linux 图片压缩技术
In earlier times, when we used to have 5 MB of storage (and not mention bulky in size unlike today's' flash drive or SD cards) and 256 MB of RAM, then people came up with an idea of shrinking data and filesystems and storing them in a more compact form. Though even today archiving, ZIP and compressing techniques used for the ease of data transfer over any network.
在早期,当我们曾经拥有5 MB的存储空间(而且不像今天的闪存驱动器或SD卡那样要占用庞大的内存)和256 MB的RAM时,人们想到了缩小数据和文件系统并存储它们的想法以更紧凑的形式。 尽管在今天,存档, ZIP和压缩技术仍可简化任何网络上的数据传输。
Our lovable Linux comes pre-loaded these features all three ZIP, compression and archiving features, you don't need 7-zip or RAR on Linux as you do need on your Window machine (poor souls :P). In our journey to explore Linux, we will get acquainted with compression on our Linux.
我们可爱的Linux预先加载了所有这三个ZIP, 压缩和归档功能 ,这些功能在Linux上并不需要Windows机器上的7-zip或RAR(可怜的人:P)。 在探索Linux的过程中,我们将熟悉Linux上的压缩 。
Before we get to start with terminal commands for compression let get a theory lesson first:
在开始使用终端命令进行压缩之前,请先上理论课:
What is compressing a file? It is simply reducing the size of the file by removing redundant information from it, and what archiving is? It is nothing but combining multiple files by which an overhead in each separate file get remove and makes it easier to transmit.
什么是压缩文件? 它只是通过从文件中删除冗余信息来减小文件的大小,什么是归档? 它只不过是组合多个文件,从而消除了每个单独文件中的开销并使其更易于传输。
Even today disks space are relatively cheap, archiving and compression still has value:
即使在今天磁盘空间相对便宜的情况下,归档和压缩仍然具有价值:
If you want to make a large number of files available, such as the source code to an application or a collection of documents, it is easier for people to download a compressed archive than it is to download individual files.
如果要提供大量文件,例如应用程序的源代码或文档集合,那么人们下载压缩的存档要比下载单个文件容易。
Log files have a habit of filling disks so it is helpful to split them by date and compress older versions.
日志文件有填充磁盘的习惯,因此按日期将其拆分并压缩较旧的版本很有帮助。
When you back up directories, it is easier to keep them all in one archive than it is to version each file.
备份目录时,将其全部保存在一个存档中比对每个文件进行版本控制要容易得多。
Some streaming devices such as tapes perform better if you're sending a stream of data rather than individual files.
如果您发送的是数据流而不是单个文件,则某些流式传输设备(例如磁带)的性能会更好。
It is proven faster to compress a file before you send it to over a slower network and decompress it on the other end than it would be to send it uncompressed.
与通过未经压缩的文件发送文件相比,事实证明,在通过较慢的网络将文件发送到另一端并对其进行解压缩之前,压缩文件的速度更快。
压缩文件 (compressing files)
Now let's dive in details of compressing files:
现在让我们深入了解压缩文件的细节:
As already told you guys, compression is nothing but removing duplicate data from a file to make it shrink in size in such a way that it can be restored back later. For example, in a text file common repeating words can be replaced with something smaller, or in an image where a solid background might is a patch of code instead of long colour codes. We all know that we can't use a compressed file so we need to decompress it before using it.
就像你们已经说过的,压缩不过是从文件中删除重复的数据,以使其大小缩小,以便以后可以还原而已。 例如,在文本文件中,常见的重复单词可以替换为较小的单词,或者在图像中,纯色背景可能是一小段代码,而不是长色代码。 我们都知道我们不能使用压缩文件,因此我们需要在使用它之前将其解压缩。
We have two broadly categorized algorithms for Compressing file, those are:
对于压缩文件,我们有两种大致分类的算法,分别是:
1) Lossy:
1)有损:
These algorithms removes information from the file that uncompressing that file will result in some lost data. Usually, we prefer Lossy compression for media files like images, videos or audios format.
这些算法从文件中删除信息,该信息解压缩该文件将导致某些数据丢失。 通常,我们更喜欢对图像,视频或音频格式的媒体文件进行有损压缩。
Why would we prefer to remove some of the data while uncompressing data? Since we use this technique with media files only as human eyes and ears don't catch minute details on a screen or speakers and thus difference can't distinguish between original or the changed version.
为什么我们更喜欢在解压缩数据时删除一些数据? 由于我们仅将这种技术与媒体文件一起使用,因为人的眼睛和耳朵无法在屏幕或扬声器上捕捉到微小的细节,因此无法区分原始版本或更改版本。
2) Lossless:
2)无损:
This algorithm makes sure that no data will be lost on uncompressing the file. We prefer lossless compression when data is important, like in text files or messages.
该算法可确保在解压缩文件时不会丢失任何数据。 当数据很重要时(例如文本文件或消息中),我们更喜欢无损压缩。
Linux中的压缩: (Compression in Linux:)
For compression, we will use the gzip utility.
对于压缩,我们将使用gzip实用程序 。
We start with compressing a file; it can be achieved with this simple command:
我们从压缩文件开始; 可以使用以下简单命令来实现:
gzip filename
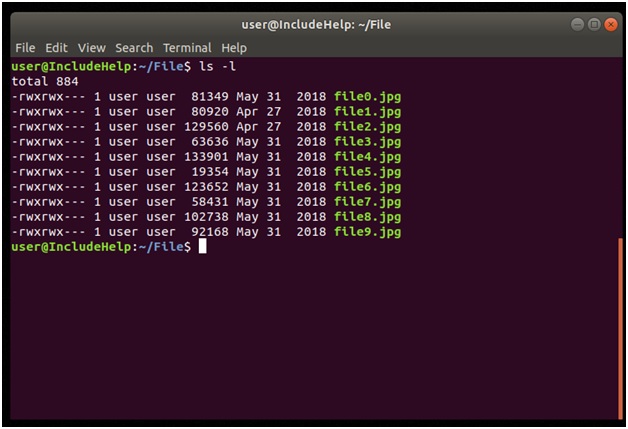
Let's see the snap below the entire file on which we will perform compression and de-compression on these files throughout the article.
让我们看一下整个文件下面的快照,在本文中我们将对这些文件执行压缩和解压缩。
Let's perform the compression:
让我们执行压缩:

