转载地址http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/34089553
今
天重温了下Javacript,给大家带来一篇Javascript博文,相信对于Javacript有一定了解的人都听过prototype原型这个概念,今天我们深度的分析下prototype与__proto__。
好了,下面看一个非常简单的例子:
- var Person = function(name)
- {
- this.name = name ;
- };
- var p = new Person("Ben");
- console.log(p.name);
代码简单的 你不用说明了,如果现在让大家根据上面的代码画一张包含Function与Object的内存图,大家肯定回想什么叫包含Function与Object,上面的代码和它们有几毛钱的关系。好了,下面我先按要求把图画出来,大家参考下:
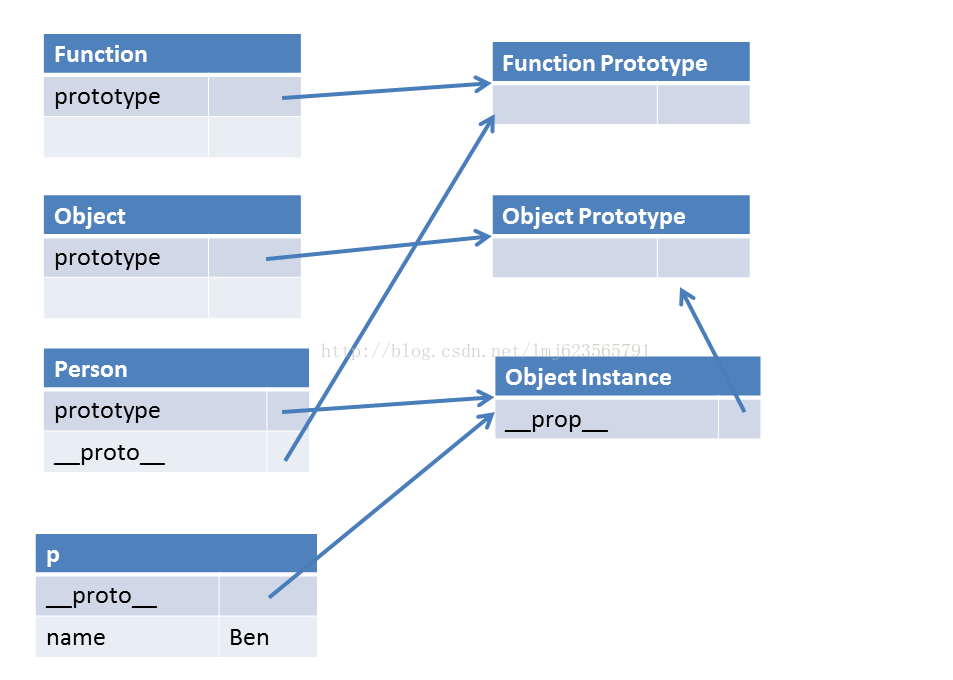
解析下:
1、任何一个由构造器产生的对象都有__proto__属性,且此属性指向该构造器的prototype。
2、所有构造器/函数的__proto__都指向Function的prototype
拿第2条对比第1条,貌似我们发现了什么,没错函数的构造器就是Function,看下面的代码:
-
- var Person = function(name)
- {
- this.name = name ;
- };
-
- function Person(name)
- {
- this.name = name ;
- }
-
- var Person = new Function("name" , "this.name = name ;" );
当然了不能说说,下面看代码验证:
- console.log(Person.__proto__ === Function.prototype);
- console.log(typeof p.__proto__);
- console.log(p.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype);
有人会问,那么Function与Object的prototype,__prop__到底是什么呢?
- console.log(Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype);
- console.log(Function.__proto__ === Function.prototype);
- console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ == Object.prototype);
- console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__);
有此可见
1、所有的构造器包括Object和Function都继承了Function.prototype的方法,由第三行可知所有的构造器都是对象,即js中一切皆为对象。
2、__proto__最终的指向都是Object.prototype,这也就是js中的原型链。
最后我们看一下Object的文档:
The following table lists properties of the Object Object.
发现Object还有个constructor属性。
1、constructor属性指向的是创建当前对象的构造函数。
2、每个函数都有一个默认的属性prototype,而这个prototype的constructor默认指向这个函数
看下面的例子:
-
- var Person = function(name)
- {
- this.name = name ;
- };
-
- var p = new Person("Ben");
-
- console.log(p.constructor === Person);
- console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person);
- console.log(Person.prototype instanceof Object);
- console.log(Person.prototype instanceof Person);
-
- Person.prototype = {name:"123"} ;
- var p2 = new Person("Ben");
- console.log(p2.constructor === Object);
- console.log(p2.constructor === Person.prototype.constructor);
- console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Object);
- console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person);
当改变Person的prototype时,会发现,Person.prototype.constructor指向了Object,主要是因为:
Person.prototype = {name:"123"} 相当于Person.prototype=new Object({name:"123"} );此时的构造器变成了Object.
好了,就介绍到这里,各位看官没事留个言,赞一个,哈~。
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/25076713
一直觉得Js很强大,由于长期不写js代码,最近刚好温故温故。
1、Javascript没有代码块作用域的概念,局部作用域是针对函数来说的。
2、如果不使用var声明的变量,默认为全局变量
3、Js中的作用域链
先看个简单的例子:只有一个函数对象,函数对象和其它对象一样,拥有可以通过代码访问的属性和一系列仅供JavaScript引擎访问的内部属性。其中一个内部属性是[[Scope]],由ECMA-262标准第三版定义,该内部属性包含了函数被创建的作用域中对象的集合,这个集合被称为函数的作用域链,它决定了哪些数据能被函数访问。
作用域链的图:
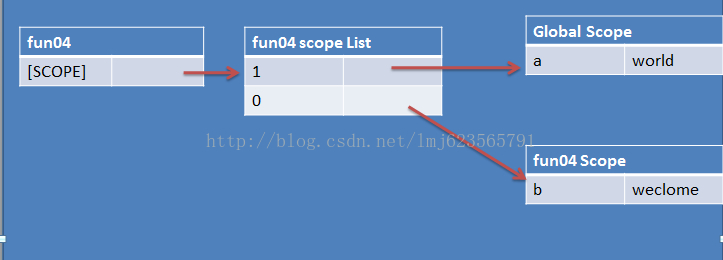
注:图中省略了,Global Scope中的window,document等,每个函数对象中的arguments,this等均未画出。
观察上面代码,存在fun03,f,g三个函数对象。
下面是作用域链的图:
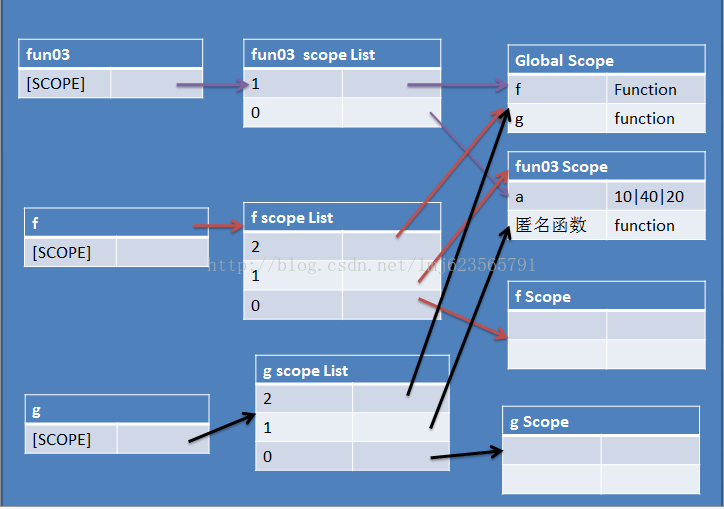
注:每个函数对象一个作用域链,这里直接画在了一起;对于变量的查找,先从链的0开始找。
函数对象 f 在代码中执行了2 次,所以a*2*2 = 40 ; 函数对象 g 在代码中执行了1次, 所以 a *2 = 20 ;
4、闭包
上面的例子可以看到,在fun03执行完成后,a的实例并没有被销毁,这就是闭包。个人对闭包的理解是:函数执行完成后,函数中的变量没有被销毁,被它返回的子函数所引用。
下面以一个特别经典的例子,同时使用作用域链解析:
相信上面的代码肯定大家都写过,本意是点击每个li,打印出它们的索引,可是事实上打印出的都是elements.length。这是为什么呢?
