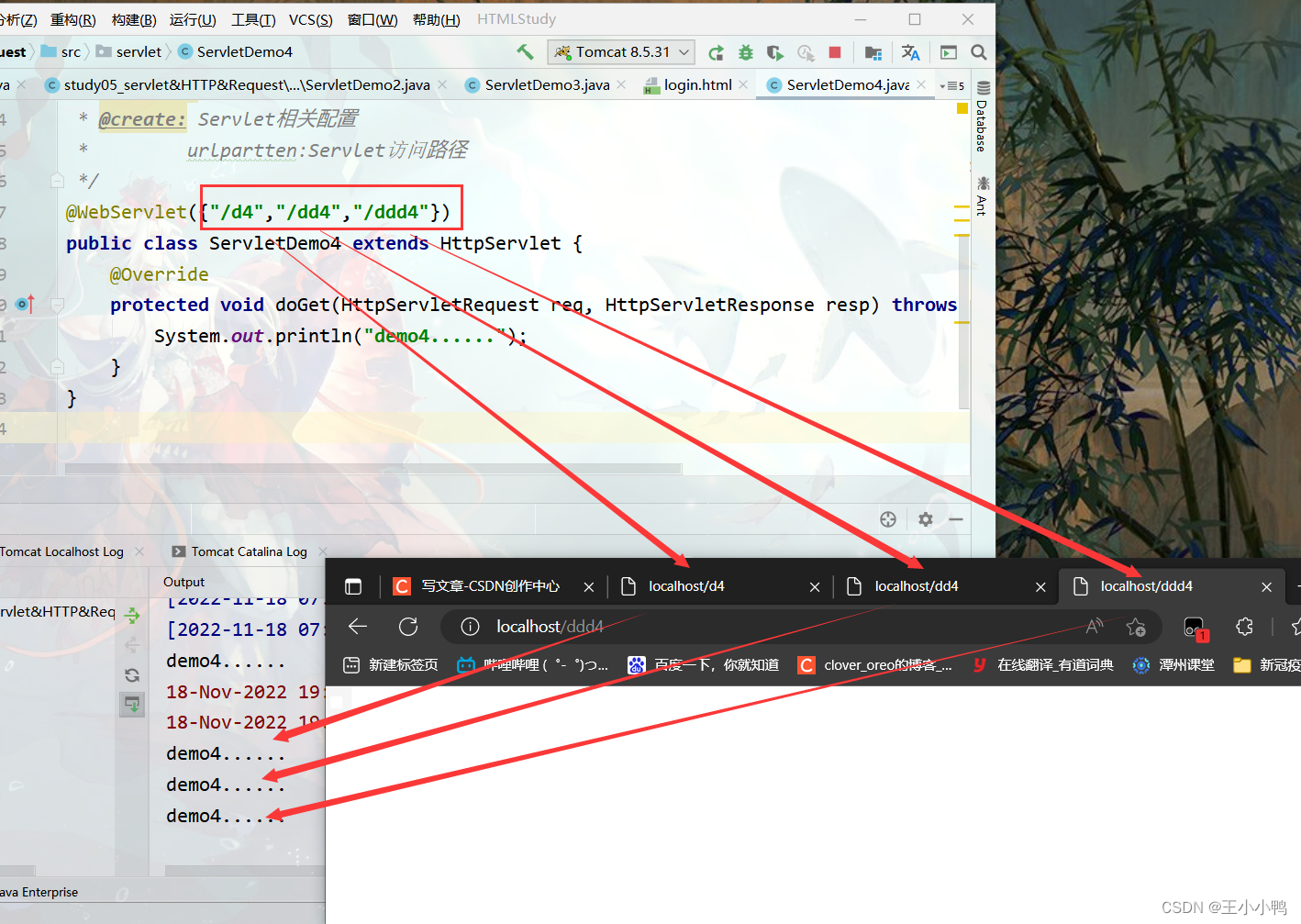
package servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 乱码酱
* @date :2022-11-18 11:15
* @program: HTMLStudy
* @create: Servlet相关配置
* urlpartten:Servlet访问路径
*/
@WebServlet({"/d4","/dd4","/ddd4"})
public class ServletDemo4 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("demo4......");
}
}
HTTP
* 概念:Hyper Text Transfer Protocol 超文本传输协议
* 传输协议:定义了,客户端和服务器端通信时,发送数据的格式
* 特点:
1. 基于TCP/IP的高级协议
2. 默认端口号:80
3. 基于请求/响应模型的:一次请求对应一次响应
4. 无状态的:每次请求之间相互独立,不能交互数据
* 历史版本:
* 1.0:每一次请求响应都会建立新的连接
* 1.1:复用连接
* 请求消息数据格式
1. 请求行
请求方式 请求url 请求协议/版本
GET /login.html HTTP/1.1
* 请求方式:
* HTTP协议有7种请求方式,常用的有2种
* GET:
1. 请求参数在请求行中,在url后。
2. 请求的url长度有限制的
3. 不太安全
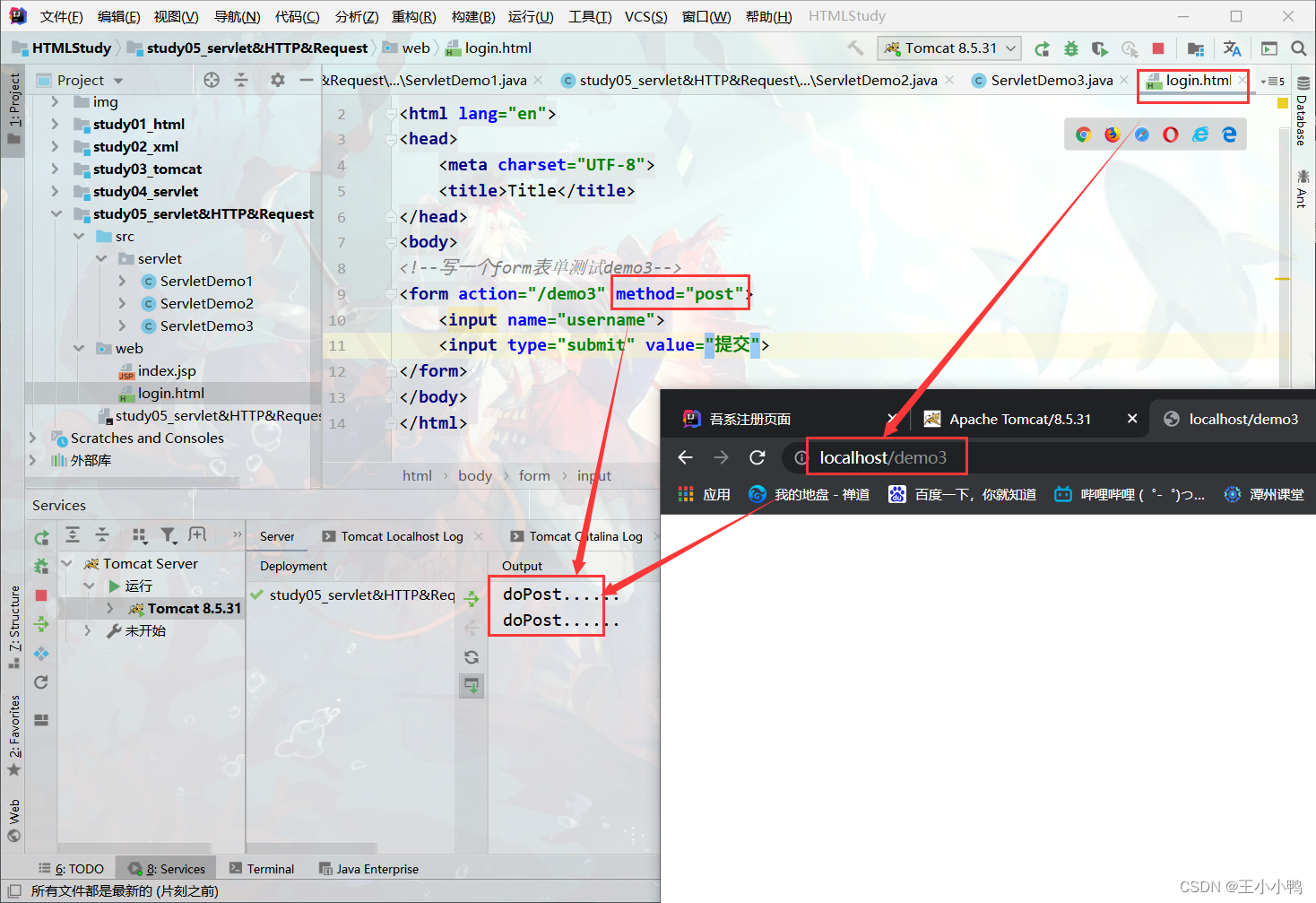
* POST:
1. 请求参数在请求体中
2. 请求的url长度没有限制的
3. 相对安全
2. 请求头:客户端浏览器告诉服务器一些信息
请求头名称: 请求头值
* 常见的请求头:
1. User-Agent:浏览器告诉服务器,我访问你使用的浏览器版本信息
* 可以在服务器端获取该头的信息,解决浏览器的兼容性问题
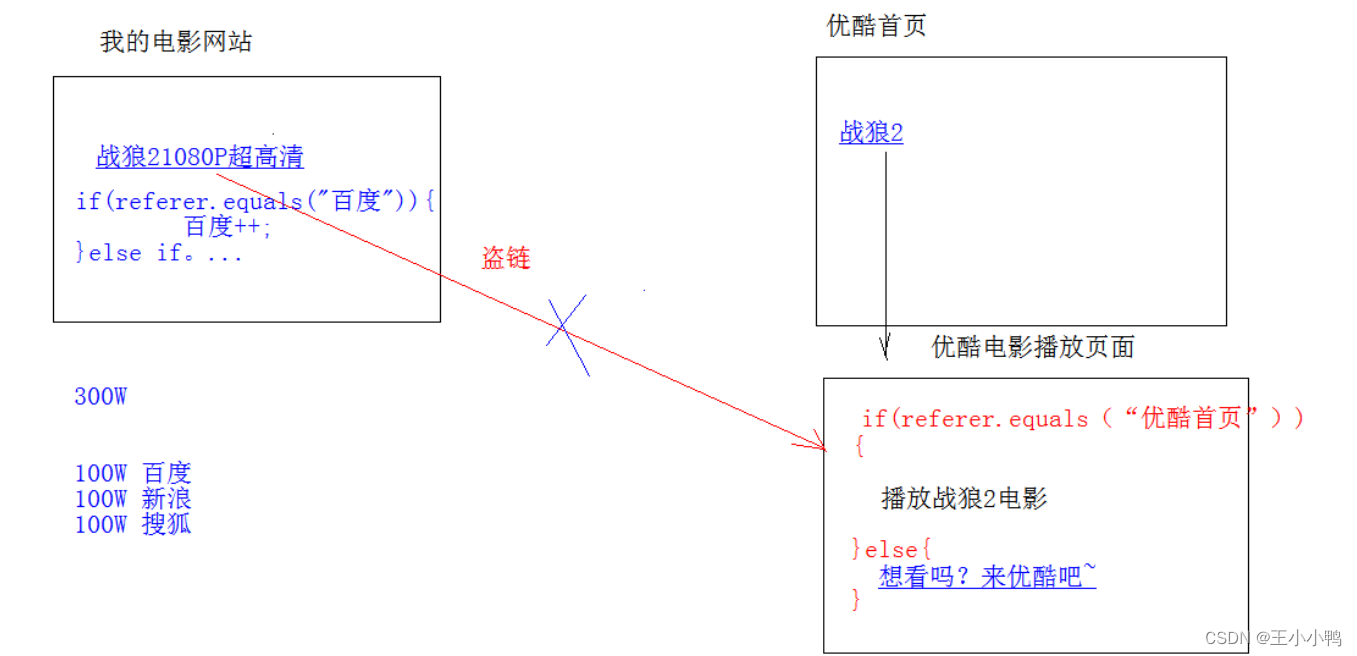
2. Referer:http://localhost/login.html
* 告诉服务器,我(当前请求)从哪里来?
* 作用:
1. 防盗链:
2. 统计工作:
3. 请求空行
空行,就是用于分割POST请求的请求头,和请求体的。
4. 请求体(正文):
* 封装POST请求消息的请求参数的
* 字符串格式:
POST /login.html HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:60.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/60.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Referer: http://localhost/login.html
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
username=zhangsan
请求行
请求方式 请求url 请求协议/版本
* 响应消息数据格式

Request
1. request对象和response对象的原理
1. request和response对象是由服务器创建的。我们来使用它们
2. request对象是来获取请求消息,response对象是来设置响应消息
2. request对象继承体系结构:
ServletRequest -- 接口
| 继承
HttpServletRequest -- 接口
| 实现
org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade 类(tomcat)
3. request功能:
1. 获取请求消息数据
1. 获取请求行数据
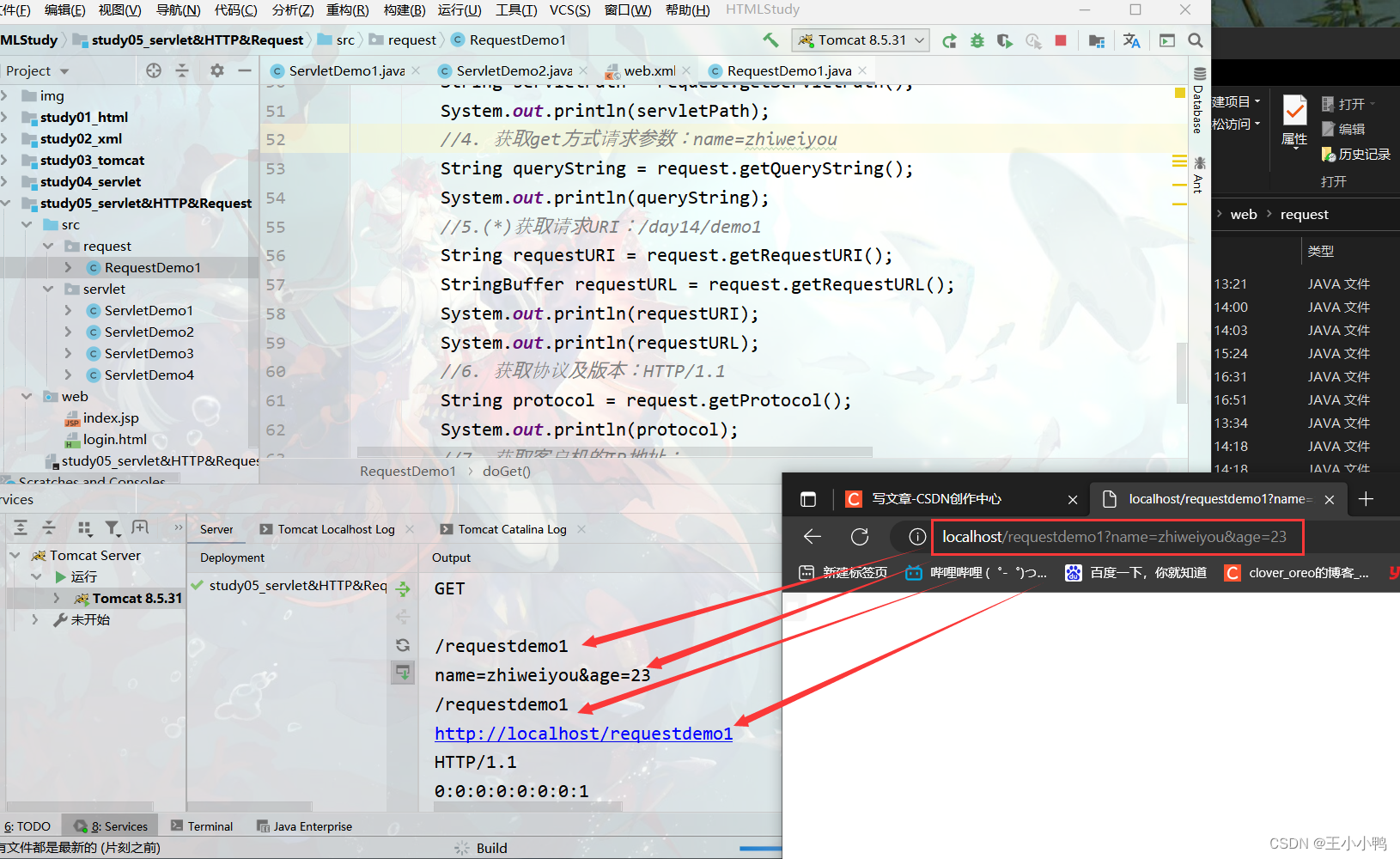
* GET /day14/demo1?name=zhangsan HTTP/1.1
* 方法:
1. 获取请求方式 :GET
* String getMethod()
2. (*)获取虚拟目录:/day14
* String getContextPath()
3. 获取Servlet路径: /demo1
* String getServletPath()
4. 获取get方式请求参数:name=zhangsan
* String getQueryString()
5. (*)获取请求URI:/day14/demo1
* String getRequestURI(): /day14/demo1
* StringBuffer getRequestURL() :http://localhost/day14/demo1
* URI:统一资源标识符 : /day14/demo1 共和国(范围更大)
* URL:统一资源定位符 : http://localhost/day14/demo1 中华人民共和国
6. 获取协议及版本:HTTP/1.1
* String getProtocol()
7. 获取客户机的IP地址:
* String getRemoteAddr()
package request;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 乱码酱
* @date :2022-11-18 23:16
* @program: HTMLStudy
* @create:演示Request对象获取请求行数据
*/
@WebServlet("/requestdemo1")
public class RequestDemo1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
/*
1. 获取请求方式 :GET
* String getMethod()
2. (*)获取虚拟目录:/day14
* String getContextPath()
3. 获取Servlet路径: /requestDemo1
* String getServletPath()
4. 获取get方式请求参数:name=zhangsan
* String getQueryString()
5. (*)获取请求URI:/day14/demo1
* String getRequestURI(): /day14/requestDemo1
* StringBuffer getRequestURL() :http://localhost/day14/requestDemo1
6. 获取协议及版本:HTTP/1.1
* String getProtocol()
7. 获取客户机的IP地址:
* String getRemoteAddr()
http://localhost/requestdemo1?name=zhiweiyou&age=23
*/
//1. 获取请求方式 :GET
String method = request.getMethod();
System.out.println(method);
