(五)Google Gson包的使用
1.简介
Gson包中,使用最多的是Gson类的toJson()和fromJson()方法:
①toJson():将java对象转化为json数据(一般为json格式的字符串) (序列化)
②fromJson():从json数据(json格式字符串)转为java对象 (反序列化)
也可以使用JsonObject和JsonArray类的无参构造函数创建实例,然后调用add()方法来构造json数据,用法与org.json包和json-lib包差不多,但却少了一些方法;这里使用Gson包还是推荐使用Gson类的toJson()和fromJson()方法。
Github上的原话:

Gson Goals:
- Provide simple
toJson()andfromJson()methods to convert Java objects to JSON and vice-versa - Allow pre-existing unmodifiable objects to be converted to and from JSON
- Extensive support of Java Generics
- Allow custom representations for objects
- Support arbitrarily complex objects (with deep inheritance hierarchies and extensive use of generic types)
Github的地址:https://github.com/google/gson
各个版本的下载地址:http://www.mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.code.gson/gson
例子:
- package gson;
- import com.google.gson.Gson;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Gson gson = new Gson();
- // 简单数据类型 转为 json
- String intStr = gson.toJson(1);
- String stringStr = gson.toJson("abcd");
- String longStr = gson.toJson(new Long(10));
- System.out.println(intStr); // int
- System.out.println(stringStr); // String
- System.out.println(longStr); // Long
- // json 转为 简单数据类型
- int id1 = gson.fromJson("1", int.class);
- Integer id2 = gson.fromJson("1", Integer.class);
- Boolean boolean1 = gson.fromJson("false", Boolean.class);
- String str = gson.fromJson("\"abc\"", String.class);
- System.out.println(id1);
- System.out.println(id2);
- System.out.println(boolean1);
- System.out.println(str);
- // java array 转为 json
- String[] strings = { "abc", "def", "ghi" };
- int[][] intInt = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
- String stringStrs = gson.toJson(strings); // String数组转为json
- String intIntStr = gson.toJson(intInt); // 多维数据转为json
- System.out.println(stringStrs);
- System.out.println(intIntStr);
- //json 转为 java array
- String[] strings2 = gson.fromJson(stringStrs, String[].class);
- int[][] intInt2 = gson.fromJson(intIntStr, int[][].class);
- for (int i = 0; i < strings2.length; i++) { //输出String[]
- System.out.print(strings2[i] + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- for (int i = 0; i < intInt2.length; i++) { //输出int[][]
- for (int j = 0; j < intInt2[i].length; j++) {
- System.out.print(intInt2[i][j] + ",");
- }
- System.out.print(" ");
- }
- }
- }
输出结果:
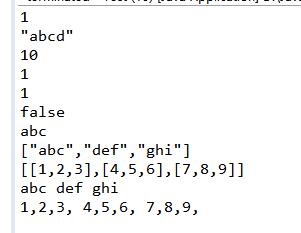
3.json与java集合、Map
例子:
- package gson;
- import java.lang.reflect.Type;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- import com.google.gson.Gson;
- import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Gson gson = new Gson();
- // Map 转 json
- Map<string object=""> map = new HashMap<string object="">();
- map.put("name", "JTZen9");
- map.put("age", 21);
- map.put("sex", "male");
- String jsonMap = gson.toJson(map);
- System.out.println(jsonMap);
- // json 转 Map
- Type type = new TypeToken<Map<string object="">>() {}.getType();
- Map<string object=""> map2 = gson.fromJson(jsonMap, type);
- System.out.println(map2.get("name") + " " + map2.get("age") + " " + map2.get("sex"));
- // java集合 转 json
- List<object> nameList = new ArrayList</object><object>();