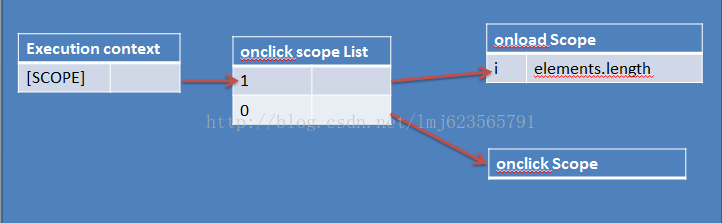
看下上面的简易的作用域链(省略了很多部分,主要是理解),此时每个onclick函数的i,指向的都是 onload 中的i 此时的 i = element.length.
下面看解决方案:
在onclick函数的外层,包了一层立即执行的函数,所以此时的n指向的 n 是立即执行的,所有都是1~elements.length 。
Javascript 进阶 封装
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/25080573
js中处处是对象,面向对象的第一步当然就是封装了,由于Js中没有类的概念,所以封装起来也比较麻烦,下面介绍两种js的封装。
1、使用约定优先的原则,将所有的私有变量以_开头
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
-
-
- var Person = function (no, name, age)
- {
- this.setNo(no);
- this.setName(name);
- this.setAge(age);
- }
- Person.prototype = {
- constructor: Person,
- checkNo: function (no)
- {
- if (!no.constructor == "string" || no.length != 4)
- throw new Error("学号必须为4位");
- },
- setNo: function (no)
- {
- this.checkNo(no);
- this._no = no;
- }, getNo: function ()
- {
- return this._no;
- }, setName: function (name)
- {
- this._name = name;
- }, getName: function ()
- {
- return this._name;
- }, setAge: function (age)
- {
- this._age = age;
- }, getAge: function ()
- {
- return this._age;
- }, toString: function ()
- {
- return "no = " + this._no + " , name = " + this._name + " , age = " + this._age;
- }
- };
- var p1 = new Person("0001", "鸿洋", "22");
- console.log(p1.toString());
- p1.setNo("0003");
- console.log(p1.toString());
- p1.no = "0004";
- p1._no = "0004";
- console.log(p1.toString());
-
- </script>
看完代码,是不是有种被坑的感觉,仅仅把所有的变量以_开头,其实还是可以直接访问的,这能叫封装么,当然了,说了是约定优先嘛,这种方式还是不错的,最起码成员变量的getter,setter方法都是prototype中,并非存在对象中,总体来说还是个不错的选择。如果你觉得,这不行,必须严格实现封装,那么看第二种方式。
2、严格实现封装
看上面的代码,去掉了this.属性名,严格的实现了封装,只能通过getter,setter访问成员变量了,但是存在一个问题,所有的方法都存在对象中,增加了内存的开销。
3、以闭包的方式封装
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
-
-
-
- var Person = (function ()
- {
- var checkNo = function (no)
- {
- if (!no.constructor == "string" || no.length != 4)
- throw new Error("学号必须为4位");
- };
-
- var times = 0;
-
- return function (no, name, age)
- {
- console.log(times++);
- var no , name , age;
- this.setNo = function (no)
- {
- checkNo(no);
- this._no = no;
- };
- this.getNo = function ()
- {
- return this._no;
- }
- this.setName = function (name)
- {
- this._name = name;
- }
-
- this.getName = function ()
- {
- return this._name;
- }
-
- this.setAge = function (age)
- {
- this._age = age;
- }
- this.
- getAge = function ()
- {
- return this._age;
- }
-
- this.setNo(no);
- this.setName(name);
- this.setAge(age);
- }
- })();
- Person.prototype = {
- constructor: Person,
- toString: function ()
- {
- return "no = " + this._no + " , name = " + this._name + " , age = " + this._age;
- }
- }
- ;
- var p1 = new Person("0001", "鸿洋", "22");
- var p2 = new Person("0002", "abc", "23");
- var p3 = new Person("0003", "aobama", "24");
-
-
- console.log(p1.toString());
- console.log(p2.toString());
- console.log(p3.toString());
-
- </script>
上述代码,js引擎加载完后,会直接执行Student = 立即执行函数,然后此函数返回了一个子函数,这个子函数才是new Student所调用的构造函数,又因为子函数中保持了对立即执行函数中checkNo(no) ,times的引用,(很明显的闭包)所以对于checkNo和times,是所有Student对象所共有的,创建3个对象后,times分别为0,1,2 。这种方式的好处是,可以使Student中需要复用的方法和属性做到私有且对象间共享。
1、基于类的继承
下面看下面的代码:
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
-
- function Person(name, age)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- Person.prototype.say = function ()
- {
- console.log(this.name + " , " + this.age);
- }
- function Student(no)
- {
- this.no = no;
- }
- <span style="white-space:pre">
-
- </span>
- Student.prototype = new Person();
- var stu1 = new Student("0001");
- stu1.name = '张三';
- stu1.age = '11';
- console.log(stu1.no);
- stu1.say();
-
-
- </script>
输出结果:
可以看到Student成功集成了Person,并且拥有了Person的say方法,核心代码其实就是一句 Student.prototype = new Person();,下面通过图解来说明原理:
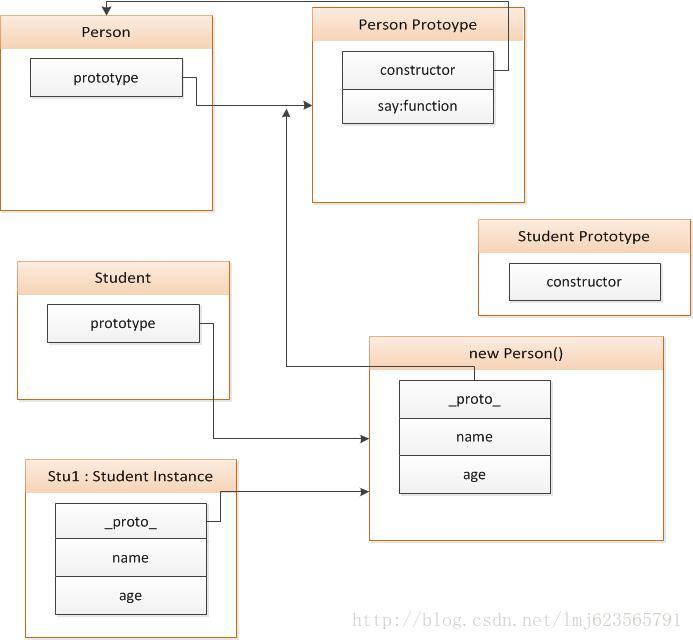
将Student.prototype指向new Person() , new Person的_proto_又指向Person Prototype;这样完成了整个继承。
但是这种方式存在问题:
问题1:当父类存在引用类型变量时,造成数据不一致,下面我们给Person添加一个hobbies属性,类型为数组。
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function Person(name, age)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- this.hobbies = [] ;
- }
- Person.prototype.say = function ()
- {
- console.log(this.name + " , " + this.age +" , " +this.hobbies);
- }
- function Student(no)
- {
- this.no = no;
- }
- Student.prototype = new Person();
-
- var stu1 = new Student("0001");
- stu1.name = '张三';
- stu1.age = '11';
- stu1.hobbies.push("soccer");
- stu1.say();
-
- var stu2 = new Student("0002");
- stu2.name = '李四';
- stu2.age = '12';
- stu2.hobbies.push("girl");
- stu2.say();
-
- </script>
输出结果:
- 张三 , 11 , soccer
- 李四 , 12 , soccer,girl
可以看出,李四的hobbies应该只有girl,但是上面的代码让所有对象共享了hobbies属性。
上述的继承方式还存在一个问题:
问题2:在Student的构造方法中,无法使用new Student("00001" , "张三" , 12) ;创建对象,并初始化name和age属性,必须stu.name, stu.age进行赋值
为了解决上述问题,对上述代码进行修改:
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
- function Person(name, age)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- this.hobbies = [];
- }
- Person.prototype.say = function ()
- {
- console.log(this.name + " , " + this.age +" , " + this.hobbies);
- }
-
- function Student(name, age, no)
- {
-
-
-
-
- Person.call(this, name, age);
- this.no = no;
- }
-
- Student.prototype = new Person();
-
- var stu1 = new Student("0001","张三",11);