//2.(*)获取虚拟目录:/day14
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
System.out.println(contextPath);
//3. 获取Servlet路径: /demo1
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
System.out.println(servletPath);
//4. 获取get方式请求参数:name=zhiweiyou
String queryString = request.getQueryString();
System.out.println(queryString);
//5.(*)获取请求URI:/day14/demo1
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
StringBuffer requestURL = request.getRequestURL();
System.out.println(requestURI);
System.out.println(requestURL);
//6. 获取协议及版本:HTTP/1.1
String protocol = request.getProtocol();
System.out.println(protocol);
//7. 获取客户机的IP地址:
String remoteAddr = request.getRemoteAddr();
System.out.println(remoteAddr);
}
}
2. 获取请求头数据
* 方法:
* (*)String getHeader(String name):通过请求头的名称获取请求头的值
* Enumeration<String> getHeaderNames():获取所有的请求头名称
3. 获取请求体数据:
* 请求体:只有POST请求方式,才有请求体,在请求体中封装了POST请求的请求参数
* 步骤:
1. 获取流对象
* BufferedReader getReader():获取字符输入流,只能操作字符数据
* ServletInputStream getInputStream():获取字节输入流,可以操作所有类型数据
* 在文件上传知识点后讲解
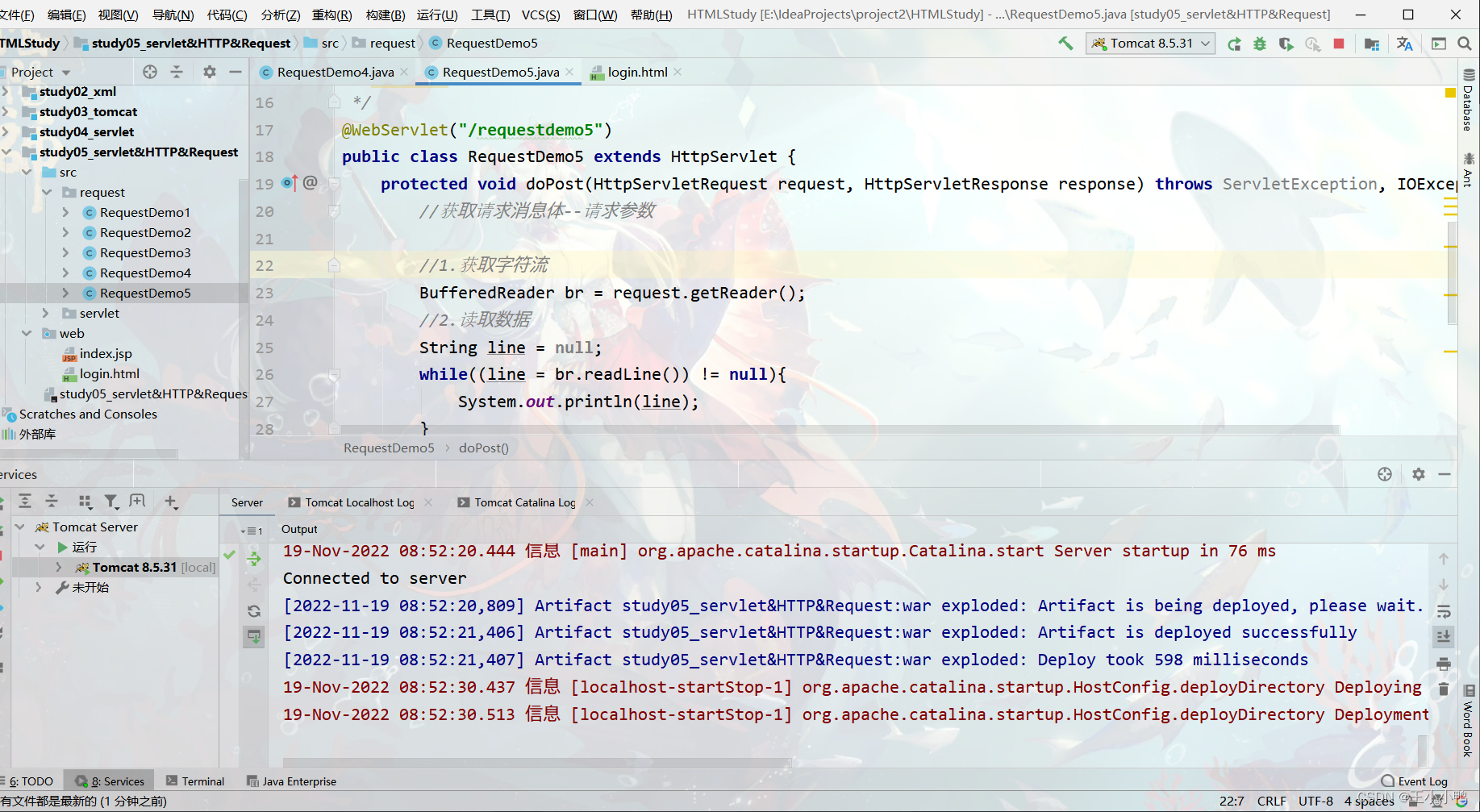
//1.获取字符流
BufferedReader br = request.getReader();
//2.读取数据
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
2. 再从流对象中拿数据
@WebServlet("/requestdemo5")
public class RequestDemo5 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取请求消息体--请求参数
//1.获取字符流
BufferedReader br = request.getReader();
//2.读取数据
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>我是注册页面</title>
</head>
<body>
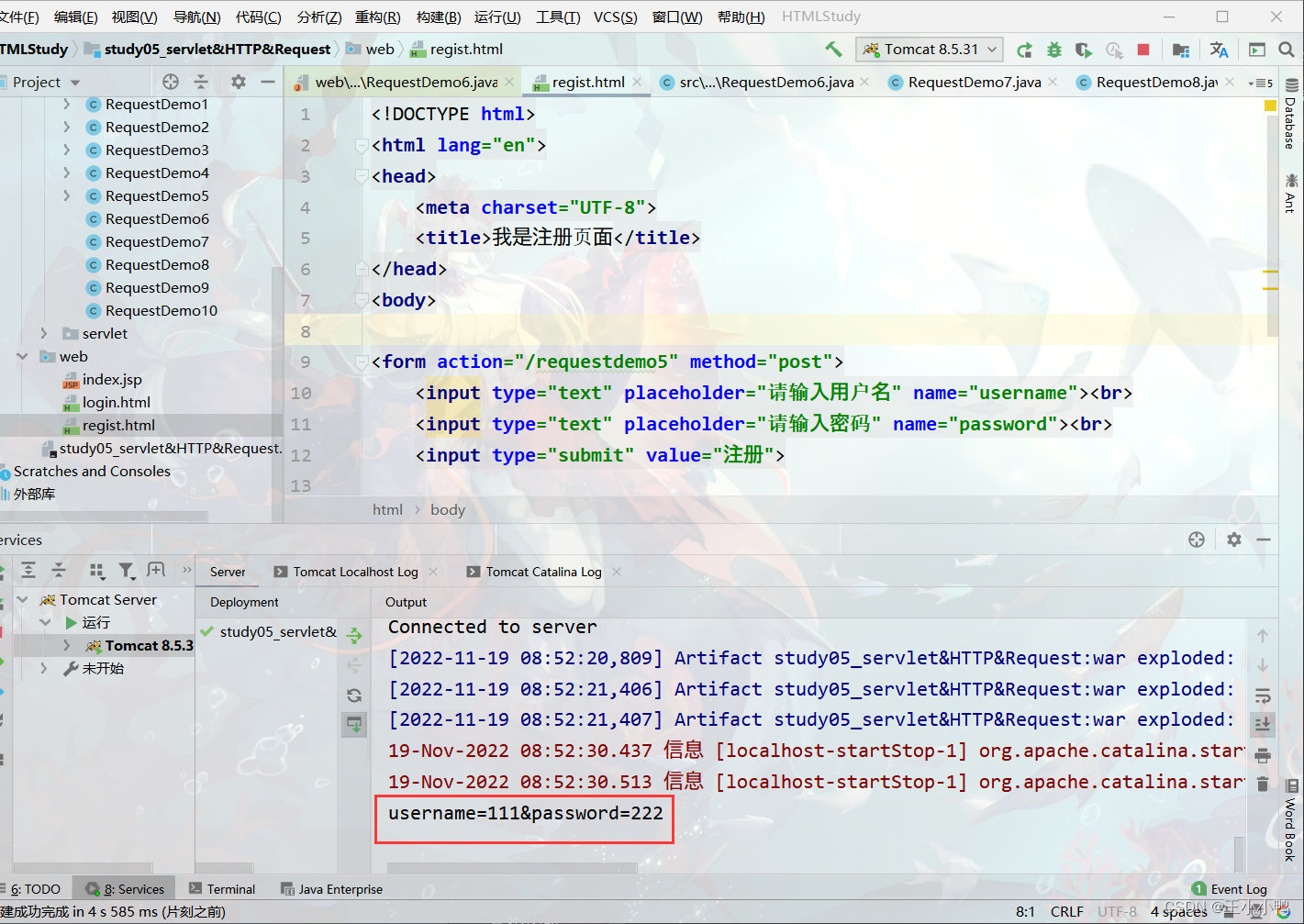
<form action="/requestdemo5" method="post">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" name="username"><br>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入密码" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>
</body>
</html>2. (*)其他功能:
1. 不论get还是post请求方式都可以使用下列方法来获取请求参数
1. String getParameter(String name):根据参数名称获取参数值 username=zs&password=123
2. String[] getParameterValues(String name):根据参数名称获取参数值的数组 hobby=xx&hobby=game
3. Enumeration<String> getParameterNames():获取所有请求的参数名称
4. Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap():获取所有参数的map集合
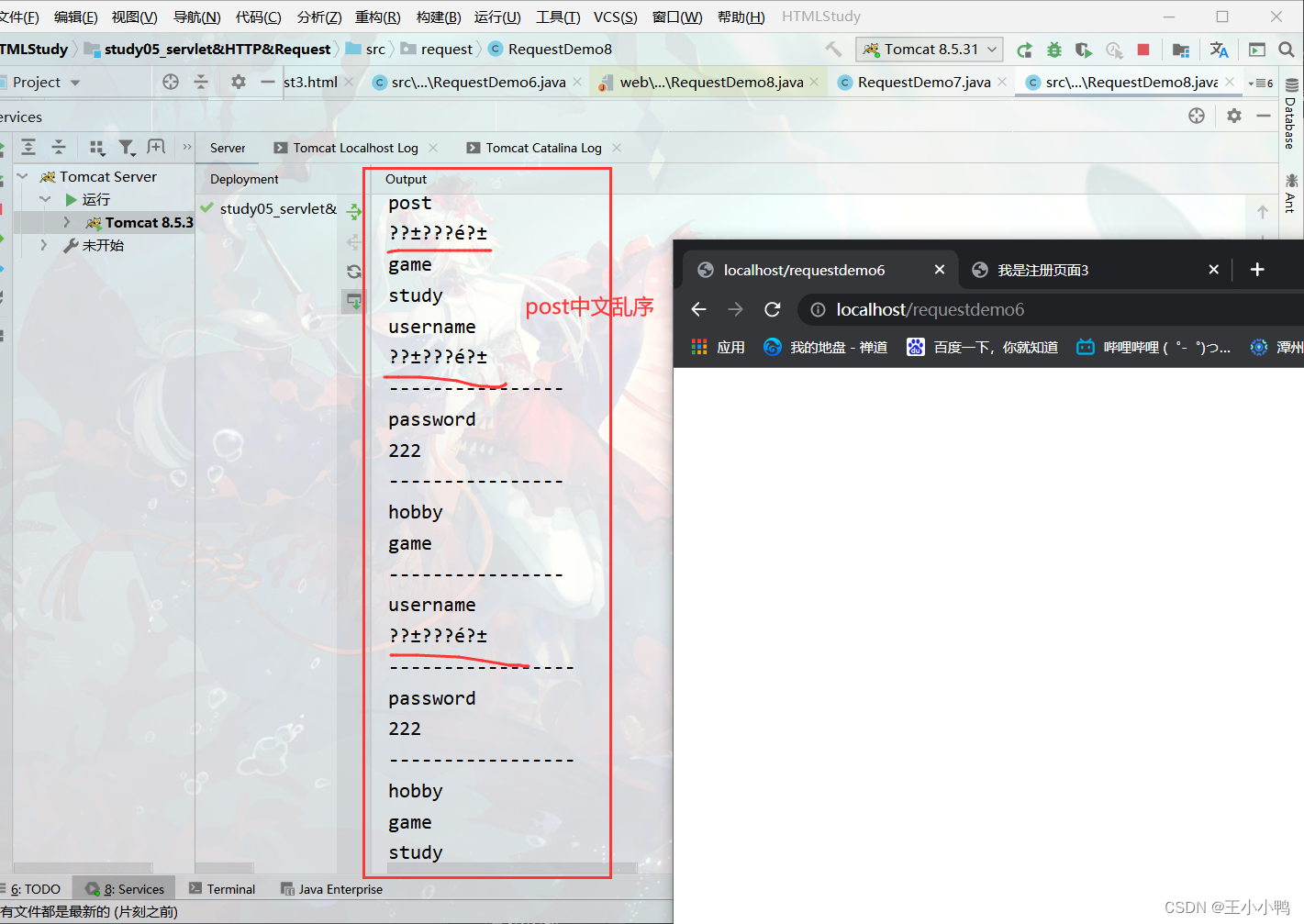
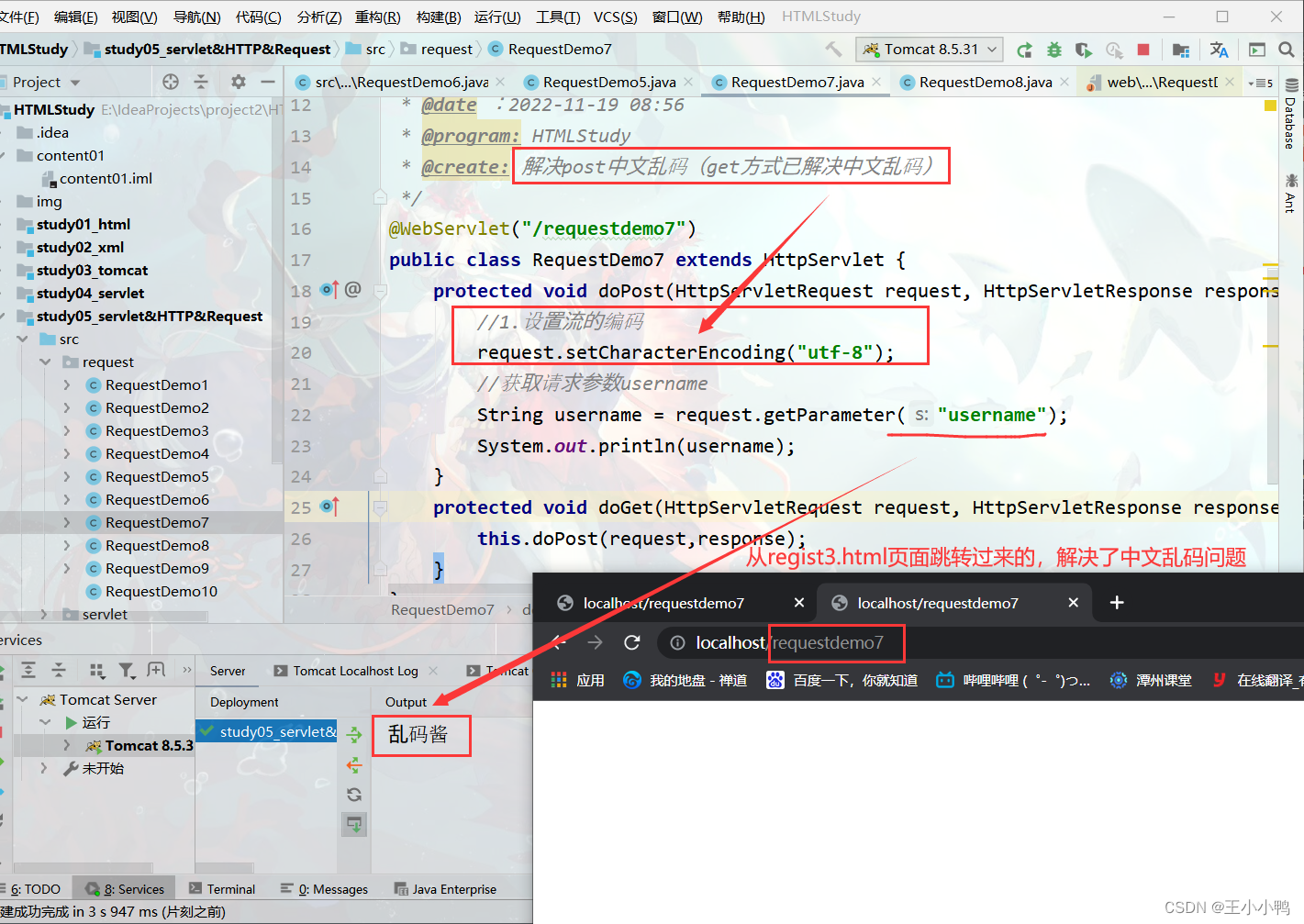
* 中文乱码问题:
* get方式:tomcat 8 已经将get方式乱码问题解决了
* post方式:会乱码
* 解决:在获取参数前,设置request的编码request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
2. 请求转发:一种在服务器内部的资源跳转方式
1. 步骤:
1. 通过request对象获取请求转发器对象:RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path)
2. 使用RequestDispatcher对象来进行转发:forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
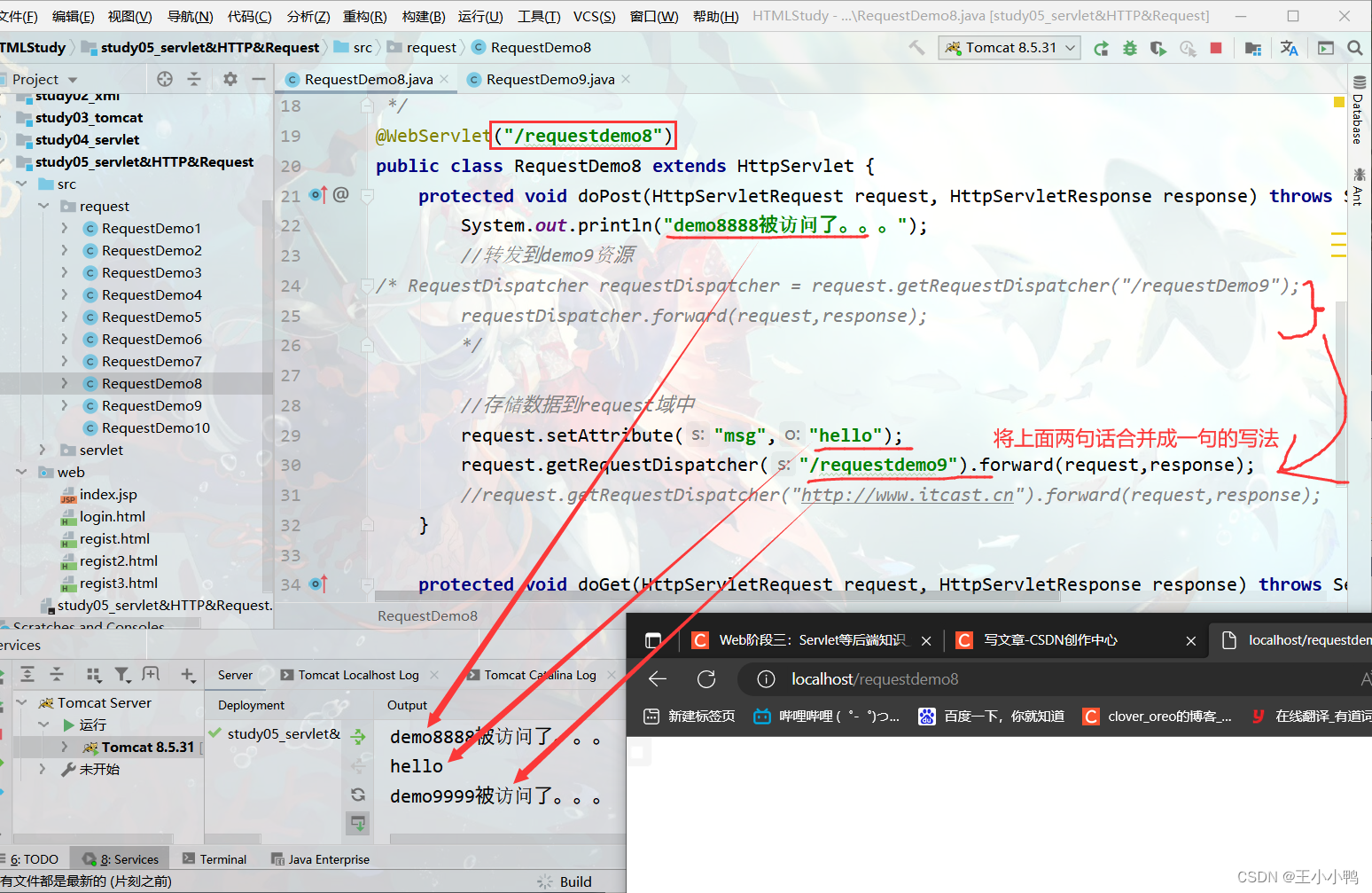
//转发到demo9资源
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("/requestDemo9");
requestDispatcher.forward(request,response);
//存储数据到request域中
request.setAttribute("msg","hello");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/requestdemo9").forward(request,response); 2. 特点:
1. 浏览器地址栏路径不发生变化
2. 只能转发到当前服务器内部资源中。
3. 转发是一次请求
3. 共享数据:
* 域对象:一个有作用范围的对象,可以在范围内共享数据
* request域:代表一次请求的范围,一般用于请求转发的多个资源中共享数据
* 方法:
1. void setAttribute(String name,Object obj):存储数据
2. Object getAttitude(String name):通过键获取值
3. void removeAttribute(String name):通过键移除键值对
* 注意:这个放于forward方法的上面,不然响应太快会导致无法获取信息!
