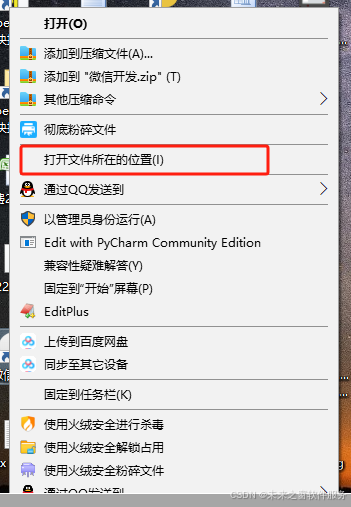
- 方便文件管理与定位
- 快速访问相关文件:当软件打开所在文件路径时,用户能够迅速找到与该软件相关的配置文件、数据文件、日志文件等。例如,一款图像编辑软件,其配置文件可能存储了用户的个性化设置,如界面布局、快捷键等;数据文件则包含了用户正在编辑的图像项目。通过打开所在文件路径,用户可以方便地对这些文件进行备份、转移或直接查看修改。
- 解决文件关联问题:如果软件在运行过程中出现文件关联错误,或者用户需要手动指定文件的打开方式,知道文件所在路径可以帮助用户准确找到文件,重新建立正确的关联,确保软件能够正常读取和处理相关文件。
- 便于软件调试与维护
- 查看日志文件:许多软件会在运行过程中生成日志文件,记录软件的运行状态、错误信息等。开发人员或技术支持人员通过打开日志文件所在路径,可以快速获取这些信息,以便分析软件出现故障的原因,及时进行调试和修复。例如,当一款游戏出现崩溃问题时,查看游戏安装目录下的日志文件,能够帮助开发人员了解崩溃发生时的具体情况,如玩家的操作、游戏的运行参数等,从而更快地找到问题并解决。
- 更新与升级软件:软件更新时,安装程序通常需要访问软件的安装目录,将新的文件覆盖旧文件,或者添加新的功能模块。明确软件所在文件路径可以确保更新过程顺利进行,避免因找不到文件而导致更新失败。同时,对于一些绿色软件(即无需安装,直接运行的软件),用户手动更新时也需要将下载的新文件放置到正确的目录中,这就需要知道软件所在的文件路径。
- 支持文件共享与协作
- 团队协作:在团队协作项目中,成员可能需要共享软件的相关文件,如项目文件、设计文档等。通过打开软件所在文件路径,用户可以方便地将文件复制到共享文件夹或通过网络共享给其他成员,确保团队成员能够及时获取最新的文件,提高协作效率。例如,在一个软件开发团队中,开发人员需要将代码文件、测试报告等共享给其他成员,明确文件路径有助于快速定位和共享这些文件。
- 文件传递与共享:当用户需要将软件生成的文件分享给他人时,知道文件所在路径可以方便地找到文件并进行传递。比如,用户使用视频编辑软件制作了一个视频,要将其分享给朋友,就可以通过打开文件路径找到视频文件,然后通过电子邮件、即时通讯工具或移动存储设备等方式将文件发送给对方
C# windows 代码
// 获取文件所在的目录
string directory = System.IO.Path.GetDirectoryName(filePath);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ =>
{
// 使用资源管理器打开该目录,并选中文件
Process.Start("explorer.exe", $"/select,\"{filePath}\"");
});
鸿蒙操作系统
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs';
import process from '@ohos.process';
export class FileUtils {
// 打开文件所在目录并选中文件
static openContainingFolder(filePath: string) {
try {
// 获取文件所在目录
const directory = fs.path.dirname(filePath);
// 使用鸿蒙系统API打开文件管理器
// 注意:鸿蒙系统没有完全等同于Windows的"/select"参数
// 这里提供两种可能的实现方式
// 方式1: 直接打开文件所在目录
this.launchFileManager(directory);
// 方式2: 尝试打开文件(系统会自动定位到文件所在目录)
// this.launchFile(filePath);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`打开文件夹失败: ${error}`);
}
}
// 启动文件管理器并定位到指定目录
private static launchFileManager(directoryPath: string) {
try {
// 创建意图,启动文件管理器
let intent = {
action: 'ohos.intent.action.VIEW',
uri: `file://${directoryPath}`,
type: 'resource/folder'
};
// 启动系统文件管理器
process.startAbility(intent);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`启动文件管理器失败: ${error}`);
// 备选方案:尝试直接打开文件
// this.launchFile(filePath);
}
}
// 直接打开文件(系统会自动定位到文件所在目录)
private static launchFile(filePath: string) {
try {
// 创建意图,启动文件关联应用
let intent = {
action: 'ohos.intent.action.VIEW',
uri: `file://${filePath}`,
type: this.getMimeType(filePath)
};
// 启动系统默认应用打开文件
process.startAbility(intent);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`打开文件失败: ${error}`);
}
}
// 根据文件扩展名获取MIME类型
private static getMimeType(filePath: string) {
const ext = fs.path.extname(filePath).toLowerCase();
switch (ext) {
case '.txt': return 'text/plain';
case '.jpg': case '.jpeg': return 'image/jpeg';
case '.png': return 'image/png';
case '.pdf': return 'application/pdf';
安卓操作系统
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void openDirectory(View view) {
// 替换为你实际的文件路径
String filePath = "/sdcard/Download/example.txt";
new OpenDirectoryTask().execute(filePath);
}
private class OpenDirectoryTask extends AsyncTask<String, Void, String> {
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
// 获取文件所在目录
String filePath = params[0];
return filePath.substring(0, filePath.lastIndexOf('/'));
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String directoryPath) {
// 创建Intent对象
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
// 将目录路径转换为Uri
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file://" + directoryPath);
// 设置Intent的数据和类型,表明要打开一个文件夹
intent.setDataAndType(uri, "resource/folder");
try {
// 启动活动以打开文件夹
startActivity(intent);
} catch (android.content.ActivityNotFoundException e) {
// 如果没有找到可以打开此Intent的应用程序,则会抛出此异常
// 在这里可以处理异常,例如提示用户没有找到文件管理器
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
苹果macos 系统
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading;
public class FileUtils
{
