目录
Java注解
Java原生注解
注解的属性也叫做成员变量,注解只有成员变量,没有方法。注解的成员变量在注解的定义中以“无形参的方法”形式来声明,其方法名定义了该成员变量的名字,其返回值定义了该成员变量的类型。
元注解
元注解是一种标注在别的注解之上的注解。如果一个注解可以标注在别的注解上,那么这个注解已然是元注解。
@Target值为TYPE
Stereotype 注解
可理解为模式化注解、角色类注解。例如:@Repository,@Component,@Service,@Bean等。
组合注解
组合注解是一种被一个或者多个元注解标注过的注解,用以撮合多个元注解的特性到新的注解。例如@SpringBootApplication
组合注解实现的基础 @AliasFor
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
//需要覆盖的注解类型。同一注解内部可以省略 annotation 属性
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}@AliasFor 将注解的一个成员名(Attribute Alias)变为另一个。成员别名可以分为以下几种。
- Explicit Aliases(显式别名)
如果一个注解中的两个成员通过 @AliasFor声明后互为别名,那么它们是明确的别名。显示别名必须成对出现。
- Implicit Aliases(隐式别名)
如果一个注解中的两个或者更多成员通过 @AliasFor 声明去覆盖同一个元注解的成员值,它们就是隐含别名。
- Transitive Implicit Aliases(传递的隐式别名)
如果一个注解中的两个或者更多成员通过 @AliasFor 声明去覆盖元注解中的不同成员,但是实际上因为覆盖的传递性导致最终覆盖的是元注解中的同一个成员,那么它们就是可传递的隐含别名。
注意:使用 @AliasFor 标注的有以下限制:一是属性都必须都有默认值且相等;二是属性的返回值类型也必须相等;三是属性双方都必须指定别名,且不能冲突。
隐式别名
使用元注解隐式别名,必须在注解上显示应用元注解。例如@SpringBootApplication 注解 覆盖 @SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackages"
)
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackageClasses"
)
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}
@AliasFor 和 @Inherited 区别
@Inherited 元注解表示被@Inherited标注过的注解,应用在class上时,可以被 class 的子类所继承。 但注意:一是类并不从它所实现的接口继承;二是方法并不从它所重载的方法继承。
@AliasFor 和 @Inherited 区别:
- @Inherited 强调子类可以继承父类的注解信息(不能获取接口上的注解信息)。
- @AliasFor 通过别名机制更强调两个注解的关系,类似 java 中类的继承。
例如 Spring 中 @Controller、@Repository、@Service 都是基于 @Component 派发出了一系列的注解,但语义更强。
注解解析工具
ava 运行时读取Annotation 需要通过反射,Spring 提供AnnotationUtils , AnnotationElementUtils 用于简化操作
AnnotationUtils解决注解别名,包括显示别名、隐式别名、传递的隐式别名。还可以查的指定注解的属性信息,但不能解决元注解属性覆盖的问题。AnnotatedElementUtils为 Spring 的元注解编程模型定义了公共 API,并支持注解属性覆盖。如果不需要支持注解属性覆盖,请考虑使用 AnnotationUtils