//存储数据到request域中
request.setAttribute("msg","hello");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/requestdemo9").forward(request,response);
//获取数据
Object msg = request.getAttribute("msg");
System.out.println(msg); 4. 获取ServletContext:(有印象即可)
* ServletContext getServletContext()
- Context n. 背景,环境;上下文,语境
-
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext(); System.out.println(servletContext); 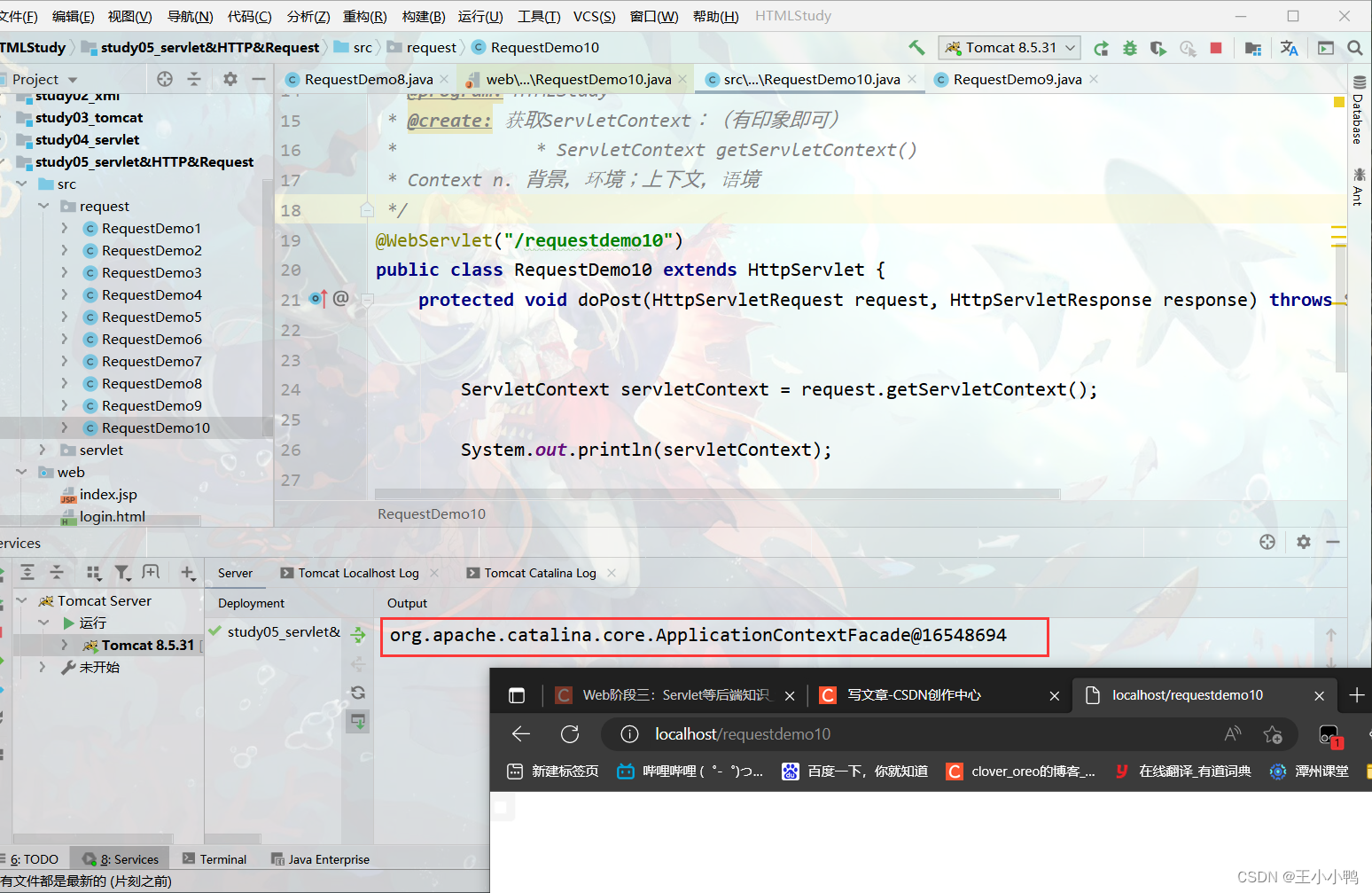
得到:
org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContextFacade@16548694
案例:通过request请求和servlet实现注册跳转界面案例及问题解决
9. BeanUtils工具类,简化数据封装
* 用于封装JavaBean的
1. JavaBean:标准的Java类
1. 要求:
1. 类必须被public修饰
2. 必须提供空参的构造器
3. 成员变量必须使用private修饰
4. 提供公共setter和getter方法
2. 功能:封装数据
2. 概念:
成员变量:
属性:setter和getter方法截取后的产物
例如:getUsername() --> Username--> username
3. 方法:
1. setProperty()
2. getProperty()
3. populate(Object obj , Map map):将map集合的键值对信息,封装到对应的JavaBean对象中
HTTP协议
1. 请求消息:客户端发送给服务器端的数据
* 数据格式:
1. 请求行
2. 请求头
3. 请求空行
4. 请求体
2. 响应消息:服务器端发送给客户端的数据
* 数据格式:
1. 响应行
1. 组成:协议/版本 响应状态码 状态码描述
2. 响应状态码:服务器告诉客户端浏览器本次请求和响应的一个状态。
1. 状态码都是3位数字
2. 分类:
1. 1xx:服务器就收客户端消息,但没有接受完成,等待一段时间后,发送1xx多状态码
2. 2xx:成功。代表:200
3. 3xx:重定向。代表:302(重定向),304(访问缓存)
4. 4xx:客户端错误。
* 代表:
* 404(请求路径没有对应的资源)
* 405:请求方式没有对应的doXxx方法
5. 5xx:服务器端错误。代表:500(服务器内部出现异常)
2. 响应头:
1. 格式:头名称: 值
2. 常见的响应头:
1. Content-Type:服务器告诉客户端本次响应体数据格式以及编码格式
2. Content-disposition:服务器告诉客户端以什么格式打开响应体数据
* 值:
* in-line:默认值,在当前页面内打开
* attachment;filename=xxx:以附件形式打开响应体。文件下载
3. 响应空行
4. 响应体:传输的数据
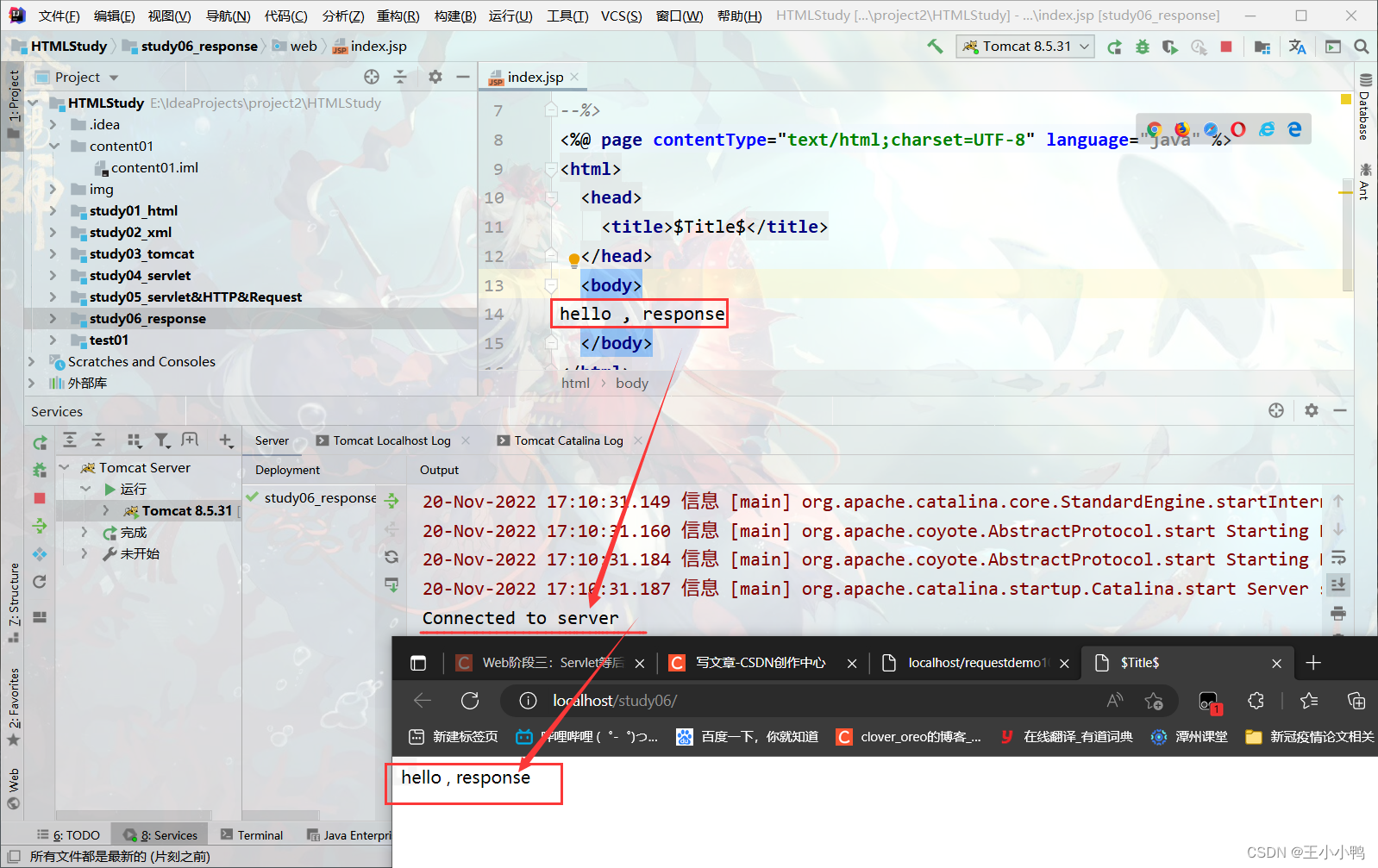
* 响应字符串格式
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html;charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 101
Date: Wed, 06 Jun 2018 07:08:42 GMT
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
hello , response
</body>
</html>
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Bdpagetype: 1
Bdqid: 0x8f881928000fce17
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Date: Sun, 20 Nov 2022 08:59:17 GMT
P3p: CP=" OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM "
Server: BWS/1.1
Set-Cookie: BDRCVFR[Fc9oatPmwxn]=aeXf-1x8UdYcs; path=/; domain=.baidu.com
Set-Cookie: BDSVRTM=23; path=/
Set-Cookie: BD_HOME=1; path=/
Set-Cookie: H_PS_PSSID=36542_37686_37492_37778_37822_37724_37534_37742_26350_37488_37791; path=/; domain=.baidu.com
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=172800
Traceid: 1668934757060730164210342544203846766103
X-Frame-Options: sameorigin
