操作系统抢占式优先级调度
In the priority scheduling, the processes are scheduled on the basis of their priority, and not on the basis of their burst time. If the preemptive mode of this scheduling is being followed, then a process with a higher priority than the currently executing process can replace the executing process. This can be well explained with the help of the following example:
在优先级调度中 ,将根据进程的优先级而不是根据突发时间来调度进程。 如果遵循此调度的抢占模式 ,则优先级高于当前正在执行的进程的进程可以替换正在执行的进程。 可以通过以下示例很好地解释这一点:
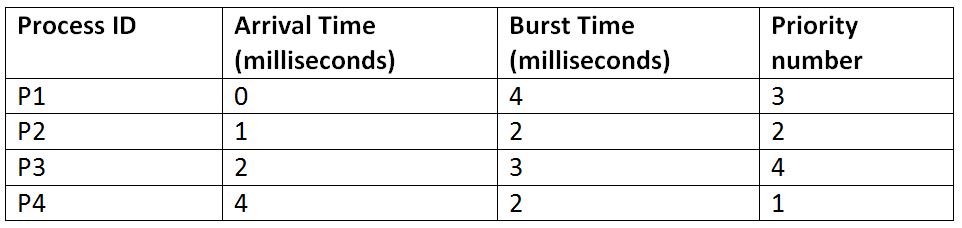
Suppose, we have four processes: P1, P2, P3 and P4, and they enter the CPU in the following manner:
假设我们有四个进程: P1 , P2 , P3和P4 ,它们以以下方式进入CPU:
As per the preemptive priority scheduling, the processes will be executed as follows:
根据抢先优先级调度 ,这些过程将按以下方式执行:
Gant Chart
甘特图

Explanation:
说明:
There is only P1 available at time 0, so it will be executed first irrespective of the priority until some other process with a higher priority is encountered by the OS.
在时间0只有P1可用,因此它将优先于优先级执行,直到OS遇到其他具有更高优先级的进程为止。
At the beginning of the 1st-time unit, we have P2 which has a higher priority than P1, so it replaces P1.
在第1 个 -时间单元的开始,我们有P2具有比P1更高的优先级,因此它取代P1。
At 2nd time unit, we have the process P3, but its priority is less than the executing process P2, so P2 keeps executing without any replacement.
在第二时间单位,我们有进程P3 ,但是它的优先级小于执行进程P2 ,因此P2继续执行而没有任何替换。
At 3rd time unit, our P2 has been completed and till now we have processes P1 and P3 left. So, P1 which has a higher priority than P3 is executed.
在第三个时间单元,我们的P2已完成,到现在为止,我们还有流程P1和P3 。 因此,执行优先级高于P3的 P1 。
At 4th time unit, we have process P4 which has the highest priority of them all. So, it replaces P1.
在第 4 个时间单位,我们有进程P4 ,它是所有进程中的最高优先级。 因此,它将替换P1 。
Since now we have no more processes left to arrive, the processes will now run according to their priorities and will complete their execution.
从现在开始,我们不再需要其他任何流程,这些流程将根据其优先级运行并完成其执行。
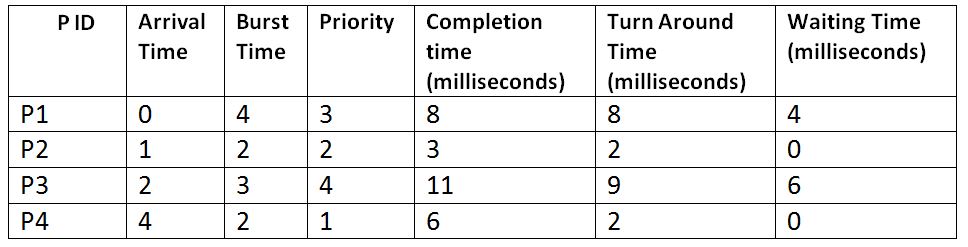
Total Turn-Around Time = 8 + 2 + 9 + 2
= 21 milliseconds
Average Turn-Around Time= Total Turn-Around Time / Total No. of Processes
= 21 / 4
= 5.25 milliseconds
Total Waiting Time = 4 + 0 + 6 + 0
= 10 milliseconds
Average Waiting Time = Total Waiting Time / Total No. of Processes
= 10 / 4
= 2.5 milliseconds
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/operating-systems/priority-scheduling-preemptive.aspx
操作系统抢占式优先级调度





















 4130
4130

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








