Data Structure 笔记1 (链表)
(作者:colinboy Email:cybbh@163.com) 2008.4.30
(内容难免出现错误或一些专业词汇使用不当,只是个人笔记,能理解总体内容就好)
链表(linked list)
表的数组实现:
package lec7;
import java.util.*;
//存储整数的链表简单数组方法实现
public class LinkedListArray {
private int list[];
private int lastItem;
//链表测试
public static void main(String args[]) {
LinkedListArray list = new LinkedListArray();
Random rd = new Random();
for(int i=0; i<20; i++) {
int rdInt = rd.nextInt(1000);
list.insert(rdInt,i);
System.out.println(rdInt);
}
System.out.println(list);
list.insert(444,3);
list.insert(666,8);
list.insert(888,2);
list.insert(000,5);
System.out.println(list);
}
//构造函数
public LinkedListArray() {
list = new int[10]; //初始数组长度,可以是任意值,这里初始化为10
lastItem = -1;
}
//插入操作的实现
public boolean insert(int item, int position) {
//判断存储链表的数组是否已满
if(lastItem + 1 >= list.length) {
int[] b = new int[list.length * 2]; //扩大数组一倍
for(int i=0; i<list.length; i++) {
b[i] = list[i]; //将老数组中的内容存入新数组
}
list = b; //将链表数组用新的大数组代替.
}
//简单错误检查
if(position < 0 && position > list.length) {
return false; //出错返回
}
//插入内容,将包含要插入位置之后的所有数组元素向后移动一个位置,
for(int i=lastItem; i>=position; i--) {
list[i+1] = list[i];
}
list[position] = item; //插入内容到指定位置
lastItem++; //更新最后元素的下标.
return true;
}
//转换链表到字符串输出
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("[");
for(int i=0; i<=lastItem; i++) {
if(i == lastItem) {
result.append(list[i]);
} else {
result.append(list[i] + ",");
}
}
result.append("]");
return result.toString();
}
}
上述链表通过把数组类型改为Object或者使用范型,可以存储任何对象.
数组实现链表的缺点为:
1. 如果我们要在链表开头或中间类似位置插入数据,就必须移动很多插入位置后面的元素为新插入的数据开辟存储空间.数组的平均插入时间和数组长度成比例.
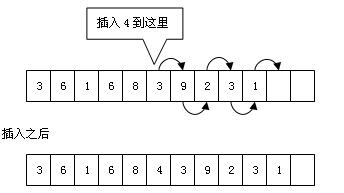
2. 数组是固定大小的,如果我们的链表长度超过了数组的长度,就必须重新分配一个新的更大的数组来存储.
优点为:
1. 链表元素的访问时间是常数时间,访问速度快.
为了避免数组实现的插入删除时间开销问题,我们可以使用很多节点存储链表,每个节点是一个链表元素,通过把各节点链接起来形成链表.
链表实现:
package lec7;
import java.util.Random;
public class LinkedList
{
private ListNode head; //头节点
private ListNode tail; //尾节点
private int length; //链表长度
//初始化链表
public LinkedList() {
head = null;
tail = null;
length = 0;
}
//获取链表长度
public int length() {
return length;
}
//添加元素到链表尾
public boolean add(int item) {
if(head == null) {
head = new ListNode(item,null);
tail = head;
} else {
tail.next = new ListNode(item,null);
tail = tail.next;
}
length++;
return true;
}
//添加元素到链表尾
public boolean addLast(int item) {
return add(item);
}
//添加元素到链表头
public boolean addFirst(int item) {
if(head == null) {
head = new ListNode(item,null);
tail = head;
} else {
head = new ListNode(item,head);
}
length++;
return true;
}
//转换链表到字符串输出
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("[");
if (head != null) {
result.append(head.item + ",");
ListNode temp = head;
while ((temp = temp.next) != null) {
if(temp == tail) {
result.append(temp.item);
} else {
result.append(temp.item + ",");
}
}
}
result.append("]");
return result.toString();
}
//测试链表
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList lklist = new LinkedList();
Random rd = new Random();
for(int i=0; i<20; i++) {
int rdInt = rd.nextInt(1000);
lklist.add(rdInt);
System.out.println(rdInt);
}
System.out.println(lklist);
lklist.addFirst(444);
lklist.addFirst(666);
lklist.addFirst(888);
lklist.addFirst(999);
System.out.println(lklist);
}
}
//链表节点
class ListNode
{
int item; //节点内容
ListNode next; //指向后继节点
public ListNode(int item) {
this.item = item;
}
public ListNode(int item, ListNode next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
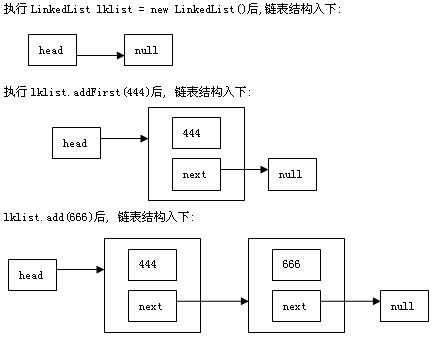
上面的链表实现并不完全比数组实现好,因为访问链表元素的平均时间和链表长度成比例,但是插入和删除数据只花费常数时间.























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








