ipv6寻址
IPV4寻址简介 (Introduction to IPV4 Addressing )
Internet protocol version 4 in any network, is a standard protocol for assigning a logical address (IP address) to hosts. You are currently using the same protocol. This protocol is capable of providing a unique address to the devices available in this world, but will not be available after a few years. Therefore its advanced version IPV6 has been introduced, which you can read in the tutorial of IPV6.
任何网络中的Internet协议版本4是用于为主机分配逻辑地址(IP地址)的标准协议。 您当前正在使用相同的协议。 该协议能够为这个世界上可用的设备提供唯一的地址,但几年后将不可用。 因此,已经引入了其高级版本IPV6,您可以在IPV6教程中阅读。
The IP address in IPV4 is 32 bits. It is represented in 4 blocks of 8 bits. The lower IPV4 address is represented in both binary and decimal form.
IPV4中的IP地址是32位。 它以4个8位的块表示。 较低的IPV4地址以二进制和十进制形式表示。
Binary: 11000000.10101000.00001010.00000001
Decimal: 192.168.10.1
These blocks represent networks and hosts. The starting block represents the network and represents the subsequent hosts that how many blocks will represent the network and how many hosts will represent these are defined by classes of IP address. If you want to know more about the format and classes of the IPV4 address, you can read it in the Addressing tutorial.
这些块代表网络和主机。 起始块代表网络,并代表随后的主机,这些主机将由IP地址的类别来定义。 如果您想了解有关IPV4地址格式和类别的更多信息,可以在《寻址》教程中阅读它。
IPV4标头 (IPV4 Header )
Internet Protocol (IP) works on layer 3 (Network Layer). They break the segments (when using TCP as protocol) or datagram (when using UDP as protocol) sent through layer layer 4 (Transport Layer) in packets. After breaking in packets, IP header is attached with these packets. This provides the necessary information receiver side related to the header packet. This information is represented by different fields in the IP header.
Internet协议(IP)在第3层(网络层)上工作。 它们破坏通过数据包的第4层(传输层)发送的段(使用TCP作为协议时)或数据报(使用UDP作为协议时)。 破坏数据包后,这些数据包将附加IP标头。 这提供了与报头分组有关的必要的信息接收方。 此信息由IP标头中的不同字段表示。
The lower IP header is represented by a diagram. After this all the fields have been explained in detail:
下层IP标头由图表表示。 之后,将详细解释所有字段:
IPv4标头图 (IPv4 Header Diagram)
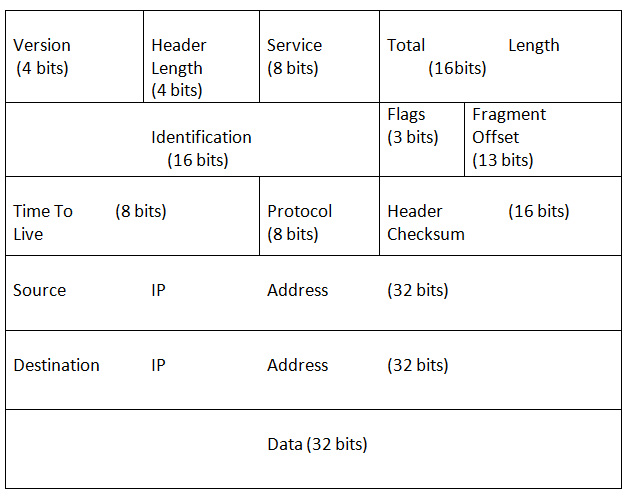
Version Number:
版本号:
The version number of Internet Protocol is used to define the version number field. Here the IPV4 header is being spoken, so the version will also be 4th.
Internet协议的版本号用于定义版本号字段。 这里说的是IPV4标头,因此版本也是4号。
Header Length:
标头长度:
The length of the IP header is defined by this field. The length of the IPV4 header is represented by 32 bit words (with options). If no option is defined in the header then this filed has value of 5 set.
IP头的长度由该字段定义。 IPV4标头的长度由32位字(带选项)表示。 如果标题中未定义任何选项,则该字段的值设置为5。
Types of Service:
服务类型:
This field defines the way by which the router should queue the packets when the packets are waiting to be forwarded. If the priority of a packet is high then this field's value is 1. This packet has 0 value for regular packets.
此字段定义当数据包等待转发时路由器应将数据包排队的方式。 如果数据包的优先级高,则此字段的值为1。对于常规数据包,此数据包的值为0。
Total Length:
总长度:
This field shows the total length of the IP data-gram. Define the header length defines the length of the field header and defines the total length of data-gram, including field data and header. This is a 16 bit field.