- stu1.hobbies.push("soccer");
- stu1.say();
-
- var stu2 = new Student("0002","李四",12);
- stu2.hobbies.push("cangjin");
- stu2.hobbies.push("basketball");
- stu2.say();
-
- </script>
输出:
- 0001 , 张三 , soccer
- 0002 , 李四 , cangjin,basketball
在Student的构造方法中使用了Person.call(this,name,age)感觉就像super(name,age)【call的第一个参数为上下文】;并且成功解决了对引用属性的共享问题,完美解决。
2、基于原型链的继承
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
-
-
-
-
-
- var Person = {
- name: "人",
- age: 0,
- hobbies: [],
- say: function ()
- {
- console.log(this.name + " , " + this.age + " , " + this.hobbies);
- }
- }
- ;
-
- var Student = clone(Person);
- Student.no ="";
- Student.sayHello = function()
- {
- console.log(this.name +"hello ") ;
- }
-
- var stu1 = clone(Student);
- stu1.name = "zhangsan";
- stu1.age = 12;
- stu1.hobbies.push("Java");
- stu1.say();
-
- var stu2 = clone(Student);
- stu2.name = "lisi";
- stu2.age = 13;
- stu2.hobbies.push("Javascript");
- stu2.say();
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function clone(obj)
- {
- var F = function ()
- {
- };
- F.prototype = obj;
- return new F();
-
- }
-
-
- </script>
输出:
- zhangsan , 12 , Java
- lisi , 13 , Java,Javascript
可以看出同样存在引用属性不一致的问题,并且整个操作全部基于对象,给人的感觉不是很好,下面通过图解解释下原理:
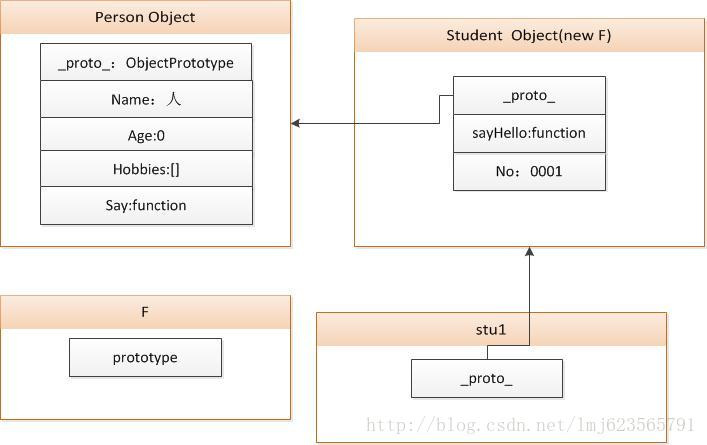
对象间通过一个clone函数,不断的返回一个新的对象,且prototype执行传入的对象,整个继承过程其实就是_proto_不断的指向,形成一个链,所以叫做原型链。
好了,已经介绍完了,js的两种集成的方式,最好使用的还是通过类的继承(上述第一种方案,解决存在问题的)。
如果代码或者讲解存在任何问题,欢迎留言指出。
Javascript的难点就是面向对象编程,上一篇介绍了Javascript的两种继承方式:Javascript 进阶 继承,这篇使用一个例子来展示js如何面向对象编程,以及如何基于类实现继承。
1、利用面向对象的写法,实现下面这个功能,实时更新数据的一个例子:
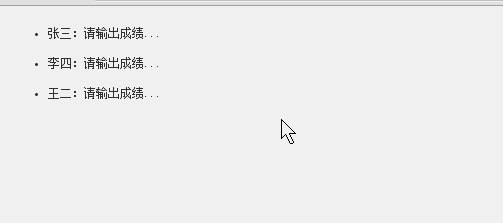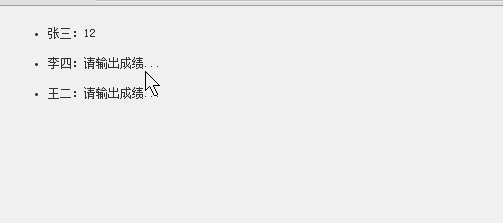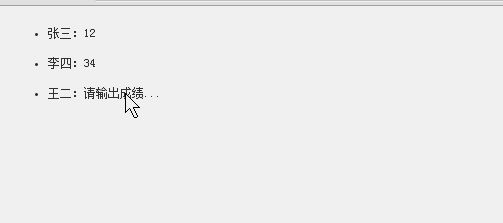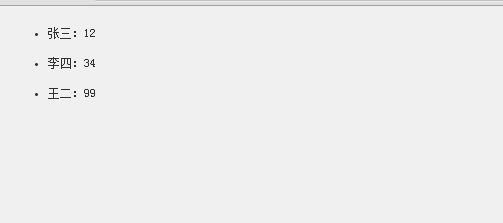
2、使用对上面类的继承,完成下面的效果:
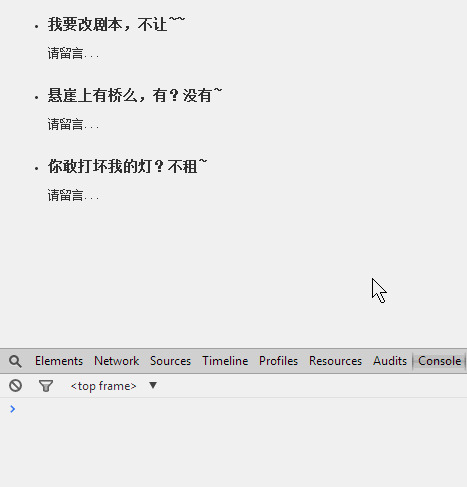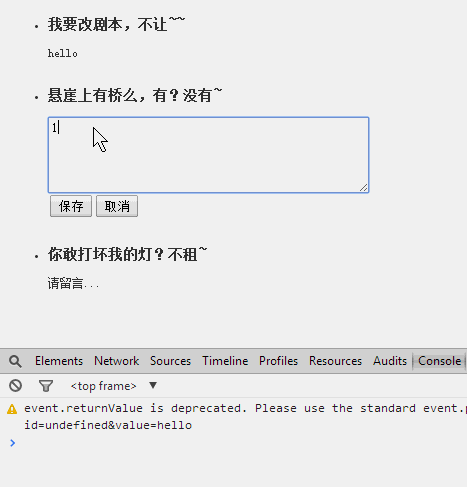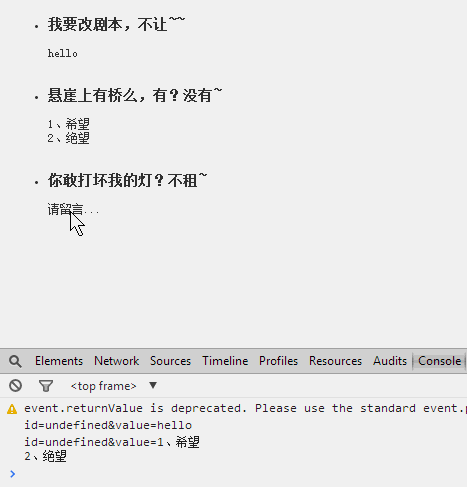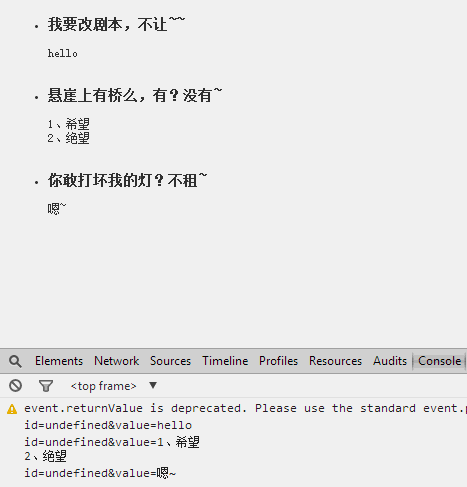
好了,不多说,js的训练全靠敲,所以如果觉得面向对象不是很扎实,可以照着敲一个,如果觉得很扎实了,提供了效果图,可以自己写试试。
1、第一个效果图代码:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function PlaceFieldEditor(id, value, parentEle)
- {
- this.id = id;
- this.value = value;
- this.parentEle = parentEle;
- this.initValue = value ;
-
- this.initElements();
- this.initEvents();
- }
-
- PlaceFieldEditor.prototype = {
- constructor: PlaceFieldEditor,
-
-
-
- initElements: function ()
- {
- this.txtEle = $("<span/>");
- this.txtEle.text(this.value);
-
- this.textEle = $("<input type='text' />");
- this.textEle.val(this.value);
-
- this.btnWapper = $("<div style='display: inline;'/>");
- this.saveBtn = $("<input type='button' value='保存'/>");
- this.cancelBtn = $("<input type='button' value='取消'/>");
- this.btnWapper.append(this.saveBtn).append(this.cancelBtn);
-
- this.parentEle.append(this.txtEle).append(this.textEle).append(this.btnWapper);
-
- this.convertToReadable();
- },
-
-
-
- initEvents: function ()
- {
- var that = this;
- this.txtEle.on("click", function (event)
- {
- that.convertToEditable();
- });
-
- this.cancelBtn.on("click", function (event)
- {
- that.cancel();
- });
-
- this.saveBtn.on("click", function (event)
- {
- that.save();
- });
-
- },
-
-
-
- convertToEditable: function ()
- {
- this.txtEle.hide();
- this.textEle.show();
- this.textEle.focus();
-
- if(this.getValue() == this.initValue )
- {
- this.textEle.val("");
- }
-
- this.btnWapper.show();
- },
-
-
-
- save: function ()
- {
- this.setValue(this.textEle.val());
- this.txtEle.html(this.getValue().replace(/\n/g,"<br/>"));
-
- var url = "id=" + this.id + "&value=" + this.value;
-
- console.log(url);
- this.convertToReadable();
- },
-
-
-
- cancel: function ()
- {
- this.textEle.val(this.getValue());
- this.convertToReadable();
- },
-
-
-
- convertToReadable: function ()
- {
- this.txtEle.show();
- this.textEle.hide();
- this.btnWapper.hide();
- },
- setValue: function (value)
- {
- this.value = value;
- },
- getValue: function ()
- {
- return this.value;
- }
- }
- ;
引入到页面代码:
- <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
- "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
- <html>
- <head>
- <title></title>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="jquery-1.8.3.js"></script>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="PlaceFieldEditor.js"></script>
-
- <script type="text/javascript">
- $(function ()
- {
-
- $("ul li").each(function ()
- {
- new PlaceFieldEditor($(this).attr("id"), "请输出成绩...", $(this));
- });
-
-
- });
-
- </script>
-
- <style type="text/css">
- body
- {
- font-size: 12px;
- color: #333;;
- }
-
- ul li
- {
- line-height: 30px;
- }
-
- </style>
- </head>
- <body>
-
-
- <ul>
- <li id="1">张三:</li>
- <li id="2">李四:</li>
- <li id="3">王二:</li>
- </ul>
-
- </body>
- </html>
嗯,代码就不详细说了,都比较简单,使用了jQuery,如果不喜欢可以使用原生js,本人比较喜欢把jQuery当作js的工具使用。
2、第二个效果图的js代码:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function PlaceAreaEditor(id, value, parentEle)
- {
- PlaceAreaEditor.superClass.constructor.call(this, id, value, parentEle);
- }
-
- extend(PlaceAreaEditor, PlaceFieldEditor);
-
- PlaceAreaEditor.prototype.initElements = function ()
- {
