前言
redis6 出来有段时间了,这个版本有不少的亮点,比如 client cache、acl、resp3、io 多线程等。对于 redis6 的新功能代码看的差不多了,复杂点主要集中在 cache track 和 io thread 上,个人对 io 多线程的设计和性能表现有些不认同。😅
压测数据本应该使用图表展现,奈何太懒.
io 多线程是怎么一回事?
redis 本身是有多个线程的,但 worker 线程只有一个,其他线程属于辅助线程,比如 aof 日志和 bio 线程。单个 worker 线程限制了 redis 的 qps 只有十几万,这里不算 pipeline 批量管道。redis 是纯内存操作,对于磁盘的操作都是异步的,为什么只有十几万 QPS? 单线程的 worker 只能跑在一个 cpu core 核心上,该线程不仅要处理 epoll,要解包,要处理内存数据,要封包,要读写 socket 等等。通过火焰图得知最大的性能点在于 socket write 系统调用上。
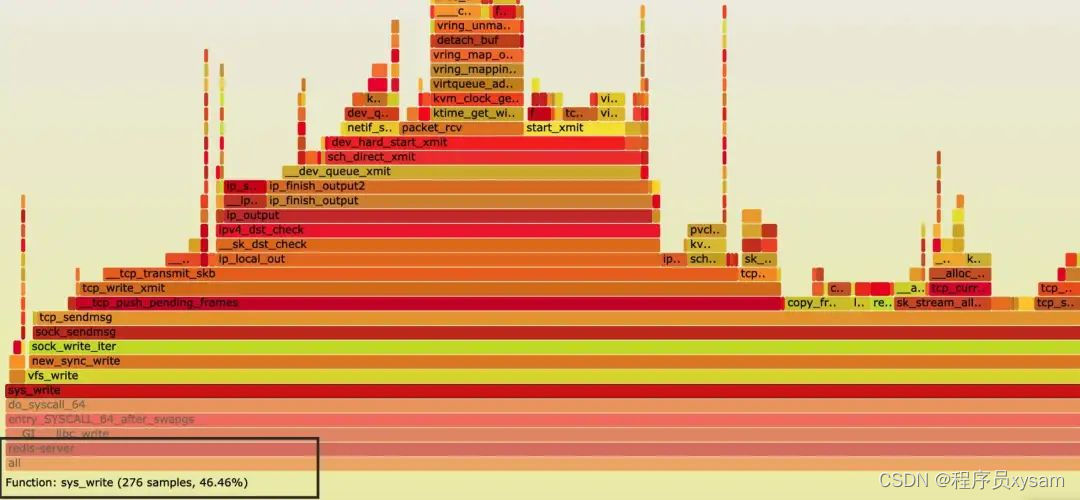
为了解决单线程的性能瓶颈,redis6 给出了 io 多线程方案,处理数据的线程还是唯一,但处理读写 socket 和解析协议由多个 io 线程解决。
那么为什么不直接开多个 wokrer 线程?规避锁竞争 ! 锁竞争会引起什么?要么忙竞争,要么上下文切换。像其他 kv 服务器可通过虚拟 db 或者分段锁来减少竞争,但这个实现会对 redis 主体代码改动太大。
主流程
具体的代码实现我就不贴代码了,避免大家看着烦心。这里简单描述下他的实现,核心就是各种的轮询。
首先 redis 在启动时根据配置来实例化几个 io 线程。这里有几个变量要描述下,io_threads_active 表示为当前 io thead 的激活状态,io_threads_list 是一个存有任务 list 的数组,io_threads 存有线程结构, io_threads_pending 表明 io thread 是否有任务, io_threads_mutex 存有每个 io thread 对应的锁,用来休眠和唤醒的。
// xiaorui.cc
void initThreadedIO(void) {
io_threads_active = 0; // 默认不激活io线程的工作状态
// 如果io thread为1,那么无意义,索性直接使用主线程处理,所以return
if (server.io_threads_num == 1) return;
// 不能超过128个io线程
if (server.io_threads_num > IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal: too many I/O threads configured. "
"The maximum number is %d.", IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM);
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < server.io_threads_num; i++) {
io_threads_list[i] = listCreate(); // 任务列表
if (i == 0) continue; /* Thread 0 is the main thread. */
pthread_t tid;
pthread_mutex_init(&io_threads_mutex[i],NULL);
// 默认io线程对应的任务为0,标识无io任务
io_threads_pending[i] = 0;
// 默认锁定io线程对应的锁上
pthread_mutex_lock(&io_threads_mutex[i]);
// 创建线程,并启动iothreadmain方法。
if (pthread_create(&tid,NULL,IOThreadMain,(void*)(long)i) != 0) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal: Can't initialize IO thread.");
exit(1);
}
io_threads[i] = tid;
}
}主线程监听 ae_epoll 并拿到有事件的客户端,然后轮询分配给各个 io 线程绑定的 io_threads_list 链表里,把每个线程的 io_threads_pending 配置为当前 io 线程所分配的事件数,其他就是空轮询等待结果了,并收尾工作。
// xiaorui.cc
int handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads(void) {
// 1. 判断是否还有client对象需要写数据给客户端
int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);
if (processed == 0) return 0; /* Return ASAP if there are no clients. */
// 2. 当io thread为1, 或者任务量少于(线程 * 2),则不使用多线程直接处理。
if (server.io_threads_num == 1 || stopThreadedIOIfNeeded()) {
return handleClientsWithPendingWrites();
}
/* Start threads if needed. */
// 3. 如果未开启io多线程,则开启,所谓的开启就是唤醒线程对应的锁。
if (!io_threads_active) startThreadedIO();
if (tio_debug) printf("%d TOTAL WRITE pending clients\n", processed);
/* Distribute the clients across N different lists. */
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);
int item_id = 0;
// 4.按照RoundRobin算法把需要返回数据的client对象分配给IO线程,简单而高效。
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;
int target_id = item_id % server.io_threads_num;
