依存关系
首先,我们需要添加所需的依赖关系,以便在项目中包含Apache POI。
如果使用Maven,则需要向pom.xml文件中添加以下依赖项
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi-ooxml -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
如果使用Gradle
在你的build.gradle 文件中加入以下内容
compile "org.apache.poi:poi:3.17"
compile "org.apache.poi:poi-ooxml:3.17"
(版本号根据自己的poi版本修改)
这里第一个poi是用来处理.xls旧版文档用
第二个poi-ooxml是用来处理.xlsx文档使用
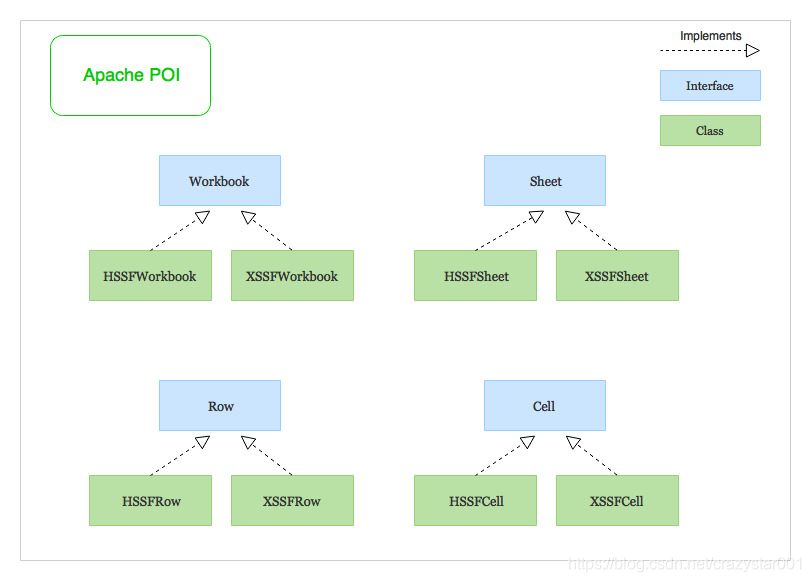
POI的专业术语
1.Workbook:工作簿,也就是一个.xlsx/.xls文档。
2.sheet:每个工作簿里有多个sheet。
3.Row:一行
4.Cell:一列
POI的两种implement
HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) :
HSSFWorkbook,HSSFSheet,HSSFRow和HSSFCell用于工作与旧的二进制文件格式的Excel文件-.xls
XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format):
XSSF实现用于处理基于XML的新文件格式- .xlsx
使用POI来读取excel–JAVA
该程序显示了在excel文件中的工作表,行和列上进行迭代的三种不同方式
import org.apache.poi.openxml4j.exceptions.InvalidFormatException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ExcelReader {
public static final String SAMPLE_XLSX_FILE_PATH = "./sample-xlsx-file.xlsx";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InvalidFormatException {
// Creating a Workbook from an Excel file (.xls or .xlsx)
Workbook workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(new File(SAMPLE_XLSX_FILE_PATH));
// Retrieving the number of sheets in the Workbook
System.out.println("Workbook has " + workbook.getNumberOfSheets() + " Sheets : ");
/*
=============================================================
Iterating over all the sheets in the workbook (Multiple ways)
=============================================================
*/
// 1. You can obtain a sheetIterator and iterate over it
Iterator<Sheet> sheetIterator = workbook.sheetIterator();
System.out.println("Retrieving Sheets using Iterator");
while (sheetIterator.hasNext()) {
Sheet sheet = sheetIterator.next();
System.out.println("=> " + sheet.getSheetName());
}
// 2. Or you can use a for-each loop
System.out.println("Retrieving Sheets using for-each loop");
for(Sheet sheet: workbook) {
System.out.println("=> " + sheet.getSheetName());
}
// 3. Or you can use a Java 8 forEach with lambda
System.out.println("Retrieving Sheets using Java 8 forEach with lambda");
workbook.forEach(sheet -> {
System.out.println("=> " + sheet.getSheetName());
});
/*
==================================================================
Iterating over all the rows and columns in a Sheet (Multiple ways)
==================================================================
*/
// Getting the Sheet at index zero
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// Create a DataFormatter to format and get each cell's value as String
DataFormatter dataFormatter = new DataFormatter();
// 1. You can obtain a rowIterator and columnIterator and iterate over them
System.out.println("\n\nIterating over Rows and Columns using Iterator\n");
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.rowIterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIterator.next();
// Now let's iterate over the columns of the current row