- this.txtEle = $("<span/>");
- this.txtEle.text(this.value);
-
- this.textEle = $("<textarea style='width:315px;height:70px;' />");
- this.textEle.text(this.value);
-
- this.btnWapper = $("<div style='display: block;'/>");
- this.saveBtn = $("<input type='button' value='保存'/>");
- this.cancelBtn = $("<input type='button' value='取消'/>");
- this.btnWapper.append(this.saveBtn).append(this.cancelBtn);
-
- this.parentEle.append(this.txtEle).append(this.textEle).append(this.btnWapper);
-
- this.convertToReadable();
-
- };
写了PlaceAreaEditor继承了PlaceFieldEditor,然后复写了initElements方法,改变了text为textarea。
extend的方法,上一篇博客已经介绍过:
-
-
-
-
- function extend(subClass, superClass)
- {
- var F = function ()
- {
- };
- F.prototype = superClass.prototype;
-
- subClass.prototype = new F();
-
- subClass.superClass = superClass.prototype;
- }
最后页面代码:
- <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
- "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
- <html>
- <head>
- <title></title>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="jquery-1.8.3.js"></script>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="PlaceFieldEditor.js"></script>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="com.zhy.extend.utils.js"></script>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="PlaceAreaEditor.js"></script>
-
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
- $(function ()
- {
- $("ul li div").each(function ()
- {
- new PlaceAreaEditor($(this).attr("id"), "请留言...", $(this));
- });
- });
-
- </script>
-
- <style type="text/css">
-
- body
- {
- font-size: 12px;
- color: #333;;
- }
-
- ul li
- {
- padding: 5px 0 8px 0 ;
- }
-
- </style>
- </head>
- <body>
-
-
- <ul>
- <li id="1"><h3>我要改剧本,不让~~</h3>
- <div>
- </div>
- </li>
-
- <li id="2"><h3>悬崖上有桥么,有?没有~ </h3>
- <div>
- </div>
- </li>
- <li id="3"><h3>你敢打坏我的灯?不租~ </h3>
- <div>
- </div>
- </li>
- </ul>
-
- </body>
- </html>
好了,结束~~ 上面的例子是根据孔浩老师的例子修改的,感谢孔浩老师,孔老师地址:
www.konghao.org。
孔老师录制了很多Java相关视频,有兴趣的可以去他网站学习!
代码或者讲解有任何问题,欢迎留言指出。
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/30490955
一直很喜欢Js,,,今天写一个Js的单例模式实现以及用法。
1、单例模式的写法
单例模式写法相当简单:
- var singleTon = {
- m1: "memeber first ",
- m2: "memeber second ",
- f1: function ()
- {
- console.log("fun1 ");
- }
- };
好了,结束了,其实就是字面量创建对象的方式,很简单吧。如果你觉得单例太简单,不用看了,那你就错了,单例在Js中用的地方挺多,话说你经常用么~。
2、单例用法一:创建命名空间
在开发中一个页面一般会引入多个Js文件,甚至这多个文件多人写的,大家都可能在全局定义init这个方法,都可能在全局声明name这是属性。这样的话就造成的命名的冲突,发生一些意想不到的问题。所以我们需要引入命名空间:
我们可以让每个程序猿写的Js在他自己的命名空间下:
-
-
-
-
- var ZhangHongYang = {};
-
- var zhy = {};
- zhy.com = {} ;
- zhy.com.js = {};
比如以每个人的名字作为命名空间,之后写方法就:ZhangHongyang.xxx();或者你习惯了Java的命名空间,也可以zhy.com.js.xxx。
3、单例实例:实现一个注册页面的Js
针对像注册页面上的Js,一般都是针对此页面写的,建议使用单例的方式书写。
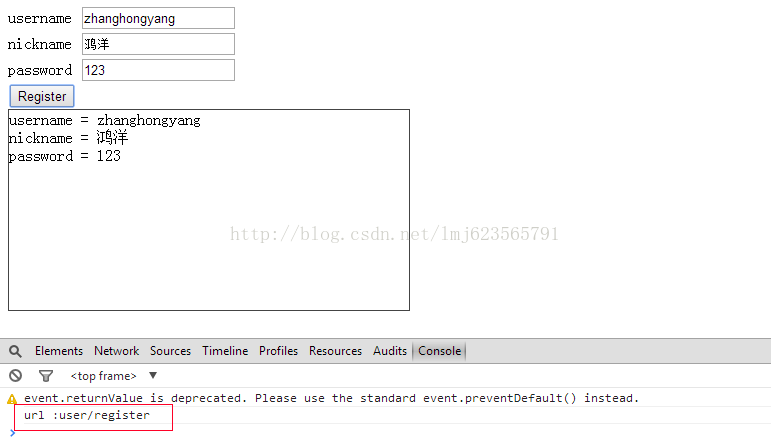
下面的展示如何使用单例的写法,实现ajax的注册功能,当然没有服务器,模拟一下:
html:
- <body>
- <form action="user/register" id="registerForm">
-
- <div>
- <label for="username">username</label>
- <input type="text" name="username" id="username"/>
- </div>
- <div>
- <label for="nickname">nickname</label>
- <input type="text" name="nickname" id="nickname"/>
- </div>
- <div>
- <label for="password">password</label>
- <input type="text" name="password" id="password"/>
- </div>
-
- <div>
- <input type="submit" value="Register"/>
- </div>
- </form>
-
- <div id="registerResult" style="width: 400px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid #444;">
-
- </div>
-
-
- </body>
当用户点击submit,会进行一些列的处理,最终将数据展示到registerResult中:
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister =
- {
- ID_FROM: "registerForm",
- ID_RESULT_CONTAINER: "registerResult",
- init: function ()
- {
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.form = $("#" + this.ID_FROM);
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.result = $("#" + ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.ID_RESULT_CONTAINER);
- this.form.submit(this.handleSubmit);
- },
- handleSubmit: function (event)
- {
-
- var datas = {};
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.form.find("input").each(function (i)
- {
-
- if (!($(this).attr("type") == "button" || $(this).attr("type") == "submit" || $(this).attr("type") == "reset" ))
- {
- datas[$(this).attr("name")] = $(this).val();
- }
- });
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.ajaxSubmit(datas);
-
- event.preventDefault();
- },
- ajaxSubmit: function (datas)
- {
- var url = ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.form.attr("action");
- console.log("url :" + url);
-
-
-
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.showResult(datas);
- },
- showResult: function (datas)
- {
- var result = "";
- for (var p in datas)
- {
- result += p + " = " + datas[p] + "<br/>";
- }
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.result.html(result);
- }
- };
-
- $(function ()
- {
- ZhangHongYang.singlePageJsForRegister.init();
- });
-
-
- </script>
我们使用单例定义了一个singlePageJsForRegister方法对象,然后将需要用到的元素的Id作为了常量,然后通过init初始化事件等,还有其他的几个函数,代码中也书写了注释。看了上面的代码可能觉得这么写好复杂,代码量也多了,但是对于Js的提升,要慢慢的学习面向对象以及结构化的写法,不能在script标签中,不断的定义各种方法,甚至在html标签中书写onclick这类的属性。Js一定要保证,html与js文件解耦;js代码整体上结构清晰;学习使用面向对象的方式处理问题。