listAddNodeTail(io_threads_list[target_id],c);
item_id++;
}
/* Give the start condition to the waiting threads, by setting the
* start condition atomic var. */
// 5. 设置标志位为写操作,统计各个io线程需要处理的client的个数
io_threads_op = IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE;
for (int j = 0; j < server.io_threads_num; j++) {
int count = listLength(io_threads_list[j]);
io_threads_pending[j] = count;
}
/* Wait for all threads to end their work. */
// 6. 空循环等待所有的IO线程完成IO读写
while(1) {
unsigned long pending = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < server.io_threads_num; j++)
pending += io_threads_pending[j];
if (pending == 0) break;
}
if (tio_debug) printf("I/O WRITE All threads finshed\n");
/* Run the list of clients again to install the write handler where
* needed. */
// 7. 如果还有数据没有写完的话则继续处理
listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
/* Install the write handler if there are pending writes in some
* of the clients. */
if (clientHasPendingReplies(c) &&
connSetWriteHandler(c->conn, sendReplyToClient) == AE_ERR)
{
freeClientAsync(c);
}
}
// 8. 清空需要写数据的client对象列表
listEmpty(server.clients_pending_write);
return processed;
}io thread 主函数每次进行 100w 次忙轮询判断是否有任务,有任务处理触发读或写,io 线程在干完任务后会清理链表并重置 io_threads_pending 状态。如果无任务,那么就对 io_threads_mutex[id]频繁的尝试加锁、放锁的操作,直到主线程触发 stopThreadedIOIfNeeded 进行 stopThreadedIO。这里的 stop 不是让其退出,只是锁定互斥而已。
io_threads_pending 的状态值 0/N 判断是否存在任务。N 为有客户端数
// xiaorui.cc
void *IOThreadMain(void *myid) {
//...省略部分代码...
while(1) {
/* Wait for start */
for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {
if (io_threads_pending[id] != 0) break;
}
/* Give the main thread a chance to stop this thread. */
if (io_threads_pending[id] == 0) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&io_threads_mutex[id]);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&io_threads_mutex[id]);
continue;
}
...
/* Process: note that the main thread will never touch our list
* before we drop the pending count to 0. */
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(io_threads_list[id],&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE) { // 写类型
writeToClient(c,0);
} else if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_READ) { // 读类型
readQueryFromClient(c->conn);
} else {
serverPanic("io_threads_op value is unknown");
}
}
// 处理完成后将自己的清空自己的链表
listEmpty(io_threads_list[id]);
// 重置状态标志值为0
io_threads_pending[id] = 0;
}
}那么主线程又如何得知 io 线程干完了?也是轮询。
// xiaorui.cc
// write
int handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads(void) {
...
while(1) {
unsigned long pending = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++)
pending += io_threads_pending[j];
if (pending == 0) break;
}
...
}
// read
int handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads(void) {
...
while(1) {
unsigned long pending = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++)
pending += io_threads_pending[j];
if (pending == 0) break;
}
...