解析流程
AnnotationUtils
用于处理注解,元注解,桥接方法(编译器为通用声明生成)以及超级方法(用于可选注解继承)的常规实用程序方法。请注意,JDK 的内省工具本身并不提供此类的大多数功能。
- getAnnotations(Method, Class) 在给定类级别查找
- findAnnotation(Method, Class) 给定方法的整个继承层次结构中的查找查找
元注解支持
大多数 find() 方法和此类中的一些 get() 方法都支持查找用作元注解的注解。
属性别名
此类中返回注解,注解数组或 AnnotationAttributes 的所有公共方法都透明地支持通过 @AliasFor 配置的属性别名。
搜索范围
一旦找到指定类型的第一个注解,此类中的方法使用的搜索算法将停止搜索注解。因此,将默默忽略指定类型的其他注解。
AnnotatedElementUtils
用于在 AnnotatedElements上查找注解,元注解和可重复注解的常规实用程序方法。 AnnotatedElementUtils 为 Spring 的元注解编程模型定义了公共 API,并支持注解属性覆盖。注意:如果属性没有显示赋值,默认值不会覆盖@AliasFor的属性值。
查找与获取语义
获取语义(Get semantics)仅限于搜索 AnnotatedElement 上存在的注解(即本地声明或继承)或在 AnnotatedElement 上方的注解层次结构中声明的注解。
查找语义(Find semantics)更加详尽,提供了语义加上对以下内容的支持:
- 如果带注解的元素是类,则在接口上搜索
- 如果带注解的元素是类,则在超类上搜索
- 解析桥接方法,如果带注解的元素是方法
- 如果带注解的元素是方法,则在接口中搜索方法
- 如果带注解的元素是方法,则在超类中搜索方法
支持 @Inherited
get 语义之后的方法将遵循 Java 的 @Inherited 批注的约定,另外本地声明的注解(包括自定义组合注解)将优于继承注解。相反,查找语义之后的方法将完全忽略 @Inherited 的存在。
源码分析
解析流程
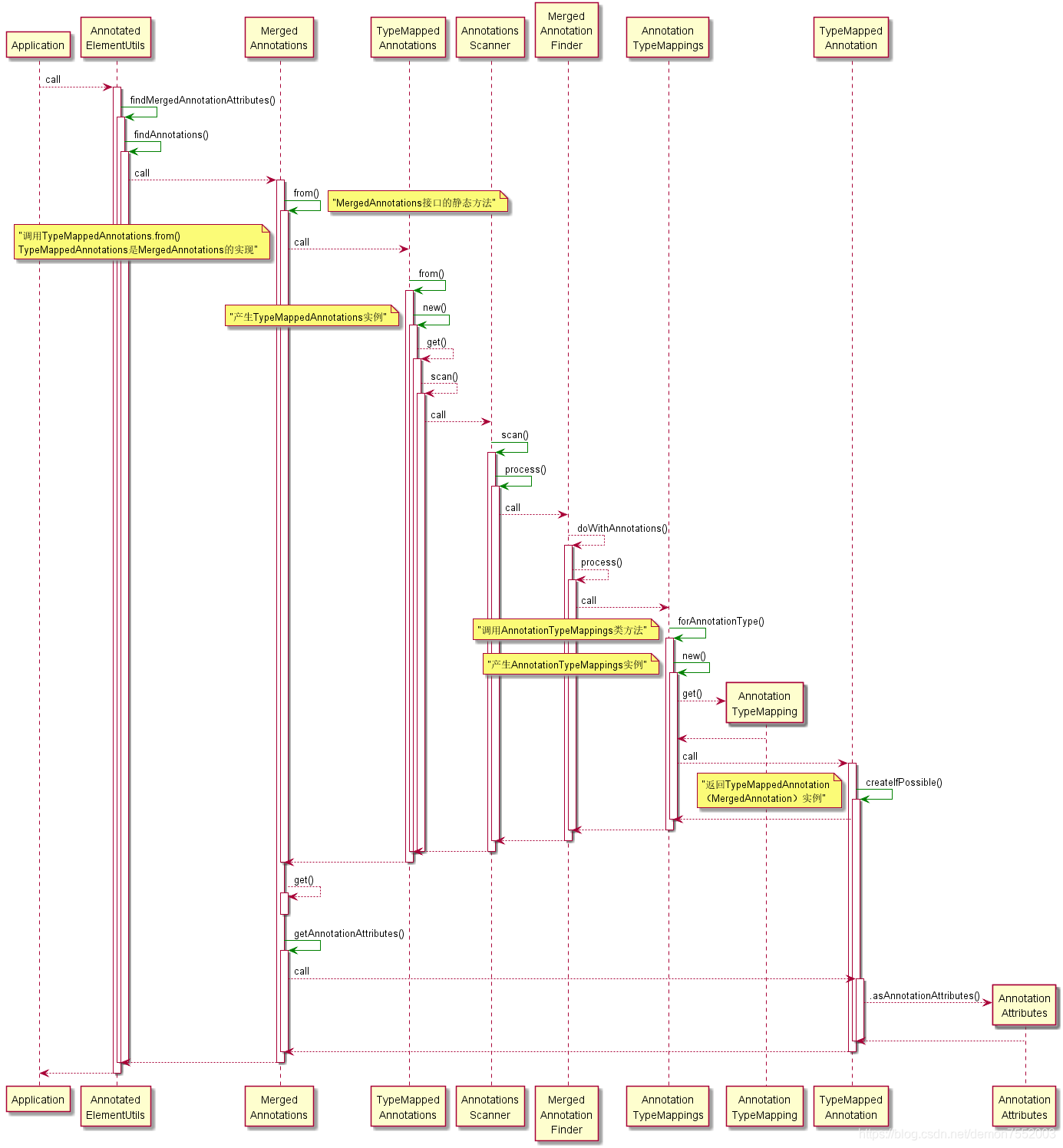
辅助类
AnnotationFilter
MergedAnnotation接口
MergedAnnotations接口
TypeMappedAnnotations
AnnotationsScanner
MergedAnnotationSelector
AnnotationTypeMapping
AnnotationTypeMappings
AnnotationTypeMapping帮助理解示例
AnnotationUtils 源码分析
AnnotatedElementUtils 源码分析





 本文详细探讨了Java注解的各类特性,包括原生注解、元注解、Stereotype注解、组合注解及@AliasFor的使用。特别介绍了@AliasFor如何创建属性别名,以及@Inherited元注解的作用。同时,文章还对比了@AliasFor和@Inherited的区别,以及Spring提供的注解解析工具AnnotationUtils和AnnotatedElementUtils的功能和适用场景。
本文详细探讨了Java注解的各类特性,包括原生注解、元注解、Stereotype注解、组合注解及@AliasFor的使用。特别介绍了@AliasFor如何创建属性别名,以及@Inherited元注解的作用。同时,文章还对比了@AliasFor和@Inherited的区别,以及Spring提供的注解解析工具AnnotationUtils和AnnotatedElementUtils的功能和适用场景。
















 691
691

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








