一 应用场景
加入一个美国人身在欧洲,假如欧洲的电压标准是230V,而美国的民用电压一般是110V,如果这个美国人想要用欧洲的电,那么需要一个转换器,把230V的电压转换为110V。
上述例子的三个类:
欧洲电压:Adaptee
美国人用电设备:Target
转换器:Adapter
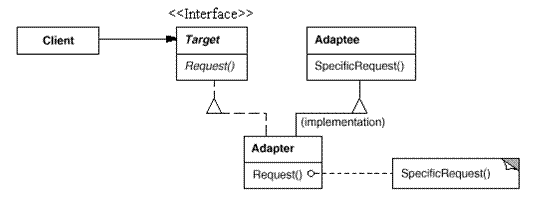
二 定义
将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口这样使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
Targe 目标抽象类:定义客户端所需要的接口,可以是一个抽象类也可以是具体类。
Adapter 适配器类:适配器可以调用另一个接口作为转换器,对Adaptee和Target进行适配。它通过继承Target并关联Adaaptee使二者产生联系。
Adaptee 适配者类:即被适配的角色,它定义了一个已经存在的接口,该接口需要适配。适配者类一般是一个具体的类,包含了客户想使用的业务方法。有些时候可能没有适配者类的源代码。
客户端调用适配器方法的时候,适配器类内部将调用适配者类的方法,而这个过程对客户是透明的。适配器的工作就是让接口不兼容不能交互的类可以一起工作。
三 C++实现
Adaptee.h
#ifndef _ADAPTEE_H_
#define _ADAPTEE_H_
#include <stdio.h>
// 抽象接口类,欧洲标准
class EuropeanSocketInterface
{
public:
EuropeanSocketInterface();
virtual ~EuropeanSocketInterface();
virtual int voltage() = 0;
virtual int live() = 0;
virtual int neutral() = 0;
virtual int earth() = 0;
};
// 欧洲的插座
class Socket:public EuropeanSocketInterface
{
public:
Socket();
virtual ~Socket();
int voltage();
int live();
int neutral();
int earth();
};
#endifAdaptee.cpp
#include "Adaptee.h"
EuropeanSocketInterface::EuropeanSocketInterface(){}
EuropeanSocketInterface::~EuropeanSocketInterface(){}
Socket::Socket(){}
Socket::~Socket(){}
int Socket::voltage()
{
return 230;
}
int Socket::live()
{
return 1;
}
int Socket::neutral()
{
return -1;
}
int Socket::earth()
{
return 0;
}
Target.h
#ifndef _TARGET_H_
#define _TARGET_H_
#include <stdio.h>
class USASocketInterface
{
public:
USASocketInterface();
virtual ~USASocketInterface();
virtual int voltage() = 0;
virtual int live() = 0;
virtual int neutral() = 0;
};
#endifTarget.cpp
#include "Target.h"
USASocketInterface::USASocketInterface(){}
USASocketInterface::~USASocketInterface(){}适配器 Adapter.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Target.h"
#include "Adaptee.h"
class Adapter:public USASocketInterface
{
private:
EuropeanSocketInterface * socket;
public:
Adapter();
virtual ~Adapter();
void plugIn(EuropeanSocketInterface * outlet);
int voltage();
int live();
int neutral();
};Adapter.cpp
#include "Adapter.h"
Adapter::Adapter(){}
Adapter::~Adapter(){}
void Adapter::plugIn(EuropeanSocketInterface * outlet)
{
socket = outlet;
}
int Adapter::voltage()
{
return 110;
}
int Adapter::live()
{
return socket->live();
}
int Adapter::neutral()
{
return socket->neutral();
}client.h
#ifndef _CLIENT_H_
#define _CLIENT_H_
#include "Target.h"
//美国的电水壶要在欧洲烧水
class ElectricKettle
{
private:
USASocketInterface * power;
public:
ElectricKettle();
virtual ~ElectricKettle();
void plugIn(USASocketInterface * supply);
void boil();
};
#endifclient.cpp
#include "Client.h"
ElectricKettle::ElectricKettle(){}
ElectricKettle::~ElectricKettle(){}
void ElectricKettle::plugIn(USASocketInterface * supply)
{
power = supply;
}
void ElectricKettle::boil()
{
if(power->voltage() > 110){
printf("kettle is on fire\n");
return;
}
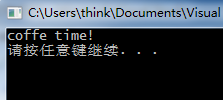
if(power->live() == 1 && power->neutral() == -1){
printf("coffe time!\n");
}
}main函数
int main()
{
Socket * socket = new Socket;
Adapter * adapter = new Adapter();
ElectricKettle * kettle = new ElectricKettle;
adapter->plugIn(socket);
kettle->plugIn(adapter);
kettle->boil();
system("pause");
}四 总结
优点:
1 将目标类和适配者类解耦,通过引入一个适配器类重用现有的适配者类,而无需修改原有代码。
2 通过适配器,客户端可以调用同一接口,因而对客户端来说是透明的,提高复用性。
3 可以方便的更换适配器,符合开闭原则。
缺点:
1 对于java,C#等不支持多重类继承的语言,一次最多只能适配一个适配器者类,不能适配多个。






















 1365
1365

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