4、如何在单例创建的对象中,定义私有方法和属性
上述单例的写法,会把所有的方法与变量暴露给使用者, 如何设置私有变量或者私有方法。
a、采用约定的方式:所有以_开头的方法和变量都是私有变量。
-
-
-
-
- var singleTon = {
- _m1: "hello",
- _f1: function ()
- {
- },
- init: function ()
- {
- }
- };
可以觉得方式1不是自己骗自己么,但是项目嘛,约定由于配置,也是可行的。实在觉得不能忍受,看方式二:
-
-
-
- var singleTon = (function ()
- {
- var _m1 = "hello";
- var _f1 = function ()
- {
- console.log(" i am a private function !");
- }
-
- return {
-
- init: function ()
- {
-
- _f1();
- }
- };
-
- })();
采用了闭包的方式,很好的实现了私有变量和私有方法的隐藏。
5、单例实例:解决Textarea的数据存储时的Html转Txt和展示时Txt转Html
在web项目中,很多情况会使用到Textarea。
a、比如留言、技能的书写等;对于这类Textarea我们有必要对用户输入的html代码做特殊处理,防止用户填写恶意代码或者把页面的样式弄乱。
b、相反来说,在Textarea中书写的换行以及空格,最终在div中显示却没有效果,都是一个空格,所有很多web开发者会选择使用只读textarea来回显用户输入内容,其实需要做一定的转换。
html:
- <body>
- <textarea style="width: 400px;height: 120px;" id="taContent">
- </textarea>
-
- <input type="button" id="convert" value="Convert"/>
- <br/>
- <br/>
-
-
- <fieldset style="width: 400px">
- <legend>html转化为Txt,供Div展示</legend>
- <div style="width: 400px;height: 120px;border: 1px solid #555;" id="divContent">
-
- </div>
- </fieldset>
-
- <br/>
- <br/>
-
- <fieldset style="width: 400px">
- <legend>Txt转化为Html,供Textarea修改</legend>
- <textarea style="width: 400px;height: 120px;" id="taEdit">
- </textarea>
- </fieldset>
-
- </body>
第一个Textarea用于用户输入,然后经过转义显示到div中,然后将转义后的数据进行逆向恢复显示到第二个TextArea中。相当与模拟了,div中展示数据和用户再次编辑数据,这些功能在项目中都相当实用。
我们的js代码:
-
-
-
- ZhangHongYang.htmlFilter = (function ()
- {
-
-
-
-
-
- function _transSpace(data)
- {
- return data.replace(/\n/g, "<br/>").replace(/\s/g, " ");
- };
-
-
-
-
-
- function _transBrace(data)
- {
- return data.replace(/</g, "<").replace(/>/g, ">");
- };
-
-
- function _resumeSpace(data)
- {
- return data.replace(/ /g, " ").replace(/<br\s*\/>/ig, "\n");
- };
- function _resumeBrace(data)
- {
- return data.replace(/</g, "<").replace(/>/g, ">");
- };
-
- return {
-
- txt2Html: function (data)
- {
- return _transSpace(_transBrace(data));
-
- }, html2Txt: function (data)
- {
- return _resumeSpace(_resumeBrace(data));
- }
- };
-
- })();
在我的命名空间下定义了htmlFilter方法,然后最后暴露两个方法Html2Txt和Txt2Html给使用者。
调用的代码:
- <script type="text/javascript">
- $(function ()
- {
- $("#convert").click(function ()
- {
- var txt = ZhangHongYang.htmlFilter.txt2Html($("#taContent").val());
- console.log(txt);
- $("#divContent").html(txt);
- $("#taEdit").val(ZhangHongYang.htmlFilter.html2Txt(txt));
- });
- });
- </script>
效果图:
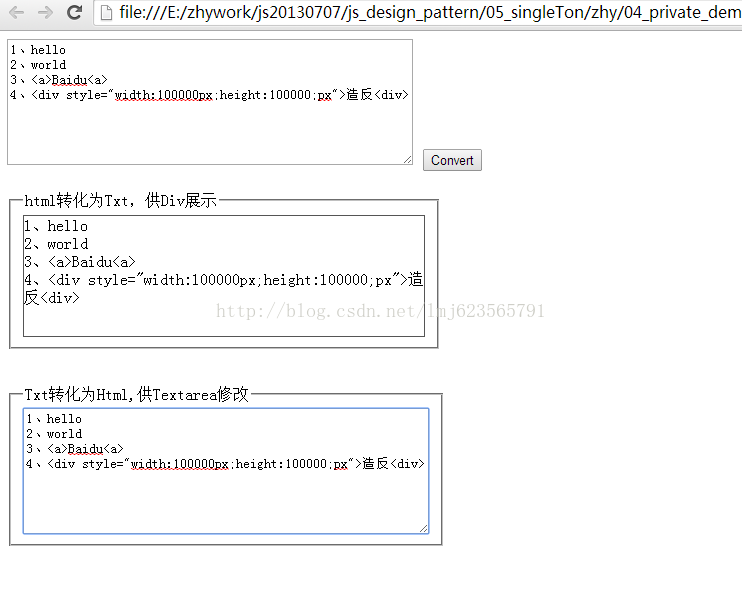
可以看到换行、空格、以及恶意的HTML代码等都得到了很好的在DIV中的显示;且最终可还原为Textarea中供编辑;如果各位项目中没有考虑到这类问题,首先你可以测试下问题,然后可以使用上面的代码解决这类问题。
6、单例写法提高多分支代码效率
相信大家都了解过ajax,对象ajax肯定离不开XMLHttpRequest,而且不同版本、类型的浏览器创建方式不一致。一般我们可能会这么写创建XMLHttpRequest的方法:
- function createXhr()
- {
- var xmlhttp;
- if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
- {
- xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
- }
- else
- {
- xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
- }
-
- return xmlhttp ;
- }
存在一个问题,每次创建XHR对象都需要进行分支判断,如果某个方法分支特别多,我们可以做进一步的优化,当浏览器加载js文件时,就决定以后调用只会用其中合适的方式,而不会走分支。
我们把代码改成:
-
-
-
- ZhangHongYang.xhrFactroy = (function ()
- {
- function _ieCreateXhr()
- {
- return new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
- }
-
- function _newCreateXhr()
- {
-
- return new XMLHttpRequest();
- }
-
- if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
- {
- return _newCreateXhr;
- }
- else
- {
- return _ieCreateXhr;
- }
- })();
当程序加载完成js文件后,会自动根据浏览器类型返回适合的方法,避免每次都会进行分支判断,我们只需要使用ZhangHongYang.xhrFactroy();创建XHR对象。
7、单例引入懒加载功能
上述的js的文件基本在引入页面后,浏览器加载就会进行大量操作占用内存,有时候我们希望等到我们去使用时再去执行一些操作,如果从未使用就省去不必要的内存消耗,我们可以进行如下改写代码:
-
-
-
- ZhangHongYang.xhrFactroy = (function ()
- {
- var _instance = null;
-
- function _constructor()
- {
- function _ieCreateXhr()
- {
- return new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
- }
-
- function _newCreateXhr()
- {
-
- return new XMLHttpRequest();
- }
-
- if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
- {
- return _newCreateXhr;
- }
- else
- {
- return _ieCreateXhr;
- }
- }
-
- return {getInstance: function ()
- {
- if (_instance == null)
- {
- _instance = _constructor();
- }
- return _instance;
-
- }};
-
- })();
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
- var xhrFactoryMethod = ZhangHongYang.xhrFactroy.getInstance();
- console.log(xhrFactoryMethod());
-
- </script>
只有使用时才会去执行_constructor()方法,而不是我们之前的一加载完成就执行。
好了,js的单例模式已经常用的方法介绍完了,以后在书写js代码时,可以尝试使用上述的方法进行书写,而不是大量定义全局function以及变量,请不要在html标签中增加事件处理的代码~
如果存在任何问题,或者有任何问题请留言~
HTML5 CSS3 诱人的实例 :模仿优酷视频截图功能
一般的视频网站对于用户上传的视频,在用户上传完成后,可以对播放的视频进行截图,然后作为视频的展示图。项目中也可以引入这样的功能给用户一种不错的体验,而不是让用户额外上传一张展示图。
效果图:

看起来还是很不错,下面我给大家分析下,极其核心代码很简单:
- _canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
- _ctx = _canvas.getContext("2d");
- _ctx.fillStyle = '#ffffff';
- _ctx.fillRect(0, 0, _videoWidth, _videoWidth);
- _ctx.drawImage(_video, 0, 0, _videoWidth, _videoHeight, 0, 0, _videoWidth, _videoHeight);
- var dataUrl = _canvas.toDataURL("image/png");
核心代码就这几行,利用了ctx.drawImage时,第一个参数可以为video对象,然后就是通过canvas拿到DataUrl,赋值给Img标签了。关键点就这些。
下面来看整个例子:
HTML:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title></title>
