Bloom索引概念介绍:
一个典型的bloom过滤可以快速的检查一个集合的元素。比如过滤器是有M个bit位的数组,初始化的时候都是用0填充的,如下图

现在,让我们更好地了解bloom过滤器的算法。如前所述,它是一个m位的数组。而且我们需要k个哈希函数。为了确定一个元素是否存在,该元素(列中的数据)将传递给哈希函数。假设这里使用两个哈希函数计算的值存储一个元素“ avi”。当单词“ avi”传递给第一个哈希函数时,假设计算的值为4,第二个计算的值为5。这里4和5都用1填充,因此,现在的位数组如下所示:
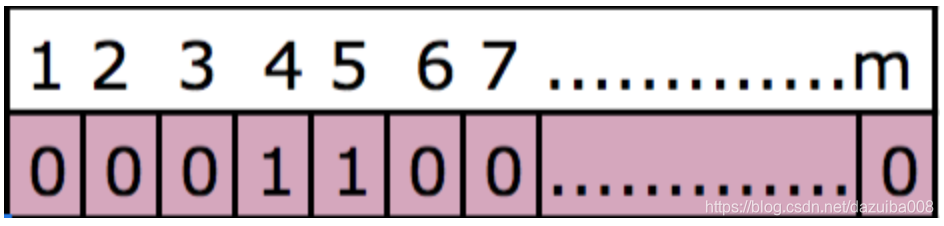
最初,所有位都为0。一旦在bloom过滤器中存储了元素“ avi”,它将第4位和第5位设置为1。现在,存储单词“ percona”。该单词再次传递给两个哈希函数,并假定第一个哈希函数计算的值为5,第二个哈希函数计算的值为6。由于之前的bit位等于5的已经是设置为1,这里不需要再修改。因此bit位数组现在如下所示:
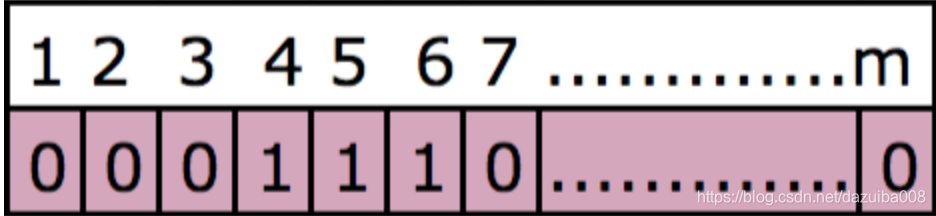
那么比如现在有一个查询,查询元素值为avi,通过哈希函数计算后4和5的值为1,所以元素avi是存在的。
bloom过滤的一些冲突
比如我们查询一个元素ton,这个元素通过哈希函数计算的两个值是4和6,虽然我们bit位数组4和6设置的是1,但是实际上并不存在ton这个元素。
正如上面介绍的,哈希函数越少,发生冲突的机会就越多。哈希函数越多,发生碰撞的机会就越少。但是,如果我们有k个哈希函数,则验证成员资格所需的时间也会随着k上升而上升。
对于DBMS,实际上我们为每个索引行构建了N个单独的过滤器。通常,索引中包含多个字段,这些字段的值构成每一行的元素集。
我们可以在索引大小和误报的概率之间找到一个权衡。
bloom索引结构

现在,我们已经了解了Bloom过滤器,知道Bloom索引使用Bloom过滤器。如果您的表中的列很多,并且在此表上使用列的组合也很多所以进行查询时,则可能需要许多索引。维护如此多的索引不仅对于数据库而言代价是昂贵的,而且在处理较大的数据集时也是性能的杀手。
因此,在所有涉及到的列上创建一个Bloom索引,则将为每个列计算一个哈希,并将其合并到每个行/记录的指定长度的单个索引条目中。创建Bloom索引时,可以指定签名的总大小(«length»),以及为索引中包含的每个单独字段设置的位数(«col1»—«col32»):
create index on ... using bloom(...) with (length=..., col1=..., col2=..., ...);
length最好设置为16的倍数。默认为80。最大为4096。每列默认位数为2。可以指定最多4095位。
举个例子:
CREATE INDEX bloom_idx_table ON tablename USING bloom (id,dept_id,zipcode)
WITH (length=80, col1=2, col2=2, col3=4);
当我们指定长度= 80且col1 = 2,col2 = 2,col3 = 4时,理论上,每行都会创建一个长度为80位的位数组。由于col1设置为2位,因此col1(column1)内部的数据将传递给两个哈希函数。假设这两个哈希函数生成的值分别为20和40。由于长度指定为80位,因此第20位和第40位的位会设置为1。现在col3中的数据将传递到四个哈希函数,并且假设生成的值为2、4、9、10。因此,将80位中的4位(2、4、9、10)设置为1。
这里会有许多空位,但是它可以使得每行的位之间具有更大的随机性。当使用签名函数,签名存储在索引页中,指向实际数据的指针也存储在索引页中。当一个查询使用=操作时,会使用bloom索引,该列已设置的多个哈希函数将生成多个哈希值。假设col3为4-则为2、4、9、10。索引数据是逐行提取的,并搜索这些行中的那些位是否设置为1。
最终,一定数量的行将所有这些位都设置为1。长度和每列的位越大,随机性越多,误报也越少。但是长度越大,索引的大小就越大。
bloom索引例子:
创建测试表,插入数据
CREATE TABLE bar (id int, dept int, id2 int, id3 int, id4 int, id5 int,id6 int,id7 int,details text, zipcode int);
INSERT INTO bar SELECT (random() * 1000000)::int, (random() * 1000000)::int,
(random() * 1000000)::int,(random() * 1000000)::int,(random() * 1000000)::int,(random() * 1000000)::int,
(random() * 1000000)::int,(random() * 1000000)::int,md5(g::text), floor(random()* (20000-9999 + 1) + 9999)
from generate_series(1,100*1e6) g;
创建b-tree索引
hank=# CREATE INDEX idx_btree_bar ON bar (id, dept, id2,id3,id4,id5,id6,zipcode);
CREATE INDEX
hank=# \di+ idx_btree_bar
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Table | Size | Description
--------+---------------+-------+-------+-------+---------+-------------
hank | idx_btree_bar | index | hank | bar | 4743 MB |
(1 row)
查看使用btree的执行计划
hank=# EXPLAIN ANALYZE select * from bar where id4 = 295294 and zipcode = 13266;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Gather (cost=1000.00..1860568.15 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=7044.680..7046.395 rows=0 loops=1)