X-Ua-Compatible: IE=Edge,chrome=1
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Response对象
* 功能:设置响应消息
1. 设置响应行
1. 格式:HTTP/1.1 200 ok
2. 设置状态码:setStatus(int sc)
2. 设置响应头:setHeader(String name, String value)
3. 设置响应体:
* 使用步骤:
1. 获取输出流
* 字符输出流:PrintWriter getWriter()
* 字节输出流:ServletOutputStream getOutputStream()
2. 使用输出流,将数据输出到客户端浏览器
* 案例:
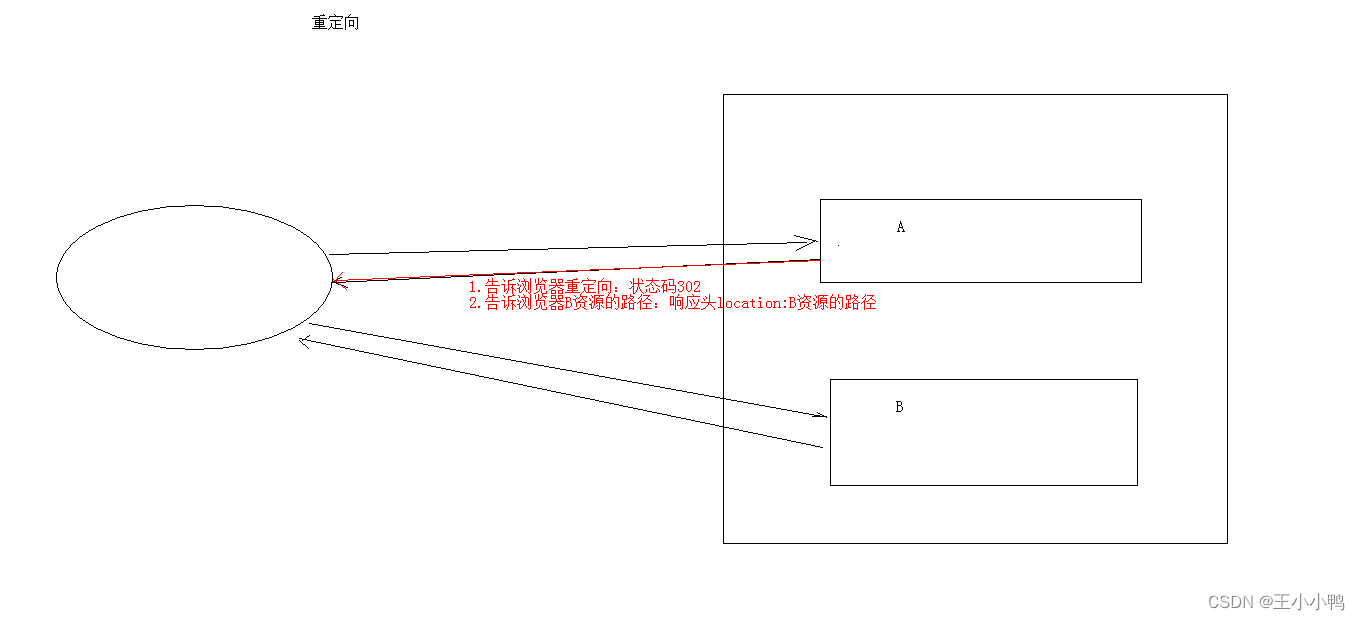
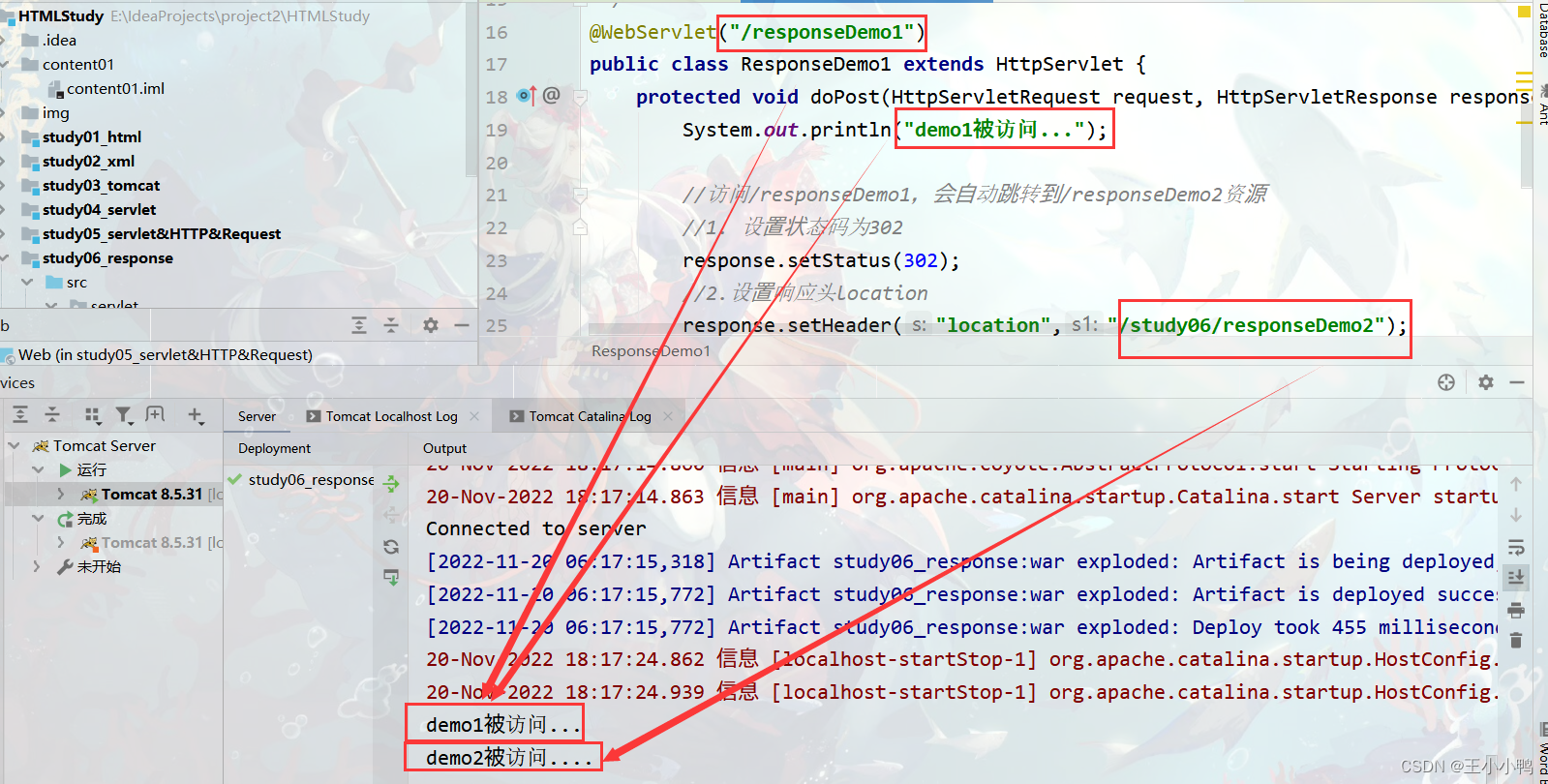
1. 完成重定向
* 重定向:资源跳转的方式
* 代码实现:
//1. 设置状态码为302
response.setStatus(302);
//2.设置响应头location
response.setHeader("location","/day15/responseDemo2");
//简单的重定向方法
response.sendRedirect("/day15/responseDemo2");
(***) * forward 和 redirect 区别(面试题)
* 重定向的特点:redirect
1. 地址栏发生变化
2. 重定向可以访问其他站点(服务器)的资源
3. 重定向是两次请求。不能使用request对象来共享数据
* 转发的特点:forward
1. 转发地址栏路径不变
2. 转发只能访问当前服务器下的资源
3. 转发是一次请求,可以使用request对象来共享数据
* 路径写法:
1. 路径分类
1. 相对路径:通过相对路径不可以确定唯一资源
* 如:./index.html
* 不以/开头,以.开头路径
* 规则:找到当前资源和目标资源之间的相对位置关系
* ./:当前目录
* ../:后退一级目录
2. 绝对路径:通过绝对路径可以确定唯一资源
* 如:http://localhost/day15/responseDemo2 /day15/responseDemo2
* 以/开头的路径
* 规则:判断定义的路径是给谁用的?判断请求将来从哪儿发出
* 给客户端浏览器使用:需要加虚拟目录(项目的访问路径) /day15/responseDemo2
* 建议虚拟目录动态获取:request.getContextPath()
* <a> , <form> 重定向...
* 给服务器使用:不需要加虚拟目录
request.getRequestDispatcher("/responseDemo1").forward(request,response);
* 转发路径
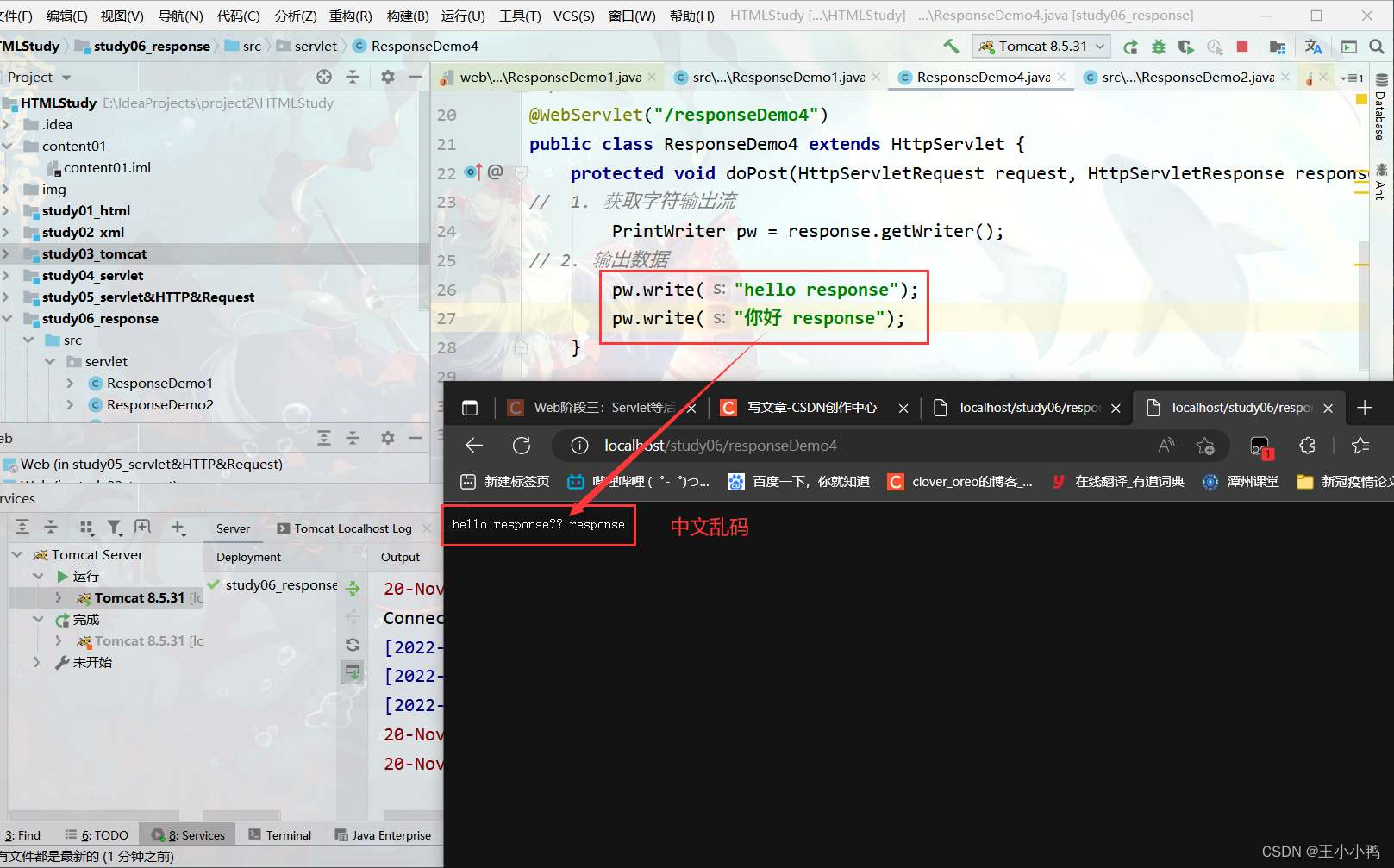
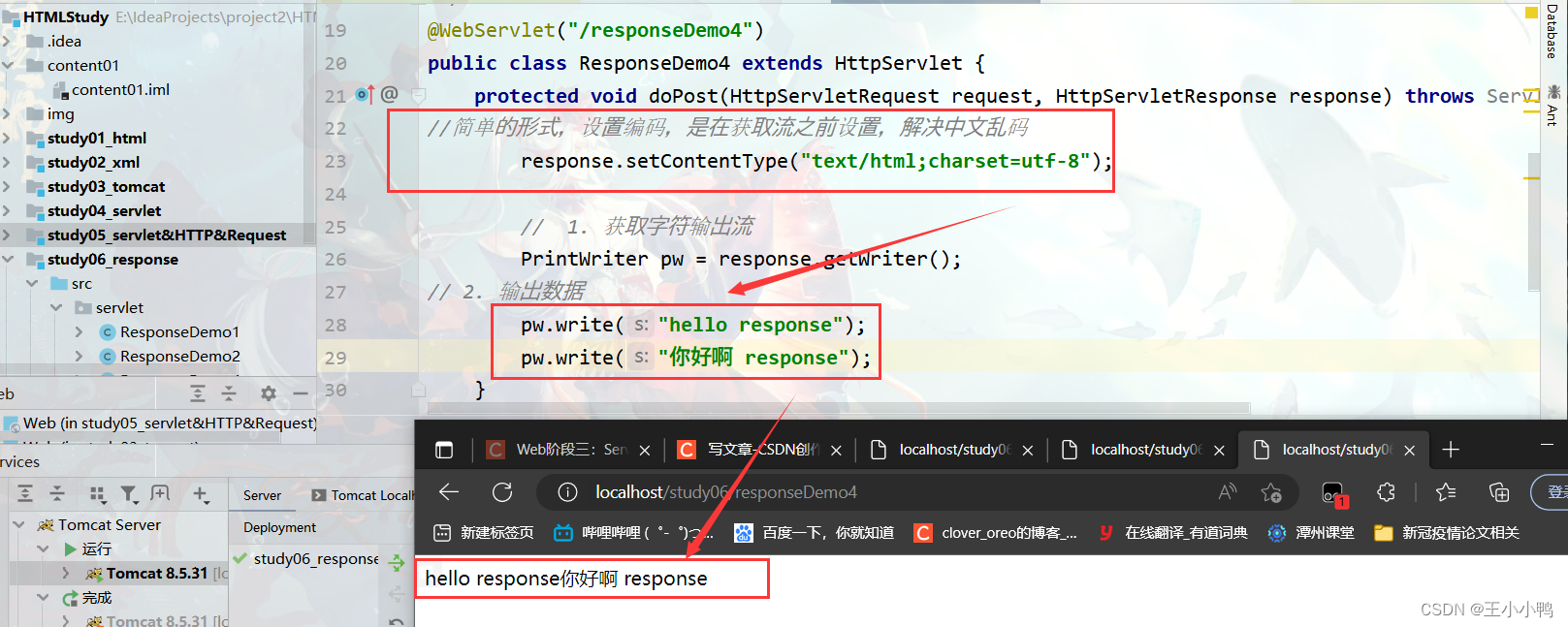
2. 服务器输出字符数据到浏览器
* 步骤:
1. 获取字符输出流
2. 输出数据
* 注意:
* 乱码问题:
1. PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();获取的流的默认编码是ISO-8859-1
2. 设置该流的默认编码
3. 告诉浏览器响应体使用的编码
//简单的形式,设置编码,是在获取流之前设置(每次编写之前写在最前面)
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
3. 服务器输出字节数据到浏览器
* 步骤:
1. 获取字节输出流
2. 输出数据
//简单的形式,设置编码,是在获取流之前设置
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
// 1. 获取字节输出流
ServletOutputStream sos = response.getOutputStream();
// 2. 输出数据
sos.write("hello".getBytes());
sos.write("你好鸭".getBytes());
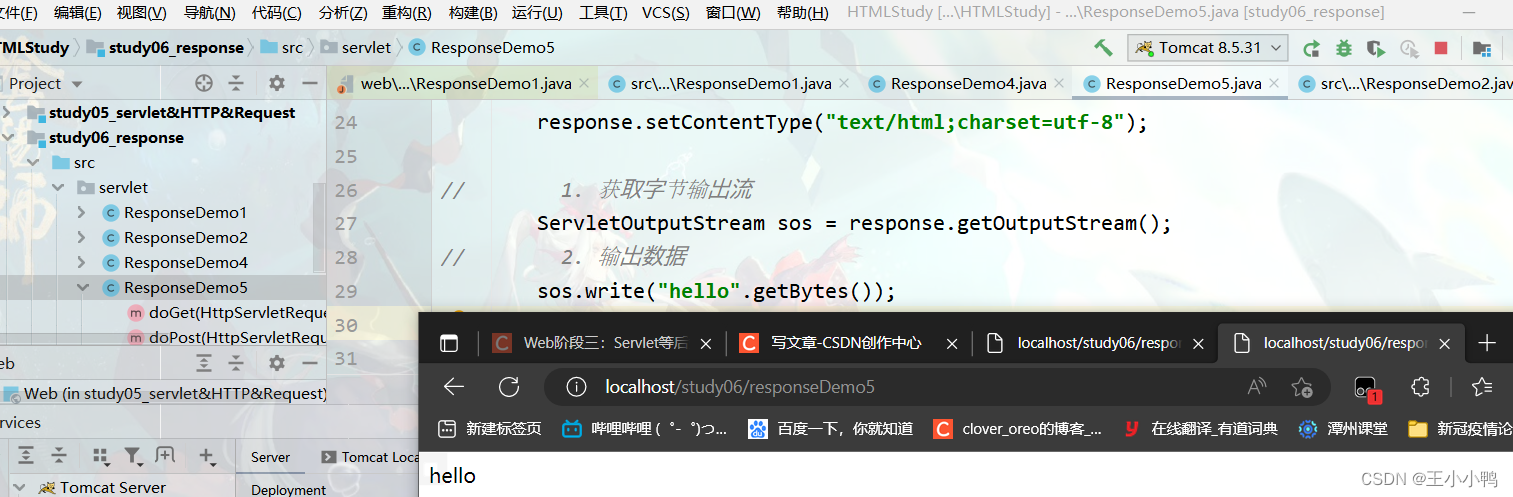
4. 验证码
1. 本质:图片
2. 目的:防止恶意表单注册
package servlet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
@WebServlet("/checkCodeServlet")
public class CheckCodeServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
int width = 100;
int height = 50;
//1.创建一对象,在内存中图片(验证码图片对象)
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(width,height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
//2.美化图片
//2.1 填充背景色
Graphics g = image.getGraphics();//画笔对象
g.setColor(Color.PINK);//设置画笔颜色
g.fillRect(0,0,width,height); //fillRect()填充