- <meta charset="utf-8">
-
- <style type="text/css">
-
-
- html
- {
- overflow: hidden;
- }
-
- body
- {
- background-color: #999;
- }
-
- video
- {
- display: block;
- margin: 60px auto 0;
- }
-
- #shotBar
- {
- position: absolute;
- bottom: 5px;
- height: 120px;
- width: 98%;
- background-color: #000;
- box-shadow: -5px -5px 10px #fff;
- border-radius: 5px;
- padding: 2px;
- overflow: auto;
- }
-
- #shotBar img
- {
- border: 3px solid #fff;
- border-radius: 5px;
- height: 110px;
- width: 210px;
- margin-left: 4px;
- }
-
-
- </style>
-
- <script type="text/javascript" src="../../../jquery-1.8.3.js"></script>
-
- <script type="text/javascript" src="videoshot.js"></script>
-
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
- $(function ()
- {
- ZhangHongyang.click2shot.init();
- });
-
- </script>
-
-
- </head>
- <body>
-
-
- <video src="media/style.mp4" controls id="video">
- </video>
- <div id="shotBar">
- </div>
- </body>
- </html>
html和css都是相当简单的。
主要看Js的代码:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- var ZhangHongyang = {};
- ZhangHongyang.click2shot = (function ()
- {
- var _ID_VIDEO = "video";
- var _ID_SHOTBAR = "shotBar";
- var _videoWidth = 0;
- var _videoHeight = 0;
- var _canvas = null;
- var _ctx = null;
- var _video = null;
-
- function _init()
- {
- _canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
- _ctx = _canvas.getContext("2d");
- _video = document.getElementById(_ID_VIDEO);
-
-
- _video.addEventListener("canplay", function ()
- {
- _canvas.width = _videoWidth = _video.videoWidth;
- _canvas.height = _videoHeight = _video.videoHeight;
- console.log(_videoWidth + " , " + _videoHeight);
- _ctx.fillStyle = '#ffffff';
- _ctx.fillRect(0, 0, _videoWidth, _videoWidth);
- $("#" + _ID_SHOTBAR).click(_click2shot);
-
- _video.removeEventListener("canplay", arguments.callee);
- });
-
- }
-
- function _click2shot(event)
- {
- _video.pause();
- _ctx.drawImage(_video, 0, 0, _videoWidth, _videoHeight, 0, 0, _videoWidth, _videoHeight);
- var dataUrl = _canvas.toDataURL("image/png");
-
-
- var $imgBig = $("<img/>");
-
- $imgBig.width(_videoWidth).height(_videoHeight).css({position: "absolute", left: _video.offsetLeft, top: _video.offsetTop, width: _videoWidth + "px", height: _videoWidth + "px"}).attr("src", dataUrl);
- $("body").append($imgBig);
-
-
- var $img = $("<img>");
- $img.attr("src", dataUrl);
- $(this).append($img);
-
- var offset = _getOffset($img[0]);
- $img.hide();
-
- $imgBig.animate({left: offset.x + "px", top: offset.y + "px", width: $img.width() + "px", height: $img.height() + "px"}, 200, function ()
- {
- $img.attr("src", dataUrl).show();
- $imgBig.remove();
- _video.play();
- });
-
-
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function _getOffset(elem)
- {
- var pos = {x: elem.offsetLeft, y: elem.offsetTop};
- var offsetParent = elem.offsetParent;
- while (offsetParent)
- {
- pos.x += offsetParent.offsetLeft;
- pos.y += offsetParent.offsetTop;
- offsetParent = offsetParent.offsetParent;
- }
- return pos;
- }
-
-
- return {init: _init}
-
- })();
需要注意的是,video.canplay事件中获取完属性和一些操作后,一定要removeEventLinstener,否则暂停播放会一直调用此方法。点击事件时,会暂停video,然后在video的位置生成一张图片,使用jquery动画移动到缩略图的位置,然后移除文档,缩略图显示,造成的动画效果。
得到图片之后的上传之类的操作,大家可以自己添加。还有很重要的一点:canvas.toDataURL("image/png");可能需要在服务器中访问才能正常使用,我把写好的页面拖到了tomcat中,大家可以随便启动个什么服务器,不然会报安全问题。
好了,如果这篇文章对你有帮助请顶一个,同时也欢迎大家留言~
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/34089553
今天给大家带来一个刮刮乐的小例子~基于HTML5 canvas的,有兴趣的可以改成android版本的,或者其他的~
效果图:

贴一张我中500w的照片,咋办啊,怎么花呢~

好了,下面开始原理:
1、刮奖区域两个Canvas,一个是front , 一个back ,front遮盖住下面的canvas。
2、canvas默认填充了一个矩形,将下面canvas效果图遮盖,然后监听mouse事件,根据mousemove的x,y坐标,进行擦出front canvas上的矩形区域,然后显示出下面的canvas的效果图。
很简单把~嘿嘿~
1、HTML文件内容:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title></title>
- <meta charset="utf-8">
-
- <script type="text/javascript" src="../../jquery-1.8.3.js"></script>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="canvas2d.js"></script>
-
- <script type="text/javascript" src="GuaGuaLe2.js"></script>
-
- <script type="text/javascript">
-
- $(function ()
- {
- var guaguale = new GuaGuaLe("front", "back");
- guaguale.init({msg: "¥5000000.00"});
- });
- </script>
- <style type="text/css">
-
-
- body
- {
- background: url("s_bd.jpg") repeat 0 0;
- }
-
- .container
- {
- position: relative;
- width: 400px;
- height: 160px;
- margin: 100px auto 0;
- background: url(s_title.png) no-repeat 0 0;
- background-size: 100% 100%;
- }
-
- #front, #back
- {
- position: absolute;
- width: 200px;
- left: 50%;
- top: 100%;
- margin-left: -130px;
- height: 80px;
- border-radius: 5px;
- border: 1px solid #444;
- }
-
- </style>
-
- </head>
- <body>
-
- <div class="container">
- <canvas id="back" width="200" height="80"></canvas>
- <canvas id="front" width="200" height="80"></canvas>
- </div>
-
-
- </body>
- </html>
2、首先我利用了一个以前写的canvas辅助类,留下来今天要用的一些方法:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function Canvas2D($canvas)
- {
- var context = $canvas[0].getContext("2d"),
- width = $canvas[0].width,
- height = $canvas[0].height,
- pageOffset = $canvas.offset();
