
What does the tty command do? It prints the name of the terminal you’re using. TTY stands for “teletypewriter.” What’s the story behind the name of the command? That takes a bit more explaining.
tty命令做什么? 它显示您正在使用的终端的名称。 TTY代表“打字机”。 命令名称背后的故事是什么? 这需要更多解释。
1800年代的电传打印机 (Teleprinters From the 1800s)
In the 1830s and 1840s, machines known as teleprinters were developed. These machines could send typed messages “down the wire” to distant locations. The messages were typed by the sender on a keyboard of sorts. They were printed on paper at the receiving end. They were an evolutionary step in telegraphy, which had previously relied on Morse and similar codes.
在1830和1840年代,开发了称为电传打印机的机器。 这些机器可以将键入的消息“线下”发送到遥远的位置。 邮件由发件人在各种键盘上键入。 它们在接收端打印在纸上。 它们是电报中的进化步骤,以前是依靠莫尔斯电码和类似的密码。
Messages were encoded and transmitted, then received, decoded, and printed. There were several techniques used to encode and decode the messages. The most famous, and one of the most prolific, was patented in 1874 by Émile Baudot, for whom the baud rate is named. His character encoding scheme pre-dated ASCII by 89 years.
消息被编码和传输,然后被接收,解码和打印。 有几种用于编码和解码消息的技术。 埃米尔· 鲍 多(ÉmileBaudot)在1874年申请了最著名的专利,也是最多产的专利之一。 他的字符编码方案比ASCII早89年。
Baudot’s encoding eventually became the closest thing to a standard in teleprinter encoding, and it was adopted by most manufacturers. Baudot’s original hardware design had only five keys, similar to piano keys. The operator was required to learn a particular key combination for each letter. Eventually, the Baudot encoding system was coupled to a traditional keyboard layout.
最终,Baudot的编码成为最接近电传打印机编码标准的事物,并且被大多数制造商采用。 鲍多的原始硬件设计只有五个键,类似于钢琴键。 要求操作员学习每个字母的特定按键组合。 最终,Baudot编码系统与传统的键盘布局相结合。
To mark that advancement, the machines were named teletypewriters. This was shortened to teletypes and eventually to TTYs. So that’s where we get the acronym TTY from, but what has telegraphy got to do with computing?
为了纪念这一进步,这些机器被称为电传打字机。 这被缩短为电传打字机,最终缩短为TTY。 这就是我们的首字母缩写 TTY,但电报与计算有何关系?
ASCII和电传 (ASCII and Telex)
When ASCII arrived in 1963, it was adopted by the teletype manufacturers. Despite the invention and widespread use of the telephone, teletypes were still going strong.
当ASCII于1963年问世时,它被电传打字机制造商采用。 尽管发明了电话并广泛使用了电话,电传打字机仍在发展。
Telex was a worldwide network of teletypes that allowed written messages to be sent around the globe. They were the principal means of transmitting written messages in the period following World War II up to the fax machine boom of the 1980s.
电传是电传打字机的全球网络,它使书面消息可以在全球范围内发送。 在第二次世界大战之后到1980年代传真机热潮期间,它们是传输书面消息的主要手段。
Computers were evolving too. They were becoming capable of interacting with users in real time, and of supporting multiple users. The old batch method of working became insufficient. People didn’t want to wait 24 hours or longer for their results. Making stacks of punched cards and waiting overnight for results was no longer acceptable.
电脑也在不断发展。 他们变得能够与用户实时交互,并支持多个用户。 旧的批处理方法变得不够用。 人们不想等待24小时或更长时间才能获得结果。 堆积成堆的打Kong卡并等待一整夜的结果不再被接受。
People needed a device that would allow them to enter instructions and get results sent back to them. People wanted efficiency.
人们需要一种允许他们输入指令并将结果发送回给他们的设备。 人们想要效率。
重新设计的电传打字机 (The Teletype Repurposed)
The teletype was the perfect candidate as an input/output device. It was, after all, a device designed to allow messages to be typed, encoded, sent, received, decoded, and printed.
电传打字机是输入/输出设备的最佳选择。 毕竟,它是一种旨在允许对消息进行键入,编码,发送,接收,解码和打印的设备。
What did the teletype care if the device at the other end of the connection wasn’t another teletype? As long as it spoke the same encoding language and could receive messages and send messages back, the teletype was happy.
如果连接另一端的设备不是另一个电传电报,电传电报关心什么? 只要电传使用相同的编码语言并且可以接收和发送回消息,电传打字机就很高兴。
And of course, it used a more-or-less standard keyboard.
当然,它使用或多或少的标准键盘。
硬件模拟电传打字机 (Hardware Emulated Teletypes)
Teletypes became the default means of interacting with the large mini and mainframe computers of that era.
电传打字成为与那个时代的小型和大型计算机交互的默认方式。
They were eventually replaced by devices that emulated those electro-mechanical machines using electronics. These had Cathode Ray Tubes (CRTs) instead of paper rolls. They didn’t shake when delivering responses from the computer. They permitted hitherto impossible functionality, such as moving the cursor around the screen, clearing the screen, bolding text, and so on.
最终,它们被使用电子设备模拟那些机电设备的设备所取代。 这些具有阴极射线管 (CRT)而不是纸卷。 从计算机传递响应时,他们没有动摇。 他们允许使用迄今为止无法实现的功能,例如在屏幕上移动光标,清除屏幕,加粗文本等。
The DEC VT05 was an early example of a virtual teletype, and an ancestor of the famous DEC VT100. Millions of DEC VT100s were sold.
DEC VT05是虚拟电传打字机的早期示例,并且是著名的DEC VT100的祖先。 售出了数百万台DEC VT100。
软件模拟电传打字机 (Software Emulated Teletypes)
In the desktop environment of Linux and other Unix-like operating systems such as macOS, the terminal window and applications such as x-term and Konsole are examples of virtual teletypes. But these are emulated entirely in software. They are called pseudo-teletypes. This was shortened to PTS.
在Linux和其他类似Unix的操作系统(例如macOS)的桌面环境中,终端窗口和应用程序(例如x-term和Konsole)是虚拟电传打字机的示例。 但是这些都是完全在软件中模拟的。 它们称为伪teletypes。 缩短为PTS。
And that’s where tty comes in.
这就是tty 。
tty能告诉我们什么? (What can tty Tell us?)
In Linux, there is a pseudo-teletype multiplexor which handles the connections from all of the terminal window pseudo-teletypes (PTS). The multiplexor is the master, and the PTS are the slaves. The multiplexor is addressed by the kernel through the device file located at /dev/ptmx.
在Linux中,有一个伪teletype多路复用器,它处理来自所有终端窗口伪teletype(PTS)的连接。 多路复用器是主机,PTS是从机。 内核通过位于/ dev / ptmx的设备文件对多路复用器进行寻址。
The tty command will print the name of the device file that your pseudo-teletype slave is using to interface to the master. And that, effectively, is the number of your terminal window.
tty命令将打印您的伪原型从属设备用来与主设备接口的设备文件的名称。 实际上,这就是终端窗口的编号。
Let’s see what tty reports for our terminal window:
让我们看看tty为我们的终端窗口报告什么:
tty

