一、监听器模式图
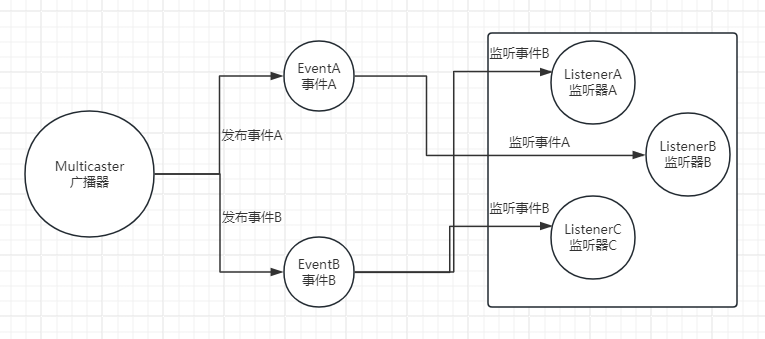
二、监听器三要素
-
广播器:用来发布事件
-
事件:需要被传播的消息
-
监听器:一个对象对一个事件的发生做出反应,这个对象就是事件监听器
三、监听器的实现方式
1、实现自定义事件
自定义事件需要继承ApplicationEvent类,并添加一个构造函数,用于接收事件源对象。该事件中添加了一个SysUser对象,用于传递用户信息。
package com.ruoyi.web.listener;
import com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.entity.SysUser;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
/**
* @Description: 自定义事件
* @Author: baiwen
* @createTime: 2024年06月19日 13:10:07
*/
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private SysUser sysUser;
public MyEvent(Object source, SysUser sysUser) {
super(source);
this.sysUser = sysUser;
}
public SysUser getSysUser() {
return sysUser;
}
}2、实现自定义监听器
自定义监听器需要实现ApplicationListener接口,并重写 onApplicationEvent方法。接口中的泛型参数为自定义事件类型,表示监听该类型的事件。可以从该事件中获取用户信息,并进行相应的处理。
package com.ruoyi.web.listener;
import com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.entity.SysUser;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Description: 自定义监听器
* @Author: baiwen
* @createTime: 2024年06月19日 13:12:39
*/
@Component
public class MyEventListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
SysUser sysUser = event.getSysUser();
System.out.println("监听到了事件,用户名:" + sysUser.getUserName());
}
}3、发布自定义事件
在需要发布事件的地方,使用ApplicationEventPublisher的publishEvent方法来发布事件。这里使用Test类来模拟事件发布,实际应用中可以根据具体需求来选择合适的发布场景。
package com.ruoyi.test;
import com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.entity.SysUser;
import com.ruoyi.web.listener.MyEvent;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: baiwen
* @createTime: 2024年06月19日 13:16:33
*/
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class MyEventPushTest {
@Resource
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
@Test
public void testpublishEvent() throws InterruptedException
{
SysUser sysUser = new SysUser();
sysUser.setUserName("zhangsan");
System.out.println("发布MyEvent事件。。。");
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent(this, sysUser));
}
}4、测试
运行MyEventPushTest类中的testpublishEvent方法,控制台会输出以下内容:
发布MyEvent事件。。。
监听到了事件,用户名:zhangsan5、其他实现方案
主要是监听器的注册方式不同,目的只有一个,把监听器加入到spring容器中。
方式一,就是上面的MyEventListener类是通过@Component注解将该类注册为Spring的Bean,从而实现监听器的功能。
方式二,可以通过在启动类中添加监听器的方式,使监听器生效。
package com.ruoyi;
import com.ruoyi.web.listener.MyEventListener;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
/**
* 启动程序
*
* @author baiwen
*/
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class })
public class RuoYiApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new SpringApplicationBuilder(RuoYiApplication.class).listeners(new MyEventListener()).run(args);
}
}方式三,可以通过配置spring.factories,使监听器生效。
在resource文件夹下创建META-INF/spring.factories文件。
配置内容如下:
# 监听器
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.ruoyi.web.listener.MyEventListener除此之外,还有第四种方式,通过@EventListener注解实现监听器的功能。通过@EventListener注解的condition属性来指定监听的事件类型。
package com.ruoyi.web.listener;
import com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.entity.SysUser;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Description: 自定义监听器2
* @Author: baiwen
* @createTime: 2024年06月19日 14:07:57
*/
@Component
public class MyEventListener2 {
@EventListener(MyEvent.class)
public void listenerApplicationStarted(MyEvent event) {
SysUser sysUser = event.getSysUser();
System.out.println("注解方式监听到了事件,用户名:" + sysUser.getUserName());
}
}发布事件后,可以看到能正常监听到事件。
发布MyEvent事件。。。
注解方式监听到了事件,用户名:zhangsan总结
以上,就是SpringBoot中实现监听器的四种方式。
至于监听器的实现原理,后续再补充。
文章转载自:树叶的一生啊





















 1374
1374

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








