前言
最近在看Redis相关资料发现redis的存储类型中有一个是zset,zset很有意思,分为两种实现一种是基于压缩列表,另一种是基于跳表实现。
压缩列表
“Redis 为了节约内存空间使用,zset 和 hash 容器对象在元素个数较少的时候,采用压 缩列表 (ziplist) 进行存储。压缩列表是一块连续的内存空间,元素之间紧挨着存储,没有任 何冗余空隙。” 我理解这句话的意思是创建一个比较小的数组,虽然需要频繁扩容但是这样可以避免占用不必要的内存空间。
跳表
着重说一下跳表,跳表也是一种数据结构,但是这种数据结构并不是常见的。它是一种在链表上添加索引来达到高效查找。传统的链表在查找的时候只能从头节点开始一个一个向后遍历,如果链表足够长,那就意味着要将链表从头遍历一次。如果在链表的每个节点上添加一系列索引,如图,那么效率就会大大提升。redis中的Zset在数据量少的情况下使用的就是跳表的实现。
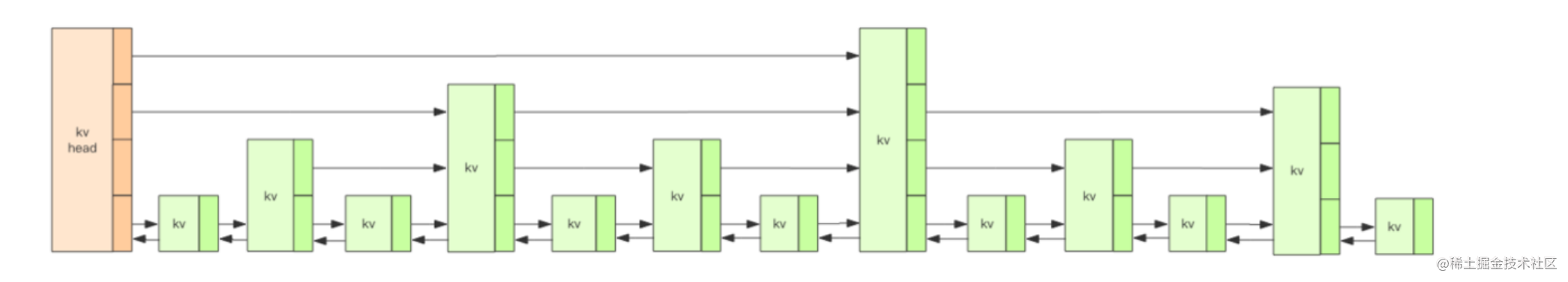

以上是一个比较直观的例子,结合最上面的图,每一个竖列为一个节点,最下面保存的是真实的数据,上面的为索引。这样的数据结果就是跳表(SkipList).
跳表的应用
在java中LinkedHashSet是一个有序的不重复的集合。LinkedHashSet是基于链表来实现的集合,下面使用java来实现一个基于跳表的set集合。
package com.cz.map;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @program: Reids
* @description: 使用跳表实现set有序集合
* @author: Cheng Zhi
* @create: 2023-04-24 10:45
**/
public class JefSkipSet<T> implements Set {
/**
* 计数器
*/
private AtomicInteger count;
/**
* 链表节点,每个节点提供向右向下指针
*/
private static class Node<T>{
Node rightNext;
Node downNext;
int key;
T value;
public Node(int key, T value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private Node head;
private int currentHightLevel = 0;
private int MAX_INDEX_LEVEL = 32;
private Random random = new Random();
public JefSkipSet() {
head = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
count = new AtomicInteger();
}
/**
* 查找节点
* @param key
* @return
*/
private Node find(int key) {
Node node = head;
while(node != null) {
if (node.rightNext == null ) {
node = node.downNext;
} else if (node.rightNext.key > key) { // 如果当前节点的右侧节点大于key,则需要下沉。
node = node.downNext;
} else if (node.rightNext.key < key) { // 如果当前节点的右侧节点小于key,则右移。
node = node.rightNext;
} else if (node.rightNext.key == key){ // 找到了直接返回
return node.rightNext;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 添加节点
* @param node
*/
private void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
Node findNode = find(node.key);
if (findNode != null) { // 如果找到直接替换值
findNode.value = node.value;
return;
}
Node tmp = head;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); // 保存所有下沉的节点,其中栈顶节点就是目标节点要插入的位置。目标节点插入到栈顶节点的后面。
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.rightNext == null) {
stack.add(tmp);
tmp = tmp.downNext;
} else if (tmp.rightNext.key > node.key) {
stack.add(tmp);
tmp = tmp.downNext;
} else if (tmp.rightNext.key < node.key) {
tmp = tmp.rightNext;
}
}
Node indexNode = null;
int level = 1;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node pop = stack.pop();
Node newNode = new Node(node.key, node.value);
newNode.downNext = indexNode;
indexNode = newNode; // 复制一份做为索引节点
if (pop.rightNext == null) {
pop.rightNext = newNode;
} else {
node.rightNext = pop.rightNext;
pop.rightNext = newNode;
}
if (level > MAX_INDEX_LEVEL) {
break;
}
// 随机产生索引节点,50%的概率会产生索引
double v = random.nextDouble();
if (v > 0.5) {
break;
}
level ++;
if (level > currentHightLevel) {
currentHightLevel = level;
// 新建head节点,保证head的索引一定是最高的
Node newHeadNode = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
newHeadNode.downNext = head;
head = newHeadNode;
stack.add(head);
}
}
count.getAndIncrement();
}
private void delete(int key) {
Node node = head;
while (node != null) {
if (node.rightNext == null) {
node = node.rightNext;
} else if (node.rightNext.key < key) {
node = node.rightNext;
} else if (node.rightNext.key > key) {
node = node.downNext;
} else if (node.rightNext.key == key) {
// 这里要做删除逻辑
node.rightNext = node.rightNext.rightNext;
node = node.downNext;
}
}
count.getAndDecrement();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return count.get();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return false;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return new Object[0];
}
/**
* 保证顺序的自增
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean add(Object o) {
// 为o计算hash
int key = o.hashCode();
Node node = new Node(key, o);
try {
add(node);
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int key = o.hashCode();
try {
delete(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
}
@Override
public boolean removeAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean retainAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean containsAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray(Object[] a) {
return new Object[0];
}
public void printStruct() {
Node teamNode=head;
int index=1;
Node last=teamNode;
while (last.downNext!=null){
last=last.downNext;
}
while (teamNode!=null) {
Node enumNode=teamNode.rightNext;
Node enumLast=last.rightNext;
System.out.printf("%-8s","head->");
while (enumLast!=null&&enumNode!=null) {
if(enumLast.key==enumNode.key)
{
System.out.printf("%-5s",enumLast.key+"->");
enumLast=enumLast.rightNext;
enumNode=enumNode.rightNext;
}
else{
enumLast=enumLast.rightNext;
System.out.printf("%-5s","");
}
}
teamNode=teamNode.downNext;
index++;
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JefSkipSet<Integer> jefSkipSet = new JefSkipSet<Integer>();
for (int i= 0; i< 50; i++) {
jefSkipSet.add("a");
}
jefSkipSet.printStruct();
System.out.println(jefSkipSet.size());
}
}
跳表的实现主要利用Node的两个指针,一个指向右边节点,一个指向下面节点。代码中使用的是随机生成索引的方式。跳表在java中的应用还有比如ConcurrentSkipListSet和ConcurrentSkipListMap。因为相对于树形结构的数据结构而言,跳表的实现还是相对简单的。这也是redis使用跳表而不使用红黑树的原因。






















 1663
1663











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