Workers Planned: 2
Workers Launched: 2
-> Parallel Seq Scan on bar (cost=0.00..1859568.05 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=7041.002..7041.002 rows=0 loops=3)
Filter: ((id4 = 295294) AND (zipcode = 13266))
Rows Removed by Filter: 33333333
Planning Time: 0.953 ms
Execution Time: 7046.426 ms
(8 rows)
hank=# EXPLAIN ANALYZE select * from bar where id5 = 281326 and id6 = 894198;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Gather (cost=1000.00..1860568.15 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=6593.022..6594.757 rows=0 loops=1)
Workers Planned: 2
Workers Launched: 2
-> Parallel Seq Scan on bar (cost=0.00..1859568.05 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=6589.518..6589.518 rows=0 loops=3)
Filter: ((id5 = 281326) AND (id6 = 894198))
Rows Removed by Filter: 33333333
Planning Time: 0.107 ms
Execution Time: 6594.788 ms
(8 rows)
创建bloom索引,大小明显比btree小很多
hank=# CREATE INDEX idx_bloom_bar ON bar USING bloom(id, dept, id2, id3, id4, id5, id6, zipcode)
WITH (length=64, col1=4, col2=4, col3=4, col4=4, col5=4, col6=4, col7=4, col8=4);
CREATE INDEX
hank=# \di+ idx_bloom_bar
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Table | Size | Description
--------+---------------+-------+-------+-------+---------+-------------
hank | idx_bloom_bar | index | hank | bar | 1342 MB |
(1 row)
查看使用bloom索引的执行计划,效率比btree要高。
hank=# EXPLAIN ANALYZE select * from bar where id4 = 295294 and zipcode = 13266;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------
Bitmap Heap Scan on bar (cost=1687292.00..1687296.02 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=1703.668..1703.668 rows=0 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: ((id4 = 295294) AND (zipcode = 13266))
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 2985661
Heap Blocks: exact=58499 lossy=36109
-> Bitmap Index Scan on idx_bloom_bar (cost=0.00..1687292.00 rows=1 width=0) (actual time=937.965..937.965 rows=98381
loops=1)
Index Cond: ((id4 = 295294) AND (zipcode = 13266))
Planning Time: 0.152 ms
Execution Time: 1703.714 ms
(8 rows)
hank=# EXPLAIN ANALYZE select * from bar where id5 = 281326 and id6 = 894198;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------
Bitmap Heap Scan on bar (cost=1687292.00..1687296.02 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=1608.545..1608.545 rows=0 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: ((id5 = 281326) AND (id6 = 894198))
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 2983795
Heap Blocks: exact=59211 lossy=36076
