习速度。当网络的一个或多个可调参数(权值或阈值)对任何一个输出都有影响时,这样的网络称为全局逼近网络。
由于对于每次输入,网络上的每一个权值都要调整,从而导致全局逼近网络的学习速度很慢,比如BP网络。如果对于
输入空间的某个局部区域只有少数几个连接权值影响输出,则该网络称为局部逼近网络,比如RBF网络。接下来重点
先介绍RBF网络的原理,然后给出其实现。先看如下图
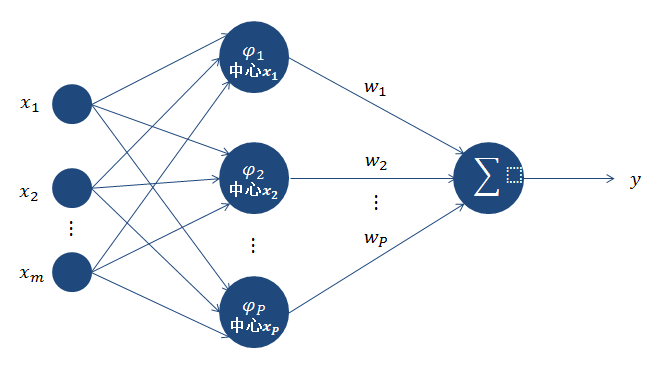


正则化的RBF网络参考这里。下面是网上找的一个比较好的Python的RBF网络实现。
代码:
- from scipy import *
- from scipy.linalg import norm, pinv
-
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
-
- class RBF:
-
- def __init__(self, indim, numCenters, outdim):
- self.indim = indim
- self.outdim = outdim
- self.numCenters = numCenters
- self.centers = [random.uniform(-1, 1, indim) for i in xrange(numCenters)]
- self.beta = 8
- self.W = random.random((self.numCenters, self.outdim))
-
- def _basisfunc(self, c, d):
- assert len(d) == self.indim
- return exp(-self.beta * norm(c-d)**2)
-
- def _calcAct(self, X):
-
- G = zeros((X.shape[0], self.numCenters), float)
- for ci, c in enumerate(self.centers):
- for xi, x in enumerate(X):
- G[xi,ci] = self._basisfunc(c, x)
- return G
-
- def train(self, X, Y):
-
-
-
-
- rnd_idx = random.permutation(X.shape[0])[:self.numCenters]
- self.centers = [X[i,:] for i in rnd_idx]
-
- print "center", self.centers
-
- G = self._calcAct(X)
- print G
-
-
- self.W = dot(pinv(G), Y)
-
- def test(self, X):
-
-
- G = self._calcAct(X)
- Y = dot(G, self.W)
- return Y
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- n = 100
- x = mgrid[-1:1:complex(0,n)].reshape(n, 1)
-
- y = sin(3*(x+0.5)**3 - 1)
-
-
-
- rbf = RBF(1, 10, 1)
- rbf.train(x, y)
- z = rbf.test(x)
-
-
- plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
- plt.plot(x, y, 'k-')
-
-
- plt.plot(x, z, 'r-', linewidth=2)
-
-
- plt.plot(rbf.centers, zeros(rbf.numCenters), 'gs')
-
- for c in rbf.centers:
-
- cx = arange(c-0.7, c+0.7, 0.01)
- cy = [rbf._basisfunc(array([cx_]), array([c])) for cx_ in cx]
- plt.plot(cx, cy, '-', color='gray', linewidth=0.2)
-
- plt.xlim(-1.2, 1.2)
- plt.show()
-
最后提供Github上的一个C++实现的RBF,供日后参考。
 2637
2637

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?