该字段显示IP数据报的总长度。 定义标题长度定义字段标题的长度,并定义数据报的总长度,包括字段数据和标题。 这是一个16位字段。
Identification:
身份证明:
This field is the identification of a segment. This is a 16 bit number, which together with the source address uniquely identifies a segment.
该字段是段的标识。 这是一个16位数字,与源地址一起唯一标识一个段。
Flags:
标志:
This field shows whether the router can fragment any segment. This field has 3 bits. The first bit is reserved. If the second bit is set in this field then it means do not fragment and if the field is set to a third bit then it means the segment is fragmented.
此字段显示路由器是否可以对任何网段进行分段。 该字段具有3位。 第一位保留。 如果在该字段中设置了第二位,则表示不分段;如果该字段设置为第三位,则意味着段已分段。
Fragment Offset:
片段偏移:
If the packet is fragmented, then this field shows the starting 8 packs of the original packet. This field is of 13 bits.
如果数据包是分段的,则此字段显示原始数据包的前8包。 该字段是13位。
Time to Live:
生存时间:
This field sets a limit. Let the value of this field be 15. If the packet does not reach the destination even after passing from 15 routers, then that packet is discarded. This is an important field from the perspective of authenthenticity. The size of this field is 8 bits.
此字段设置限制。 将该字段的值设为15。如果即使从15个路由器经过后数据包仍未到达目的地,则该数据包将被丢弃。 从真实性的角度来看,这是一个重要的领域。 该字段的大小为8位。
Protocol:
协议:
This field contains the name of the protocol that passed the packet network layer because for de-multiplexing on the receiver side, it should know which protocol to pass the data.
该字段包含通过分组网络层的协议的名称,因为为了在接收方进行多路分解,它应该知道要通过哪个协议来传输数据。
Header Checksum:
标头校验和:
This field is used to check errors. When the packet is sent from source then this field has a value that is calculated by the algorithm through the header. When this packet reaches the receiver side, then the value is calculated by the same algorithm back to the head if the value matches the source side then it is believed that the packet error is free. This field is of 8 bits.
此字段用于检查错误。 从源发送数据包时,此字段具有一个值,该值由算法通过标头计算。 当该分组到达接收器侧时,则如果该值与源侧匹配,则通过相同的算法将该值返回头部,则认为该分组错误是免费的。 该字段是8位。
Source IP Address:
源IP地址:
This represents the IP address of the field source. The size of this field is 32 bits.
这表示字段源的IP地址。 该字段的大小为32位。
Destination IP Address:
目的IP地址:
The destination address is represented by this field. The size of this field is 32 bits.
目的地址由该字段表示。 该字段的大小为32位。
Options:
选项:
This field represents some options that some packets can use. Although this field is not used, whenever it is used, the header length exceeds 32 bits.
该字段表示某些数据包可以使用的某些选项。 尽管不使用此字段,但无论何时使用,标题头长度都超过32位。
Data:
数据:
This field contains the main data that is passed by the transport layer protocols to the IP.
该字段包含传输层协议传递给IP的主要数据。
IPV4地址类型 (IPV4 Address Types )
Whenever IPV4 packets are sent or received, they are sent / received by one of the three types given address. Let's us learn about them in detail.
每当发送或接收IPV4数据包时,都会通过三种给定地址类型之一发送/接收IPV4数据包。 让我们详细了解它们。
Unicast
单播
A unicast address represents a specific host. This type of address represents the specific destination host in the IPV4 packet. This type of address is used for one-to-one communication. For example a host of LAN A will send a packet to a host of LAN B, then it will be called unicast addressing.
单播地址表示特定的主机。 这种类型的地址代表IPV4数据包中的特定目标主机。 此类地址用于一对一通信。 例如,LAN A的主机将向LAN B的主机发送一个数据包,然后将其称为单播寻址。
Multicast
多播
Multicast addresses are used to send a packet to more than one host. These are used for one-to-many communication. For example, a host can send a packet to an IP address group in another network. These packets are only received by those hosts that are in the multicast group.
组播地址用于将数据包发送到多个主机。 这些用于一对多通信。 例如,主机可以将数据包发送到另一个网络中的IP地址组。 这些数据包仅由多播组中的那些主机接收。
Broadcast
广播
Broadcast addresses are used by IPV4 to spread the packet of a single host across the network. This is a one-to-all communication. For example, a host can send a packet to the other available hosts in the LAN.
IPV4使用广播地址在网络上传播单个主机的数据包。 这是一对一的通信。 例如,主机可以将数据包发送到LAN中的其他可用主机。
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/computer-networks/ipv4-addressing.aspx
ipv6寻址





















 838
838

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








