Introduction
This is the third of five articles about Host Workflow communication.
In this series of articles, I try to show the different possibilities to implement communication, from the simplest case to the more complex. I am not planning to be exhaustive, but I will try to give a general panoramic in order to get us a good idea about the thematic. Because I also don’t like large articles, I have divided the series in to the followings parts:
- Part I: Simplest communication case: Communication Host -> Workflow by parameters.
- Part II: Intercommunications Workflow -> Host through CallExternalMethod Activity
- Part III: Intercommunications Host -> Workflow through HandleExternalEvent Activity.
- Part IV: Organisation of the communication classes: Communication manager, wca.exe utility, and Wwca.exe Windows front-end for wca.exe
- Part V: Intercommunications with a Workflow instance using the Correlation parameter
Background
In Part II, we understood how to pass information to a Workflow when it is launched and how the workflow can return information to the host. 在第二部分讲述当workflow启动时把信息传递给workflow,以及workflow把信息返回给主程序。But, you can have a more complex situation, 考虑复杂一些的情况one that you must send information to the Workflow, not in the initialization phase but in an intermediate point, 可能再中间某个点给workflow信息,而不是在启动时,or you have to send information more often in the workflow's life time. 或者在workflow运行期间需要经常给workflow传递信息Also, you need to be able to send information in a determinate point of the Workflow flux. 或者在workflow的结束状态给workflow信息Those entire requirements can be fulfilled with the Activity HandleExternalEvent. 这些需求可以用Active HandleExternalEvent实现。
With HandleExternalEvent, you can stop the workflow and wait for a determinate external event, and when the event is received, the Workflow can continue the execution of the next activity.
使用HandleExternalEvent, 可以停止一个workflow等待一个特定的内部事件,当事件到来后,workflow能继续执行下面的动作。
HandleExternalEvent gets information from the Host in the Event Arguments parameter defined in the Event.
HandleExternalEnent 从主程序中定义的事件参数中获取信息
If we compare CallExternalMethod with HandleExternalEvent, we can see that both call a piece of software that is defined in another thread in another application. The first calls a method, and the second waits for an Event.
As you can see, you must supply the command or the number to the workflow each time the user clicks the Add button in the Host application. Obviously, you can not supply these information in the initialization of the Workflow.
…OK, you can run the Workflow each time you need the calculation; give the number, and the total is returned as a parameter, but I want to show you how to use the Workflow to control the process….
The HandleExternalEvent Activity waits for the defined external event and you are sure that the data is received at the right moment. HandleExternalEvent Activity 等待定义的外部事件The data is returned by using the CallExternalMethod that was explained in Part II of this article. 数据使用CallExternalMethod 返回主程序
To implement the communication, we need to fulfill a specific pattern that is similar to CallExternalMethod, but now, we need to define an external event. 这里需要定义一个外部事件In short, we need to do the following steps:
下面是需要做的工作
Create the following interface and classes:
- An interface with the method definition called by the
CallExternalMethodactivity 一个由CallExternalMethod调用的接口及方法and the External Event handled by theHandleExternalEventactivity. 由HandleExternalEvent 处理的外部事件 - A class that implements the interface. 一个类实现上述接口In this class, you implement the method that is called by
CallExternalMethod. 在类中实现由CallExternalMethod调用的方法.In this method, you add the code to send the information to the host, and the event to be handled by theHandleExternalEventactivity. 通过方法中包括传送信息给主程序的代码和由HandleExternalEvent 处理的事件 - You should create a special Event Arguments class to send the information to the Workflow. 需要创建一个Event Argument class 用来传递信息给workflow. Arguments for External Events need to inherit from a special Event Argument class:
ExternalDataEventArgs. 外部事件的参数必须从一个Event Argument class:ExternalDataEventArgs继承。This special event argument comes with a constructor that needs the GUID from the instanced workflow that we want to communicate with. 这个事件参数有一个机构体,该结构体需要workflow的GUID。In our example, that is not very important because we only have an instance of the Workflow, but that plays an important role if we are working with different Workflows in the same time. 在本例中只有一个workflow实例,但如果同时有不同的workflow,GUID就很重要。 - You should also implement the Event Argument class to receive the information from the method called by
CallExternalMethodin the host. 需要实现Event Argument Class用以接收由主程序CallExternalMethod 产生的信息。
In the host application, do the following steps: 在主程序端需要的操作
- You must create an instance of the
ExternalDataExchangeServiceclass and register it in the Workflow runtime. 创建ExternalDataExchangeService class 的一个实例,并在workflow runtime中注册。 - You must create an instance of
CommunicationCalculatorand add it to the ExternalDataExchangeService instance (created in point 1). 创建一个CommunicationCalculator实例,并把该实例加到ExternalDataExchangeService instance 中(步骤1中建立)。 - If you use an event to drive the communication WF –> Host, you must also handle the communication event in your host class. 如果使用事件通信,在主程序中需要处理通信事件。
- To communicate with the Workflow, you must raise the created External Event and pass the information through the created Event arguments. 要同workflow通信,必须建立External Event。
In the Workflow: 在workflow中
- You must insert a
CallExternalMethodactivity. 使用CallExternalMethod activity - In it, register the communication interface and the method to call. 在CallExternalMethod activity中注册communication interface以及方法。
- You must have a
HandleExternalEventactivity for each event that you want to handle to receive information from the host application. In this case, you need only one. 每一个事件必须对应一个aHandleExternalEventactivity 用于操作从主程序获取的信息。 - You should configure this
HandleExternalEventactivity with the declared communication interface and the event to call. Eventually, you can also define an event to be called after the external event is processed. 用声明的communication interface 和事件配置HandleExternalEvent activity 。此外还可以定义一个事件在external event 被处理后执行。 - You should declare a public
CalculadorEventArgumentsto receive the information for the external event. 需要声明一个public 类型的CalculadorEventArguments用于接收external event的信息。
In the following example, we have more code that we will explain here. That is because we don’t explain in depth what we need to for the functional logic for these examples, we concentrate only in the passing of the information.
