托管豆
这篇文章是本教程第1部分的继续。
在“ com.mb”包中,您将需要创建以下类:
package com.mb;
import org.primefaces.context.RequestContext;
import com.util.JSFMessageUtil;
public class AbstractMB {
private static final String KEEP_DIALOG_OPENED = 'KEEP_DIALOG_OPENED';
public AbstractMB() {
super();
}
protected void displayErrorMessageToUser(String message) {
JSFMessageUtil messageUtil = new JSFMessageUtil();
messageUtil.sendErrorMessageToUser(message);
}
protected void displayInfoMessageToUser(String message) {
JSFMessageUtil messageUtil = new JSFMessageUtil();
messageUtil.sendInfoMessageToUser(message);
}
protected void closeDialog(){
getRequestContext().addCallbackParam(KEEP_DIALOG_OPENED, false);
}
protected void keepDialogOpen(){
getRequestContext().addCallbackParam(KEEP_DIALOG_OPENED, true);
}
protected RequestContext getRequestContext(){
return RequestContext.getCurrentInstance();
}
}package com.mb;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import javax.faces.bean.*;
import com.facade.DogFacade;
import com.model.Dog;
@ViewScoped
@ManagedBean
public class DogMB extends AbstractMB implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Dog dog;
private List<Dog> dogs;
private DogFacade dogFacade;
public DogFacade getDogFacade() {
if (dogFacade == null) {
dogFacade = new DogFacade();
}
return dogFacade;
}
public Dog getDog() {
if (dog == null) {
dog = new Dog();
}
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public void createDog() {
try {
getDogFacade().createDog(dog);
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Created With Sucess');
loadDogs();
resetDog();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void updateDog() {
try {
getDogFacade().updateDog(dog);
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Updated With Sucess');
loadDogs();
resetDog();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void deleteDog() {
try {
getDogFacade().deleteDog(dog);
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Deleted With Sucess');
loadDogs();
resetDog();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public List<Dog> getAllDogs() {
if (dogs == null) {
loadDogs();
}
return dogs;
}
private void loadDogs() {
dogs = getDogFacade().listAll();
}
public void resetDog() {
dog = new Dog();
}
}package com.mb;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.faces.bean.*;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.model.User;
@SessionScoped
@ManagedBean(name='userMB')
public class UserMB implements Serializable {
public static final String INJECTION_NAME = '#{userMB}';
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private User user;
public boolean isAdmin() {
return user.isAdmin();
}
public boolean isDefaultUser() {
return user.isUser();
}
public String logOut() {
getRequest().getSession().invalidate();
return '/pages/public/login.xhtml';
}
private HttpServletRequest getRequest() {
return (HttpServletRequest) FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().getRequest();
}
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
}package com.mb;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.*;
import javax.faces.bean.*;
import com.facade.*;
import com.model.*;
import com.sun.faces.context.flash.ELFlash;
@ViewScoped
@ManagedBean
public class PersonMB extends AbstractMB implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final String SELECTED_PERSON = 'selectedPerson';
private Dog dog;
private Person person;
private Person personWithDogs;
private Person personWithDogsForDetail;
private List<Dog> allDogs;
private List<Person> persons;
private DogFacade dogFacade;
private PersonFacade personFacade;