//2.2画边框
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.drawRect(0,0,width - 1,height - 1); //drawRect()画
String str = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghigklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789";
//生成随机角标
Random ran = new Random();
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
int index = ran.nextInt(str.length());
//获取字符
char ch = str.charAt(index);//随机字符
//2.3写验证码
g.drawString(ch+"",width/5*i,height/2);
}
//2.4画干扰线
g.setColor(Color.GREEN); //设颜色
//随机生成坐标点 两点(x1,y1)(x2,y2)确定一条直线
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int x1 = ran.nextInt(width);
int x2 = ran.nextInt(width);
int y1 = ran.nextInt(height);
int y2 = ran.nextInt(height);
g.drawLine(x1,y1,x2,y2);
}
//3.将图片输出到页面展示
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",response.getOutputStream());
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request,response);
}
}
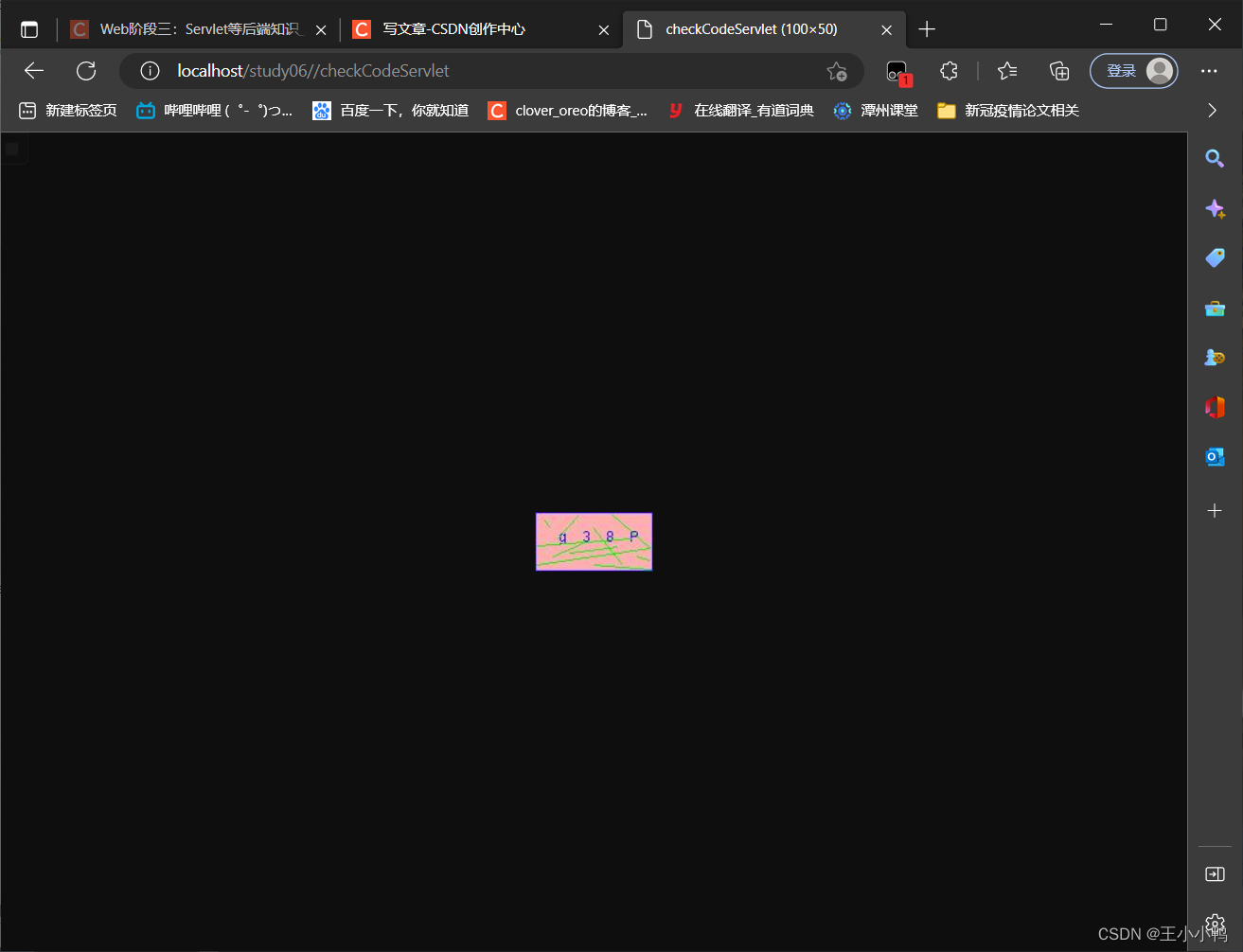
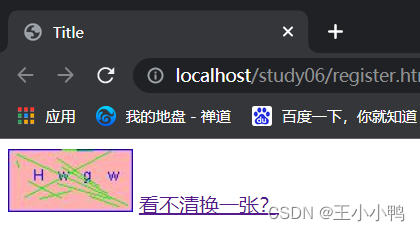
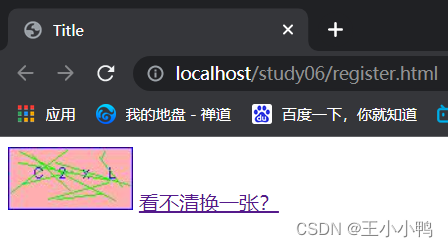
动态刷新:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
/*
分析:
点击超链接或者图片,需要换一张
1.给超链接和图片绑定单击事件
2.重新设置图片的src属性值
*/
window.onload = function(){
//1.获取图片对象
var img = document.getElementById("checkCode");
//2.绑定单击事件
img.onclick = function(){
//加时间戳
var date = new Date().getTime();
img.src = "/study06/checkCodeServlet?"+date; //加入永不重复的时间,确保每次刷新都不重复
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<img id="checkCode" src="/study06/checkCodeServlet" />
<a id="change" href="">看不清换一张?</a>
</body>
</html>ServletContext对象
1. 概念:代表整个web应用,可以和程序的容器(服务器)来通信
2. 获取:
1. 通过request对象获取
request.getServletContext();
2. 通过HttpServlet获取
this.getServletContext();
总结:两种方式获取的地址都是同一个,两者==
//1. 通过request对象获取
ServletContext context1 = request.getServletContext();
//2. 通过HttpServlet获取
ServletContext context2 = this.getServletContext();
System.out.println(context1);
System.out.println(context2);
System.out.println(context1 == context2);//true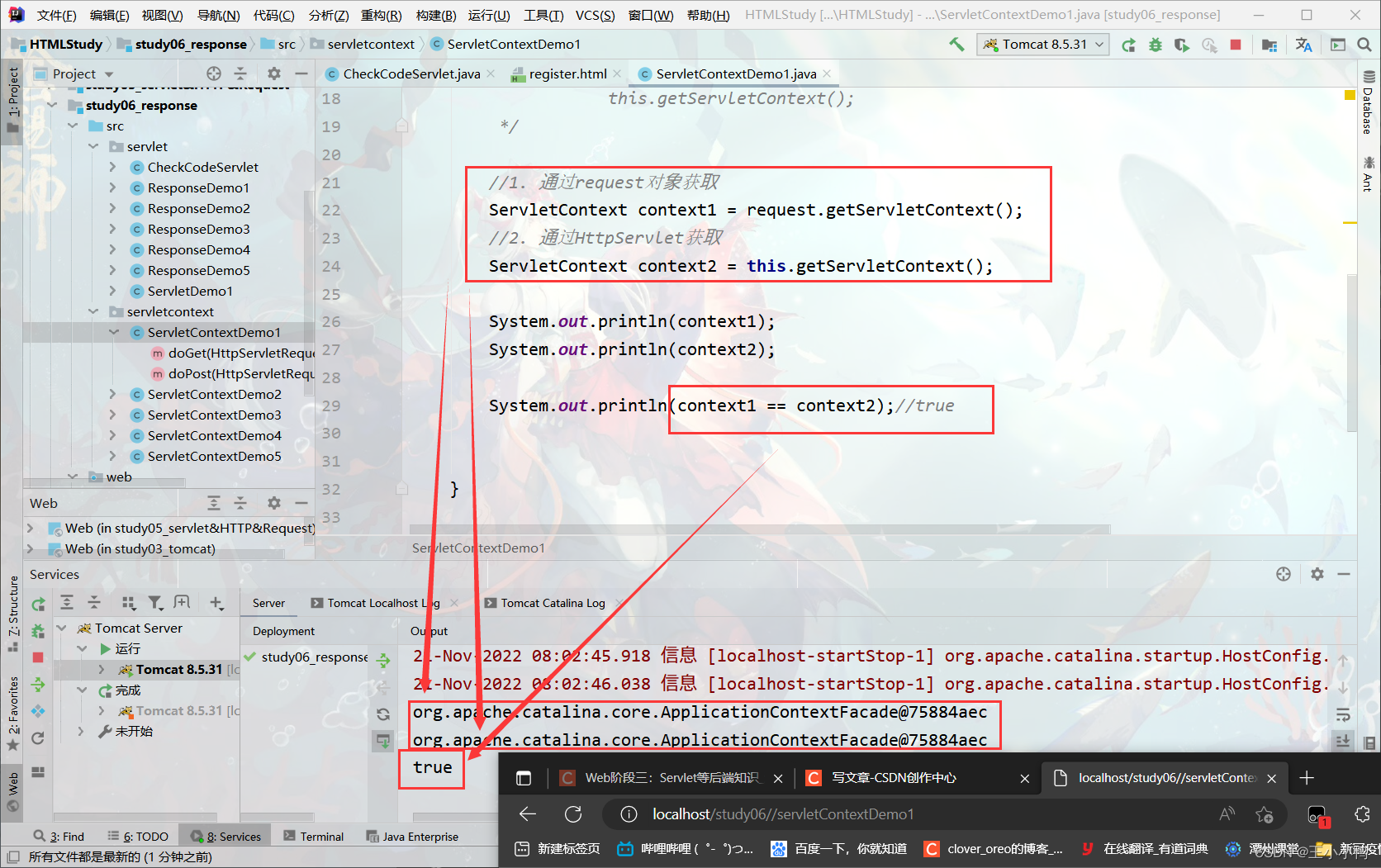
3. 功能:
1. 获取MIME类型:
* MIME类型:在互联网通信过程中定义的一种文件数据类型
* 格式: 大类型/小类型 text/html image/jpeg
* 获取:String getMimeType(String file)
//1. 通过HttpServlet获取对象
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
//2. 定义文件名称
String filename = "a.jpg";//image/jpeg
//3.获取MIME类型
String mimeType = context.getMimeType(filename);
System.out.println(mimeType);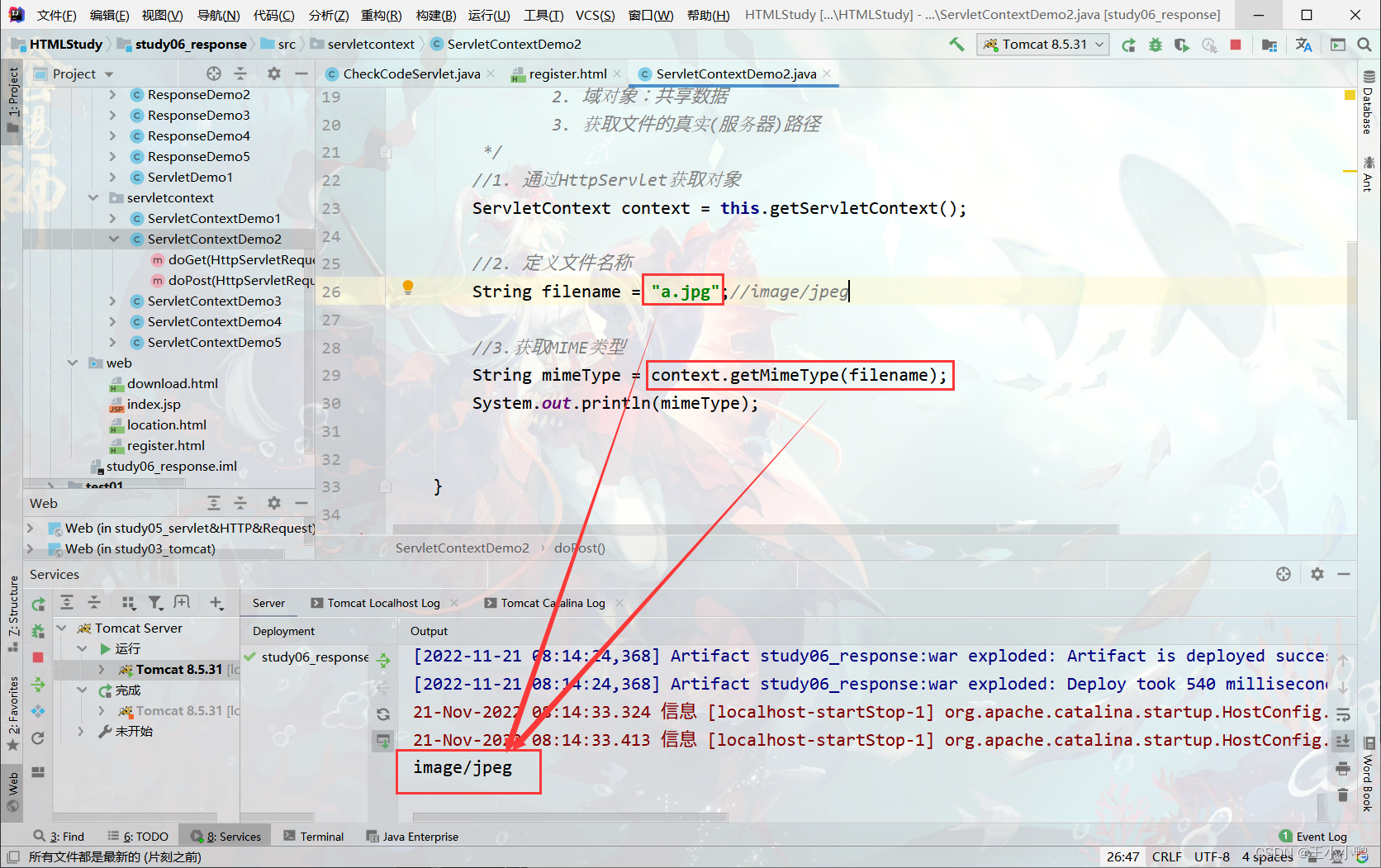
2. 域对象:共享数据
1. setAttribute(String name,Object value)