You can see the result class structure for our example in the following diagram:

What is new here? The CalculadorEventArguments, as you see, makes a relation between two threads and it is all done through ICommunicationCalculator. CalculadorEventArguments 在两个线程之间起关联作用。The event to communicate data from the Workflow is raised in the host and is received from the HandleExternalEvent activity.
Now, we explain in detail how the program works.
Using the code
To use the companion code, create an empty VS2008 solution and unzip the companion ZIP file in to the created project directory. In Visual Studio, add the three unzipped projects to the solutions. Build your solution.
The best part is downloading the code that is attached to this article. You can also developer your own ideas and copy and paste with creativity the code about the communication explained in the following paragraph.
The example project is a Windows project that adds integer numbers to a total field. You can add numbers, reset it, or exit from the program. You have three buttons to launch these functions.
In this project, we use an individual project to group all the classes that we need to implement the communication between the host and the workflow.
A. WFCommunication Interface Project
Create a project to hold the classes that you need to communicate the host with the workflow. Select a class project and name it WFCommunicationInterface. You can also revise the project in the attached code.
Open to add a file and select in New, the Item Interface item, then name it to ICommunicationCalculator. This file must have all the methods and events that are called or consumed by the workflow.
建立一个Interface, 命名为ICommunicationCalculator,包含由workflow调用的事件和方法
Add the following code to the class:
/// <summary>
/// This interfaces must have all method to communicate
/// between WF to Host and all Events to communicate Host to WF
/// </summary>
[ExternalDataExchange]
public interface ICommunicationCalculator
{
#region Communication WF - > Host (explained in Part II)
/// <summary>
/// External Method to return result to host
/// </summary>
/// <param name="""total""" />calculated total</param />
void SendTotalToHost(Int64 total);
#endregion
#region Communication Host -> WF
/// <summary>
/// External Event to send information to workflow (number)
/// </summary>
event EventHandler<CalculadorEventArguments>SendCommandAndDataToWF;
#endregion
}
Here, you must define an event to do the communication between the host and the workflow. The EventHandler has a special EventArguments: CalculatorEventArguments. 必须定义一个用于host和workflow通讯的事件。EventHandler(事件委托)有一个特殊的事件参数CalculatorEventArguments
Now, create a new class file and add to the project. Name it as CalculatorEventArguments and create the following class:
下面完成CalculatorEventArguments的定义
/// <summary>
/// See the attribute "Serializable" This argument must be
/// passed fromHost to Workflow
/// through a underline Intercomunication Process.
/// You must mark as serializable!!
/// </summary>
[Serializable]
public class CalculadorEventArguments: ExternalDataEventArgs
{
#region Create properties to hold the values to send to Workflow
string _command = "RESET";
int _valueToAdd = 0;
public string Command
{
get { return _command; }
set { _command = value; }
}
public int ValueToAdd
{
get { return _valueToAdd; }
set { _valueToAdd = value; }
}
#endregion
#region Create a Constructor with the InstanceId to pass to base class
public CalculadorEventArguments(Guid instanceID)
:base(instanceID)
{
}
#endregion
The event makes space for the information that we need to pass to the workflow: the command string and the integer to be added to the total sum. 这个事件定义了传给workflow的信息:command string 和一个integer(加到total sum 上)
Here, the two important points are the [serializable] attribute and the base class for the class. 注意两点:[serializable] 属性和基类的类型。You must decorate the class with the [serializable] attribute. This event argument must be used between threads in an inter communication process, and so it must be serializable.