public static void OpenContainingFolder(string filePath)
{
try
{
// 确保路径有效
filePath = Path.GetFullPath(filePath);
if (!File.Exists(filePath))
{
Console.WriteLine("错误:文件不存在 - " + filePath);
return;
}
// 在新线程中执行,防止阻塞
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => {
try
{
// 创建进程启动信息
ProcessStartInfo startInfo = new ProcessStartInfo
{
FileName = "open",
Arguments = $"-R \"{filePath}\"", // -R 参数表示 Reveal,即打开目录并选中文件
UseShellExecute = false,
CreateNoWindow = true
};
// 启动进程
using (Process process = new Process())
{
process.StartInfo = startInfo;
process.Start();
process.WaitForExit();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"打开文件夹时出错: {ex.Message}");
}
});
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"处理文件路径时出错: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
LINUX 操作系统
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
// 线程函数参数结构体
typedef struct {
char *file_path;
} ThreadArgs;
// 验证文件路径是否有效
int is_valid_path(const char *path) {
if (path == NULL || *path == '\0') {
return 0;
}
struct stat st;
if (stat(path, &st) != 0) {
return 0; // 文件不存在
}
return 1;
}
// 在新线程中打开文件夹
void* open_folder_thread(void *arg) {
ThreadArgs *args = (ThreadArgs *)arg;
const char *file_path = args->file_path;
if (!is_valid_path(file_path)) {
fprintf(stderr, "错误:无效的文件路径:%s\n", file_path);
free(args);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// 复制文件路径
char *path_copy = strdup(file_path);
if (path_copy == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "内存分配失败\n");
free(args);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// 提取目录部分
char *last_slash = strrchr(path_copy, '/');
if (last_slash != NULL) {
*last_slash = '\0'; // 截断路径
} else {
strcpy(path_copy, "."); // 当前目录
}
// 构建命令
char command[1024];
snprintf(command, sizeof(command), "xdg-open \"%s\"", path_copy);
// 执行命令
int result = system(command);
if (result != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "执行命令失败,返回值:%d\n", result);
}
free(path_copy);
free(args);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// 异步打开文件所在目录
void open_containing_folder_async(const char *file_path) {
if (file_path == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "错误:文件路径为空\n");
return;
}
// 分配线程参数
ThreadArgs *args = (ThreadArgs *)malloc(sizeof(ThreadArgs));
if (args == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "内存分配失败\n");
return;
}
// 复制文件路径
args->file_path = strdup(file_path);
if (args->file_path == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "内存分配失败\n");
free(args);
return;
}
// 创建线程
pthread_t thread;
int result = pthread_create(&thread, NULL, open_folder_thread, args);
if (result != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "创建线程失败,错误码:%d\n", result);
free(args->file_path);
free(args);
} else {
// 分离线程,让系统自动回收资源
pthread_detach(thread);
}
}
int main() {
const char *file_path = "/home/user/Music/song.mp3";
open_containing_folder_async(file_path);
printf("已请求打开文件夹...\n");
sleep(1); // 等待线程启动
return 0;
}
QT跨平台语言
#include <QApplication>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QVBoxLayout>
#include <QFileDialog>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
QWidget window;
QVBoxLayout layout(&window);
QPushButton selectButton("选择文件");
QPushButton openButton("打开文件所在目录");
layout.addWidget(&selectButton);
layout.addWidget(&openButton);
QString selectedFilePath;
QObject::connect(&selectButton, &QPushButton::clicked, [&]() {
selectedFilePath = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(&window, "选择文件");
});
QObject::connect(&openButton, &QPushButton::clicked, [&]() {
if (!selectedFilePath.isEmpty()) {
FileUtils::openContainingFolder(selectedFilePath);
} else {
QMessageBox::warning(&window, "警告", "请先选择文件");
}
});
window.show();
return a.exec();
}
#include "main.moc"






























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








