Espresso是google出的一款UI单元测试的框架。
首先配置下gradle:
defaultConfig中配置testImstrumentationRunner:
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"dependencies里面配置如下:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.0.1'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:runner:0.4'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:rules:0.4'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.1'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.uiautomator:uiautomator-v18:2.1.2'
}
build variants需要配置成 Android Instrumentation Tests模式:
先来看看ui测试布局activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="sayHello"
android:text="button test!"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edittext"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>MainActivity中注册click点击事件:
public void sayHello(View view) {
mTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview);
mEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edittext);
mTextView.setText("Hello, " + mEditText.getText().toString() + "!");
}这里我们在androidTest包下面建立相关单元测试类MainActivityInstrumentationTest:
package com.example.hongentao.junitdemo;
import android.support.test.rule.ActivityTestRule;
import android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnit4;
import android.test.suitebuilder.annotation.LargeTest;
import org.junit.Rule;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import static android.support.test.espresso.Espresso.onView;
import static android.support.test.espresso.action.ViewActions.click;
import static android.support.test.espresso.action.ViewActions.closeSoftKeyboard;
import static android.support.test.espresso.action.ViewActions.typeText;
import static android.support.test.espresso.assertion.ViewAssertions.matches;
import static android.support.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withId;
import static android.support.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withText;
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
@LargeTest
/**
* Created by hongentao on 16/2/26.
*/
public class MainActivityInstrumentationTest {
private static final String STRING_TO_BE_TYPED = "Peter is greate!!! we will be fine! and something will be ok!";
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule<MainActivity> mActivityRule = new ActivityTestRule<>(
MainActivity.class);
@Test
public void OnclickJunitTest() {
onView(withId(R.id.edittext)).perform(typeText(STRING_TO_BE_TYPED), closeSoftKeyboard()); //line 1
onView(withId(R.id.button)).perform(click()); //line 2
String expectedText = "Hello, " + STRING_TO_BE_TYPED + "!";
onView(withId(R.id.textview)).check(matches(withText(expectedText))); //line 3
}
}楼上注解的含义:
@Test: 标识一个测试方法。一个测试类中可以有多个测试方法,每个测试方法需要用一个@Test注解来标识。
@Rule: 简单来说,是为各个测试方法提供一些支持。具体来说,比如我需要测试一个Activity,那么我可以在@Rule注解下面采用一个ActivityTestRule,该类提供了对相应Activity的功能测试的支持。该类可以在@Before和@Test标识的方法执行之前确保将Activity运行起来,并且在所有@Test和@After方法执行结束之后将Activity杀死。在整个测试期间,每个测试方法都可以直接对相应Activity进行修改和访问。
我们来分析下OnclickJunitTest()方法具体的含义:
@Test
public void OnclickJunitTest() {
onView(withId(R.id.edittext)).perform(typeText(STRING_TO_BE_TYPED), closeSoftKeyboard()); //line 1
onView(withId(R.id.button)).perform(click()); //line 2
String expectedText = "Hello, " + STRING_TO_BE_TYPED + "!";
onView(withId(R.id.textview)).check(matches(withText(expectedText))); //line 3
}line1代码讲解:
onView(withId(R.id.edittext))—>找到id为editText的View.
perform(typeText(text), closeSoftKeyboard)—>我们来看下源码:
/**
* Performs the given action(s) on the view selected by the current view matcher. If more than one
* action is provided, actions are executed in the order provided with precondition checks running
* prior to each action.
*
* @param viewActions one or more actions to execute.
* @return this interaction for further perform/verification calls.
*/
public ViewInteraction perform(final ViewAction... viewActions) {
checkNotNull(viewActions);
for (ViewAction action : viewActions) {
doPerform(action);
}
return this;
}根据注释大概可以看出:根据当前被匹配的View,按照相应的ViewAction按照顺序依次执行。
所以上面 perform(typeText(text), closeSoftKeyboard)的含义为:将text值赋给editText(typeText是将赋值行为转为viewAction),然后关闭closeSoftKeyboard。
看下closeSoftKeyboard的源码:
}
/**
* Returns an action that closes soft keyboard. If the keyboard is already closed, it is a no-op.
*/
public static ViewAction closeSoftKeyboard() {
return actionWithAssertions(new CloseKeyboardAction());
}通过注释以及返回值一目了然:
line2代码讲解:
onView(withId(R.id.button)).perform(click())—找到id为button的按钮,执行click点击事件:
line3代码讲解:
onView(withId(R.id.textview)).check(matches(withText(expectedText)));—-找到id为textview的TextView,检查他的值与期盼的值作比较。
来看看怎么运行单元测试代码:
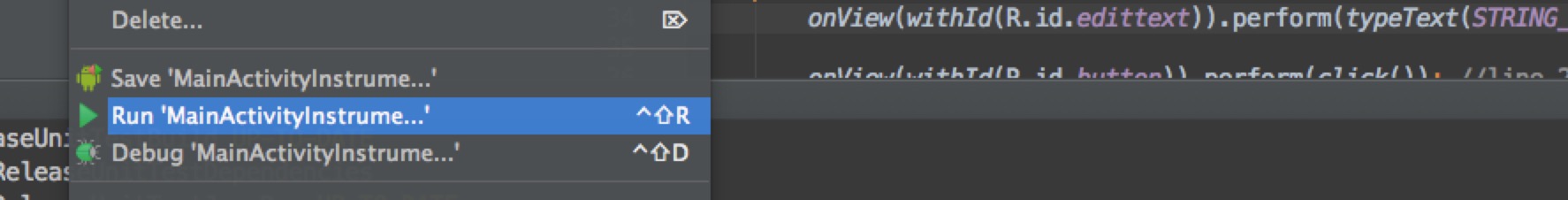
在相应的测试类上点击右键 —run-MainActivityInstrume…如下图所示:
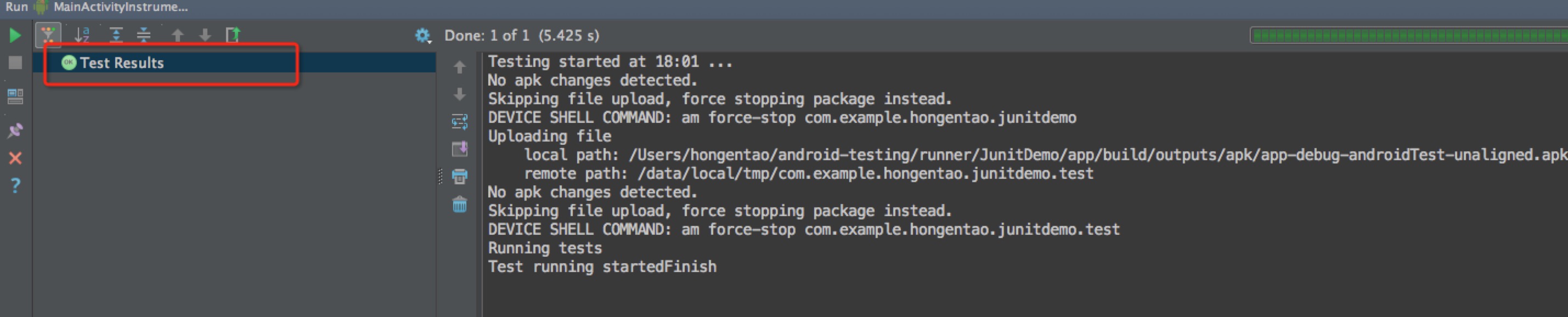
来看看相应的单元测试结果:
好了这期就介绍到这里。






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