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
String cellValue = dataFormatter.formatCellValue(cell);
System.out.print(cellValue + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 2. Or you can use a for-each loop to iterate over the rows and columns
System.out.println("\n\nIterating over Rows and Columns using for-each loop\n");
for (Row row: sheet) {
for(Cell cell: row) {
String cellValue = dataFormatter.formatCellValue(cell);
System.out.print(cellValue + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 3. Or you can use Java 8 forEach loop with lambda
System.out.println("\n\nIterating over Rows and Columns using Java 8 forEach with lambda\n");
sheet.forEach(row -> {
row.forEach(cell -> {
String cellValue = dataFormatter.formatCellValue(cell);
System.out.print(cellValue + "\t");
});
System.out.println();
});
// Closing the workbook
workbook.close();
}
}
这里我们没有用像HSSFWorkbook和这样的具体类XSSFWorkbook来创建工作簿的实例,而是用一个WorkbookFactory来代替创建工作簿,这样我们两种类型文件都能适用(.xls/.xlsx)
这个程序用了三种遍历方法
这里使用了DataFormatter来格式化并获取每个单元格的值作为String。
通过CellType检索单元格值
private static void printCellValue(Cell cell) {
switch (cell.getCellTypeEnum()) {
case BOOLEAN:
System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString());
break;
case NUMERIC:
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
System.out.print(cell.getDateCellValue());
} else {
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue());
}
break;
case FORMULA:
System.out.print(cell.getCellFormula());
break;
case BLANK:
System.out.print("");
break;
default:
System.out.print("");
}
System.out.print("\t");
}
接下来你可以从主函数调用这个方法来输出每个cell的值
sheet.forEach(row -> {
row.forEach(cell -> {
printCellValue(cell);
});
System.out.println();
});
创建一个Excel文件并且向里面写入数据
注:这里用XSSFWorkbook来创建Workbook实例,适用.xlsx文件
import org.apache.poi.openxml4j.exceptions.InvalidFormatException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class ExcelWriter {
private static String[] columns = {"Name", "Email", "Date Of Birth", "Salary"};
private static List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<>();
// Initializing employees data to insert into the excel file
static {
Calendar dateOfBirth = Calendar.getInstance();
dateOfBirth.set(1992, 7, 21);
employees.add(new Employee("Rajeev Singh", "rajeev@example.com",
dateOfBirth.getTime(), 1200000.0));
dateOfBirth.set(1965, 10, 15);
employees.add(new Employee("Thomas cook", "thomas@example.com",
dateOfBirth.getTime(), 1500000.0));
dateOfBirth.set(1987, 4, 18);
employees.add(new Employee("Steve Maiden", "steve@example.com",
dateOfBirth.getTime(), 1800000.0));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InvalidFormatException {
// Create a Workbook
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); // new HSSFWorkbook() for generating `.xls` file
/* CreationHelper helps us create instances of various things like DataFormat,
Hyperlink, RichTextString etc, in a format (HSSF, XSSF) independent way */