public void createPerson() {
try {
getPersonFacade().createPerson(person);
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Created With Sucess');
loadPersons();
resetPerson();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void updatePerson() {
try {
getPersonFacade().updatePerson(person);
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Updated With Sucess');
loadPersons();
resetPerson();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void deletePerson() {
try {
getPersonFacade().deletePerson(person);
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Deleted With Sucess');
loadPersons();
resetPerson();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void addDogToPerson() {
try {
getPersonFacade().addDogToPerson(dog.getId(), personWithDogs.getId());
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Added With Sucess');
reloadPersonWithDogs();
resetDog();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void removeDogFromPerson() {
try {
getPersonFacade().removeDogFromPerson(dog.getId(), personWithDogs.getId());
closeDialog();
displayInfoMessageToUser('Removed With Sucess');
reloadPersonWithDogs();
resetDog();
} catch (Exception e) {
keepDialogOpen();
displayErrorMessageToUser('Ops, we could not create. Try again later');
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Person getPersonWithDogs() {
if (personWithDogs == null) {
if (person == null) {
person = (Person) ELFlash.getFlash().get(SELECTED_PERSON);
}
personWithDogs = getPersonFacade().findPersonWithAllDogs(person.getId());
}
return personWithDogs;
}
public void setPersonWithDogsForDetail(Person person) {
personWithDogsForDetail = getPersonFacade().findPersonWithAllDogs(person.getId());
}
public Person getPersonWithDogsForDetail() {
if (personWithDogsForDetail == null) {
personWithDogsForDetail = new Person();
personWithDogsForDetail.setDogs(new ArrayList<Dog>());
}
return personWithDogsForDetail;
}
public void resetPersonWithDogsForDetail(){
personWithDogsForDetail = new Person();
}
public String editPersonDogs() {
ELFlash.getFlash().put(SELECTED_PERSON, person);
return '/pages/protected/defaultUser/personDogs/personDogs.xhtml';
}
public List<Dog> complete(String name) {
List<Dog> queryResult = new ArrayList<Dog>();
if (allDogs == null) {
dogFacade = new DogFacade();
allDogs = dogFacade.listAll();
}
allDogs.removeAll(personWithDogs.getDogs());
for (Dog dog : allDogs) {
if (dog.getName().toLowerCase().contains(name.toLowerCase())) {
queryResult.add(dog);
}
}
return queryResult;
}
public PersonFacade getPersonFacade() {
if (personFacade == null) {
personFacade = new PersonFacade();
}
return personFacade;
}
public Person getPerson() {
if (person == null) {
person = new Person();
}
return person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public List<Person> getAllPersons() {
if (persons == null) {
loadPersons();
}
return persons;
}
private void loadPersons() {
persons = getPersonFacade().listAll();
}
public void resetPerson() {
person = new Person();
}
public Dog getDog() {
if (dog == null) {
dog = new Dog();
}
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public void resetDog() {
dog = new Dog();
}
private void reloadPersonWithDogs() {
personWithDogs = getPersonFacade().findPersonWithAllDogs(person.getId());
}
}package com.mb;
import javax.faces.bean.*;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.facade.UserFacade;
import com.model.User;
@RequestScoped
@ManagedBean
public class LoginMB extends AbstractMB {
@ManagedProperty(value = UserMB.INJECTION_NAME)
private UserMB userMB;
private String email;
private String password;