-> Bitmap Index Scan on idx_bloom_bar (cost=0.00..1687292.00 rows=1 width=0) (actual time=534.797..534.797 rows=99218
loops=1)
Index Cond: ((id5 = 281326) AND (id6 = 894198))
Planning Time: 0.147 ms
Execution Time: 1608.593 ms
(8 rows)
如果只是固定的两列,那么创建这两列的组合索引会比bloom更好,如果是多列,而且查询条件可能是任意列,那么bloom更适合一些。
误报:
就像最开始介绍的,可能会有误报的情况,为了减少误报,我们一般可以增加签名长度length,和每列的bit位数,但是这样会增加索引的大小。如果增加了,还是没有减少误报,可以维持长度不变。
使用时注意的点:
- 通过上面的测试中,我们已经看到Bloom索引的性能比btree索引更好。但是,实际上,如果我们在两列之上创建了一个btree索引,则使用btree索引的查询执行速度将比使用Bloom索引的查询执行得快得多。该索引不会替换btree索引,但是我们可以用单个Bloom索引替换大块索引。
- 就像哈希索引一样,bloom索引仅适用于相等运算符。
- bloom长度以及列的bit位设置,可以参考http://blog.coelho.net/database/2016/12/11/postgresql-bloom-index.html
操作类:
比如以下一张表有字符类型,默认不支持bloom索引
hank=# \d flights_bi
Table "hank.flights_bi"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
--------------------+--------------------------+-----------+----------+---------
airport_code | character(3) | | |
airport_coord | point | | |
airport_utc_offset | interval | | |
flight_no | character(6) | | |
flight_type | text | | |
scheduled_time | timestamp with time zone | | |
actual_time | timestamp with time zone | | |
aircraft_code | character(3) | | |
seat_no | character varying(4) | | |
fare_conditions | character varying(10) | | |
passenger_id | character varying(20) | | |
passenger_name | text | | |
create index flights_bi_bloom on flights_bi,创建索引会报错
using bloom(airport_code, airport_utc_offset, flight_no, flight_type, aircraft_code, seat_no, fare_conditions, passenger_id, passenger_name)
with (length=96, col1=7, col2=7, col3=7, col4=7, col5=7, col6=7, col7=7, col8=7, col9=7);
ERROR: data type character has no default operator class for access method "bloom"
HINT: You must specify an operator class for the index or define a default operator class for the data type.
查看支持的操作类别
select opcname, opcintype::regtype
from pg_opclass
where opcmethod = (select oid from pg_am where amname = 'bloom')
order by opcintype::regtype::text;
为其他数据类型创建类似的类也很容易。 Bloom访问方法的运算符类必须只包含一个运算符-等式-包含一个辅助的哈希函数。查找任意类型所需的运算符和函数的最简单方法是查看系统目录中的“哈希”方法的运算符类:
select distinct
opc.opcintype::regtype::text,
amop.amopopr::regoperator,
ampr.amproc
from pg_am am, pg_opclass opc, pg_amop amop, pg_amproc ampr
where am.amname = 'hash'
and opc.opcmethod = am.oid
and amop.amopfamily = opc.opcfamily
and amop.amoplefttype = opc.opcintype
and amop.amoprighttype = opc.opcintype
and ampr.amprocfamily = opc.opcfamily
and ampr.amproclefttype = opc.opcintype
order by opc.opcintype::regtype::text;
opcintype | amopopr | amproc
-----------+----------------------+--------------
abstime | =(abstime,abstime) | hashint4
aclitem | =(aclitem,aclitem) | hash_aclitem
anyarray | =(anyarray,anyarray) | hash_array
anyenum | =(anyenum,anyenum) | hashenum
anyrange | =(anyrange,anyrange) | hash_range
...