2. getAttribute(String name)
3. removeAttribute(String name)
* ServletContext对象范围:所有用户所有请求的数据
Demo3:
//通过HttpServlet获取
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
//设置数据
context.setAttribute("msg","haha");
Demo4:
//通过HttpServlet获取
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
//获取数据
Object msg = context.getAttribute("msg");
System.out.println(msg);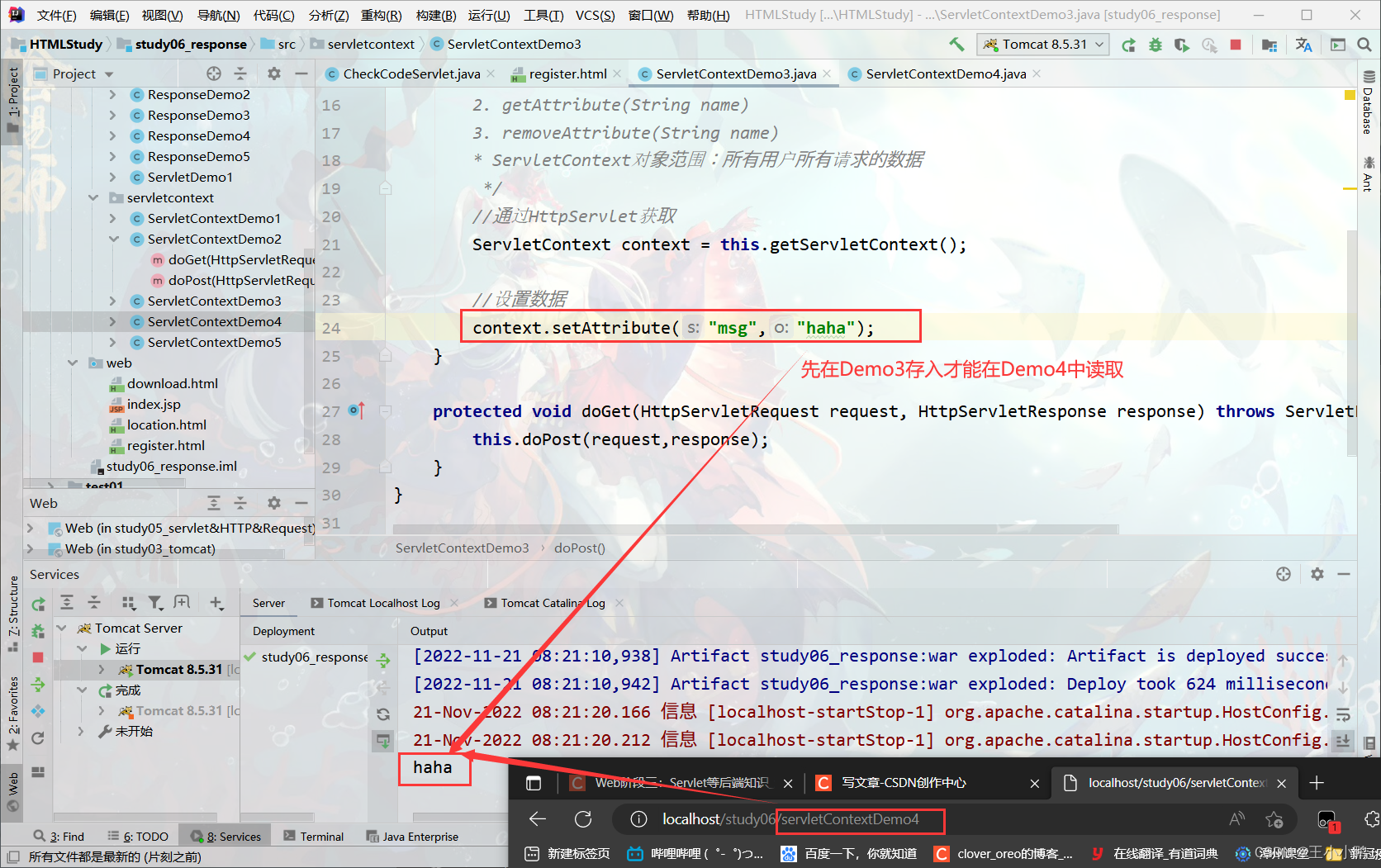
3. (*)获取文件的真实(服务器)路径
文件可以放在src下、web下、WEB-INF下
1. 方法:String getRealPath(String path)
String b = context.getRealPath("/b.txt");//web目录下资源访问
System.out.println(b);
String c = context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/c.txt");//WEB-INF目录下的资源访问
System.out.println(c);
String a = context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");//src目录下的资源访问
System.out.println(a);
// 通过HttpServlet获取
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
// 获取文件的服务器路径
String b = context.getRealPath("/b.txt");//web目录下资源访问
System.out.println(b);
// File file = new File(realPath);
String c = context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/c.txt");//WEB-INF目录下的资源访问
System.out.println(c);
String a = context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");//src目录下的资源访问
System.out.println(a);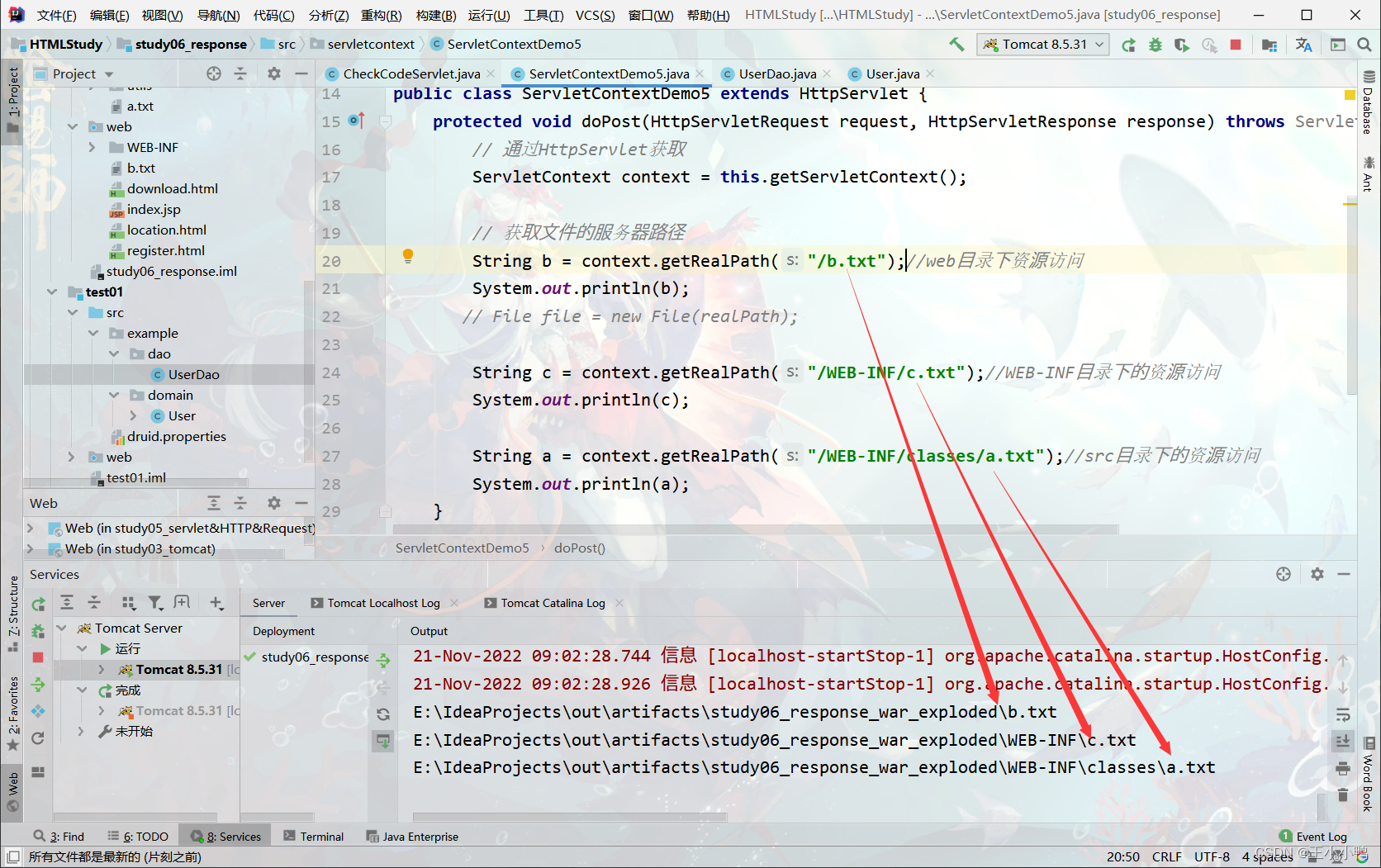
案例:
* 文件下载需求:
1. 页面显示超链接
2. 点击超链接后弹出下载提示框
3. 完成图片文件下载
* 分析:
1. 超链接指向的资源如果能够被浏览器解析,则在浏览器中展示,如果不能解析,则弹出下载提示框。不满足需求
2. 任何资源都必须弹出下载提示框
3. 使用响应头设置资源的打开方式:
* content-disposition:attachment;filename=xxx
<body>
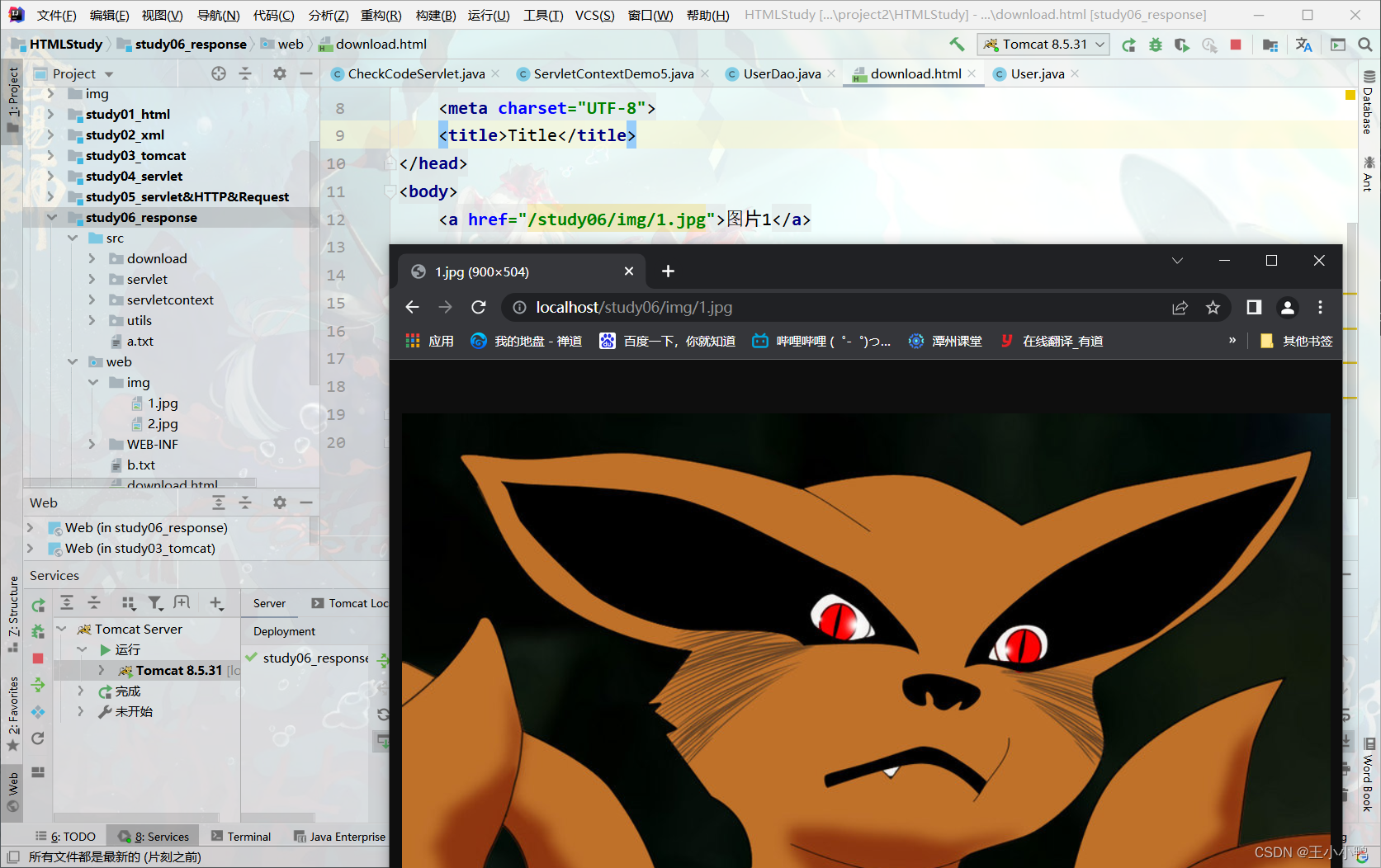
<a href="/study06/img/1.jpg">图片1</a>
<a href="/study06/img/诸葛渊.avi">诸葛渊视频</a>
<hr>
<!--使用响应头设置资源的打开方式:
* content-disposition:attachment;filename=xxx-->
<a href="/study06/downloadServlet?filename=1.jpg">图片1</a>
<a href="/study06/downloadServlet?filename=意气风发正少年.avi">羡羡视频</a>
</body>* 步骤:
1. 定义页面,编辑超链接href属性,指向Servlet,传递资源名称filename
2. 定义Servlet
1. 获取文件名称
2. 使用字节输入流加载文件进内存
3. 指定response的响应头: content-disposition:attachment;filename=xxx
4. 将数据写出到response输出流
* 问题:
* 中文文件问题
* 解决思路:
1. 获取客户端使用的浏览器版本信息
2. 根据不同的版本信息,设置filename的编码方式不同
图片加载成功:
找不到.mp4格式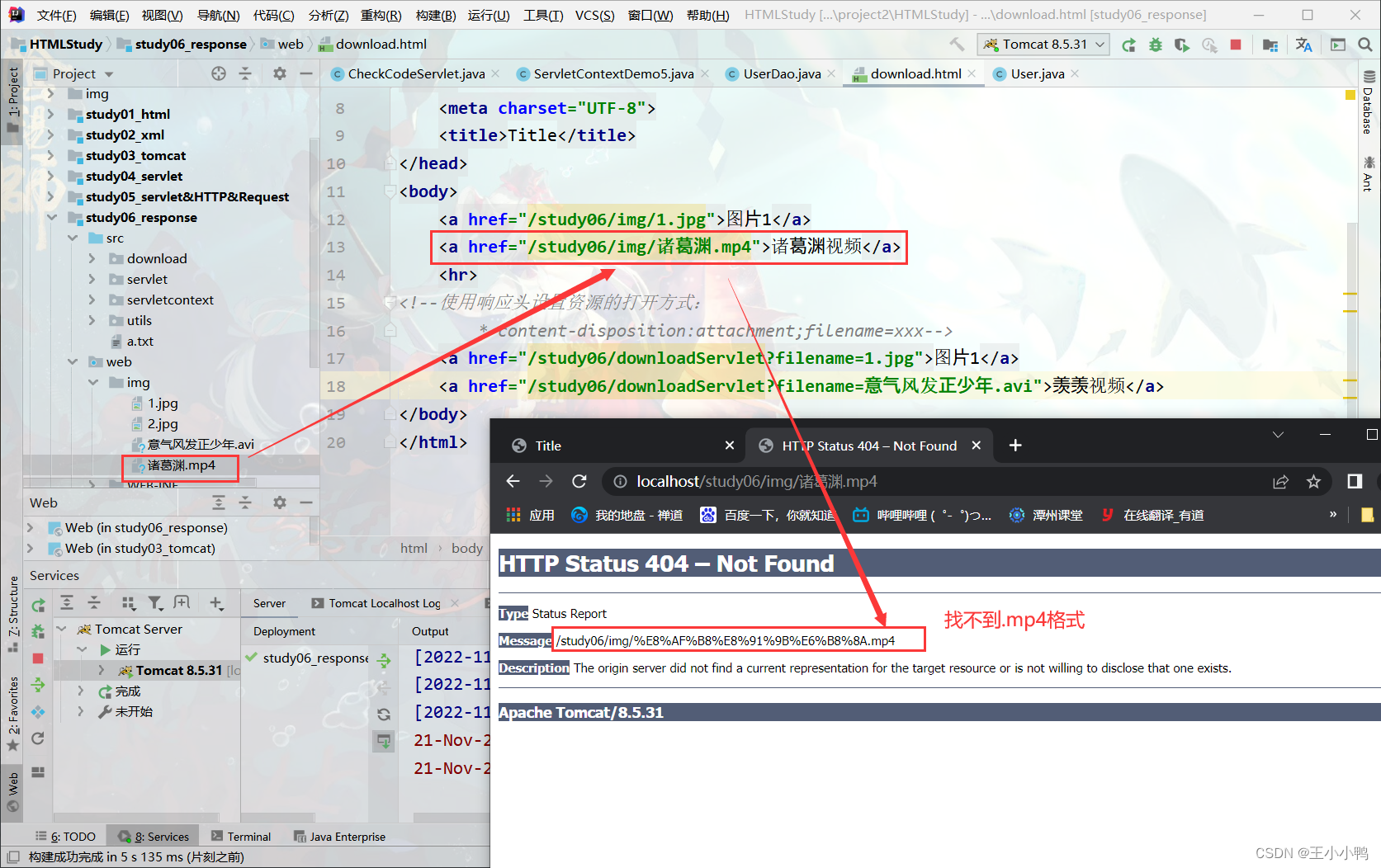
改成.avi就可以实现点击超链接后弹出下载提示框
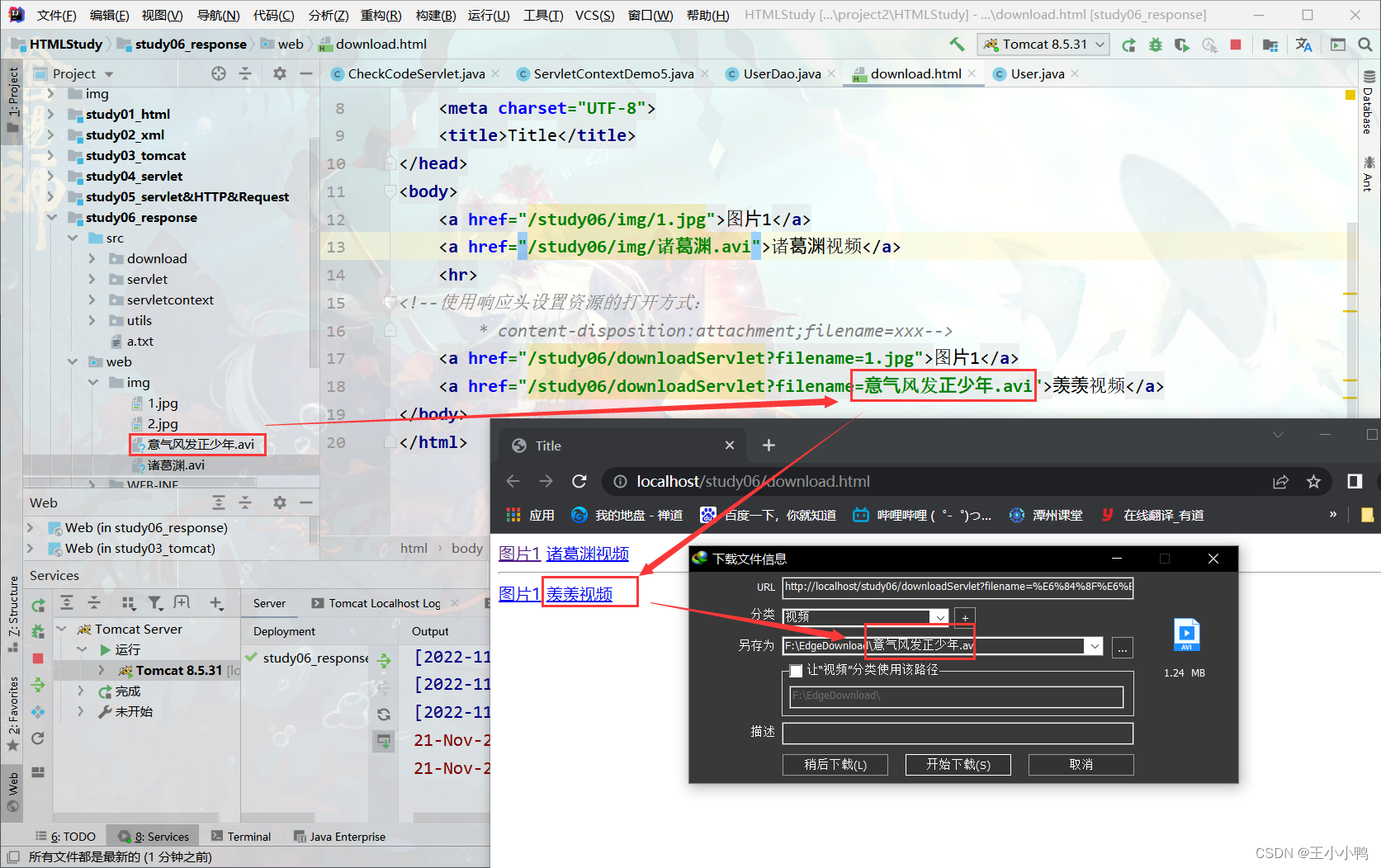
系统找不到指定路径:
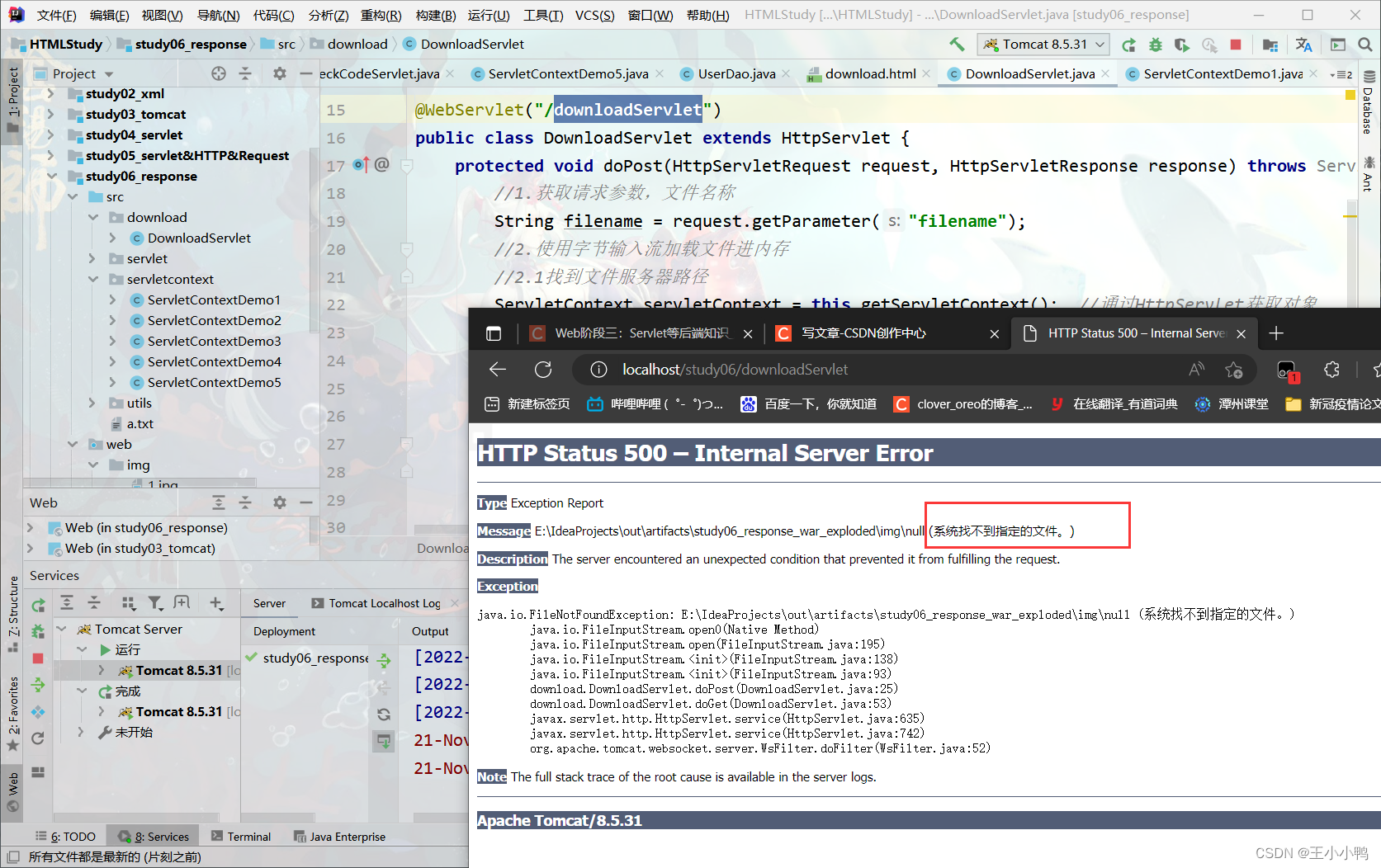
找了一早上加半个下午,破案了—— 出现原因:这个文件输出路径是E:\IdeaProjects\out\artifacts\study06_response_war_exploded\img,而我复制.jpg&.avi的路径在E:\IdeaProjects\project2\HTMLStudy\study06_response\web\img,
一个是输出路径,一个是文件夹所在路径,两者没有匹配,我将文件内的内容复制到输出路径后就能正常输出了,王德发!