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String login() {
UserFacade userFacade = new UserFacade();
User user = userFacade.isValidLogin(email, password);
if(user != null){
userMB.setUser(user);
FacesContext context = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance();
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) context.getExternalContext().getRequest();
request.getSession().setAttribute('user', user);
return '/pages/protected/index.xhtml';
}
displayErrorMessageToUser('Check your email/password');
return null;
}
public void setUserMB(UserMB userMB) {
this.userMB = userMB;
}
}关于上面的代码:
- 所有ManagedBeans仅负责VIEW操作; ManagedBeans应该负责处理业务方法的唯一结果。 ManagedBeans中没有业务规则。 在视图层中执行一些业务操作非常容易,但这不是一个好习惯。
- LoginMB类使用另一个ManagedBean(UserMB),并在其中注入了它。 要将一个ManagedBean注入另一个ManagedBean中,您必须执行以下操作:
- 在注入的ManagedBean顶部使用@ManagedProperty
- PersonMB类可能会因为其太大而接受重构操作。 这样的PersonMB可以使新手开发人员更轻松地理解代码。
关于@ViewScoped的观察
您将在带有@ViewScoped批注的托管bean中看到一些重新加载和重置方法。 这两种方法都需要重置对象状态。 例如,狗对象将在方法执行后保存视图中的值(持久保存在数据库中,在对话框中显示值)。 如果用户打开创建对话框并成功创建了一条狗,则该狗对象将在用户停留在同一页面时保留所有值。 如果用户再次打开创建对话框,则将在此处显示最后记录的狗的所有数据。 这就是为什么我们有重置方法的原因。
如果更新数据库中的对象,则用户视图中的对象也必须接收此更新,ManagedBean对象也必须接收此新数据。 如果您在数据库中更新了狗名,则狗列表也应收到此更新的狗。 您可以在数据库中查询此新数据,也可以仅更新托管Bean值。
开发人员必须注意:
- 重新加载查询数据库的托管Bean数据(重新加载方法) :如果重新加载ManagedBean对象的激发查询附带大量数据,则其查询可能会影响应用程序性能。 开发人员可以使用具有延迟加载的数据表。 单击此处查看有关Lazy Datatable的更多信息 。
- 在不查询数据库的情况下,直接在托管Bean中重新加载更新的对象 :假设user1更新了数据库中的dog1名称,同时user2更新了dog2年龄。 如果user1更新dog2,则user1将看到有关dog2的旧数据,这可能会导致数据库完整性问题。 该方法的解决方案可以是数据库表中的版本字段。 在更新发生之前,将检查此字段。 如果版本字段不具有数据库中找到的相同值,则可能引发异常。 使用这种方法,如果user1更新dog2,则版本值将不同。
JSFMessageUtil
在“ com.util”包中,创建以下类:
package com.util;
import javax.faces.application.FacesMessage;
import javax.faces.application.FacesMessage.Severity;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
public class JSFMessageUtil {
public void sendInfoMessageToUser(String message) {
FacesMessage facesMessage = createMessage(FacesMessage.SEVERITY_INFO, message);
addMessageToJsfContext(facesMessage);
}
public void sendErrorMessageToUser(String message) {
FacesMessage facesMessage = createMessage(FacesMessage.SEVERITY_WARN, message);
addMessageToJsfContext(facesMessage);
}
private FacesMessage createMessage(Severity severity, String mensagemErro) {
return new FacesMessage(severity, mensagemErro, mensagemErro);
}
private void addMessageToJsfContext(FacesMessage facesMessage) {
FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().addMessage(null, facesMessage);
}
}此类将处理将显示给用户的所有JSF消息。 此类将帮助我们的ManagedBeans失去类之间的耦合。
创建一个类来处理对话框动作也是一个好主意。
配置文件
在源“ src”文件夹中,创建以下文件:
“ log4.properties ”
# Direct log messages to stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
# Root logger option
log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, stdout
# Hibernate logging options (INFO only shows startup messages)
log4j.logger.org.hibernate=ERROR
# Log JDBC bind parameter runtime arguments
#log4j.logger.org.hibernate.type=TRACE“ messages.properties ”
#Actions
welcomeMessage=Hello! Show me the best soccer team logo ever
update=Update
create=Create
delete=Delete
cancel=Cancel
detail=Detail
logIn=Log In
add=Add
remove=Remove
ok=Ok
logOut= Log Out
javax.faces.component.UIInput.REQUIRED={0}: is empty. Please, provide some value
javax.faces.validator.LengthValidator.MINIMUM={1}: Length is less than allowable minimum of u2018u2019{0}u2019u2019
noRecords=No data to display
deleteRecord=Do you want do delete the record
#Login / Roles Validations
loginHello=Login to access secure pages
loginUserName=Username
loginPassword=Password
logout=Log Out
loginWelcomeMessage=Welcome
accessDeniedHeader=Wow, our ninja cat found you!