}性能测试
redis6 之前的 benchmark 是单线程,所以多线程的压测需要使用 redis6 的 redis-benchmark 命令,并配置线程数。
不开 io 线程下压测结果
// xiaorui.cc
benchmark 6379 clients 16
121212.12 requests per second
125000.00 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 32
124984.37 requests per second
129032.26 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 64
129023.93 requests per second
129023.93 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 128
129015.61 requests per second
131147.55 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 256
126959.95 requests per second
131104.56 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 512
126935.77 requests per second
133288.91 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 1024
119331.74 requests per second
119353.11 requests per second
开启 4 个 io 线程进行压测,在 redis 连接数小于 64 个时,qps 提升 50%左右,大于 64 个时,提升接近 90%了。
// xiaorui.cc
benchmark 6379 clients 16
181785.12 requests per second
190476.19 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 32
228519.20 requests per second
235211.09 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 64
242394.84 requests per second
257964.67 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 128
235183.45 requests per second
257997.94 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 256
228519.20 requests per second
253774.91 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 512
221926.31 requests per second
249906.28 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 1024
228284.45 requests per second
242688.98 requests per second
开启 8 个 io thread 线程的效果。8 个线程把 8 个 cpu core 负载跑的差不多了,但 qps 却不升反降。
// xiaorui.cc
benchmark 6379 clients 16
126968.01 requests per second
129015.61 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 32
121197.42 requests per second
126968.01 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 64
109583.04 requests per second
131138.94 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 128
140331.19 requests per second
142846.94 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 256
145422.81 requests per second
156862.75 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 512
150886.45 requests per second
159936.03 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 1024
150840.94 requests per second
163198.69 requests per second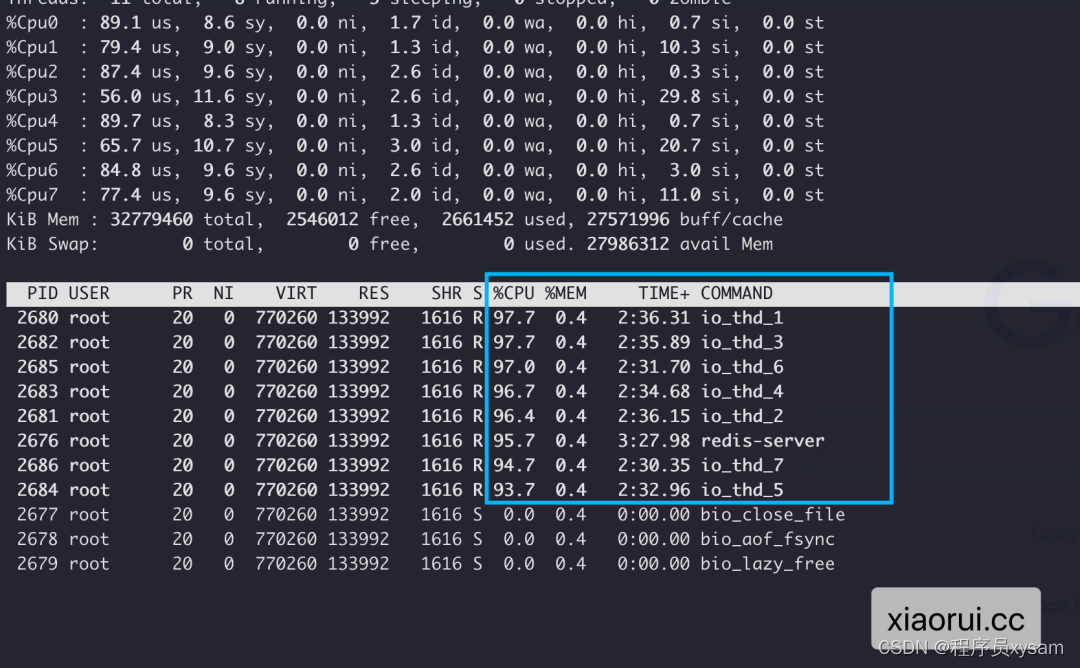
redis6 的性能瓶颈?