Download.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<!--* 文件下载需求:
1. 页面显示超链接
2. 点击超链接后弹出下载提示框
3. 完成图片文件下载-->
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/study06/img/1.jpg">图片1</a>
<!-- 当教父太危险了带上这个吧.jpg-->
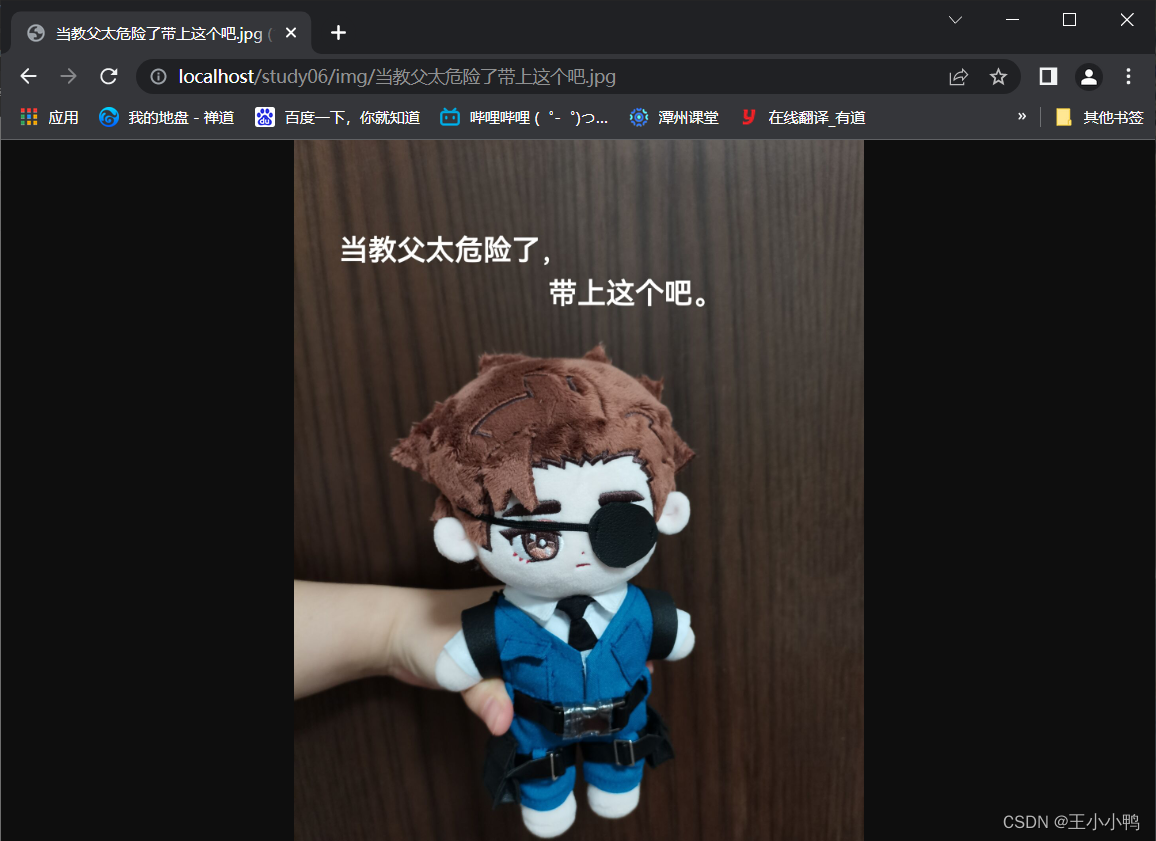
<a href="/study06/img/当教父太危险了带上这个吧.jpg">Alessio</a>
<a href="/study06/img/诸葛渊.avi">诸葛渊视频</a>
<hr>
<!--使用响应头设置资源的打开方式:
* content-disposition:attachment;filename=xxx-->
<a href="/study06/downloadServlet?filename=二乔开心.jpg">二乔图片</a>
<a href="/study06/downloadServlet?filename=意气风发正少年.avi">羡羡视频</a>
</body>
</html>DownloadServlet.java
package download;
import utils.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/downloadServlet")
public class DownloadServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.获取请求参数,文件名称
String filename = request.getParameter("filename");
//2.使用字节输入流加载文件进内存
//2.1找到文件服务器路径
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext(); //通过HttpServlet获取对象
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/img/" + filename);
//E:\IdeaProjects\project2\HTMLStudy\study06_response\web\img\当教父太危险了带上这个吧.jpg
//2.2用字节流关联
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//3.设置response的响应头
//3.1设置响应头类型:content-type
String mimeType = servletContext.getMimeType(filename);//获取文件的mime类型
response.setHeader("content-type", mimeType);