accessDeniedText=Sorry but you can not access that page. If you try again, that ninja cat gonna kick you harder! >= )
accessDeniedButton=You got-me, take me out. =/
#Person
person=Person
personPlural=Persons
personName=Name
personAge=Age
personDogs=These dogs belongs to
personAddDogTo=Add the selected Dog To
personRemoveDogFrom=Remove the selected Dog from
personEditDogs=Edit Dogs
#Dog
dog=Dog
dogPlural=Dogs
dogName=Name
dogAge=Age看一下“ lo4j.properties ”,注释#log4j.logger.org.hibernate.type = TRACE行。 如果要查看由Hibernate创建的查询,则需要将文件的其他配置从ERROR编辑为DEBUG,并从上面的行中删除#。
您将能够看到Hibernate执行的查询及其参数。
xhtml页面,面
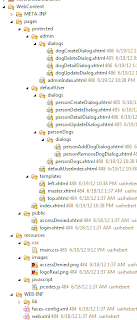
在WebContent文件夹中,您将找到以下文件:
让我们看看如何将Facelets应用于项目。 在“ / WebContent / pages / protected / templates /”文件夹下创建以下文件:
“ left.xhtml ”
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC '-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN'
'http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd'>
<html xmlns='http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'
xmlns:ui='http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets'
xmlns:h='http://java.sun.com/jsf/html'
xmlns:p='http://primefaces.org/ui'>
<h:body>
<ui:composition>
<h:form>
<p:commandButton styleClass='menuButton' icon='ui-icon-arrowstop-1-e' rendered='#{userMB.admin or userMB.defaultUser}' action='/pages/protected/defaultUser/defaultUserIndex.xhtml' value='#{bundle.personPlural}' ajax='false' immediate='true' />
<br />
<p:commandButton styleClass='menuButton' icon='ui-icon-arrowstop-1-e' rendered='#{userMB.admin}' action='/pages/protected/admin/adminIndex.xhtml' value='#{bundle.dogPlural}' ajax='false' immediate='true' />
<br />
</h:form>
</ui:composition>
</h:body>
</html>“ master.xhtml ”
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC '-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN'
'http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd'>
<html xmlns='http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'
xmlns:ui='http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets'
xmlns:h='http://java.sun.com/jsf/html'
xmlns:p='http://primefaces.org/ui'
xmlns:f='http://java.sun.com/jsf/core'>
<h:head>
<title>CrudJSF</title>
<h:outputStylesheet library='css' name='main.css' />
<meta http-equiv='Content-Type' content='text/html; charset=UTF-8' />
</h:head>
<h:body>
<f:view contentType='text/html; charset=UTF-8' encoding='UTF-8' >
<div id='divTop' style='vertical-align: middle;'>
<ui:insert name='divTop'>
<ui:include src='top.xhtml' />
</ui:insert>
</div>
<div id='divLeft'>
<ui:insert name='divLeft'>
<ui:include src='left.xhtml' />
</ui:insert>
</div>
<div id='divMain'>
<p:growl id='messageGrowl' />
<ui:insert name='divMain' />
</div>
<h:outputScript library='javascript' name='jscodes.js' />
</f:view>
</h:body>
</html>“ top.xhtml”
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC '-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN'
'http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd'>
<html xmlns='http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'
xmlns:ui='http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets'
xmlns:h='http://java.sun.com/jsf/html'
xmlns:p='http://primefaces.org/ui'>
<h:body>
<ui:composition>
<div id='topMessage'>
<h1>
<h:form>
#{bundle.loginWelcomeMessage}: #{userMB.user.name} | <p:commandButton value='#{bundle.logOut}' action='#{userMB.logOut()}' ajax='false' style='font-size: 20px;' />
</h:form>
</h1>
</div>
</ui:composition>
</h:body>
</html>上面的代码将作为应用程序所有xhtml页面的基础。 应用Facelets模式重用xhtml代码非常重要。 在下面,您可以在xhtml页面中看到如何应用Facelets,请注意,开发人员只需要覆盖所需的部分:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC '-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN' 'http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd'>
<html xmlns='http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml' xmlns:ui='http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets' xmlns:h='http://java.sun.com/jsf/html'
xmlns:f='http://java.sun.com/jsf/core' xmlns:p='http://primefaces.org/ui' >
<h:body>
<ui:composition template='/pages/protected/templates/master.xhtml'>
<ui:define name='divMain'>
#{bundle.welcomeMessage} :<br/>
<h:graphicImage library='images' name='logoReal.png' />
</ui:define>
</ui:composition>
</h:body>
</html>注意,只有“ divMain ”被覆盖,其他部分保持不变。 这是Facelets的最大优点,您无需在每个页面中使用网站的所有区域。
继续第三部分 。
参考:在uaiHebert博客上,我们的JCG合作伙伴 Hebert Coelho的Tomcat JSF Primefaces JPA Hibernate完整Web应用程序 。
翻译自: https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2012/07/full-web-application-tomcat-jsf_04.html





















 155
155

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