通过 perf 采集 redis6 在 benchmark 压测时的数据,分析瓶颈点在于忙轮询。性能瓶颈跟 redis6 的多线程本身设计有大关系的,当每次调用 aeApiPoll 获取的事件超过 io 线程数的两倍时,就会触发 io 线程的调度。io 线程在完成任务后会尝试轮询任务,直到有新任务或 100w 次的轮询后进入 pthread_mutex_lock 休眠。

redis conf 注释里为什么推荐 io thread 为 4 个?通过上面的 8 个线程已经测试得出,在超过 4 个 io 线程后性能不升反降的。原因?还是轮询。
⚠️ 在 cpu 64 core 的服务器已测试 8、16、32 io thread 线程,benchmark 数据会随着线程数增长越来越不理想,体现在 cpu 的开销和 qps 反差大。⚠️
cpu 不同 benchmark 压测结果自然也不同,我分别使用云厂商常用的 intel 铂金和黄金 cpu 测试,压测结果有明显差异,这个跟 cpu 主频和多级缓存的大小有关系。使用 Platinum 8269CY 2.5mhz 做测试,他的 io thread 多线程提升在 50%-60%左右。但由于 Platinum cpu 多级缓存大,减少了 cache miss,所以 QPS 本就比前面 gold 系列表现的好。
压力测试 ” Intel Platinum 8269CY CPU @ 2.50GHz ” 的表现,下面是不开启 io 线程。
// xiaorui.cc
benchmark 6379 clients 16
156838.14 requests per second
163251.97 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 64
166638.89 requests per second
170212.77 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 128
163265.31 requests per second
170212.77 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 256
166652.77 requests per second
166666.67 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 512
163185.39 requests per second
163251.97 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 1024
166611.14 requests per second
159961.61 requests per second
开启 4 个 io 线程的压测表现。
// xiaorui.cc
benchmark 6379 clients 16
199980.00 requests per second
205107.16 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 64
266560.06 requests per second
266666.66 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 128
257964.67 requests per second
281491.91 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 256
249937.52 requests per second
266560.06 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 512
250156.34 requests per second
266631.12 requests per second
benchmark 6379 clients 1024
263088.66 requests per second
285551.09 requests per second如简单 QPS 来分析,开不开 io 多线程都要比 ” Intel Gold 6151 CPU @ 3.00GHz” 高一些 。在 redis 的场景来说,cpu 多级缓存大小很重要。由于云平台屏蔽了相关检测,使用 perf 无法探测到 cache miss。
// xiaorui.cc
perf stat -a -e cache-misses,cache-references -- sleep 10
Performance counter stats for 'system wide':
<not supported> cache-misses
<not supported> cache-references
10.000744488 seconds time elapsed
不太推荐使用 redis6 多线程?
就拿官方推荐的 4 个 io thread 线程来说,4 个 io 线程加主线程都 cpu 100% 的情况下才可超过接近一倍的 qps,那还真不如使用 redis cluster 集群方案 😅。当然 redis cluster 是有运维成本,对于一些组合的多指令需要智能客户端或代理层解决。
在社区中跟阿里云 redis 团队聊过,他们的 redis 多线程为流水线模型,减少了过多的轮询开销。设计上有些像 memcached,类似 multi reactor 的网络模型设计,主线程去监听新连接,通过 pipe 来通知其他线程新连接,其他线程各自构建 event loop。😅
下面是在社区里找到的关于阿里云 redis 流水线模型设计,单看设计模型确实要比 redis6 显得优雅些,也更好理解。但由于阿里云 redis 非开源版,所以性能消耗如何不得而知了。
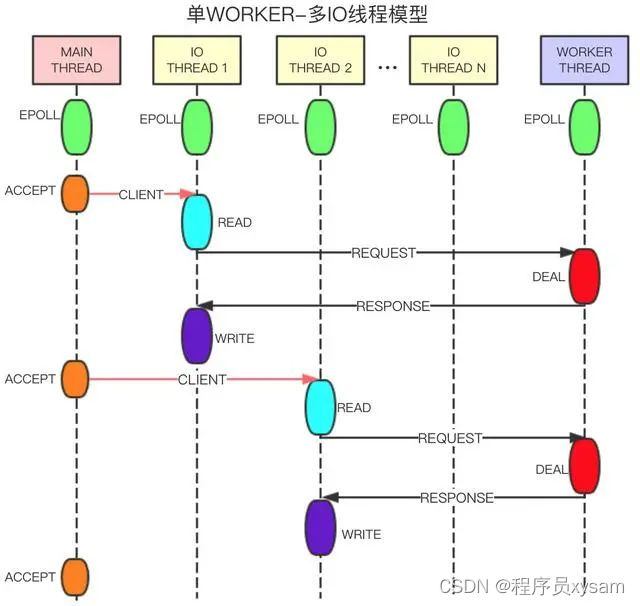
主线程接受连接,创建 client,将连接转发给 IO 线程。IO 线程处理连接的读写事件,解析命令,将解析的完整命令转发给 WORKER 线程处理,发送 response 包,负责删除连接等。WORKER 线程负责命令的处理,生成客户端回包,定时器事件的执行等。
主线程,IO 线程,WORKER 线程都有单独的事件驱动,线程之间通过无锁队列交换数据,通过管道进行消息通知。这样的设计可以让不同工种的线程都可以并行跑起来,而 redis6 同一时间只能跑一块逻辑,要么正监听获取 ae 事件, 要么几个 io thread 在解封包,要么在执行数据处理逻辑,而阿里云的 redis 看设计是可以同时工作起来。
据阿里云 redis 团队说,在常规使用的需求下,他们的提升最少有三倍左右。近几年阿里云对 redis 的代码贡献已经排在第三了,仅次于作者和 redislabs。阿里云真是没少折腾呀。😁
总结
redis6 的 io 多线程到底实不实用?看你的需求了,个人建议上 redis 集群来扩展高并发的需求。


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