The second point is the inheritance from ExternalEventArgs. 这个类从ExternalEventArgs继承。This special event argument has a constructor that take as parameter the GUID or the identifier for the workflow instance. 这个事件含有对workflow instance的标识You must use this identifier to guarantee that the information goed to the right instance of the Workflow. 使用此标识确保信息被传送到正确的workflow instance.The framework uses this parameter to derive the event to the correct instance of the workflow. 主程序使用此参数驱动事件传递给正确的workflow instance. You know that you can have multiples instances of the same workflow that run concurrently. We will see this in detail in another article.
You should also create an event to send to the host when the external method SendCommandAndDataToWp is executed. That is a normal event as you can see in the following code: 当外部方法SendCommandAndDataToWp执行后, 还需要建立向主程序发送的事件。这是一个普通事件
/// <summary >
/// Argument to be used when the WF send the result to
/// Host. Note that you dont need to use the serializable attribute
/// neither derived the class from ExternalEventArguments
/// That is because the event dont need to pass any Thread frontier.
/// </summary >
public class SummeEventArgs: EventArgs
{
Int64 _summe = 0;
public Int64 Summe
{
get {return _summe;}
set {_summe = value;}
}
}
As you see, we use a normal argument to return the sum total from the workflow to the host. 使用一个普通的参数把sum值从workflow传递给host. In the last step, we need to implement the ICommunicationCalculator interface.最后需要完成ICommunicationCalculator 接口。Create a new file in the project, create a new class to create the file, and write the following code:
public class CommunicationCalculator: ICommunicationCalculator
{
#region Zone Workflow to Host communication
/// <summary >
/// Watch that this Event is not in the communication Interface.
/// because is internal of the implementation of SendTotalToHost
/// and internal to the Host programmation.
/// </summary >
public event EventHandler<summeeventargs > ReturnSummeEvent;
public void SendTotalToHost(Int64 total)
{
SummeEventArgs e = new SummeEventArgs();
e.Summe = total;
EventHandler<SummeEventArgs> sendData = this.ReturnSummeEvent;
if (sendData != null)
{
sendData(this, e);
}
}
#endregion
#region Zone Host to Workflow comunnication
/// <summary >
/// This is the external Even to should handled by the WF to receive the information
/// </summary >
public event EventHandler<CalculadorEventArguments> SendCommandAndDataToWF;
public void ReiseEventSendCommandAndDataToWF(Guid instanceID,
string command, int numberToAdd)
{
if (SendCommandAndDataToWF != null)
{
CalculadorEventArguments e = new CalculadorEventArguments(instanceID);
e.ValueToAdd = numberToAdd;
e.Command = command;
SendCommandAndDataToWF(null, e);
}
}
#endregion
}
We can analyze the code in parts. The first part has the communication between the workflow and the host that we showed in the second part of this series of articles. The second is new, but as you see is very simple to implement. You only need to define an instance for the external argument to be used. The workflow can automatically get this event and handle it.
The second procedure is a helper procedure to raise the event in the host. The use of this helper procedure encapsulates the call to the SendCommandAndDataToWF event.
B. Host application
As we see in the second part of this series of articles, you must register the communication service that we have created in step A as an ExternalDataService. 注册一个Communication service.
The code is quasi the same and you can see it here:
#region Add support to the Communication Service
//Declare a ExternalDataExchangeService class
ExternalDataExchangeService dataservice = new ExternalDataExchangeService();
//Add to workflow runtime
_workflowRuntime.AddService(dataservice);
//Declare our CommunicationService instance
cservice = new CommunicationCalculator();
//Add to the ExternalDataService
dataservice.AddService(cservice);
//Add a handler to Service Event (retrieve Summe from Workflow)
cservice.ReturnSummeEvent +=
new EventHandler<summeeventargs> (cservice_ReturnSummeEvent);
#endregion end of support to Communication Service.....
As you can see, the code is the same as in the example in the previous article.
Here, in the click events for each command, each button fires a command in the workflow that we must transport to the workflow. To do this operation, we must raise the external event. See the following code in the buttons' Click events:
#region Send data and commands to Workflow
/// <summary>
/// Send to workflow the operation ADD and the number to add.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void bAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(IsValidNumber(tbNumber.Text))
{
//Raise the event...to add a number
cservice.ReiseEventSendCommandAndDataToWF(instance.InstanceId,
"ADD", int.Parse(tbNumber.Text));
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Send to Workflow that reset the accumulate summe
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void bReset_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Raise the event...to add a number
cservice.ReiseEventSendCommandAndDataToWF(instance.InstanceId, "RESET", 0);
} /// <summary>
/// Close the application
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void bExit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Raise the event...to exit form workflow
cservice.ReiseEventSendCommandAndDataToWF(instance.InstanceId, "EXIT", 0);
this.Close();
}
#endregion
We can see that it is simple calling the ReiseEventSendCommandAndDataToWF method from the communication interface. This method raises an external event in the workflow. The next section explain how to use this event.
