1. 概述: 最大堆(大顶堆)
一句话 heap:一种数据结构,完全二叉树(若二叉树高 h,则除过最底层 h 层,其他 1~h-1 层都是满的;并且最底层从左到右不能有空隙)。有最大堆和最小堆两种,最大堆即根节点的键值比其他所有节点键值都大;最小堆即根节点的键值比其他所有节点键值都小。在实现上,它没有选择一般的二叉树数据结构(即一个节点包含指向两个孩子的指针),使用的是数组;heap 最为常用的操作是上溯和下溯,在“维持堆”和“堆排序”中经常用到。
最小堆和最大堆思路如出一辙,只讨论最大堆。对于一个大顶堆,如下结论成立:
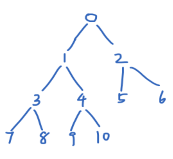
- 数组从 index为 1 的地方开始存放第一个节点:
- 第
i个节点的父节点的 index 为 (i/2) - 第
i个节点的 left 孩子节点的 index 为 (2* i) - 第
i个节点的 right 孩子节点的 index 为 (2* i + 1)
这里根节点就规定是[1],那么最后一个 非叶子 节点就是[last/2]
- 当然,从 index为 0 的地方开始存放第一个节点,稍微复杂一点,我们下面的代码就是使用了这个。
- 第
i个节点的父节点的 index 为( i-1 ) / 2 - 第
i个节点的 left 孩子节点的 index 为2* i + 1 - 第
i个节点的 right 孩子节点的 index 为2* i + 2
根节点就是[0],那么最后一个 非叶子 节点就是[ ( last - 1 ) / 2 ] (也就是最后一个节点的父亲)
2. 实现
maxheap.h
#ifndef __MAX_HEAP
#define __MAX_HEAP
void shiftDown(int *a, int pos, int last);
void shiftDown2(int *a, int pos, int last);
void ShiftUp(int *a, int pos);
//============================================================
void maxHeapBuild(int *a, int size);
void maxHeapSort(int *a, int size);
//============================================================
#define PRIOR_QUEUE_BASE_SIZE 50
#define PRIOR_QUEUE_MAX_SIZE 100
#define PRIOR_QUEUE_INCREASE_SIZE 10
typedef struct
{
int *a;
int totalSize;
int validSize; //validSize 其实也是第一个空闲的位置
//mutex SHOULD be used
}PriorQueue;
void createPriorQueue(PriorQueue **ppPriorQueue);
void destroyPriorQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue);
void enPriorQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue,int prior);
int dePriorQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue);
void showQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue);
#endifmaxheap.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "maxHeap.h"
//一般在操作堆顶后,用此做 shiftDown 调整
//eg.1 删除堆顶: 交换堆顶和最后元素(其实根本不用交换,直接用last覆盖堆顶),then size--
//eg.2 新添一个节点在pos位置(或者更改堆顶点),如果这个pos节点
// 比较小(和左右子节点比),那么此节点会一直 沉到它应该呆的位置
void shiftDown(int *a, int pos, int last) //last 是最后一个节点的 index
{
int left = 2*pos+1; //pos 的左孩子的 index
int right = 2*pos+2; //pos 的右孩子的 index
int max = pos;
int tmp;
if(pos <= (last-1)/2) //叶子节点没必要调整
{
if(left <= last && a[left] > a[max])
max = left;
if(right <= last && a[right] > a[max])
max = right; //now,max已经是父子三人中最大的那个元素的 index 了