-
-
- context.font = "24px Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif";
- context.textBaseline = "top";
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- this.drawRect = function (start, end, isFill)
- {
- var w = end.x - start.x , h = end.y - start.y;
- if (isFill)
- {
- context.fillRect(start.x, start.y, w, h);
- }
- else
- {
- context.strokeRect(start.x, start.y, w, h);
- }
- };
-
-
-
-
-
-
- this.caculateTextCenterPos = function (text)
- {
- var metrics = context.measureText(text);
- console.log(metrics);
-
- var textWidth = metrics.width;
- var textHeight = parseInt(context.font);
-
- return {
- x: width / 2 - textWidth / 2,
- y: height / 2 - textHeight / 2
- };
- }
- this.width = function ()
- {
- return width;
- }
- this.height = function ()
- {
- return height;
- }
- this.resetOffset = function ()
- {
- pageOffset = $canvas.offset();
- }
-
-
-
- $(window).resize(function ()
- {
- pageOffset = $canvas.offset();
- });
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- this.getCanvasPoint = function (pageX, pageY)
- {
- return{
- x: pageX - pageOffset.left,
- y: pageY - pageOffset.top
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- this.clearRect = function (start)
- {
- context.clearRect(start.x, start.y, 10, 10);
- return this;
- };
-
-
-
-
-
-
- this.drawTextInCenter = function (text, fill)
- {
- var point = this.caculateTextCenterPos(text);
- if (fill)
- {
- context.fillText(text, point.x, point.y);
- }
- else
- {
- context.strokeText(text, point.x, point.y);
- }
- };
-
-
-
-
-
- this.penWidth = function (newWidth)
- {
- if (arguments.length)
- {
- context.lineWidth = newWidth;
- return this;
- }
- return context.lineWidth;
- };
-
-
-
-
-
-
- this.penColor = function (newColor)
- {
- if (arguments.length)
- {
- context.strokeStyle = newColor;
- context.fillStyle = newColor;
- return this;
- }
-
- return context.strokeStyle;
- };
-
-
-
-
-
-
- this.fontSize = function (fontSize)
- {
- if (arguments.length)
- {
- context.font = fontSize + "px Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif";
-
- return this;
- }
-
- return context.fontSize;
- }
-
-
- }
这个类也就对Canvas对象进行了简单的封装,设置参数,绘制图形什么的,比较简单,大家可以完善下这个类~
3、GuaGuaLe.js
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function GuaGuaLe(idFront, idBack)
- {
- this.$eleBack = $("#" + idBack);
- this.$eleFront = $("#" + idFront);
- this.frontCanvas = new Canvas2D(this.$eleFront);
- this.backCanvas = new Canvas2D(this.$eleBack);
-
- this.isStart = false;
-
- }
-
- GuaGuaLe.prototype = {
- constructor: GuaGuaLe,
-
-
-
-
-
- mergeAttr: function (desAttr)
- {
- var defaultAttr = {
- frontFillColor: "silver",
- backFillColor: "gold",
- backFontColor: "red",
- backFontSize: 24,
- msg: "谢谢惠顾"
- };
- for (var p in desAttr)
- {
- defaultAttr[p] = desAttr[p];
- }
-
- return defaultAttr;
-
- },
-
-
- init: function (desAttr)
- {
-
- var attr = this.mergeAttr(desAttr);
-
-
- this.backCanvas.penColor(attr.backFillColor);
- this.backCanvas.fontSize(attr.backFontSize);
- this.backCanvas.drawRect({x: 0, y: 0}, {x: this.backCanvas.width(), y: this.backCanvas.height()}, true);
- this.backCanvas.penColor(attr.backFontColor);
- this.backCanvas.drawTextInCenter(attr.msg, true);
-
- this.frontCanvas.penColor(attr.frontFillColor);
- this.frontCanvas.drawRect({x: 0, y: 0}, {x: this.frontCanvas.width(), y: this.frontCanvas.height()}, true);
-
- var _this = this;
-
- this.$eleFront.mousedown(function (event)
- {
- _this.mouseDown(event);
- }).mousemove(function (event)
- {
- _this.mouseMove(event);
- }).mouseup(function (event)
- {
- _this.mouseUp(event);
- });
- },
- mouseDown: function (event)
- {
- this.isStart = true;
- this.startPoint = this.frontCanvas.getCanvasPoint(event.pageX, event.pageY);
- },
- mouseMove: function (event)
- {
- if (!this.isStart)return;
- var p = this.frontCanvas.getCanvasPoint(event.pageX, event.pageY);
- this.frontCanvas.clearRect(p);
- },
- mouseUp: function (event)
- {
- this.isStart = false;
- }
- };
通过用户传入的两个canvas的id,然后生成一个对象,进行初始化操作,设置事件。当然了也提供用户设置可选的参数,各种颜色,已经刮开后显示的信息等,通过{
frontFillColor: "silver",
backFillColor: "gold",
backFontColor: "red",
backFontSize: 24,
msg: "谢谢惠顾"
};传给init方法进行设置。
好了,然后就基本完工了,测试一下:
基本实现了刮开图层,但是存在一个小问题,就是当用户滑动特别快时,会出现一些断点,当然也可以忽略,不过我们准备提供一下解决方案:

产生原因:由于鼠标移动速度过快,产生的断点;解决方案:将mousemove中两次的鼠标左边,进行拆分成多个断点坐标:
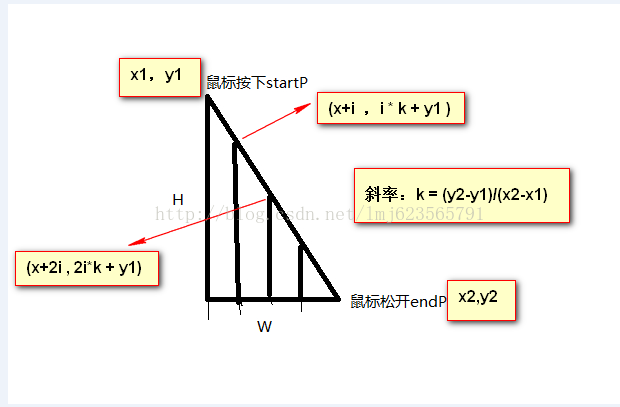
如上图,把两点之间进行连线,根据斜率,然后分成多个小段,分别获得线段上的坐标(有四种可能,有兴趣可以画画图,计算下,代码如下):
- var k;
- if (p.x > this.startPoint.x)
- {
- k = (p.y - this.startPoint.y) / (p.x - this.startPoint.x);
- for (var i = this.startPoint.x; i < p.x; i += 5)
- {
- this.frontCanvas.clearRect({x: i, y: (this.startPoint.y + (i - this.startPoint.x) * k)});
- }
- } else
- {
- k = (p.y - this.startPoint.y) / (p.x - this.startPoint.x);
- for (var i = this.startPoint.x; i > p.x; i -= 5)
- {
- this.frontCanvas.clearRect({x: i, y: (this.startPoint.y + ( i - this.startPoint.x ) * k)});
- }
- }
- this.startPoint = p;
4、最后贴一下完整的GuaGuaLe.js
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- function GuaGuaLe(idFront, idBack)
- {
- this.$eleBack = $("#" + idBack);