创建相应类型的操作类
CREATE OPERATOR CLASS character_ops
DEFAULT FOR TYPE character USING bloom AS
OPERATOR 1 =(character,character),
FUNCTION 1 hashbpchar;
CREATE OPERATOR CLASS interval_ops
DEFAULT FOR TYPE interval USING bloom AS
OPERATOR 1 =(interval,interval),
FUNCTION 1 interval_hash;
没有为点(«point»类型)定义哈希函数,因此,我们无法在此类字段上构建Bloom索引(我们也无法在此类型字段上执行哈希联接一样)
再次创建bloom索引,可以成功创建:
create index flights_bi_bloom on flights_bi
using bloom(airport_code, airport_utc_offset, flight_no, flight_type, aircraft_code, seat_no, fare_conditions, passenger_id, passenger_name)
with (length=96, col1=7, col2=7, col3=7, col4=7, col5=7, col6=7, col7=7, col8=7, col9=7);
CREATE INDEX
索引使用示例:
demo=# explain(costs off,analyze)
demo-# select * from flights_bi where passenger_name='MIROSLAV SIDOROV';
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on flights_bi (actual time=538.068..547.563 rows=2 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: (passenger_name = 'MIROSLAV SIDOROV'::text)
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 38505
Heap Blocks: exact=21615
-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_bi_bloom (actual time=494.661..494.661 rows=38507 loops=1)
Index Cond: (passenger_name = 'MIROSLAV SIDOROV'::text)
Planning Time: 1.836 ms
Execution Time: 547.865 ms
(8 rows)
demo=# explain(costs off,analyze)
demo-# select * from flights_bi where passenger_name='MARFA SOLOVEVA';
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on flights_bi (actual time=2427.699..2440.877 rows=2 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: (passenger_name = 'MARFA SOLOVEVA'::text)
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 3944432
Heap Blocks: exact=45113 lossy=67335
-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_bi_bloom (actual time=647.666..647.667 rows=212177 loops=1)
Index Cond: (passenger_name = 'MARFA SOLOVEVA'::text)
Planning Time: 0.122 ms
Execution Time: 2441.853 ms
(8 rows)
demo=# explain(costs off,analyze) select * from flights_bi where passenger_id='5864 006033';
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on flights_bi (actual time=3972.010..4455.119 rows=2 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: ((passenger_id)::text = '5864 006033'::text)
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 9611533
Heap Blocks: exact=49039 lossy=165728
-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_bi_bloom (actual time=679.561..679.562 rows=425937 loops=1)
Index Cond: ((passenger_id)::text = '5864 006033'::text)
Planning Time: 0.149 ms
Execution Time: 4457.026 ms
(8 rows)
demo=# explain(costs off,analyze)
demo-# select * from flights_bi where passenger_id='2461 559238';
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on flights_bi (actual time=429.633..430.485 rows=2 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: ((passenger_id)::text = '2461 559238'::text)
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 30644
Heap Blocks: exact=27407
-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_bi_bloom (actual time=376.100..376.100 rows=30646 loops=1)
Index Cond: ((passenger_id)::text = '2461 559238'::text)
Planning Time: 0.116 ms
Execution Time: 430.524 ms
(8 rows)
demo=# explain(costs off,analyze)
demo-# select * from flights_bi
demo-# where passenger_name='MIROSLAV SIDOROV'
demo-# and passenger_id='5864 006033';
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on flights_bi (actual time=499.568..499.683 rows=2 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: (((passenger_id)::text = '5864 006033'::text) AND (passenger_name = 'MIROSLAV SIDOROV'::text))
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 357
Heap Blocks: exact=354
-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_bi_bloom (actual time=498.976..498.976 rows=359 loops=1)
Index Cond: (((passenger_id)::text = '5864 006033'::text) AND (passenger_name = 'MIROSLAV SIDOROV'::text))
Planning Time: 0.147 ms
Execution Time: 499.721 ms
(8 rows)
可以看到同一字段不同的值,效率是不同的,可以看到Rows Removed by Index Recheck越多的,查询会越慢。
BRIN和Bloom比较:
- 这两种类型在使用区域上有点类似,适合大表,数据量多,需要通过不同的字段进行查询,但是搜索精度不高。
- BRIN索引更紧凑(例如,在我们的示例中,最大可达几十兆字节),并且可以支持按范围进行搜索,并且与文件中数据的物理排序有关,因此存在很大的局限性。bloom索引更大(数百兆字节),没有限制,可以使用合适的哈希函数。
属性
支持多列,并且在单列创建bloom索引没有任何意义
amname | name | pg_indexam_has_property
--------+---------------+-------------------------
bloom | can_order | f
bloom | can_unique | f
bloom | can_multi_col | t
bloom | can_exclude | f
只支持位图扫描
name | pg_index_has_property
---------------+-----------------------
clusterable | f
index_scan | f
bitmap_scan | t
backward_scan | f
name | pg_index_column_has_property
--------------------+------------------------------
asc | f
desc | f
nulls_first | f
nulls_last | f
orderable | f
distance_orderable | f
returnable | f
search_array | f
search_nulls | f
最后:
当我们有一个表存有大量数据和大量列时,Bloom索引非常有用,因为在表中创建大量索引,尤其是在OLAP环境中,创建索引也会很耗时,插入效率会很低。这个时候您可以考虑测试单个bloom索引的效率,查看是否可以避免创建大量的单独索引或复合索引,这些索引可能占用额外的磁盘空间而又不会提高性能。








 本文深入探讨了Bloom索引的概念及其在数据库管理系统(DBMS)中的应用,详细讲解了Bloom过滤器的工作原理,如何利用Bloom索引提高查询效率,特别是在面对大量数据和多列查询时的优势。
本文深入探讨了Bloom索引的概念及其在数据库管理系统(DBMS)中的应用,详细讲解了Bloom过滤器的工作原理,如何利用Bloom索引提高查询效率,特别是在面对大量数据和多列查询时的优势。
















 1900
1900

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