Explanation
说明
We simply used gzip with our file2 (remember to mention its extension).
我们只是将gzip与我们的file2一起使用(请记住提及其扩展名)。
Notice its initial size was 1291560 bytes after compressing it with gzip we have file2 with an extension .jpg.gz - where, gz is for gzip and .jpg its own, also after compression we size of file2.jpg is 129100 bytes.
请注意它的初始大小为1291560个字节使用gzip后,我们有文件2与扩展.jpg.gz -其中, 广州是gzip和.jpg文件自身的,也经过file2.jpg的压缩,我们大小为129100个字节。
In the later part of the snapshot, we used gunzip which is used for decompressing all the files.
在快照的后半部分,我们使用了gunzip,该文件用于解压缩所有文件。
See it's that simple, and we can also perform these operations on multiple files at once:
就是这么简单,我们也可以一次对多个文件执行以下操作:
gzip filename1 filename2 filename3

Explanation
说明
In the above snap, we compressed multiple files at once. We used gzip file* which is equivalent gzip file0.jpg file1.jpg... file9.jpg.
在上面的快照中,我们一次压缩了多个文件。 我们使用了gzip file * ,相当于gzip file0.jpg file1.jpg ... file9.jpg 。
Once files are compressed, we can check all the status regarding their compression with "–l" option:
压缩文件后,我们可以使用“ –l”选项检查有关其压缩的所有状态:
gzip –l filename1 filename2 ...
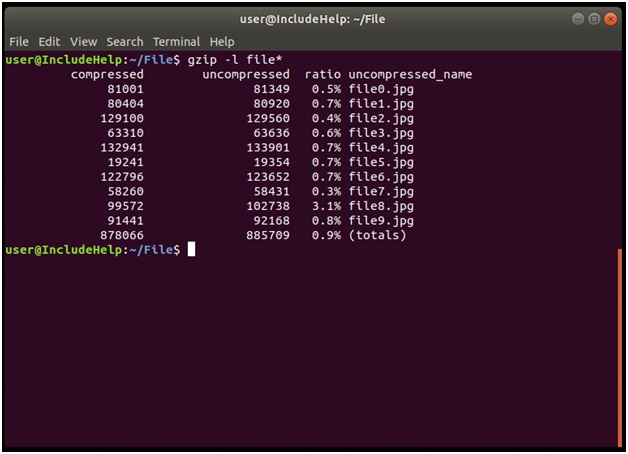
Explanation
说明
After compressing files we used gzip –l operation all files with .gz extension. It will result out all the necessary information viz. compressed size (current size), uncompressed size (old size), compression ratio etc.
压缩文件后,我们使用gzip –l操作所有扩展名为.gz的文件。 它将得出所有必要的信息, 即 。 压缩大小(当前大小),未压缩大小(旧大小),压缩率等。
Note:
注意:
1. We can also decompress with gzip by using:
1.我们还可以使用以下命令使用gzip解压缩 :
gzip –d filename
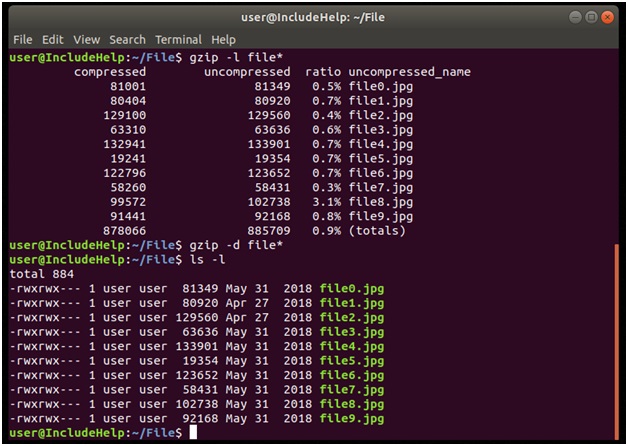
gzip –d will only accept file names with .gz otherwise it will give an error.
gzip –d将仅接受带有.gz的文件名,否则将给出错误。
2. gzip/gunzip v. bzip2/bunzip2
2. gzip / gunzip诉bzip2 / bunzip2
Just like gzip we have bzip2, both have similar options and operations but the difference is in the compression algorithm used by both.
就像gzip一样,我们有bzip2 ,两者都有相似的选项和操作,但是两者的区别在于两者使用的压缩算法。
gzip uses Lempel-Ziv encoding whereas bzip2 uses Burrows-Wheeler Block sorting.
gzip使用Lempel-Ziv编码,而bzip2使用Burrows-Wheeler块排序。
bzip2 compression ratio is higher than gzip that mean, files are smaller when compressed with bzip2 than that of gzip but bzip2 costs more CPU time.
bzip2的压缩比是比gzip更高,当使用bzip2比的gzip的但bzip2的成本更多的CPU时间压缩均值,文件较小。
Extension bz or bz2 is for the bzip2 support unlike gzip with .gz
扩展名bz或bz2用于bzip2支持,与带有.gz的 gzip不同
Recommended Articles:
推荐文章:
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/linux/compression-techniques.aspx
linux 图片压缩技术





















 1042
1042











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








