前言
这两天碰到面试题,说是页面调度算法,之前在操作系统书上有了解过,LRU(近期最少使用),还有OPT(最佳页面替换算法)、FIFO(先进先出页面置换算法),今天先来实现LRU 最近最少使用。
LRU 原理
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
参照网上的写法,给出以下例子做个参考:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <unordered_map> 3 #include <list> 4 #include <utility> 5 using namespace std; 6 using namespace stdext; 7 8 class LRUCache { 9 public: 10 LRUCache(int capacity) { 11 m_capacity = capacity; 12 } 13 14 int get(int key) { 15 int retValue = -1; 16 unordered_map<int, list<pair<int, int> > ::iterator> ::iterator it = cachesMap.find(key); 17 18 //如果在Cashe中,将记录移动到链表的最前端 19 if (it != cachesMap.end()) 20 { 21 retValue = it->second->second; 22 //移动到最前端 23 list<pair<int, int> > ::iterator ptrPair = it->second; 24 pair<int, int> tmpPair = *ptrPair; 25 caches.erase(ptrPair++); 26 caches.push_front(tmpPair); 27 28 29 //修改map中的值 30 cachesMap[key] = caches.begin(); 31 } 32 return retValue; 33 } 34 35 void set(int key, int value) { 36 37 unordered_map<int, list<pair<int, int> > ::iterator> ::iterator it = cachesMap.find(key); 38 39 if (it != cachesMap.end()) //已经存在其中 40 { 41 list<pair<int, int> > ::iterator ptrPait = it->second; 42 ptrPait->second = value; 43 //移动到最前面 44 pair<int, int > tmpPair = *ptrPait; 45 caches.erase(ptrPait); 46 caches.push_front(tmpPair); 47 48 49 //更新map 50 cachesMap[key] = caches.begin(); 51 } 52 else //不存在其中 53 { 54 pair<int, int > tmpPair = make_pair(key, value); 55 56 57 if (m_capacity == caches.size()) //已经满 58 { 59 int delKey = caches.back().first; 60 caches.pop_back(); //删除最后一个 61 62 63 //删除在map中的相应项 64 unordered_map<int, list<pair<int, int> > ::iterator> ::iterator delIt = cachesMap.find(delKey); 65 cachesMap.erase(delIt++); 66 } 67 68 69 caches.push_front(tmpPair); 70 cachesMap[key] = caches.begin(); //更新map 71 } 72 } 73 74 75 private: 76 int m_capacity; //cashe的大小 77 list<pair<int, int> > caches; //用一个双链表存储cashe的内容 78 unordered_map< int, list<pair<int, int> > ::iterator> cachesMap; //使用map加快查找的速度 79 }; 80 81 82 int main(int argc, char **argv) 83 { 84 LRUCache s(2); 85 s.set(2, 1); 86 s.set(1, 1); 87 cout << s.get(2) << endl; 88 s.set(4, 1); 89 s.set(5, 2); 90 cout << s.get(5) << endl; 91 cout << s.get(4) << endl; 92 getchar(); 93 return 0; 94 }
在vs 2015 进行运行 ,输出:
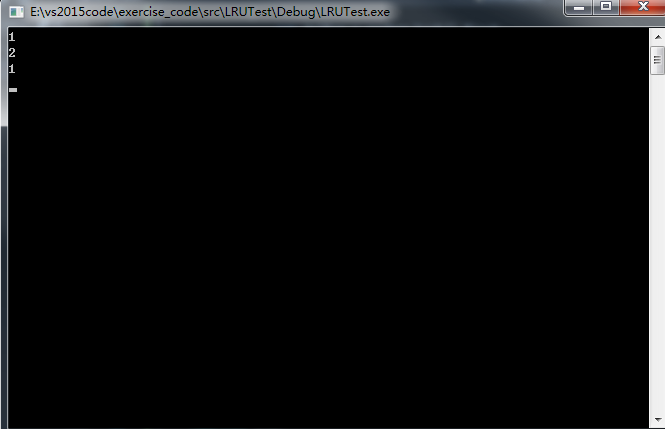
解释:程序首先会初始化2个存储空间的LRUCache类,依次插进{2, 1 },{1,1} ,之后输出 key=2 => value=1 ,之后插进 {4, 1} , 因为已经满了所以替换掉最近没有使用的{1 ,1} ,变成了 { 4,1} ,{2,1} ,之后又插进{5, 2} ,又替换掉了 {2,1} ,变成了 {4, 1} ,{5,2},然后输出剩下两个key,再重新排序谁最近使用过。
用到的知识是 : 双链表 + 哈希表 (使用map,内部元素自动排序;使用unordered_map内部不会进行有序排序)
页面调度算法(LRU)的原理 :缓存机制中新数据或击中的数据放到链表头部,表示最近使用的数据,如果链表满,从尾部淘汰数据。但只用链表会存在一个问题,击中数据的时间复杂度为O(n),每次需要遍历链表,所以引入哈希表,时间复杂度降到O(1),以空间换时间。





















 146
146











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








