编程时可通过fcntl函数设置文件的阻塞特性。
设置为阻塞:fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,0);
设置为非阻塞:fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,O_NONBLOCK);
fcntl -- manipulate file descriptor
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd,.../*arg*/);
cmd:
F_GETFD(void):read the file descriptor flags; arg is ignored.
F_SETFD(long): set the file descriptor flags to the value specified by arg.
FD_CLOEXEC: the close-on-exec flag. If the FD_CLOEXEC bit is 0, the file descriptor will remain open across an exec, otherwise it will be closed.
F_SETFL(long): set the file status flags to the value specified by arg.
---- File access mode (O_RDONLY,O_WRONLY,O_RDWR)
F_GETFL(void) :read the file status flags; arg is ignored.
复习从管道中读数据的特点:
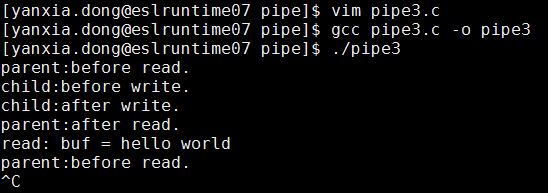
1)默认用read函数从管道中读数据是阻塞的。
2)调用write函数向管道里写数据,当缓冲区已满时write也会阻塞。
3)通信过程中,读端口全部关闭后,写进程向管道内写数据时,写进程会(收到SIGPIPE信号)退出。
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char * argv[])
{
int fd_pipe[2];
char buf[] = "hello world";
pid_t pid;
if(pipe(fd_pipe) < 0)
perror("pipe");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
sleep(3);
printf("child:before write.\n");
write(fd_pipe[1],buf,strlen(buf));
printf("child:after write.\n");
_exit(0);
}else{
fcntl(fd_pipe[0],F_SETFL,0); //set read block
while(1){
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
printf("parent:before read.\n");
read(fd_pipe[0],buf,sizeof(buf));//wait 3s
printf("parent:after read.\n");
printf("read: buf = %s\n",buf);
sleep(1);
}
//wait(NULL);//parent process,wait any child process's termination
}
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
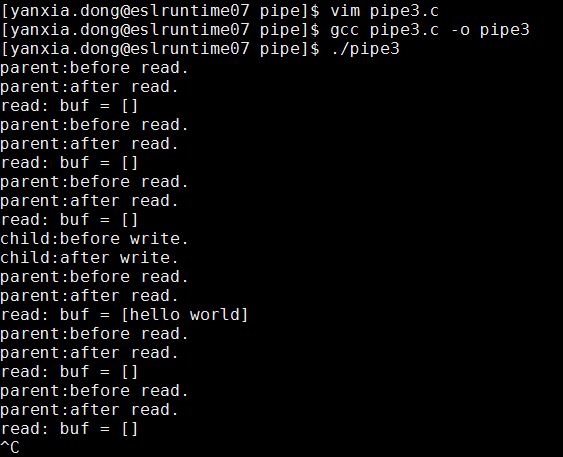
修改管道的属性是非阻塞的后,即使管道里面为空,也不会阻塞,输出空字符即可。
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char * argv[])
{
int fd_pipe[2];
char buf[] = "hello world";
pid_t pid;
if(pipe(fd_pipe) < 0)
perror("pipe");
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
sleep(3);
printf("child:before write.\n");
write(fd_pipe[1],buf,strlen(buf));
printf("child:after write.\n");
_exit(0);
}else{
fcntl(fd_pipe[0],F_SETFL,O_NONBLOCK); //set read non block
while(1){
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
printf("parent:before read.\n");
read(fd_pipe[0],buf,sizeof(buf));//no need wait
printf("parent:after read.\n");
printf("read: buf = [%s]\n",buf);
sleep(1);
}
//wait(NULL);//parent process,wait any child process's termination
}
return 0;
}编译运行后输出结果如下:






















 3612
3612











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