The response shows we are connected to the device file at /dev/pts/0.
响应显示我们已连接到/ dev / pts / 0处的设备文件。
Our terminal window, which is a software emulation of a teletype (TTY), is interfaced to the pseudo-teletype multiplexor as a pseudo-teletype (PTS). And it happens to be number zero.
我们的终端窗口是电传打字机(TTY)的软件仿真,它以伪电传打字机(PTS)的形式连接到伪电传复用器。 它恰好是零。
沉默的选择 (The Silent Option)
The -s (silent) option causes tty to generate no output.
-s (静默)选项使tty不产生任何输出。
tty -s

It does is produce an exit value, however:
它确实会产生一个退出值,但是:
0: if standard input is coming from a TTY device, emulated or physical.
0 :如果标准输入来自TTY设备(模拟的或物理的)。
1: if standard input is not coming from a TTY device.
1 :如果标准输入不是来自TTY设备。
2: Syntax error, incorrect command line parameters were used.
2 :语法错误,使用了错误的命令行参数。
3: A write error has occurred.
3 :发生写入错误。
This is likely to be most useful in Bash scripting. But, even on the command line, we can demonstrate how to have a command executed only if you are running in a terminal window (a TTY or a PTS session).
这在Bash脚本中可能是最有用的。 但是,即使在命令行上,我们也可以演示仅在终端窗口(TTY或PTS会话)中运行时如何执行命令。
tty -s && echo "In a tty"

Because we are running in a TTY session, our exit code is 0, and the second command is executed.
因为我们在TTY会话中运行,所以我们的退出代码为0,并执行了第二个命令。

谁指挥 (The who Command)
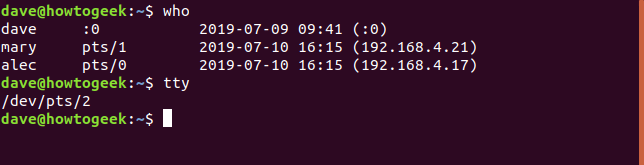
Other commands can reveal your TTY number. The who command will list information for all logged in users, including yourself.
其他命令可以显示您的TTY号码。 who命令将列出所有登录用户(包括您自己)的信息。
Alec and Mary are remotely connected to the Linux computer. They are connected to PTS one and two.
Alec和Mary远程连接到Linux计算机。 它们连接到PTS一和二。
User dave is shown as connected to “:0”.
用户dave显示为已连接到“:0”。
This represents the screen and keyboard physically connected to the computer. Even though the screen and keyboard are hardware devices, they are still connected to the multiplexor through a device file. tty reveals that it is /dev/pts/2.
这表示物理连接到计算机的屏幕和键盘。 即使屏幕和键盘是硬件设备,它们仍然通过设备文件连接到多路复用器。 tty显示它是/ dev / pts / 2。
who
tty
访问TTY (Accessing a TTY)
You can access a full-screen TTY session by holding down the Ctrl+Alt keys, and pressing one of the function keys.
您可以通过按住Ctrl + Alt键并按功能键之一来访问全屏TTY会话。
Ctrl+Alt+F3 will bring up the login prompt of tty3.
Ctrl + Alt + F3将弹出tty3的登录提示。