if(max != pos) //max 是某个子节点的 index
{
//swap(a[pos], a[max]);
tmp = a[pos];
a[pos] = a[max];
a[max] = tmp;
shiftDown(a, max, last);
}
}
}
//heapShiftDown 之非递归实现(迭代实现)
void shiftDown2(int *a, int pos, int last)
{
int left; //pos 的左孩子的 index
int right; //pos 的右孩子的 index
int max = pos; //先假设 pos 最大
int tmp;
int flag = 0; //为1表示已经满足最大堆约束
while(pos <= (last-1)/2 && (flag==0)) //叶子节点没必要调整
{
left = 2*pos+1; //pos 的左孩子的 index
right = 2*pos+2; //pos 的右孩子的 index
//max = pos; //先假设 pos 最大
if(left <= last && a[left] > a[max])
max = left;
if(right <= last && a[right] > a[max])
max = right; //now,max已经是父子三人中最大的那个元素的 index 了
if(max != pos) //max 是某个子节点的 index
{
//swap(a[pos], a[max]);
tmp = a[pos];
a[pos] = a[max];
a[max] = tmp;
//
pos = max;
}
else
{
flag = 1;
}
}
}
//当改动了heap的最后一个元素的时候需要调用此 ShiftUp 调整一下
void ShiftUp(int *a, int pos)
{
int flag = 0;
int tmp;
while((pos > 0) && (flag==0)) //如果已经是堆顶了(pos == 0),就不要再调整了
{
if(a[pos] > a[(pos-1)/2])
{
//swap(a[pos], a[(pos-1)/2]);
tmp = a[pos];
a[pos] = a[(pos-1)/2];
a[(pos-1)/2] = tmp;
//
}
else
{
flag = 1;
}
pos = (pos-1)/2;
}
}
//============================= 堆排序 ================================================
//将一个数组搞成一个最大堆(并不严格排序!),a[0]不管他了???
void maxHeapBuild(int *a, int size)
{
int i;
//last=size-1,last的parent就是 (last-1)/2 = size/2 -1
for(i = size/2 - 1; i>=0; i--) //从所有有孩子的节点往上遍历(相当于挨个插入节点了)
{
shiftDown2(a,i,size-1);
}
}
//将一个数组搞成最大堆,然后利用最大堆属性
//慢慢将数组搞成严格排序
void maxHeapSort(int *a, int size)
{
int i;
int tmp;
maxHeapBuild(a, size);
for(i = size-1; i>=0; i--)
{
//swap(a[i], a[1]); //交换堆顶 a[0] 和最后一个元素(即 将最大值放在了最后)
tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[0];
a[0] = tmp;
//最大值放在最后,同时最后的那个值也放在了堆顶,肯定需要重新调整为 maxHeap,
//(最后的那个元素已经不把他当作堆中一员了)
shiftDown(a,0,i-1);
}
}
//============================= 优先级队列 ==============================================
void createPriorQueue(PriorQueue **ppPriorQueue)
{
PriorQueue *p = NULL;
if(!ppPriorQueue)
{
printf("createPriorQueue:invalid param..\n");
return;
}
p = (PriorQueue *)malloc(sizeof(PriorQueue));
if(!p)
{
printf("createPriorQueue:no avail mem for PriorQueue struct..\n");
return;
}
p->a = (int *)malloc(PRIOR_QUEUE_BASE_SIZE*sizeof(int)); //sizeof(int)忘掉写了,会导致free失败?