//3.2设置响应头打开方式:content-disposition
// response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filemane=" + filename);
//解决中文文件名问题
//1.获取user-agent请求头
String agent = request.getHeader("user-agent");
//2.使用工具类方法编码文件名即可
filename = DownLoadUtils.getFileName(agent, filename); //编码方法封装在工具类里
response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename=" + filename);
//4.将输入流的数据写出到输出流中
ServletOutputStream sos = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] buff = new byte[1024 * 8];//字节数组作为返回区
int len = 0; //读到的个数
while ((len = fis.read(buff)) != -1) { //如果长度未到达缓冲文件末尾则一直读取
sos.write(buff, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
}
于是我大胆尝试,想看看如果将输出路径下的文件全删了,只保留模块内的文件看能不能正常输出
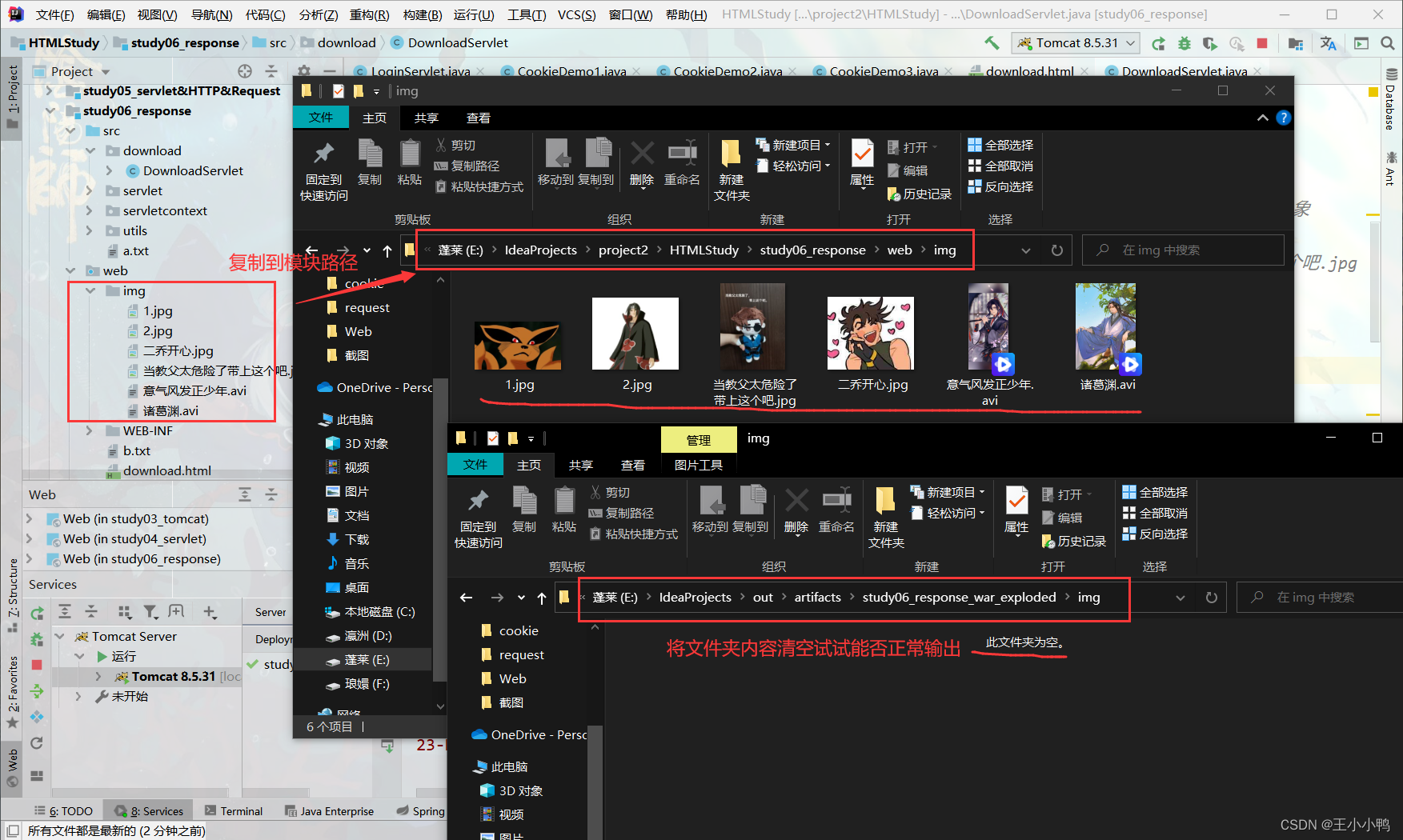
结果全员404,无法找到指定资源路径
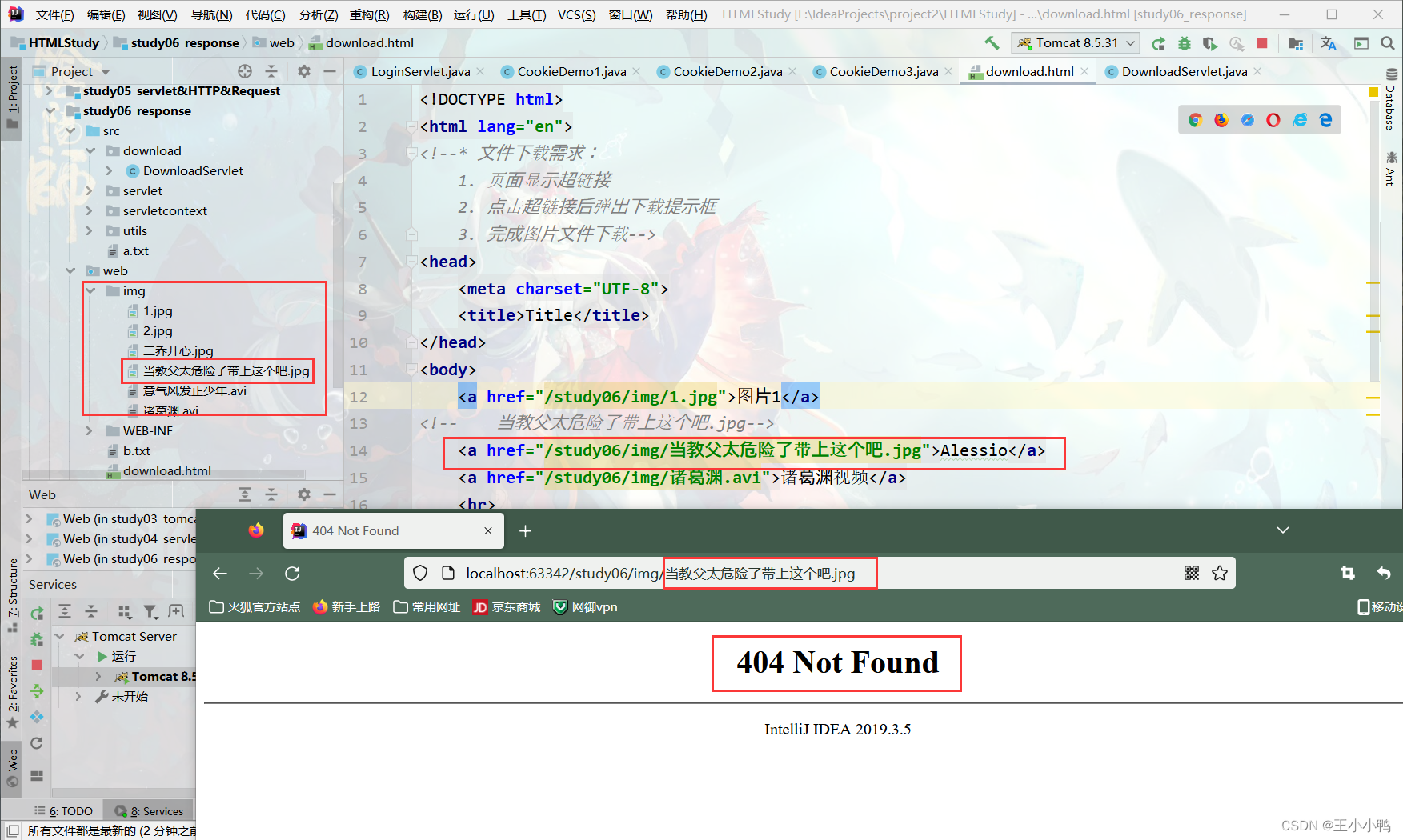
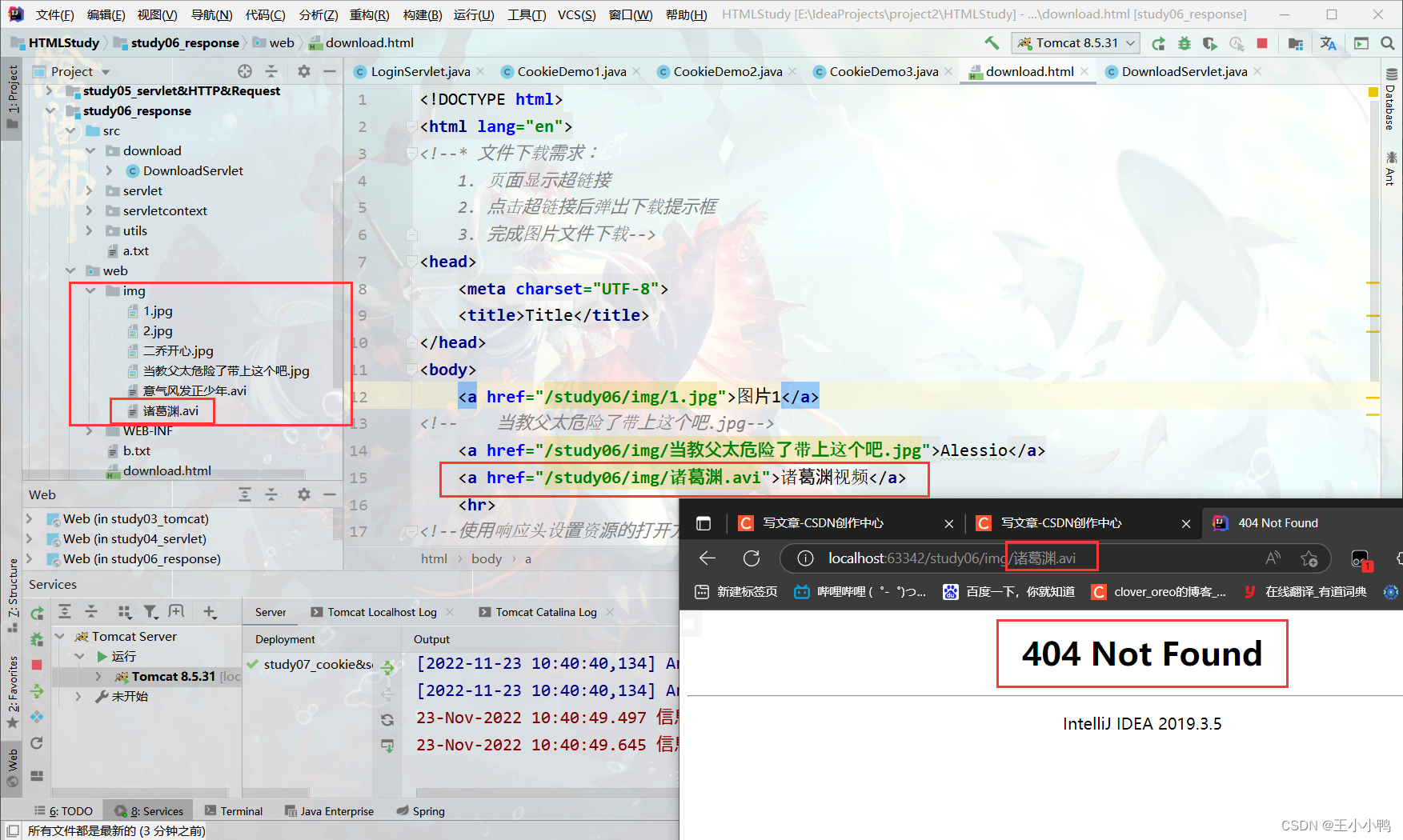
查阅资料后得知: response中表示响应,我们经常用于设置返回给客户端的内容〈输出),out也是给用户做输出使用的。
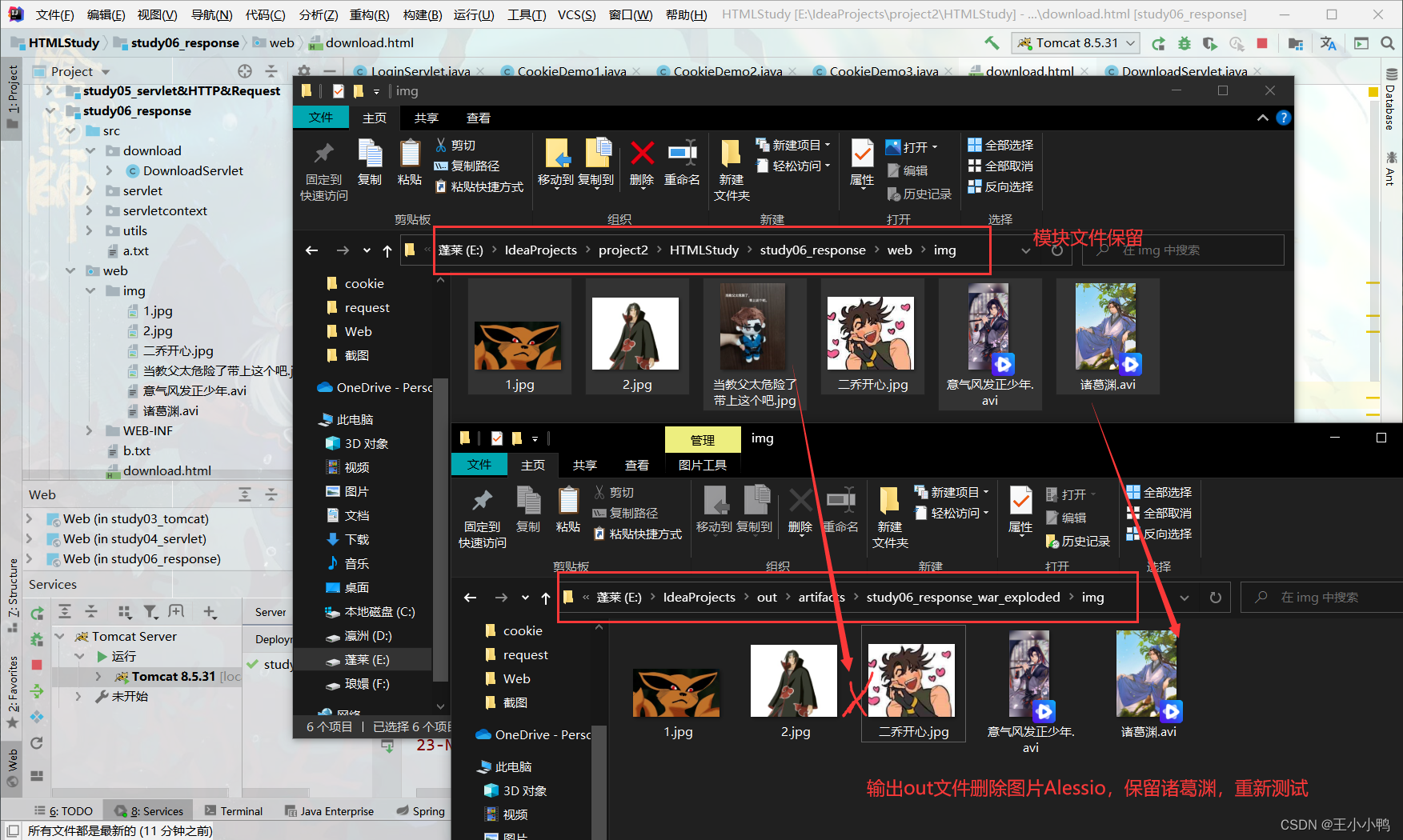
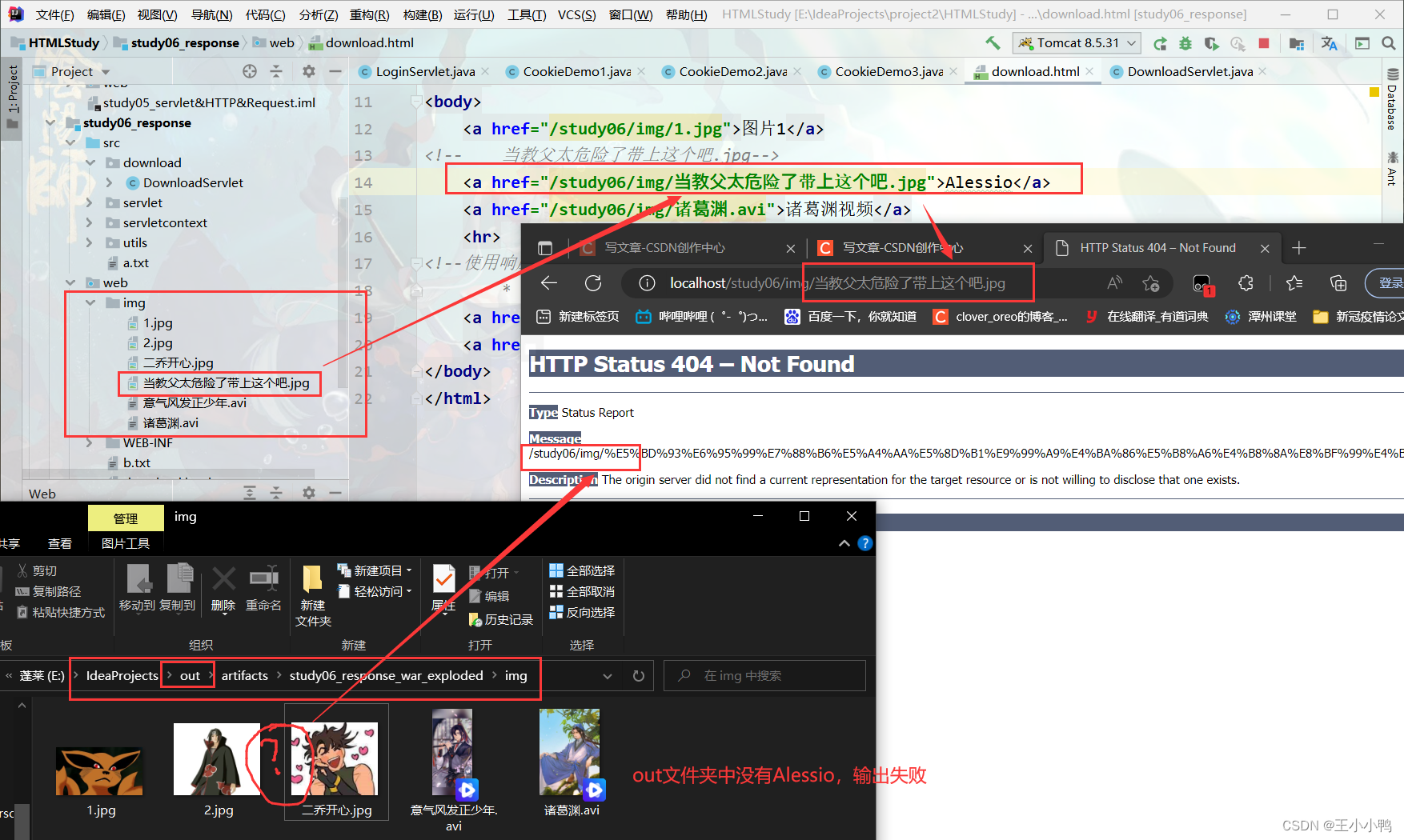
果然,Alessio的图片加载失败404了,诸葛渊成功了,out才是真正的输出文件路径
QAQ
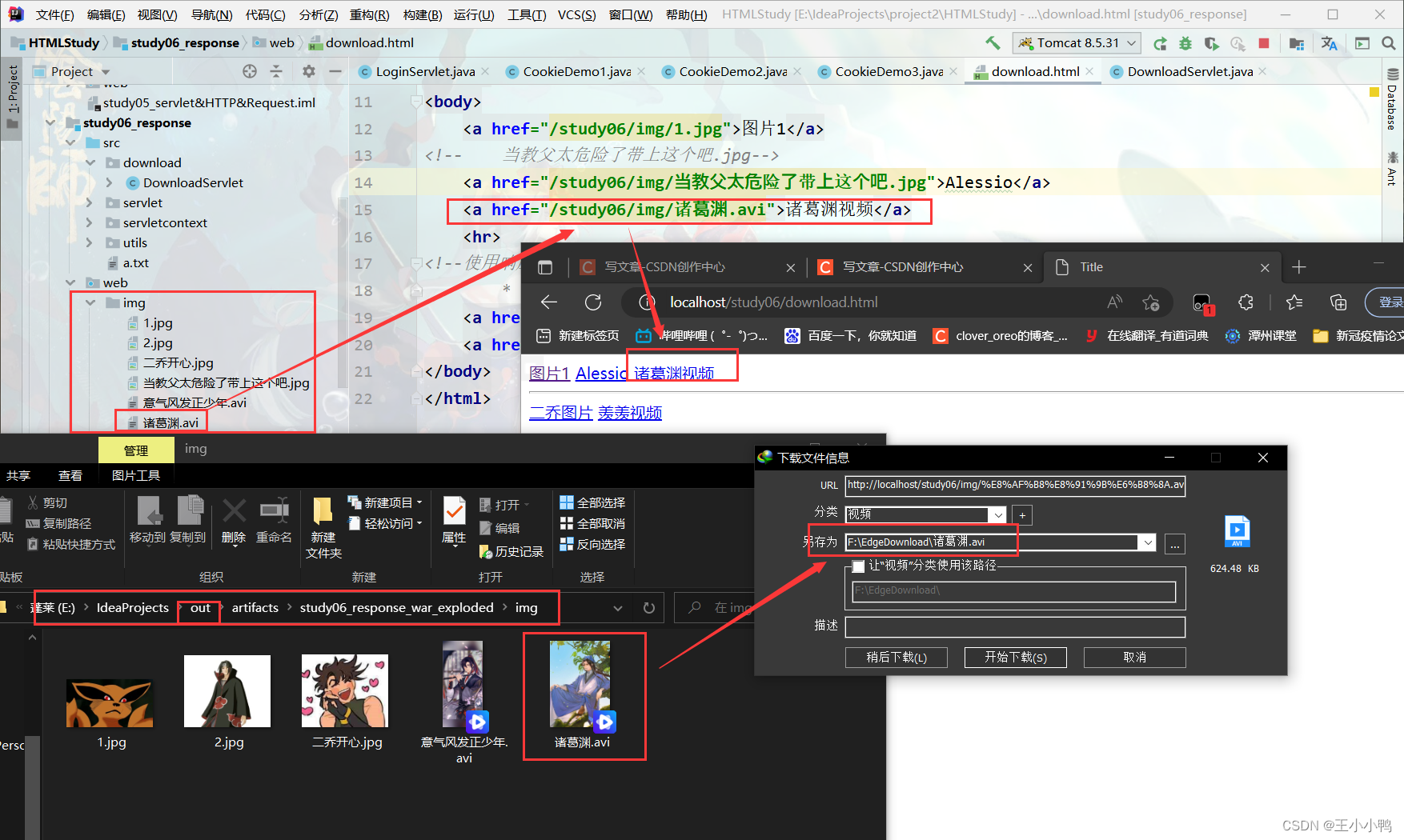
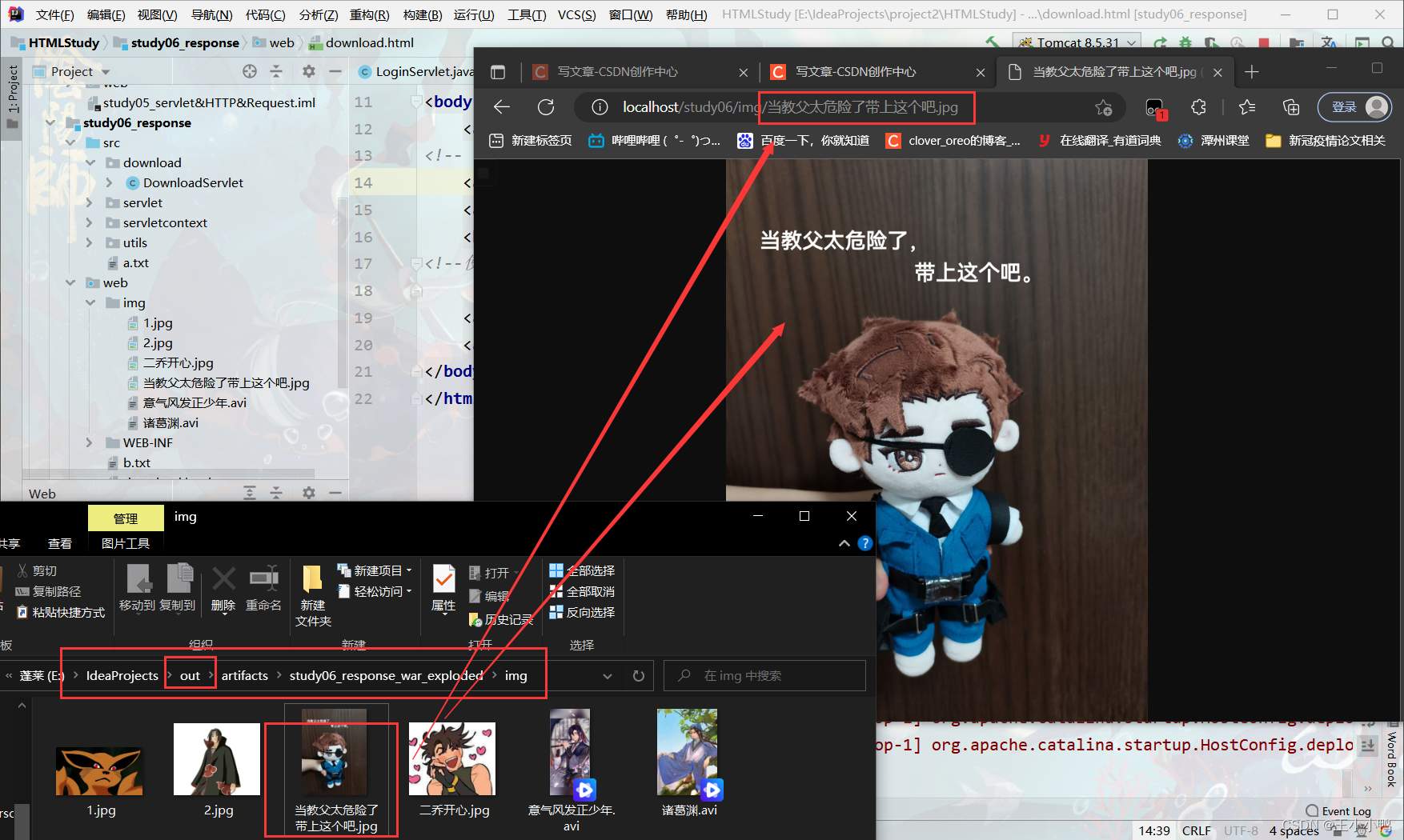
在out文件夹加上图片就能正常输出了
JAVA Idea中各个包.idea,out,src,web所放类的作用说明
 每次都要重新启动服务,我真的受不了辣!
每次都要重新启动服务,我真的受不了辣!
























 132
132











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