C. The workflow application
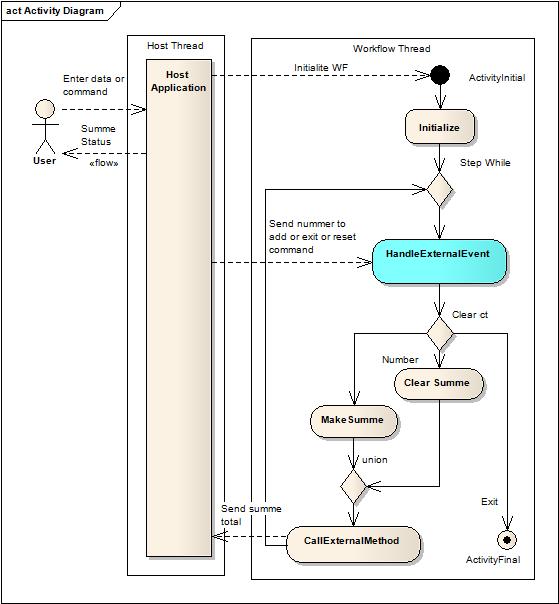
Now, we need to configure the workflow application. In the following figure, we can see the implementation of the workflow to resolve the example task:

As you can see here, the sequence is simple, and we use the simple IfElse activities to select the right command and do the job.
Also, we use a While activity to wait for the command from the host and then execute it. The sequence ends when the Exit command is received. You can see the details of the implementation in the code.
You can see that the HandleExternalEvent Activity is directly after the beginning of the while loop. The HandleExternalEvent activity stops the flow of the workflow until the event is received. Then, we can be secure that the command and data are received at the right moment in the flow of the workflow. To configure the HandleExternalEvent activity is simple. The following figure shows how to configure it for our example.

As you can see, you need to declare the InterfaceType, the name of the event, and a variable that holds the information that the event from the Host gives us. You only need to declare a variable type CalculadorEventArguments, as you can see in the following code:
/// <summary>
/// The HandleExternalEvent use this property to store the data from the Host
/// </summary>
public jagg.ClassCommunication.CalculadorEventArguments _returnedArguments =
default(CalculadorEventArguments);
Here, you can also see the property Invoked. You can use this property to invoke a method that is executed after the event is received. You can use this method to accommodate the received parameter in the right position in your workflow, or to do another task that you need. In our situation, we pass the received information to two internal variables:
/// <summary>
/// This method is call after the handlerExternalEvent activities finish.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void SetResponseInVariables(object sender, ExternalDataEventArgs e)
{
_numberToAdd = _returnedArguments.ValueToAdd;
_command = _returnedArguments.Command;
}
And that is all!
You can see the complete application in the attached code.
Resume
The basic steps to pass information from a Host to a Workflow using the HandleExternalEvent activity are:
Create the followings interface and classes:
- An interface with the event definition consumed by the
HandleExternalEventactivity and decorated with the header:[ExternalDataExchange]. - A class that implements the interface. In this class, you implement the event to be consumed by
HandleExternalEventin the Workflow, and you can also implement the method that raises the event in the host application.
In the Host application, do the following:
- Register an instance of the
ExternalDataExchangeServiceclass in the Workflow runtime. - Add the instance of the communication class to the
ExternalDataExchangeServiceinstance. - At the point of the application that you can send information to the Workflow, call the routine created to raise the external event in the Workflow and pass as parameters the information that you want to pass to the Workflow.
In the Workflow:
- Drop a
HandleExternalEventActivity at the point of the Workflow that you want to get the information from the Host. - In the
HandleExternalEventActivity properties, register the Communication Interface, the event to be consumed, and the variable or the property to hold the information returned by the event.
Now, we have the basic tool to deal with the communication between a workflow and a host. We can resolve many problems that need to send information in a specific point of the workflow and return the information to the host. But all it is a little complex. You must register the service in one part of the program, and configure the HandleExternalEvent and CallExternalMethod classes. In the next part, we will cover the tool and a method to automatically generate a custom communication class and better organize the communication process.





















 145
145

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