if(!(p->a))
{
printf("createPriorQueue:no avail mem for PriorQueue array..\n");
return;
}
p->totalSize = PRIOR_QUEUE_BASE_SIZE;
p->validSize = 0;
*ppPriorQueue = p;
}
void destroyPriorQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue)
{
if(!pPriorQueue)
{
printf("destroyPriorQueue:invalid param..\n");
return;
}
if(pPriorQueue->a)
free(pPriorQueue->a);
free(pPriorQueue);
}
void enPriorQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue,int prior)
{
int *pTmp = NULL;
if(!pPriorQueue)
{
printf("enPriorQueue:invalid param..\n");
return;
}
if(pPriorQueue->validSize >= pPriorQueue->totalSize)
{
if(pPriorQueue->totalSize + PRIOR_QUEUE_INCREASE_SIZE > PRIOR_QUEUE_MAX_SIZE)
{
printf("enPriorQueue:exceed max size, will not alloc mem for heap any more\n");
return;
}
pTmp = pPriorQueue->a;
pPriorQueue->a = (int *)malloc((pPriorQueue->totalSize+PRIOR_QUEUE_INCREASE_SIZE)*sizeof(int));
if(!pPriorQueue->a)
{
printf("enPriorQueue:no avail mem for PriorQueue array..\n");
return;
}
memcpy(pPriorQueue->a,pTmp,pPriorQueue->totalSize);
pPriorQueue->totalSize += PRIOR_QUEUE_INCREASE_SIZE;
printf("enPriorQueue:increase heap size success..\n");
free(pTmp);
pTmp = NULL;
}
pPriorQueue->a[pPriorQueue->validSize] = prior;
ShiftUp(pPriorQueue->a, pPriorQueue->validSize);
pPriorQueue->validSize++;
}
int dePriorQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue)
{
int prior;
if(!pPriorQueue)
{
printf("dePriorQueue:invalid param..\n");
return -1;
}
if(pPriorQueue->validSize == 0)
{
printf("dePriorQueue:prior queue is empty..\n");
return -1;
}
prior = pPriorQueue->a[0];
pPriorQueue->validSize--;
pPriorQueue->a[0] = pPriorQueue->a[pPriorQueue->validSize]; //直接用最后一个覆盖[0]
shiftDown2(pPriorQueue->a, 0, pPriorQueue->validSize-1); //原来的那个最后一个已经不算再内了
return prior;
}
//for debug
void showQueue(PriorQueue *pPriorQueue)
{
int i;
if(!pPriorQueue)
return;
for(i=0;i<pPriorQueue->validSize;i++)
{
printf("%d ,",pPriorQueue->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "maxHeap.h"
#define MAX_HEAP_NUM 10000
int maxHeap_test()
{
int prior;
PriorQueue *pPQ = NULL;
int i = 0;
int *abc = malloc(MAX_HEAP_NUM*sizeof(int));
srand(0); //生成随机种子
printf("\n====================随机生成 %d 个数==============================\n",MAX_HEAP_NUM);
for(i=0;i<MAX_HEAP_NUM;i++)
{
abc[i] = rand()%(10*MAX_HEAP_NUM);
printf("%d ",abc[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n==================== 优先级队列 ==============================\n");
createPriorQueue(&pPQ);
printf("PQ");
for(i=0;i<MAX_HEAP_NUM/10;i++)
{
printf("<== %d ",abc[i]);
enPriorQueue(pPQ,abc[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
{
prior = dePriorQueue(pPQ);
printf("==> %d \n",prior);
//showQueue(pPQ);
}
destroyPriorQueue(pPQ);
pPQ = NULL;
printf("\n==================== 堆排序 ==============================\n");
maxHeapSort(abc, MAX_HEAP_NUM);
for(i=0;i<MAX_HEAP_NUM;i++)
{
printf("%d ",abc[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}3. 后话
-
堆排序 O(N*logN):
-
求一个数组中(N个元素)中最小的K个数:
- 快速排序,然后取前K个数 O(N*logN)+Q(K)
- 维护一个含有K个数的最大堆(刚开始即为初始的K个数),然后后面(N-K)个数依次与heap[1](大顶)比较,小于它则入围(直接覆盖heap[1]),更新大顶堆。否则不更新 N*O(logK) (只要K比N小,就比上面的有优势,最差也是和上面一样)
- 快排 Partition 找到第k小的数,再遍历一遍 O()
- 利用最大堆实现优先级队列(数组方式实现的哦):
- 入队就是插入元素到堆。a[size++] = new,then shiftUp()
- 出队当然出优先级最高的了,即将堆顶出队。a[0] = a[size-1],then shiftDown()
这种方式实现的是一个不稳定的优先级队列,即当两个相同值(这个值就被认为是 prior)被插入时,shift后并不保证他们之间的相对顺序不改变。
网上有个人说了一个实现稳定优先级队列的方法:
最大堆实现的优先级队列只保存不同的prior,同时prior还作为key被存入一个hashmap,冲突时采用链接法将节点链接起来。当插入节点时,之前没有相同的prior才入队。当冲突链上所有节点都被删除时,才出队
























 2471
2471

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








