binding:定义一个接口,映射对应的配置文件中的特定语句
public interface SysUserMapper {
SysUser getSysUser(Long userId);
}
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.yanlink.mapper.SysUserMapper">
<select id="getSysUser" resultType="SysUser">
select id,name,password,sex from sys_user where id=#{id}
</select>
>之后mybatis初始化配置binding的时候就可以发现配置是否正确,
并且用了Binding之后,我们操作数据库就如下这种方式了
SysUserMapper = session.getMapper(SysUserMapper.class);
SysUser = sysUserMapper.getSysUser();Binding组件的类关系
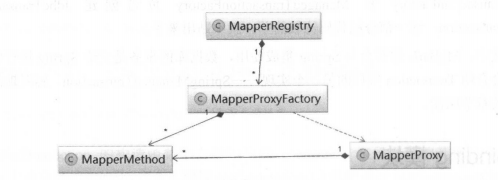
MapperRegistry
Mapper接口及其对象的代理工厂注册中心。
我们看看其类代码中的属性
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
}这里有两个属性:
一个是Configuration所有的mybatis配置都在这里
一个是Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>,class是接口对象,也就是上面例子的SysUserMapper.class
MapperProxyFactory:
是创建MapperProxy的工厂
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}MapperProxyFactory两个属性:
接口类对象: mapperInterface
缓存: key 是 mapperinterface 接口中 某方法对应的 Method 对象, value 是对应的 MapperMethod 对象
MapperProxyFactory.newInstance()创建了一个mapperInterface代理类,对应上例中的SysUserMapper代理对象,
MapperProxy
MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler,这里的动态代理和我们平常演示的哪种有点差别。
invoke调用都了MapperMethod中
MapperMethod
首先认识SqlCommand和MethodSignature两个类
1、SqlCommand
public static class SqlCommand {
private final String name;
private final SqlCommandType type;
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
final String methodName = method.getName();
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
}
}
}type是一个枚举类,所有类型如下
UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH;
name:是mapper的xml文件中的namespace属性+sql语句的id,如上例,name:com.yanlink.mapper.SysUserMapper.getSysUser
2、MethodSignature
public static class MethodSignature {
private final boolean returnsMany;
private final boolean returnsMap;
private final boolean returnsVoid;
private final boolean returnsCursor;
private final boolean returnsOptional;
private final Class<?> returnType;
private final String mapKey;
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);
if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;
} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();
} else {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
}
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
}MethodSignature做了两件比较重要的事情:
1、 确定了返回的类型
2、 确定了输入参数类型,及解析输入参数,生成map
ParamNameResolver是解析参数的
public class ParamNameResolver {
private static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
String name = null;
// 找到对应参数@Param注解,获取注解的值
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
}
// 所有的参数名称加到了names
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
// 每一个参数在map中有两个key,一个是@Param标注的名,一个是默认的GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX+索引名
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1);
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
}
在调用MethodSignature的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam,会获取一个参数的map,每个参数对应两个key,一个是@Param中标注的名称,一个是param+index。
我们最好使用@Param标注。
再来看MapperMethod中核心方法execute,我这里我只关注了SELECT,其他的逻辑一样的。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case SELECT:
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
return result;
}
}这里调用了sqlSession的selectOne,基本上就到了核心逻辑处理环节了。






















 308
308











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








