一、Retinex 理论基础
(1)色彩恒常性(Color Constancy):Retinex 理论认为,在不同的光照条件下, 同一个物体的颜色应该是相对稳定的。也就是说,人类的视觉系统能够将物体的 颜色与周围环境的光线相互抵消,从而使得人们感知到的颜色基本上保持不变。
(2)全反射(Full Reflectance):Retinex 理论假设,人类的视觉系统能够分离 物体的表面反射光和阴影部分,从而更好地感知到物体的表面颜色。这意味着, 人们能够将物体的颜色感知与光线的亮度变化相分离。
(3)多尺度比较(Multi-Scale Comparison):Retinex 理论认为,人类的视觉系 统在感知颜色和亮度时,会同时比较多个尺度上的信息。也就是说,人们会比较 物体表面的反射光与周围环境的光在不同尺度上的差异,从而更加准确地感知颜 色和亮度。
观察到的图像 S(x,y) 是光照产生的入射图像 L(x,y) 与物体反射率 R(x,y) 的乘积
S = L × R
对两边取对数
log(R) = log(S)- log(L)
入射图像分量很难直接得到,因此,使用高斯滤波与原始图像进行卷 积操作来代替入射图像分量
log(R) = log(S)- log(S * G)
“ * ” 代表卷积, G 代表高斯滤波
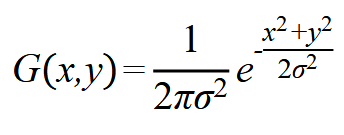
x和y表示距离中心像素的偏差;σ表示高斯核的标准差。当σ值过小时, 滤波器的范围很小,导致平滑效果不够明显,此时图像的原始细节和噪声保留较 多;当σ值过大时,对图像的平滑效果较好,但过度光滑也会导致图像缺乏边缘 细节。
二、多尺度融合(Multi-Scale Retinex, MSR)
单尺度 σ 只能保持某一频段的细节。MSR 把 k 个不同 σi 的G的结果做平均:
log( R ) = (1/k) ∑ ( log( S )- log( S * G ) )
三、色彩恢复(Color Restoration, CR)
MSR 把三个通道独立处理,会导致严重的色偏/灰化。MSRCR 引入颜色恢复因子 C(x,y):
** R’ = C × R **
Ci表示第i个通道的色彩恢复因子;α和β表示调节参数,α控制颜色修复的强度,β控制颜色修复的影响程度;∑ Ii 表示原始图像的三个通道 在每个像素位置的和
Ci = β × [ log( α × Ii ) – log( Σ Ii ) ]
四、线性映射 & 后处理
线性拉伸到 0~1:
norm = ( R’ – min) / (max – min)
最后在公式中加入一个增益值G和偏移值b得到最终的 MSRCR 算法
Output = G · norm + b
代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# -------------------- 参数区 --------------------
sigmas = (15, 80, 250) # 高斯核尺度
alpha = 125.0 # 色彩恢复强度
beta = 46.0 # 增益
G = 192.0 # 最终增益
b = -30.0 # 最终偏置
# ----------------------------------------------
def single_scale_retinex(img, sigma):
"""单尺度 Retinex"""
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (0, 0), sigma)
retinex = np.log10(img + 1e-6) - np.log10(blurred + 1e-6)
return retinex
def multi_scale_retinex(img, sigmas):
"""多尺度 Retinex 取平均"""
msr = np.zeros_like(img, dtype=np.float32)
for s in sigmas:
msr += single_scale_retinex(img, s)
return msr / len(sigmas)
def color_restoration(img, msr, alpha, beta):
"""色彩恢复因子 C"""
img_sum = np.sum(img, axis=2, keepdims=True) + 1e-6
C = beta * (np.log10(alpha * img + 1) - np.log10(img_sum))
return C * msr
def msrcr(img_bgr):
"""主函数:MSRCR"""
img = img_bgr.astype(np.float32) + 1.0 # 避免 log(0)
msr = multi_scale_retinex(img, sigmas)
img_cr = color_restoration(img, msr, alpha, beta)
msrcr_result = G * (img_cr - np.min(img_cr)) / (np.max(img_cr) - np.min(img_cr)) + b
msrcr_result = np.clip(msrcr_result, 0, 255)
return msrcr_result.astype(np.uint8)
def simplest_color_balance(img, low_clip=1, high_clip=99):
"""简单的 1%-99% 线性拉伸"""
out = np.zeros_like(img)
for ch in range(3):
a = np.percentile(img[:, :, ch], low_clip)
b = np.percentile(img[:, :, ch], high_clip)
channel = np.clip(img[:, :, ch], a, b)
out[:, :, ch] = 255 * (channel - a) / (b - a + 1e-6)
return out.astype(np.uint8)
# ------------------ 运行示例 ------------------
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = 'OIP-C.jpg' # 换成自己的图片
img_bgr = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img_bgr is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(img_path)
result = msrcr(img_bgr)
result = simplest_color_balance(result, low_clip=1, high_clip=99)
# 可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title('Original')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.title('MSRCR')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 保存
cv2.imwrite('msrcr_output.jpg', result)




















 5660
5660

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