- nameList.add("JTZen9");
- nameList.add(map);
- nameList.add("DSMGYH");
- String jsonNames = gson.toJson(nameList);
- System.out.println(jsonNames);
- // json 转 java集合
- type = new TypeToken<List</object><object>>() {}.getType();
- List</object><object> list = gson.fromJson(jsonNames, type);
- for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
- System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
- }
- }
- }
输出结果:
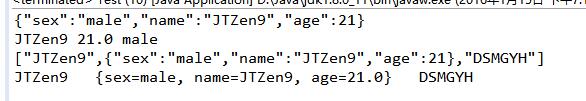
- package gson;
- import com.google.gson.Gson;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student = new Student();
- student.setName("JTZen9");
- student.setAge(21);
- student.setSex("male");
- Gson gson = new Gson();
- // java bean 转 json
- String beanStr = gson.toJson(student);
- System.out.println(beanStr);
- // json 转 java bean
- Student student2 = gson.fromJson(beanStr, Student.class);
- System.out.println(student2.getName() + " " + student2.getAge() + " " + student2.getSex());
- // 转为json数据时,只会转换属性值的字段
- Student stu = new Student();
- stu.setName("JTZen9");
- stu.setAge(21);
- String test = gson.toJson(stu);
- System.out.println(test); //没有sex字段
- }
- }
输出结果:
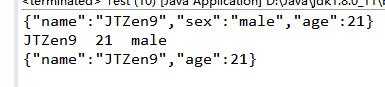
json-lib包中,JSONObject.fromObject()构造的json数据,全部的字段都包含,没有赋值的都为空;
Gson包的toJson()方法和org.json包的new JSONObject()方法,转换java bean为json数据时,只会转换有赋值的字段。
- {
- "roomname":[
- {
- "PCnum":0,
- "num":2,
- "name":"biubiubiu",
- "time":"十二月 18, 2015"
- },
- {
- "PCnum":0,
- "num":1,
- "name":"jtz",
- "time":"十二月 19, 2015"
- },
- {
- "PCnum":0,
- "num":1,
- "name":"jtzeng",
- "time":"十二月 19, 2015"
- }
- ]
- }
使用JsonObject和JsonArray的配合来使用也是可以解析的,但是这样解析起来就比较麻烦,当json数据又多又复杂时候更是麻烦,所以这里有一种简单的方法,首先定义一个对应json数据字段的java类:
- package gson;
- import java.util.List;
- public class JsonBean {
- public List<roomdata> roomname;
- public class RoomData {
- public int PCnum;
- public int num;
- public String name;
- public String time;
- }
- }
然后,测试如下:
- package gson;
- import java.lang.reflect.Type;
- import com.google.gson.Gson;
- import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //要解析json数据
- String json = "{'roomname':[{'PCnum':0,'num':2,'name':'biubiubiu','time':'Dec 22, 2015'},"
- + "{'PCnum':0,'num':1,'name':'jtz','time':'Dec 18, 2015'},"
- + "{'PCnum':0,'num':0,'name':'JTZen9','time':'Dec 22, 2015'}]}";
- Gson gson = new Gson();
- Type type = new TypeToken<jsonbean>(){}.getType();
- JsonBean jsonBean = gson.fromJson(json, type);
- System.out.println(jsonBean.roomname.size());
- for (int i = 0; i < jsonBean.roomname.size(); i++) {
- System.out.println(jsonBean.roomname.get(i).name + " 、 "
- + jsonBean.roomname.get(i).PCnum + " 、 "
- + jsonBean.roomname.get(i).num + " 、 "
- + jsonBean.roomname.get(i).time);
- }
- }
- }
输出的结果如下:
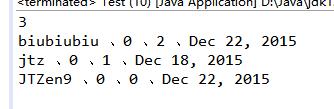
需要注意的是:定义的类中,属性字段名必须跟json数据的key字段名一样。
org.json包、json-lib包、Gson包,终于搞清楚了些,做课程作业时糊里糊涂的。相比之下,感觉Gson挺好用的,往后深入探究探究Gson。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/Zen99T/article/details/50523357
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/Zen99T/article/details/50523357
























 104
104

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