CreationHelper createHelper = workbook.getCreationHelper();
// Create a Sheet
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee");
// Create a Font for styling header cells
Font headerFont = workbook.createFont();
headerFont.setBold(true);
headerFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 14);
headerFont.setColor(IndexedColors.RED.getIndex());
// Create a CellStyle with the font
CellStyle headerCellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
headerCellStyle.setFont(headerFont);
// Create a Row
Row headerRow = sheet.createRow(0);
// Create cells
for(int i = 0; i < columns.length; i++) {
Cell cell = headerRow.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(columns[i]);
cell.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
}
// Create Cell Style for formatting Date
CellStyle dateCellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
dateCellStyle.setDataFormat(createHelper.createDataFormat().getFormat("dd-MM-yyyy"));
// Create Other rows and cells with employees data
int rowNum = 1;
for(Employee employee: employees) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
row.createCell(0)
.setCellValue(employee.getName());
row.createCell(1)
.setCellValue(employee.getEmail());
Cell dateOfBirthCell = row.createCell(2);
dateOfBirthCell.setCellValue(employee.getDateOfBirth());
dateOfBirthCell.setCellStyle(dateCellStyle);
row.createCell(3)
.setCellValue(employee.getSalary());
}
// Resize all columns to fit the content size
for(int i = 0; i < columns.length; i++) {
sheet.autoSizeColumn(i);
}
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("poi-generated-file.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
// Closing the workbook
workbook.close();
}
}
在上面的程序中,我们首先使用XSSFWorkbook类创建了一个工作簿。然后我们创建了一个名为“ Employee”的工作表。之创建了标题行和列。标题单元格用了不同的字体样式。
创建标题行后,我们从employ list中创建了其他行和列。
接下来,我们使用sheet.autoSizeColumn()方法来调整所有列的大小以适合内容的大小。
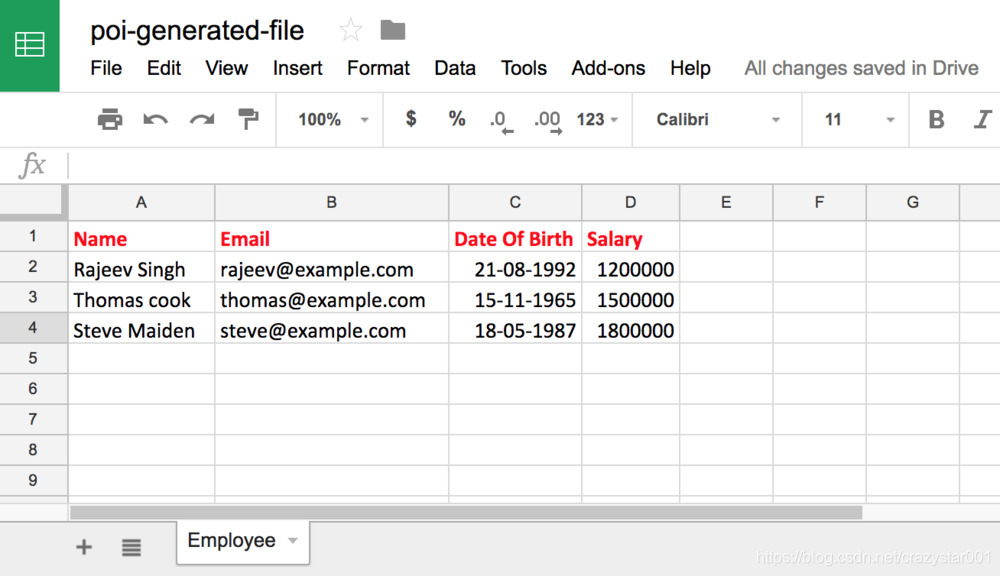
最后,我们输出写入文件。以下是通过运行上述程序生成的文件:
下面是对现有的文件打开并进行追加读写
private static void modifyExistingWorkbook() throws InvalidFormatException, IOException {
// Obtain a workbook from the excel file
Workbook workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(new File("existing-spreadsheet.xlsx"));
// Get Sheet at index 0
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// Get Row at index 1
Row row = sheet.getRow(1);
// Get the Cell at index 2 from the above row
Cell cell = row.getCell(2);
// Create the cell if it doesn't exist
if (cell == null)
cell = row.createCell(2);
// Update the cell's value
cell.setCellType(CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue("Updated Value");
// Write the output to the file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("existing-spreadsheet.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
// Closing the workbook
workbook.close();
}
附上Github中的实例:
java-read-write-excel-file-using-apache-poi





















 3485
3485











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