- this.$eleFront = $("#" + idFront);
- this.frontCanvas = new Canvas2D(this.$eleFront);
- this.backCanvas = new Canvas2D(this.$eleBack);
-
- this.isStart = false;
-
- }
-
- GuaGuaLe.prototype = {
- constructor: GuaGuaLe,
-
-
-
-
-
- mergeAttr: function (desAttr)
- {
- var defaultAttr = {
- frontFillColor: "silver",
- backFillColor: "gold",
- backFontColor: "red",
- backFontSize: 24,
- msg: "谢谢惠顾"
- };
- for (var p in desAttr)
- {
- defaultAttr[p] = desAttr[p];
- }
-
- return defaultAttr;
-
- },
-
-
- init: function (desAttr)
- {
-
- var attr = this.mergeAttr(desAttr);
-
-
- this.backCanvas.penColor(attr.backFillColor);
- this.backCanvas.fontSize(attr.backFontSize);
- this.backCanvas.drawRect({x: 0, y: 0}, {x: this.backCanvas.width(), y: this.backCanvas.height()}, true);
- this.backCanvas.penColor(attr.backFontColor);
- this.backCanvas.drawTextInCenter(attr.msg, true);
-
- this.frontCanvas.penColor(attr.frontFillColor);
- this.frontCanvas.drawRect({x: 0, y: 0}, {x: this.frontCanvas.width(), y: this.frontCanvas.height()}, true);
-
- var _this = this;
-
- this.$eleFront.mousedown(function (event)
- {
- _this.mouseDown(event);
- }).mousemove(function (event)
- {
- _this.mouseMove(event);
- }).mouseup(function (event)
- {
- _this.mouseUp(event);
- });
- },
- mouseDown: function (event)
- {
- this.isStart = true;
- this.startPoint = this.frontCanvas.getCanvasPoint(event.pageX, event.pageY);
- },
- mouseMove: function (event)
- {
- if (!this.isStart)return;
- var p = this.frontCanvas.getCanvasPoint(event.pageX, event.pageY);
- this.frontCanvas.clearRect(p);
- },
- mouseUp: function (event)
- {
- this.isStart = false;
- }
- };
转载请标明出处:
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/34089553
好了,收工吃饭~
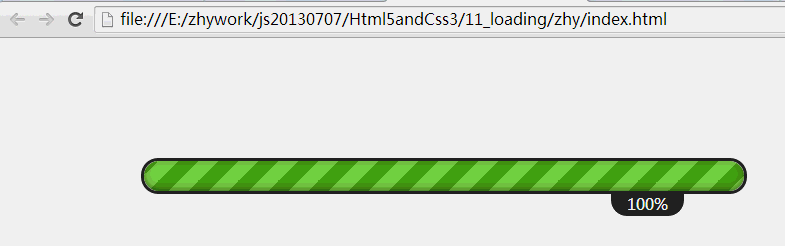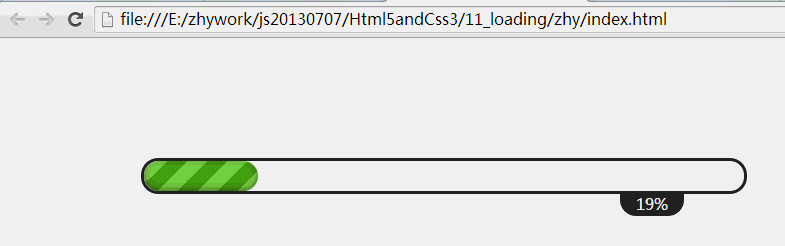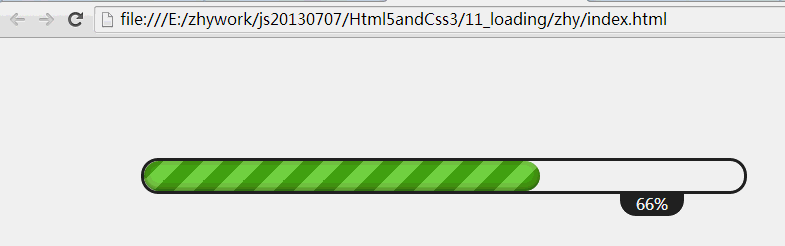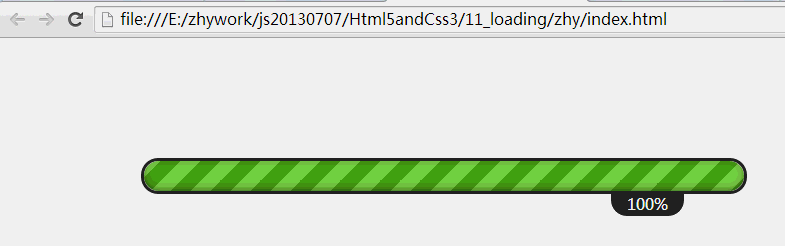
今天给大家带来一个比较炫的进度条,进度条在一耗时操作上给用户一个比较好的体验,不会让用户觉得在盲目等待,对于没有进度条的长时间等待,用户会任务死机了,毫不犹豫的关掉应用;一般用于下载任务,删除大量任务,网页加载等;如果有使用html5为手机布局的,也可以用于手机中~
效果图:
1、html结构:
- <div id="loadBar01" class="loadBar">
- <div>
- <span class="percent">
- <i></i>
- </span>
- </div>
- <span class="percentNum">0%</span>
- </div>
简单分析下: div.loadBar代表整个进度条
div.loadBar div 设置了圆角表框 ,div.loadBar div span 为进度 (动态改变宽度), div.loadBar div span i 为进度填充背景色(即width=100%)
HTML的结构,大家可以自己设计,只要合理,都没有问题~
2、CSS:
- body
- {
- font-family: Thoma, Microsoft YaHei, 'Lato', Calibri, Arial, sans-serif;
- }
-
- #content
- {
- margin: 120px auto;
- width: 80%;
- }
-
- .loadBar
- {
- width: 600px;
- height: 30px;
- border: 3px solid #212121;
- border-radius: 20px;
- position: relative;
- }
-
- .loadBar div
- {
- width: 100%;
- height: 100%;
- position: absolute;
- top: 0;
- left: 0;
- }
-
- .loadBar div span, .loadBar div i
- {
- box-shadow: inset 0 -2px 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, .4);
- width: 0%;
- display: block;
- height: 100%;
- position: absolute;
- top: 0;
- left: 0;
- border-radius: 20px;
- }
-
- .loadBar div i
- {
- width: 100%;
- -webkit-animation: move .8s linear infinite;
- background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left top, #7ed047 0%, #7ed047 25%, #4ea018 25%, #4ea018 50%, #7ed047 50%, #7ed047 75%, #4ea018 75%, #4ea018 100%);
- background-size: 40px 40px;
- }
-
- .loadBar .percentNum
- {
- position: absolute;
- top: 100%;
- right: 10%;
- padding: 1px 15px;
- border-bottom-left-radius: 16px;
- border-bottom-right-radius: 16px;
- border: 1px solid #222;
- background-color: #222;
- color: #fff;
-
- }
-
- @-webkit-keyframes move
- {
- 0%
- {
- background-position: 0 0;
- }
- 100%
- {
- background-position: 40px 0;
- }
- }
此时效果为:
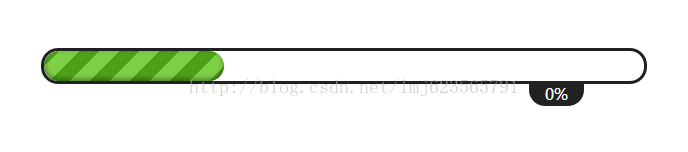
整体布局就是利用position relative和absolute~
比较难的地方就是,渐变条的实现:
我们采用
a、从左上到右下的渐变
b、颜色分别为:0-25% 为#7ed047 , 25%-50% 为#4ea018 , 50%-75%为#7ed047 , 75%-100%为#4ea018
c、背景的大小为40px 40px 这个设置超过高度就行, 越大,条文宽度越宽
分析图:
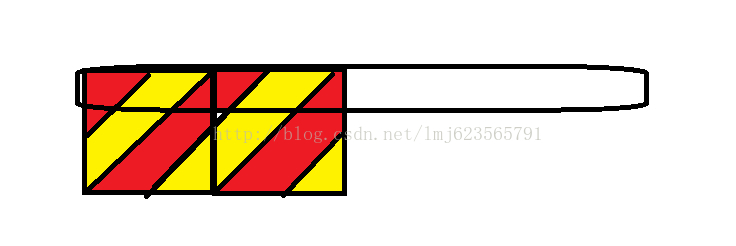
设置的原理就是上图了,同时可以背景宽度设置越大,条文宽度越大;
3、设置Js,创建LoadBar对象
- function LoadingBar(id)
- {
- this.loadbar = $("#" + id);
- this.percentEle = $(".percent", this.loadbar);
- this.percentNumEle = $(".percentNum", this.loadbar);
- this.max = 100;
- this.currentProgress = 0;
- }
- LoadingBar.prototype = {
- constructor: LoadingBar,
- setMax: function (maxVal)
- {
- this.max = maxVal;
- },
- setProgress: function (val)
- {
- if (val >= this.max)
- {
- val = this.max;
- }
- this.currentProgress = parseInt((val / this.max) * 100) + "%";
- this.percentEle.width(this.currentProgress);
- this.percentNumEle.text(this.currentProgress);
-
-
- }
- };
我们创建了一个LoadBar对象,同时公开了两个方法,一个设置最大进度,一个设置当前进度;比如下载文件最大进度为文件大小,当前进度为已下载文件大小。
4、测试
最后我们测试下我们的代码:
- $(function ()
- {
-
- var loadbar = new LoadingBar("loadBar01");
- var max = 1000;
- loadbar.setMax(max);
- var i = 0;
- var time = setInterval(function ()
- {
- loadbar.setProgress(i);
- if (i == max)
- {
- clearInterval(time);
- return;
- }
- i += 10;
- }, 40);
- });
ps:对于js对象的设计,尽可能的考虑实用性~
最后完工~哈~ 吃饭吃饭~










































 160
160

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