If you log in and issue the tty command, you’ll see you are connected to /dev/tty3.
如果登录并发出tty命令,您将看到已连接到/ dev / tty3。
This isn’t a pseudo-teletype (emulated in software); it is a virtual teletype (emulated in hardware). It is using the screen and keyboard connected to your computer, to emulate a virtual teletype like the DEC VT100 used to do.
这不是伪teletype(在软件中模拟)。 它是虚拟电传打字机(在硬件中模拟)。 它使用连接到计算机的屏幕和键盘来模拟虚拟电传打字机,例如用于DEC VT100的虚拟电传打字机。
You can use function keys Ctrl+Alt with function keys F3 to F6 and have four TTY sessions open if you choose. For example, you could be logged into tty3 and press Ctrl+Alt+F6 to go to tty6.
您可以将功能键Ctrl + Alt与功能键F3至F6结合使用,并且可以选择打开四个TTY会话。 例如,您可以登录tty3并按Ctrl + Alt + F6转到tty6。

To get back to your graphical desktop environment, press Ctrl+Alt+F2.
要返回图形桌面环境,请按Ctrl + Alt + F2。
Pressing Ctrl+Alt+F1 will return you to the login prompt of your graphical desktop session.
按Ctrl + Alt + F1将返回图形桌面会话的登录提示。
At one time, Ctrl+Alt+F1 through to Ctrl+Alt+F6 would open up the full-screen TTY consoles, and Ctrl+Alt+F7 would return you to your graphical desktop environment. If you are running an older Linux distribution, this might be how your system behaves.
一次,从Ctrl + Alt + F1到Ctrl + Alt + F6将打开全屏TTY控制台,而Ctrl + Alt + F7将使您返回图形桌面环境。 如果运行的是较旧的Linux发行版,则可能是系统的行为。
This was tested on current releases of Manjaro, Ubuntu, and Fedora and they all behaved like this:
这已在Manjaro,Ubuntu和Fedora的当前版本上进行了测试,它们的行为均如下所示:
Ctrl+Alt+F1: Returns you to the graphical desktop environment log in screen.
Ctrl + Alt + F1 :使您返回图形桌面环境登录屏幕。
Ctrl+Alt+F2: Returns you to the graphical desktop environment.
Ctrl + Alt + F2 :使您返回图形桌面环境。
Ctrl+Alt+F3: Opens TTY 3.
Ctrl + Alt + F3 :打开TTY 3。
Ctrl+Alt+F4: Opens TTY 4.
Ctrl + Alt + F4 :打开TTY 4。
Ctrl+Alt+F5: Opens TTY 5.
Ctrl + Alt + F5 :打开TTY 5。
Ctrl+Alt+F6: Opens TTY 6.
Ctrl + Alt + F6 :打开TTY 6。
Having access to these full-screen consoles allows people using command-line only installations of Linux—and many Linux servers are configured this way— to have multiple consoles available.
可以访问这些全屏控制台,使人们可以仅使用命令行安装Linux,并且以这种方式配置了许多Linux服务器,从而可以使用多个控制台。
Ever been working on a Linux machine with a graphical desktop environment and had something cause your session to freeze? Now you can hop over to one of the TTY console sessions so that you can try to rectify the situation.
您是否曾经在具有图形桌面环境的Linux机器上工作,并且有什么原因导致会话冻结? 现在,您可以跳到TTY控制台会话之一,以便尝试纠正这种情况。
You can use top and ps to try to identify the failed application, then use kill to terminate it, or just use shutdown to try to close down as gracefully as the state of the computer will allow.
您可以使用top和ps尝试识别失败的应用程序,然后使用kill终止它,或者仅使用shutdown尝试在计算机状态允许的范围内正常关闭。
具有悠久历史的三封小字母 (Three Little Letters With a Lot of History)
The tty command gets its name from a device from the late 1800s, appeared in Unix in 1971, and is part of Linux and Unix-like operating systems to this day.
tty命令的名称来自1800年代后期的设备,该命令于1971年出现在Unix中,并且至今仍是Linux和类Unix操作系统的一部分。
The little chap has quite a tale behind him.
这个小家伙在他身后有一个传奇。
翻译自: https://www.howtogeek.com/428174/what-is-a-tty-on-linux-and-how-to-use-the-tty-command/























 3946
3946

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








