1.File类
File类可以在程序中 操作文件和目录。File类是通过建立File类对象,在调用File类的对象来进行相关操作的。
示例:
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("f:/我的歌声里.txt");
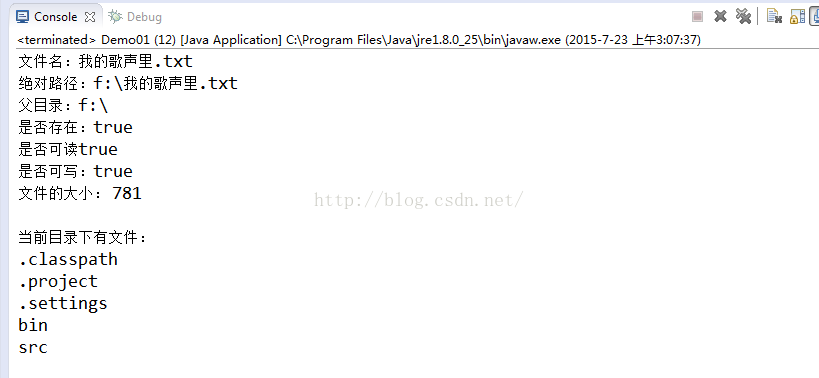
//访问文件名相关
String name = f.getName();
System.out.println("文件名:" + name);
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("绝对路径:" + absolutePath);
String parent = f.getParent();
System.out.println("父目录:" + parent);
//检测相关
System.out.println("是否存在:" + f.exists());
System.out.println("是否可读" + f.canRead());
System.out.println("是否可写:" + f.canWrite());
//获取文件信息
System.out.println("文件的大小: " + f.length());
//以当前路径创建File对象
File file = new File(".");
String[] list = file.list();
//遍历目录下的文件
System.out.println();
System.out.println("当前目录下有文件:");
for(String name1:list){
System.out.println(name1);
}
}
}运行结果:
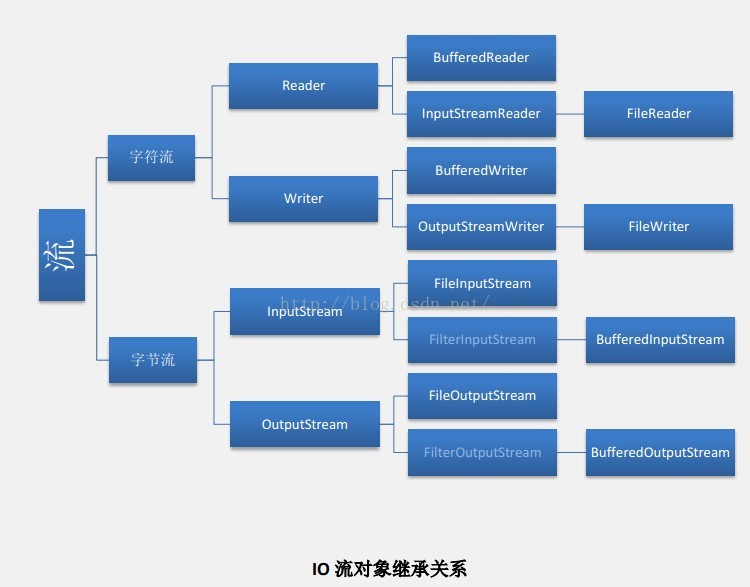
2.IO流的分类
按照方向:输入流和输出流
按照流的大小:字节流和字符流
按照流的角色:节点流和处理流
流的类关系图如下:
3.字节流和字符流
字节流:FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream
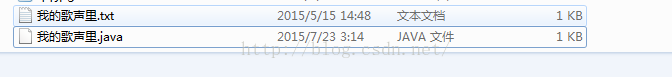
示例:把文件复制成另外的文件
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 需求把文件“我的歌声里.txt” 复制并改文件名为 “我的歌声里.java”
*
*/
//创建输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("f:/我的歌声里.txt"));
//创建输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File("f:/我的歌声里.java"));
//创建接收字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//循环输入输出
while((len = is.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
os.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
//关闭资源
os.close();
is.close();
}
}运行结果:
字符流:FileReader和FileWriter
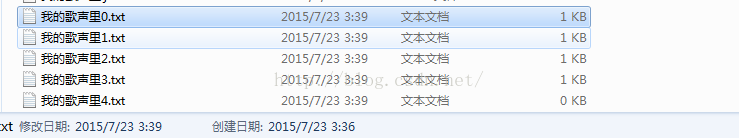
示例:切割文件
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader r = null;
FileWriter w = null;
try {
int count = 0;//定义一个标记
int flag = 0;//文件名标记
r = new FileReader("f:/我的歌声里.txt");
w = new FileWriter("f:/我的歌声里" + flag +".txt");
char[] chars = new char[10];
int len = 0;
while((len = r.read(chars)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(chars, 0, len));
w.write(chars, 0, len);
w.flush();
count++;
//定义切割的条件
if(count >10 ){
flag++;
w = new FileWriter("f:/我的歌声里" + flag +".txt");
count = 0;
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
w.close();
r.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行结果
4.转换流
转换流:把字节流转换为字符流,一次来实现性能优化
InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter
示例:
public class Demo04 {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//键盘输入到文件
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("f:/我的文件.txt"));
int count = 0;
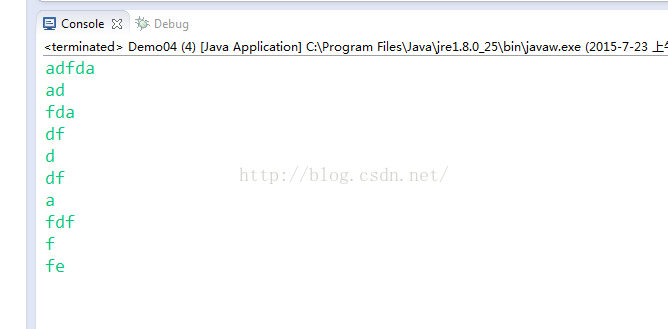
while((len = isr.read(chars)) != -1){
osw.write(chars, 0, len);
osw.flush();
count++;
if(count == 10){
break;
}
}
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}运行结果:
5.缓冲流
把流读到缓冲区,然后再一次读到内存中来,以此来提高性能
BuffererInputStream 和BufferedOutputStream
BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//读取并复制保存图片
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("f:/qq.jpg")));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("f:/qqq.png")));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(line);
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}运行结果:
6.对象序列化
对象流:ObjectInStream和 ObjectOutputStream
Serialiazable关键字:标记接口可序列化
transient关键字:标记瞬态实例变量
示例:
public class Demo06 {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
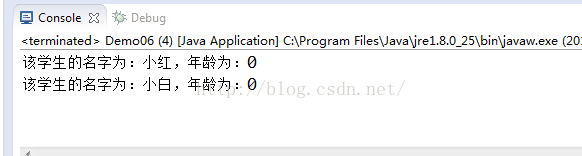
Student s1 = new Student("小红", 19);
Student s2 = new Student("小白", 18);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("f:/序列化.txt"));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.writeObject(s2);
s2.setName("小白白");
oos.writeObject(s2);//更改变量的属性,即使重新序列化也不会改变原属性值
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("f:/序列化.txt"));
Student rs1 = (Student) ois.readObject();
Student rs2 = (Student) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(rs1);
System.out.println(rs2);
}
}
class Student implements Serializable{
private String name;//学生姓名
private transient int age;//年龄设置为瞬时变量,将不被序列化
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "该学生的名字为:" + name + ",年龄为:" + age;
}
}
























 569
569

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








